0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views18 pagesSurface Topography for Engineers
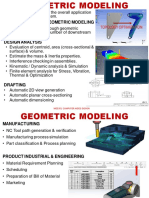
This document summarizes a lecture on surface topography. It discusses how machining leaves characteristic surface textures and defines key terms like roughness, waviness and form. It also defines quantitative parameters like Ra and Rq that are used to describe surface roughness. Finally, it explains how 3D surface measurements can be performed using either contact stylus profilometry or non-contact laser profilometry by moving the surface or the measurement instrument.
Uploaded by
er.kashif.farooqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views18 pagesSurface Topography for Engineers
This document summarizes a lecture on surface topography. It discusses how machining leaves characteristic surface textures and defines key terms like roughness, waviness and form. It also defines quantitative parameters like Ra and Rq that are used to describe surface roughness. Finally, it explains how 3D surface measurements can be performed using either contact stylus profilometry or non-contact laser profilometry by moving the surface or the measurement instrument.
Uploaded by
er.kashif.farooqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd