100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views9 pagesConstruction Specs Writing Guide
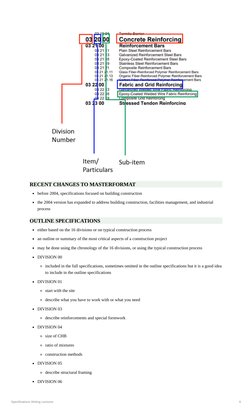
The document provides an overview of specifications writing, including definitions, history, and importance. It discusses how specifications have evolved over time from single documents describing all materials/work, to being broken into categories/sections for increased complexity. This led to the development of standardized specification formats, starting with the Construction Specification Institute's (CSI) 1963 format organizing specifications into 16 divisions. The CSI format was later incorporated into the Uniform Construction Index and further updated over time, including expanding the number of divisions to 50 in 2004. Divisions are important as they provide a standard framework and organized checklist for project specifications.
Uploaded by
Alaine LazaroCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views9 pagesConstruction Specs Writing Guide
The document provides an overview of specifications writing, including definitions, history, and importance. It discusses how specifications have evolved over time from single documents describing all materials/work, to being broken into categories/sections for increased complexity. This led to the development of standardized specification formats, starting with the Construction Specification Institute's (CSI) 1963 format organizing specifications into 16 divisions. The CSI format was later incorporated into the Uniform Construction Index and further updated over time, including expanding the number of divisions to 50 in 2004. Divisions are important as they provide a standard framework and organized checklist for project specifications.
Uploaded by
Alaine LazaroCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Definitions and History: Covers the definitions pertinent to specifications and traces the historical development and systematization of building specifications.
- Importance of Specifications: Discusses the essential roles and impacts specifications have on construction quality, costs, and communication.
- Specification Formats and Divisions: Details the different formats used in specifications, such as Masterformat and its division systems.
- Recent Changes and Outline Specifications: Highlights updates to Masterformat and outlines the general content structure of specifications.
- Elements of Specification Composition: Discusses elements of writing specifications, focusing on style, standards, and formatting to ensure clarity and precision.