Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Planes
Uploaded by
slovak.jaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Planes
Uploaded by
slovak.jaCopyright:
Available Formats
Planes, also known as airplanes or aircraft, are vehicles designed for air
travel. They have played a transformative role in transportation, commerce,
and global connectivity. Here are key aspects of planes:
1. Types of Aircraft: There are various types of aircraft, each designed for
specific purposes. Commercial airliners transport passengers, cargo planes
carry goods, military aircraft serve defense purposes, and general aviation
includes private and recreational flying.
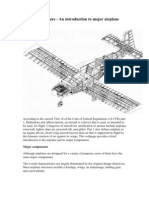
2. Components of an Aircraft:
Fuselage: The main body of the plane, housing the crew, passengers,
and cargo.
Wings: Provide lift and stability during flight.
Empennage (Tail Section): Includes the horizontal stabilizer, vertical
stabilizer, and rudder, contributing to stability and control.
Engines: Power the aircraft and generate thrust for propulsion.
Landing Gear: Supports the plane during takeoff and landing,
retracting during flight.
3. Principles of Flight:
Lift: Generated by the wings, opposing the force of gravity.
Thrust: Produced by the engines, moving the plane forward.
Drag: Resistance encountered as the plane moves through the air.
Gravity: The force pulling the aircraft downward.
4. Commercial Aviation: Commercial planes transport millions of
passengers globally each day. Major manufacturers include Boeing and
Airbus. Airlines operate a variety of models, such as the Boeing 737, Airbus
A320, and larger aircraft like the Boeing 747 or Airbus A380.
5. Military Aircraft: Military planes serve diverse roles, including fighters
for air combat (e.g., F-16), bombers for strategic attacks (e.g., B-2 Spirit), and
reconnaissance planes (e.g., U-2 Dragon Lady).
6. General Aviation: General aviation encompasses private and recreational
flying. Small planes, such as Cessna and Piper models, are used for personal
transportation, flight training, and leisure activities.
7. Jet Engines: Jet engines are commonly used in modern aircraft. They
operate on the principle of jet propulsion, drawing in air, compressing it,
mixing it with fuel, igniting the mixture, and expelling the exhaust gases to
produce thrust.
8. Aviation Safety: Rigorous safety measures, including maintenance
inspections, pilot training, and air traffic control systems, contribute to the
safety of air travel. Advancements in technology, such as collision avoidance
systems, enhance aviation safety.
9. Impact on Globalization: Air travel has significantly contributed to
globalization by facilitating rapid and efficient transportation of people and
goods across vast distances. It has interconnected economies, cultures, and
societies around the world.
10. Future Trends: Ongoing advancements, including the development of
more fuel-efficient aircraft, exploration of electric and hybrid propulsion,
and innovations in supersonic and hypersonic travel, represent the future of
aviation.
Planes have revolutionized the way we connect with the world, making
long-distance travel accessible and contributing to the growth of
economies and societies across the globe.
You might also like
- AirplaneDocument1 pageAirplaneLNNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design - Unit 1Document25 pagesAircraft Design - Unit 1Ragul K MAMSENo ratings yet
- PlanesDocument1 pagePlanesnaidooriNo ratings yet
- AirplanesDocument7 pagesAirplanesAldrin Edgar Billones DyNo ratings yet
- 2 Air Transport in GeneralDocument29 pages2 Air Transport in GeneralJozee Johnson JosephNo ratings yet
- Eoa Unit-I NotesDocument16 pagesEoa Unit-I NotesNarendra KoradeNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structure - An Introduction To Major Airplane ComponentsDocument9 pagesAircraft Structure - An Introduction To Major Airplane ComponentsPj BaroesNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Aircraft Wing Design and StructureDocument63 pagesIntroduction to Aircraft Wing Design and StructureManepalli Harshavardhanan100% (1)
- Wing Chapter-3Document77 pagesWing Chapter-3Abel BatuNo ratings yet
- FVD Lab ManualDocument39 pagesFVD Lab ManualSaideep KaredlaNo ratings yet
- نسخة مضغوطة من Final Project 2Document10 pagesنسخة مضغوطة من Final Project 2sq.vp76No ratings yet
- Introduction to Major Airplane ComponentsDocument10 pagesIntroduction to Major Airplane ComponentsAdi Putra100% (1)
- History and Introduction to Aircraft WingsDocument66 pagesHistory and Introduction to Aircraft WingsMohammed Ibrahim Khan100% (1)
- 01 - Airport Lecture 1-2Document90 pages01 - Airport Lecture 1-2Najwa Dhea DenintaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructureDocument11 pagesAircraft StructureVagesh VagesNo ratings yet
- Types of Aircraft: Lighter-Than-AirDocument13 pagesTypes of Aircraft: Lighter-Than-AirAli ÇakircaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to AvionicsDocument86 pagesIntroduction to AvionicsKannan100% (1)
- FX Training Center: Aviation KnowledgeDocument12 pagesFX Training Center: Aviation KnowledgeFahmi PrayogiNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structure 2Document4 pagesAircraft Structure 2raj mohanNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Hindustan Aeronautics Limited LucknowDocument26 pagesAcknowledgement: Hindustan Aeronautics Limited LucknowPriyank VermaNo ratings yet
- PlaneDocument2 pagesPlanewijiroNo ratings yet
- AIRCRAFT COMPONENTS MANUAL AMT 628Document17 pagesAIRCRAFT COMPONENTS MANUAL AMT 628Carl Vincent SurnitNo ratings yet
- Amt 4101 Activity 2Document15 pagesAmt 4101 Activity 2Brendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 2023Document10 pagesChapter 3 2023ismain.niniNo ratings yet
- Đ NG Cơ Máy Bay Chương 1Document42 pagesĐ NG Cơ Máy Bay Chương 1Phạm ThiênNo ratings yet
- Aviation Industry Evolution and Career OpportunitiesDocument5 pagesAviation Industry Evolution and Career Opportunitiesケーシー リン マナロNo ratings yet
- Pilot's Encyclopedia of Aeronautical Knowledge: Federal Aviation AdministrationFrom EverandPilot's Encyclopedia of Aeronautical Knowledge: Federal Aviation AdministrationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- PlanesDocument1 pagePlanesМарко ПаунковићNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. Examples of Different Categories of Aircraft, Clockwise From Top Left: Lighter-Than-Air, Glider, Rotorcraft, and AirplaneDocument2 pagesFigure 1. Examples of Different Categories of Aircraft, Clockwise From Top Left: Lighter-Than-Air, Glider, Rotorcraft, and AirplaneAli ÇakircaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Aviation IndustryDocument7 pagesEvolution of Aviation Industryケーシー リン マナロNo ratings yet
- Aeronautical Project Report On Aircraft StructureDocument12 pagesAeronautical Project Report On Aircraft StructuresumanbabaNo ratings yet
- SH ReportDocument96 pagesSH ReportjoelawrenceNo ratings yet
- 1633512964III - Sem - AIR - TRANSPORTATION - AND - AIRPORT - OPERATIONS - PDF MAINDocument67 pages1633512964III - Sem - AIR - TRANSPORTATION - AND - AIRPORT - OPERATIONS - PDF MAINAloo Charles. OchukaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Propulsion Seminar ReportDocument24 pagesAircraft Propulsion Seminar ReportJerin JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Avionics 238Document3 pagesAvionics 238tashi namgyalNo ratings yet
- How Word A AircraftDocument1 pageHow Word A Aircraftmarcodaniel.mlaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project-Naisha Singh S6BDocument11 pagesPhysics Project-Naisha Singh S6Bnaishasingh.10No ratings yet
- Hindustan Aeronautics LimitedDocument35 pagesHindustan Aeronautics LimitedShantanu AgarwalNo ratings yet
- AIRCRAFT MANUFACTURING PROCESS OVERVIEWDocument49 pagesAIRCRAFT MANUFACTURING PROCESS OVERVIEWNikhil Chandra RNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructuresDocument3 pagesAircraft StructuresAli ÇakircaNo ratings yet
- Ringka, Dzharl - Activity 1Document3 pagesRingka, Dzharl - Activity 1Dzharl RingkaNo ratings yet
- SpiceJet: A Brief History of India's Budget AirlineDocument68 pagesSpiceJet: A Brief History of India's Budget AirlineSamrat RaiNo ratings yet
- major-components-manualDocument12 pagesmajor-components-manualCarl Vincent SurnitNo ratings yet
- Acft StructureDocument58 pagesAcft Structurejocampo.aceserphNo ratings yet
- Airport Planning and DesigningDocument78 pagesAirport Planning and Designingayoushika abrolNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structures I Chapter-1Document163 pagesAircraft Structures I Chapter-1Ejigayehu Lemma100% (1)
- AirplanesDocument2 pagesAirplanesA WNo ratings yet
- AIR CARGO MANAGEMENTDocument69 pagesAIR CARGO MANAGEMENTAjay ADNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Notes - FundamentalsDocument19 pagesPreliminary Notes - Fundamentalssarathkumar sebastinNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructuresDocument6 pagesAircraft StructuresFurkanNo ratings yet
- Ve Unit 4Document16 pagesVe Unit 4vamshimohanNo ratings yet
- Landing Gear Arrangement - 5 Main Components of An AircraftDocument8 pagesLanding Gear Arrangement - 5 Main Components of An AircraftSuVam LeoChanNo ratings yet
- Air Plane Types and It's Generation: DR / Mefreh MeladDocument6 pagesAir Plane Types and It's Generation: DR / Mefreh Meladاحمد تاشهاويNo ratings yet
- Heavier-Than-Air - Aerodynes: Fixed-WingDocument3 pagesHeavier-Than-Air - Aerodynes: Fixed-WingBen DoverNo ratings yet
- Pia Internship ReportDocument12 pagesPia Internship Reportbanny BeitNo ratings yet
- Parts of AircraftDocument27 pagesParts of Aircrafthuseyinova747No ratings yet
- Types of Aircraft WingsDocument3 pagesTypes of Aircraft WingsAshley Anthony XhigahNo ratings yet
- Helicopter Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-21BFrom EverandHelicopter Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-21BRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Al KynesDocument12 pagesAl KynesjolanpascualNo ratings yet
- Intermittent Fasting Facts and Myths: Metabolic Benefits of Intermittent FastingDocument4 pagesIntermittent Fasting Facts and Myths: Metabolic Benefits of Intermittent FastingIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- MandrakeDocument6 pagesMandrakeEmry Kamahi Tahatai KereruNo ratings yet
- HYBRIFLEX® RRH Hybrid Cable Solution 12 X 24, 6AWG, Low-Inductance, Single-Mode Fiber, DLC Connectors Top and Bottom, 240 FTDocument3 pagesHYBRIFLEX® RRH Hybrid Cable Solution 12 X 24, 6AWG, Low-Inductance, Single-Mode Fiber, DLC Connectors Top and Bottom, 240 FTNoame Pauline SimbajonNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Y9aDocument9 pagesComprehension Y9angwenping5No ratings yet
- Your Msa Scba System: Cleaning/DisinfectingDocument1 pageYour Msa Scba System: Cleaning/Disinfectingjohn rajNo ratings yet
- Saa6d170e-5 HPCR Egr Sen00190-04Document415 pagesSaa6d170e-5 HPCR Egr Sen00190-04Ahmad Mubarok100% (4)
- Biosystems Engineering BS CurriculumDocument2 pagesBiosystems Engineering BS CurriculumAsiiimweNo ratings yet
- Modern Chicken Types & BreedsDocument14 pagesModern Chicken Types & BreedsMelody DacanayNo ratings yet
- JW1782BDocument13 pagesJW1782BGustavo AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Mater BiDocument10 pagesMater BihanjunyieeNo ratings yet
- Banaba Tea Aids Weight LossDocument5 pagesBanaba Tea Aids Weight LossAveriAlonzoNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument24 pagesCerebral PalsyUday Kumar100% (1)
- Toyota Vehicle Glossary TermsDocument31 pagesToyota Vehicle Glossary TermsEdward Ugochukwu AdighibeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Purva Swadhyaya QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Purva Swadhyaya QuestionsSurrender to Krishna AlwaysNo ratings yet
- Mine Pool AtlasDocument172 pagesMine Pool AtlasRishiraj SahooNo ratings yet
- Flaxseed Paper PublishedDocument4 pagesFlaxseed Paper PublishedValentina GarzonNo ratings yet
- Prog 4534543Document559 pagesProg 4534543Vasile TroianNo ratings yet
- Plant Associated Biofilms: Causes and ConsequencesDocument32 pagesPlant Associated Biofilms: Causes and ConsequencesGarima DhirNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesDocument35 pagesUnit 1 The Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesNishant GawadNo ratings yet
- Technical Plan For Roll Forming Machine: Model: WLFM40-250-1000Document5 pagesTechnical Plan For Roll Forming Machine: Model: WLFM40-250-1000ibrahimadiop1No ratings yet
- Cambridge English Pre A1 Starters Classroom Activities PDFDocument16 pagesCambridge English Pre A1 Starters Classroom Activities PDFFrank Guevara100% (2)
- March 31-Drugs PDFDocument10 pagesMarch 31-Drugs PDFfan-a-tykNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Vision in Pharma IndustryDocument20 pagesSupply Chain Vision in Pharma Industryixion11100% (1)
- Ujian Akhir Semester Gasal Dinas Pendidikan Kabupaten Sukabumi SMP Negeri 1 Cireunghas TAHUN PELAJARAN 2017/ 2018Document3 pagesUjian Akhir Semester Gasal Dinas Pendidikan Kabupaten Sukabumi SMP Negeri 1 Cireunghas TAHUN PELAJARAN 2017/ 2018DodiSaputraNo ratings yet
- Panasonic Conduit CatalogDocument8 pagesPanasonic Conduit CatalogAhmed Said100% (2)
- GY HM 100 Service ManualDocument36 pagesGY HM 100 Service Manualvideoengr100% (1)
- 2) Inequality GraphsDocument14 pages2) Inequality Graphsmanobilli30No ratings yet
- A ETHICS-101 Activity-3Document3 pagesA ETHICS-101 Activity-3Liz FuentesNo ratings yet
- Development of Automatic Mini Fan with PIR SensorDocument8 pagesDevelopment of Automatic Mini Fan with PIR SensorToheebdareNo ratings yet