Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BTX Group
Uploaded by
Angel Gail Sornido BayaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BTX Group
Uploaded by
Angel Gail Sornido BayaCopyright:
Available Formats
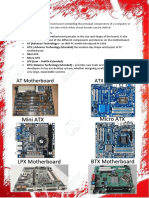
BTX
BALANCED TECHNOLOGY EXTENDED
BTX SYSTEM CASE
AND COMPONENTS
BTX (Balanced Technology eXtended) is a form factor for PC motherboards designed to replace the aging ATX
technology. It has been designed to bring latest technologies that need more power and produce more heat into
small form factor housings.
The revolutionary BTX technology has not died. It has simply never been popular with small and medium system
integrators due to the difficulty to get hold of BTX components. Due to its outstanding benefits, A-brand
professional PC providers such as Fujitsu Siemens Computers, Dell and HP have fully integrated BTX into their
systems and will continue to do so. We now provide all necessary BTX components, so like many of our customers,
win more tenders and contracts by using the outstanding benefits of BTX as unique selling points.
The outstanding acoustic and thermal improvements achieved by BTX technology are
due to a new layout of the motherboard. The CPU is cooled down directly from the fresh
air blown in by the front fan, and all components are strategically situated and
orientated to optimize the front to back air flow path. This can reduce the temperature
by 5 to 10 degrees compared to the ATX system. The only fan required is the massive
CPU cooler. The result is a dramatic reduction of noise, heat, power consumption and
consequently system size.
BTX Motherboard:
BTX, Micro BTX or PicoBTX motherboards are all designed to avoid the obstructed air
flow that is forced around components in ATX systems. They are optimised for the
newest technologies including PCI Express and SATA.
Balance technology extended was designed to reduce the problems of the circa-1996 ATX standards by decreasing
power consumption and heat. The BTX standards provided efficient design for small and large systems and new
features such as:
An increased number of expansion slots
Better electrical and thermal regulation
Multiple system sizes and configurations
Support for high-mass motherboard components
Enhanced cooling capabilities with a straighter air flow path
Reduced latency between the northbridge and southbridge
Better component placement for back-panel input/output (I/O) controllers
Reduced height requirements, which benefit system integration for blade servers and rack mounts
BTX advantages:
-Smaller and super silent systems (No extra fan needed).
-New component locations on motherboard reduce latency between devices. For example, the Northbridge and
Southbridge chips are located near each other and the hardware they control.
-Improved board design for a better signal transmission to memory and power supply.
-Improved cooling with only one high quality fan controlled by PWM technology.
-Higher components durability.
-Higher system stability guaranteed by efficient cooling of active components.
-Improved motherboard support to avoid board deflection due to heavy loads (heatsink, PCI cards…)
DEAD END OF BTX
The BTX was first introduced by Gateway Inc. and then by MPC Corporation and Dell Inc. It was also used in Apple’s
Mac Pro but was not BTX compliant. By September 2006, Intel canceled development; this was largely due to the
lack of backward compatibility with the ATX form factor.
BTX COMPONENTS
BTX Cooler:
The BTX Cooler system is the only fan required for most BTX systems. It cools down the
CPU efficiently as well as all other components. It is controlled by PWM technology
(Pulse Width Modulation) to offer an even more efficient and silent cooling.
BTX Chassis:
The BTX chassis is a mirror image of the ATX and both systems are
therefore not compatible. It has an integrated SRM (Support
Retention Module) and specific mounting holes to support heavy
loads and avoid motherboard deflection. Most chassis offer some
screwless features for easy installation.
BTX Power Supply Unit:
The BTX Power Supply Unit is the same as a standard 24pin ATX
PSU. Its physical size may vary depending on the size of the
chassis.
Other components:
All other components such as Processors, Hard drives, Optical drives, Memory etc… are the same as the ones used
with ATX.
You might also like
- GameCube Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #10From EverandGameCube Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #10No ratings yet
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- Experiment:-4: 1) AT (Advanced Technology)Document4 pagesExperiment:-4: 1) AT (Advanced Technology)Vishv PatelNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Form FactorsDocument3 pagesMotherboard Form FactorsasyrafidzNo ratings yet
- Types of MotherboardDocument6 pagesTypes of MotherboardmarianneNo ratings yet
- 01motherboard Form FactorsDocument13 pages01motherboard Form FactorsckreedlyfNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument38 pagesMotherboardpiusamantaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard ComponentsDocument24 pagesMotherboard ComponentsCarol MutugiNo ratings yet
- And Its Form FactorsDocument13 pagesAnd Its Form FactorsLong Live TauNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument30 pagesMotherboardJhan Rhoan Salazar100% (1)
- Module - MotherboardDocument37 pagesModule - Motherboardyuva_sriNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Assignment 1Document2 pagesUnit 4 Assignment 1miller44No ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ Certification (Chapter 01)Document0 pagesCompTIA A+ Certification (Chapter 01)Wasantha KumaraNo ratings yet
- Ece018 - Digital Electronics 2 - Reflection Paper 1Document2 pagesEce018 - Digital Electronics 2 - Reflection Paper 1John Wilfredd CurimoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard ArchitectureDocument15 pagesMotherboard ArchitectureAbhishek DebNo ratings yet
- CHMA NotesFewContentsDocument158 pagesCHMA NotesFewContentsSayyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument18 pagesHandoutHenock TadesseNo ratings yet
- Motherboards: The Main Board On A PCDocument85 pagesMotherboards: The Main Board On A PCUmar SheriffNo ratings yet
- MOTHERBOARDDocument70 pagesMOTHERBOARDCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Computer CaseDocument16 pagesComputer CaseSnehal TembhurkarNo ratings yet
- ATX Standard DesktopDocument4 pagesATX Standard DesktopAlem GirmaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Lesson 5 CSSDocument4 pagesWeek 5 Lesson 5 CSSShe SheNo ratings yet
- Mini ATX Micro ATX: AT Motherboard ATX MotherboardDocument1 pageMini ATX Micro ATX: AT Motherboard ATX MotherboardErric MarquezNo ratings yet
- BTX Computer Motherboard Power Management SolutionsDocument11 pagesBTX Computer Motherboard Power Management SolutionsTukang SadapNo ratings yet
- Components of MotherboardDocument4 pagesComponents of MotherboardMayur GoreNo ratings yet
- ATX Power Supplies (PG)Document16 pagesATX Power Supplies (PG)jimshwueNo ratings yet
- Hardware Components of ServerDocument14 pagesHardware Components of ServerRipunjay MishraNo ratings yet
- Css MOTHERBOARD - TRANSESDocument7 pagesCss MOTHERBOARD - TRANSESRonalyn SiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document52 pagesAssignment 2Kyla Ysabel SimpronNo ratings yet
- Practical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodDocument7 pagesPractical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodAarunain PandavdraNo ratings yet
- Hardware BibleDocument123 pagesHardware BibleMitko JosifoskiNo ratings yet
- What Is Motherboard:-: 1 Integrated 2 Non IntegratedDocument5 pagesWhat Is Motherboard:-: 1 Integrated 2 Non IntegratedHitesh SinglaNo ratings yet
- Inggris MotherboardDocument4 pagesInggris Motherboards4tr10.d1m4sNo ratings yet
- What Is A Motherboard ?Document13 pagesWhat Is A Motherboard ?Ian OffemariaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardDocument7 pagesMotherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardMustafa MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Form FactorsDocument5 pagesMotherboard Form FactorsShe Real LeanNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram Oc PCDocument40 pagesBlock Diagram Oc PCreghunathevNo ratings yet
- Motherboards & ChipsetsDocument51 pagesMotherboards & ChipsetsRamesh Gandla PadmashaliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Mastering Lan and Trouble ShootingDocument17 pagesUnit 1-Mastering Lan and Trouble Shootingbala smileyNo ratings yet
- CSS PrintDocument6 pagesCSS Printjhazmineiloveyou123No ratings yet
- C7015-0020 - Ultra-Compact Industrial PC in IP65: Multi-Core Capability Directly at The MachineDocument3 pagesC7015-0020 - Ultra-Compact Industrial PC in IP65: Multi-Core Capability Directly at The MachineKrishnamurthy KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Computer Power User - March 2015Document88 pagesComputer Power User - March 2015tulbyNo ratings yet
- Otherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3Document54 pagesOtherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3somerandomhedgehog100% (1)
- Motherboard - Wikipedia PDFDocument46 pagesMotherboard - Wikipedia PDFLorien Lolong LamanNo ratings yet
- Ini Mini ItxDocument11 pagesIni Mini ItxMaxi PullaNo ratings yet
- Building The New PCDocument11 pagesBuilding The New PCthesingh_0No ratings yet
- Chapter-01 (First Look at Computer Parts and Tools) What'S Inside The Case (Casing)Document10 pagesChapter-01 (First Look at Computer Parts and Tools) What'S Inside The Case (Casing)Al Arafat RummanNo ratings yet
- ATX - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesATX - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediakldeep3221No ratings yet
- Components of A MotherboardDocument14 pagesComponents of A MotherboardvcinfotechNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard PresentationDocument21 pagesComputer Motherboard PresentationKoushal JainNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: 6 September 2008Document11 pagesMotherboard: 6 September 2008aaron-ryan-3857No ratings yet
- MicroFusion350 FlyerDocument1 pageMicroFusion350 FlyerSteveNo ratings yet
- Motherboard - Wikipedia PDFDocument41 pagesMotherboard - Wikipedia PDFDance plus 3No ratings yet
- ATX - Wikipedia PDFDocument18 pagesATX - Wikipedia PDFoff emNo ratings yet
- Baby at Form FactorDocument35 pagesBaby at Form FactorLouie RazalasNo ratings yet
- Summary Report in TRDocument9 pagesSummary Report in TREllie KimNo ratings yet
- Mother BoardDocument29 pagesMother BoardSwayamprakash PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document58 pagesChapter 1vipanaroraNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Compact Fanless ComputerDocument2 pagesData Sheet: Compact Fanless Computerbbbru1No ratings yet
- Topic 2b Motherboard Form FactorsDocument5 pagesTopic 2b Motherboard Form FactorsTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Scalefusion OverviewDocument19 pagesScalefusion OverviewParag DharmadhikariNo ratings yet
- Installing A Windows 10 Operating System To A ComputerDocument22 pagesInstalling A Windows 10 Operating System To A ComputerEdelmerck B. FerrerNo ratings yet
- Apple HistoryDocument4 pagesApple HistoryKarthikPillaiNo ratings yet
- Technical FeasibilityDocument4 pagesTechnical FeasibilityGil John AwisenNo ratings yet
- 15092023-Notebook ThinkPad L14 Intel Gen2 20X2CTODocument3 pages15092023-Notebook ThinkPad L14 Intel Gen2 20X2CTOLeandro GomesNo ratings yet
- PTCL 3G Evo Tab - Software Update Step by Step Visual GuideDocument4 pagesPTCL 3G Evo Tab - Software Update Step by Step Visual GuidePTCL_EVO_TAB_REVIEWNo ratings yet
- Master Boot RecordDocument7 pagesMaster Boot Recordshinde_jayesh2005No ratings yet
- Basic PC Troubleshooting: A Starter's Guide To PC UsersDocument29 pagesBasic PC Troubleshooting: A Starter's Guide To PC UsersJuliet CapuletNo ratings yet
- DP Chipset 14036 DriversDocument706 pagesDP Chipset 14036 Driverss npNo ratings yet
- Lenovo T430Document1 pageLenovo T430Wilfredo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Practical No 3 - Motherboard Components and TypesDocument10 pagesPractical No 3 - Motherboard Components and TypesAshish SethiNo ratings yet
- Bios and CmosDocument16 pagesBios and CmosKartik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lenovo ThinkPad T430 DatasheetDocument4 pagesLenovo ThinkPad T430 DatasheetKathleen AquinoNo ratings yet
- PSP RetroPie - RetroPie-Setup WikiDocument3 pagesPSP RetroPie - RetroPie-Setup WikiBobbyNo ratings yet
- Data Flow Diagram (Laptop Assembly Plant)Document15 pagesData Flow Diagram (Laptop Assembly Plant)Kanku BaruahNo ratings yet
- Analysis Report Vietnam ExportDocument932 pagesAnalysis Report Vietnam ExportSulaiman YahyaNo ratings yet
- Authorization Letter To Claim MoneyDocument25 pagesAuthorization Letter To Claim MoneyTacloban City Jail-MD Health Service UnitNo ratings yet
- Mbox2 Firmware v143 33126Document1 pageMbox2 Firmware v143 33126mailenableNo ratings yet
- eSIM Disadvantages How To Connect ?Document9 pageseSIM Disadvantages How To Connect ?Vukkalker NandiniNo ratings yet
- What Is Nox App Player For Windows?Document3 pagesWhat Is Nox App Player For Windows?testNo ratings yet
- H61M-P31 (G3) (MS-7788v1.0) m-ATX MainboardDocument1 pageH61M-P31 (G3) (MS-7788v1.0) m-ATX Mainboardcarlos antonioNo ratings yet
- Lenovo IdeaPad Y510p I7 4700MQ 15.6 - NotebookDocument4 pagesLenovo IdeaPad Y510p I7 4700MQ 15.6 - NotebookGerardo Manuel LedesmaNo ratings yet
- PC Worth Price ListDocument9 pagesPC Worth Price ListJoenard SarmientoNo ratings yet
- List of Inventory On E-Classroom Equipment / Materials: Carmen Central Elementary School Sped CenterDocument2 pagesList of Inventory On E-Classroom Equipment / Materials: Carmen Central Elementary School Sped CenterJane HarlyNo ratings yet
- Lenovo-Legion-Slim-7 15inch AMD DatasheetDocument2 pagesLenovo-Legion-Slim-7 15inch AMD DatasheetCristian HaivazNo ratings yet
- Debug 1214Document6 pagesDebug 1214masnantosmartNo ratings yet
- Bug ReportDocument7 pagesBug ReportFajarbopa Mantel Ahhab Al-WasyiNo ratings yet
- Lenovo V15 G2 ITL 82KB0002BMDocument2 pagesLenovo V15 G2 ITL 82KB0002BMMuhammed SabeehNo ratings yet
- Pos Order LineDocument34 pagesPos Order LineIbnu UbadahNo ratings yet
- Harga Jual AtkDocument52 pagesHarga Jual AtkMuhammad Fadil HijratullahNo ratings yet