Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WS Experimental Design and Separation Techniques
Uploaded by
keech.Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WS Experimental Design and Separation Techniques
Uploaded by
keech.Copyright:
Available Formats
Experimental Design and Separation Techniques
Name:_____________ Grade 8 Sec.........
Section A
Q.1: Multiple Choice Questions.
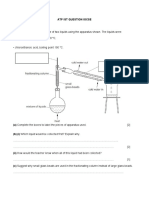
1.The diagram shows how to obtain pure water from seawater. Where do water
molecules lose energy?
2. Some chemical compounds are purified by recrystallisation.
What can be used to test the purity of the crystals?
A melting point
B colour of crystals
C size of crystals
D solubility
3.In an experiment, a student needs to measure out 36.50 cm3 of a solution.
Which piece of apparatus would measure this volume most accurately?
A beaker
B burette
C measuring cylinder
D pipette
4. A coin is dissolved in an acid. Chromatography is used to test the solution formed.
The diagram shows the chromatogram obtained.
What is the coin made from?
A a metal element
B a non-metal element
C a mixture of metals
D a mixture of non-metal
CHM Work Sheet (Experimental Design and Separation Technique) Grade 8
Page 1 of 5
Section B (Structure Questions)
(d).Three dye mixtures, J, K and L, were spotted onto a piece of chromatography
paper. Three pure dyes, X, Y and Z, were also spotted onto the same piece of paper.
(i) Suggest why the base line was drawn in pencil and not in ink.
............................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii)Which dye mixture, J, K or L, contains a dye which did not move during this
chromatography?
............................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Which dye mixture, J, K or L, contains both dye X and dye Y?
............................................................................................................................... [1]
(iv) Which dye mixture, J, K or L, does not contain dye Z?
............................................................................................................................... [1]
[Total: 04]
Q.2. (d) The apparatus shown is used to get pure water from impure mineral water.
(i) Complete the diagram by putting the correct labels in the three boxes. [3]
(ii) Describe how this apparatus separates pure water from dissolved ionic solids.
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................. [2]
CHM Work Sheet (Experimental Design and Separation Technique) Grade 8
Page 2 of 5
(iii) Water purity is important in everyday life.
Describe one other area of everyday life where purity of substances is important.
...................................................................................................................[1][Total: 06]
Q.3A list of techniques used to separate mixtures is given below.
Fractional distillation Simple distillation Crystallization
Filtration Diffusion
From the list choose the most suitable technique to separate the following.
1. Water from aqueous copper(II) sulphate……………………………….
2. Helium from a mixture of helium and argon…………………………………
3. Copper(II) sulphate from aqueous copper(II) sulphate………………………….
4. Ethanol from aqueous ethanol……………………………………………………
5. Barium sulphate from a mixture of water and barium sulphate…………………
[Total: 5]
Q.4Lavandulol is found in lavender plants. The formula of lavandulol is shown below.
(a) State the names of the two products formed when lavandulol is burnt in
excess oxygen.
………………………………………and………………………………………..[1]
(d) Lavandulol can be extracted from lavender flowers by distillation using the
apparatus shown below. The lavandulol is carried off in small droplets with the
steam.
CHM Work Sheet (Experimental Design and Separation Technique) Grade 8
Page 3 of 5
(i) State the name of the piece of apparatus labelled A.
…………………………………………………………………………………….[1]
(ii) What is the temperature of the water at point X in the diagram?
……………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(iii) The lavandulol and water are collected in the beaker.
What information in the diagram shows that lavandulol is less dense than water?
……………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(c) Lavender flowers contain a variety of different pigments (colourings).
A student separated these pigments using paper chromatography.
The results are shown in the diagram below.
(i) Put an X on this diagram to show where the mixture of pigments was placed at the
start of the experiment. [1]
(ii) How many different pigments have been separated?
…………………………………………………………………………………..[1]
(iii) Draw a diagram to show how the chromatography apparatus was set up.
On your diagram label
• the solvent
• the origin line
[1]
(iv) During chromatography, the solvent evaporates and then diffuses throughout the
chromatography jar.
What do you understand by the term diffusion?
……………………………………………………………………………………..[1]
CHM Work Sheet (Experimental Design and Separation Technique) Grade 8
Page 4 of 5
Q.6.The apparatus below was used to separate ethanol from water.
(a) Complete the empty boxes to name the pieces of apparatus. [3]
(b) Indicate by an arrow where heat is applied. [1]
(c) Name this separation process.
...................................................................................................................................[2]
CHM Work Sheet (Experimental Design and Separation Technique) Grade 8
Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- Quiz Yr10 ChemDocument7 pagesQuiz Yr10 ChemTorenkuNo ratings yet
- Gib BracingDocument36 pagesGib BracingStefan Reuther100% (1)
- APznzaZhjXonT6wjrMbAbaGQdF3GVqEL_2K_STbaTtygsTGEJWUQdj4t554hqJ3JsujW0mrUpE7djk31TYXYBvyLTuzFLUWQF9HAuA4PF8hlIp11RSHGMko9FhPK47hx93AEZzzK9ulvcXLQNfNDx3M364xHNDSs8viIVJJnLQxqtLScyc51WZBQH17M0Q8uTmJagFsqBnddemPPcv7Document8 pagesAPznzaZhjXonT6wjrMbAbaGQdF3GVqEL_2K_STbaTtygsTGEJWUQdj4t554hqJ3JsujW0mrUpE7djk31TYXYBvyLTuzFLUWQF9HAuA4PF8hlIp11RSHGMko9FhPK47hx93AEZzzK9ulvcXLQNfNDx3M364xHNDSs8viIVJJnLQxqtLScyc51WZBQH17M0Q8uTmJagFsqBnddemPPcv7dawoodsindi123No ratings yet
- My TestDocument18 pagesMy Testscribble_55No ratings yet
- GRADE 8 SCIENCE EXAM PAPER2 3rd TERMDocument18 pagesGRADE 8 SCIENCE EXAM PAPER2 3rd TERMTijani Basit AbiodunNo ratings yet
- S.3 EOT CHEM WMSSDocument8 pagesS.3 EOT CHEM WMSSDaniel ComboniNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Document12 pages1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Krish PatelNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument6 pagesChemAya KurdiNo ratings yet
- 0620 s03 QP 2 PDFDocument16 pages0620 s03 QP 2 PDFSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 5072/02: Secondary Four Special & ExpressDocument16 pagesChemistry 5072/02: Secondary Four Special & ExpressKen TanNo ratings yet
- 1st Question Experimental DesignDocument16 pages1st Question Experimental DesignHayaa KhanNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Mid Term Exam 2016Document24 pagesForm 1 Mid Term Exam 2016Anonymous zBKpeANo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Final Exams 2024Document7 pagesGrade 7 Final Exams 2024Saheed AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 9647/02: Hwa Chong Institution C1 Block Test Higher 2Document10 pagesChemistry 9647/02: Hwa Chong Institution C1 Block Test Higher 220Y3G HONG JIN KAINo ratings yet
- Sda 3 Form 4Document13 pagesSda 3 Form 4Crystal MachipisaNo ratings yet
- Latih Tubi T1Document17 pagesLatih Tubi T1nurlisa2010No ratings yet
- Biology 2018 PDFDocument13 pagesBiology 2018 PDFAysha AmzadNo ratings yet
- Elements Comp and MixDocument10 pagesElements Comp and MixShebin PaulNo ratings yet
- Mock 1B P6Document3 pagesMock 1B P6Omar Hany mohamed samirNo ratings yet
- End of Unit Test: Biology: PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Biology: PhotosynthesisLovy Le ErNo ratings yet
- Accounting QuestionDocument25 pagesAccounting Questionmay thansinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Alternative To PracticalDocument4 pagesChemistry Alternative To PracticalMCHNo ratings yet
- BUKIT BATOK SEC SCH Chemistry 6092 1.2 Methods of purification and analysisDocument4 pagesBUKIT BATOK SEC SCH Chemistry 6092 1.2 Methods of purification and analysisMr Plays shitNo ratings yet
- SCLP Samaj School Year 10 Chemistry Revision WorksheetDocument11 pagesSCLP Samaj School Year 10 Chemistry Revision WorksheetHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certifi Cate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certifi Cate of Secondary Educationnairah2000No ratings yet
- Specimen Paper Chemistry 2012Document9 pagesSpecimen Paper Chemistry 2012TaleyveeNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Chem 11Document7 pagesChem 11Raheem Abdul ManyambaNo ratings yet
- 5124 w07 QP 3Document16 pages5124 w07 QP 3Sudibyo GunawanNo ratings yet
- Experimental Techinque Past Papers QuestionsDocument4 pagesExperimental Techinque Past Papers Questionschemking7933% (3)
- Science G9 Chem EXT P2 QPDocument9 pagesScience G9 Chem EXT P2 QPrecruitthykingNo ratings yet
- Classified Chemistry Cambridge Igcse Paper 6 ScienceDocument358 pagesClassified Chemistry Cambridge Igcse Paper 6 ScienceMoumenNo ratings yet
- 6243 j04 qp02Document16 pages6243 j04 qp02Ruwan BandaraNo ratings yet
- Model Chem 1Document7 pagesModel Chem 1Khurshida BegumNo ratings yet
- Chem Yr 10 End TermDocument11 pagesChem Yr 10 End TermBarminga KamurenNo ratings yet
- 0620 s03 QP 2 Model Answers FinalDocument21 pages0620 s03 QP 2 Model Answers Finaleleanorhmtan33% (3)
- Mock Examination Chemistry & Physics 3º ESO JUNE-2004 Time Allowed: 50 MinDocument4 pagesMock Examination Chemistry & Physics 3º ESO JUNE-2004 Time Allowed: 50 MinmenolitoNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Exercise On Separation TechniquesDocument11 pagesExercise On Separation TechniquesBaiye RandolfNo ratings yet
- SMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Document16 pagesSMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Mohd Faizal Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Gradfe 10C End of Term 2 2019 Test Chemistry (5070)Document4 pagesGradfe 10C End of Term 2 2019 Test Chemistry (5070)Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiDocument12 pagesChemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiEmily VinciNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 QNDocument19 pagesPaper 2 QNchuasioklengNo ratings yet
- Jan 07Document16 pagesJan 07Evelyn L-XingNo ratings yet
- Jan 09 Unit1Document20 pagesJan 09 Unit1Didie HusniNo ratings yet
- Pure Chem p2 - 26pgDocument26 pagesPure Chem p2 - 26pgJhomer CrespoNo ratings yet
- 10 Methods of Separation 1Document8 pages10 Methods of Separation 1linesajithmiNo ratings yet
- Mount Everest Breathing TestDocument14 pagesMount Everest Breathing TestVikas ShahNo ratings yet
- 09 JJ H2 Prelim P2Document15 pages09 JJ H2 Prelim P2etherfoxxNo ratings yet
- 5070 s14 QP 42Document16 pages5070 s14 QP 42Fatima AliNo ratings yet
- Chemical reactions and propertiesDocument14 pagesChemical reactions and propertiesHan LingNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Unit 3 Class: XI Subject: Chemistry Total Marks: 25Document8 pagesAssignment On Unit 3 Class: XI Subject: Chemistry Total Marks: 25Shafiqun NabiNo ratings yet
- FORM 1 2023 END T3 CHEMISTRY QN - TEACHER - CO - .KE - SET - ADocument9 pagesFORM 1 2023 END T3 CHEMISTRY QN - TEACHER - CO - .KE - SET - AYussuf HirowNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 9647/02: Hwa Chong Institution C1 Block Test Higher 2Document10 pagesChemistry 9647/02: Hwa Chong Institution C1 Block Test Higher 220Y3G HONG JIN KAINo ratings yet
- Cell Water Potential & Synaptic Transmission Biology QuestionsDocument9 pagesCell Water Potential & Synaptic Transmission Biology QuestionsThen MoliNo ratings yet
- Islamiyat (Supporting Verses For Paper 2)Document15 pagesIslamiyat (Supporting Verses For Paper 2)keech.No ratings yet
- Northern MountainsDocument9 pagesNorthern Mountainskeech.No ratings yet
- Islamiyat (Supporting Verses For Paper 1)Document24 pagesIslamiyat (Supporting Verses For Paper 1)keech.No ratings yet
- Grade 9 HomeworkDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Homeworkkeech.No ratings yet
- PHYSICAL QUANTITIES: BASIC AND DERIVED MEASUREMENTSDocument3 pagesPHYSICAL QUANTITIES: BASIC AND DERIVED MEASUREMENTSkeech.No ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Computer ScienceDocument1 pageGrade 9 - Computer Sciencekeech.No ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Quantity SurveyingDocument40 pagesChapter-4 Quantity SurveyingAbdanur JihadNo ratings yet
- Connecting Rod Material AnalysisDocument36 pagesConnecting Rod Material Analysispramo_dass0% (1)
- PTF30 Autonics PDFDocument4 pagesPTF30 Autonics PDFFarraziNo ratings yet
- MPI Detects Surface FlawsDocument172 pagesMPI Detects Surface FlawsRamesh RNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff-Love Plate Theory - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesKirchhoff-Love Plate Theory - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaV ARUL RAJNo ratings yet
- Valvulas de Muestreos de Filtros Larox y Panenevis LVC - Lva - LVHDocument36 pagesValvulas de Muestreos de Filtros Larox y Panenevis LVC - Lva - LVHMark BukerNo ratings yet
- ENEC Serie 221 RichtigDocument45 pagesENEC Serie 221 RichtigAli KayaNo ratings yet
- Shelly Kegan DeathDocument5 pagesShelly Kegan Deathmaqw123No ratings yet
- Exercise: Exercise 1: Choose The Best Answer To Complete The Blank in Each of The FollowingDocument3 pagesExercise: Exercise 1: Choose The Best Answer To Complete The Blank in Each of The FollowingNgọc Phương Linh LêNo ratings yet
- CONCRETE LAB MANUALDocument20 pagesCONCRETE LAB MANUALsidNo ratings yet
- Norma MAT2004Document12 pagesNorma MAT2004Marcelo Carvalho100% (1)
- DR RS Tutorial Sheet-Mechanical OperationsDocument8 pagesDR RS Tutorial Sheet-Mechanical OperationsNguyễn Hoàng QuânNo ratings yet
- Chp01 - Capacitors (Notes)Document6 pagesChp01 - Capacitors (Notes)sherry mughalNo ratings yet
- ASDO Marine Structures Tie Bar DesignCapDocument2 pagesASDO Marine Structures Tie Bar DesignCapFelipe Strafite CusterNo ratings yet
- Probability ORIG 2021 CE April 2021Document8 pagesProbability ORIG 2021 CE April 2021Joshua Lacaña SaltivanNo ratings yet
- Curvas de Crecimiento MicrobianoDocument30 pagesCurvas de Crecimiento Microbianoluis villamarinNo ratings yet
- Process Capability Indices For Skewed PopulationsDocument11 pagesProcess Capability Indices For Skewed PopulationsYo GoldNo ratings yet
- Atom Levels Term SymbolDocument21 pagesAtom Levels Term SymbolUlfa WulandariNo ratings yet
- Umat SANISAND README PDFDocument4 pagesUmat SANISAND README PDFDebdeep SarkarNo ratings yet
- 9th STD Science 1st Term 1 Mark 2 Mark Questions in EnglishDocument48 pages9th STD Science 1st Term 1 Mark 2 Mark Questions in EnglishGayathri MohanrajNo ratings yet
- ESci 110 - N046 - Lesson 7.3 AssessmentDocument6 pagesESci 110 - N046 - Lesson 7.3 AssessmentIvy PerezNo ratings yet
- June 2019 QP - Unit 4 WJEC Further Maths A-LevelDocument7 pagesJune 2019 QP - Unit 4 WJEC Further Maths A-LevelDarren DowlingNo ratings yet
- Mode Convert For The RF Cold TestDocument4 pagesMode Convert For The RF Cold TestNarayan KarkiNo ratings yet
- What Is Image Processing?Document5 pagesWhat Is Image Processing?JggNo ratings yet
- Letter of Mehran Tavakoli Keshe - 18.4.2014Document3 pagesLetter of Mehran Tavakoli Keshe - 18.4.2014jc200312127869100% (1)
- What Is Mathematics GoedelDocument238 pagesWhat Is Mathematics Goedeledgartepe4324No ratings yet
- Black Hole Hawking RadiationDocument18 pagesBlack Hole Hawking RadiationManjunath.RNo ratings yet
- Thermal Radiation PresentationDocument42 pagesThermal Radiation PresentationRajan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Submitted by Submitted To: Lab Report-01 Determination of Soil Bulk Density by Field MethodDocument4 pagesSubmitted by Submitted To: Lab Report-01 Determination of Soil Bulk Density by Field MethodMd. Murshedul Islam 173-47-091No ratings yet