Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment:-4: 1) AT (Advanced Technology)
Uploaded by
Vishv PatelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment:-4: 1) AT (Advanced Technology)
Uploaded by
Vishv PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
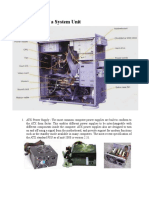
COMPUTER MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING
EXPERIMENT:- 4
AIM :- Observe the different types of motherboards, form factors And write the
difference between the desktop motherboard and laptop motherboard, all in one desktop
motherboard,server motherboard.
Motherboard form factors:-
Determines general layout, size and feature placement on the motherboard.
Form factors such as physical size, shape, component placement, power supply
connectors etc.
1) AT (Advanced Technology):
Oldest and biggest form factor and popular until Baby AT.
Capable of using 386 processor.
12' inch size and was difficult to install, service and upgrade.
2) Baby AT:
Standard in computer industries and still being used in Pentium class products.
CPU socket is placed in such a way that it can interfere with longer bus cards.
Limitation over peripheral card installation.
I/O ports are connected to pin-outs near the floppy drive which results in jumbling
of ribbon cables.
3) ATX (Advanced Technology Extended):
ATX stands for Advanced Technology eXtended. latest motherboards all are called
as ATX motherboards. designed by ATX form factor. In this motherboards, we find
MPGA Processor Sockets, DDR Ram slots, PCI slots, AGP slots, Primary and
secondary IDE interfaces, SATA connectors, 20pin and 24 pin ATX power
connector and Ports.
Improvement done in easy to use, support for current and future I/O, and also to
current and future technology.
New mounting configuration for power supply.
Processor relocated away from expansion slots to allow full length add-in cards.
Tapi Diploma Engg. College, Surat
COMPUTER MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING
4) Micro ATX:
Supports current and new processor technologies.
AGP (Accelerated graphics port) to have high performance graphics.
Smaller in size and less power supply.
Tapi Diploma Engg. College, Surat
COMPUTER MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING
5) LPX (Low Profile Extension) and Mini LPX:
Based on design by western digital.
Usually found in desktop pc's.
Case are slim-line, low profile case with riser card arrangement for expansion cards.
Riser card arrangement means expansion boards are parallel rather than
perpendicular.
This make smaller case but limits number of expansion slots to two or three.
High quality product at low cost but makes difficult to upgrade and repair.
6) NLX (New Low Profile Extended):
Supports current and future processor technologies.
Also supports new AGP and tall memory technology.
Installing and upgrading the system is easy.
Tapi Diploma Engg. College, Surat
COMPUTER MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING
7) BTX Balanced Technology extended:
BTX was developed to reduce or avoid some of the issues that came up while using latest
technologies. Newer technologies often demand more power and they also release more
heat when implemented on motherboards in accordance with the circa-
1996 ATX specification. The ATX standard and the BTX standard, both were proposed by
Intel. The further development of BTX retail products was canceled in September 2006 by
Intel after the acceptance of Intel’s decision to focus again on low-power CPUs after
suffering issues such as scaling and thermal with the Pentium 4.
The first company to use, or to be precise, implement BTX was Gateway Inc, followed
by Dell and MPC. Apple’s MacPro uses only some of the elements of the BTX design
system but it is not BTX compliant. This type of motherboard has some improvements over
previous technologies:
Low-profile – With the larger demand for ever-smaller systems, a redesigned
backplane that shaves inches off the height requirements is a benefit to system
integrators and enterprises which use rack mounts or blade servers.
Thermal design – The BTX design provides a straighter path of airflow with lesser
difficulties, which results in better overall cooling capabilities. Instead of a dedicated
cooling fan, a large 12 cm case-fan is mounted, that draws its air directly from
outside the computer and then cools the CPU through an air duct. Another feature of
BTX is the vertical mounting of the motherboard on the left-hand side. This kind of
feature results in the graphics card heat sink or fan facing upwards, rather than in the
direction of the adjacent expansion card.
Structural design – The BTX standard specifies distinct locations for hardware
mounting points and hence reduces latency between key components. It also reduces
the physical strain imposed on the motherboard by heat sinks, capacitors and other
components which are dealing with electrical and thermal regulation.
Tapi Diploma Engg. College, Surat
You might also like
- Types of MotherboardDocument6 pagesTypes of MotherboardmarianneNo ratings yet
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- Practical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodDocument7 pagesPractical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodAarunain PandavdraNo ratings yet
- GameCube Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #10From EverandGameCube Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #10No ratings yet
- MOTHERBOARDDocument70 pagesMOTHERBOARDCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- And Its Form FactorsDocument13 pagesAnd Its Form FactorsLong Live TauNo ratings yet
- What Is A Motherboard ?Document13 pagesWhat Is A Motherboard ?Ian OffemariaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Form FactorsDocument3 pagesMotherboard Form FactorsasyrafidzNo ratings yet
- Topic 2b Motherboard Form FactorsDocument5 pagesTopic 2b Motherboard Form FactorsTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard ArchitectureDocument15 pagesMotherboard ArchitectureAbhishek DebNo ratings yet
- Motherboards: The Main Board On A PCDocument85 pagesMotherboards: The Main Board On A PCUmar SheriffNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardDocument7 pagesMotherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardMustafa MuhammedNo ratings yet
- BTX GroupDocument2 pagesBTX GroupAngel Gail Sornido BayaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Form FactorsDocument5 pagesMotherboard Form FactorsShe Real LeanNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument18 pagesHandoutHenock TadesseNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ Certification (Chapter 01)Document0 pagesCompTIA A+ Certification (Chapter 01)Wasantha KumaraNo ratings yet
- Otherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3Document54 pagesOtherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3somerandomhedgehog100% (1)
- Module - MotherboardDocument37 pagesModule - Motherboardyuva_sriNo ratings yet
- Motherboard ComponentsDocument24 pagesMotherboard ComponentsCarol MutugiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Assignment 1Document2 pagesUnit 4 Assignment 1miller44No ratings yet
- Summary Report in TRDocument9 pagesSummary Report in TREllie KimNo ratings yet
- Components of MotherboardDocument4 pagesComponents of MotherboardMayur GoreNo ratings yet
- Hardware BibleDocument123 pagesHardware BibleMitko JosifoskiNo ratings yet
- Principle Maintenance Doc 1Document7 pagesPrinciple Maintenance Doc 1DhaweNo ratings yet
- Chapter-01 (First Look at Computer Parts and Tools) What'S Inside The Case (Casing)Document10 pagesChapter-01 (First Look at Computer Parts and Tools) What'S Inside The Case (Casing)Al Arafat RummanNo ratings yet
- Inggris MotherboardDocument4 pagesInggris Motherboards4tr10.d1m4sNo ratings yet
- Hardware Organization of PCS: Types of Motherboard and Their DetailsDocument25 pagesHardware Organization of PCS: Types of Motherboard and Their DetailsGrewal YankeejattNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument38 pagesMotherboardpiusamantaNo ratings yet
- What Is Motherboard:-: 1 Integrated 2 Non IntegratedDocument5 pagesWhat Is Motherboard:-: 1 Integrated 2 Non IntegratedHitesh SinglaNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument30 pagesMotherboardJhan Rhoan Salazar100% (1)
- How Motherboards WorkDocument5 pagesHow Motherboards Workapi-19737301No ratings yet
- Week 5 Lesson 5 CSSDocument4 pagesWeek 5 Lesson 5 CSSShe SheNo ratings yet
- Lesson 02 - Main Parts of ComputerDocument22 pagesLesson 02 - Main Parts of ComputerDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Mother Board Form FactorsDocument10 pagesLesson 2 Mother Board Form FactorsagwonadavidNo ratings yet
- CSS PrintDocument6 pagesCSS Printjhazmineiloveyou123No ratings yet
- Bing MotherboardDocument3 pagesBing Motherboards4tr10.d1m4sNo ratings yet
- Building The New PCDocument11 pagesBuilding The New PCthesingh_0No ratings yet
- Motherboard - Wikipedia PDFDocument41 pagesMotherboard - Wikipedia PDFDance plus 3No ratings yet
- Motherboard TerminologyDocument8 pagesMotherboard TerminologyshockkrewNo ratings yet
- Mboard TshootingDocument29 pagesMboard TshootingDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Motherboard - 11Document58 pagesMotherboard - 11jmkcbeNo ratings yet
- Components of System UnitDocument8 pagesComponents of System UnitIvan Louie Cruto100% (1)
- Baby at Form FactorDocument35 pagesBaby at Form FactorLouie RazalasNo ratings yet
- Motherboard - Wikipedia PDFDocument46 pagesMotherboard - Wikipedia PDFLorien Lolong LamanNo ratings yet
- Computer MotherboardDocument15 pagesComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument13 pagesMotherboardblablaNo ratings yet
- Components of A MotherboardDocument14 pagesComponents of A MotherboardvcinfotechNo ratings yet
- CHMA NotesFewContentsDocument158 pagesCHMA NotesFewContentsSayyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Hardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519Document46 pagesHardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519crecbhoomi21No ratings yet
- The Main Circuit Board of A MicrocomputerDocument16 pagesThe Main Circuit Board of A Microcomputeramandeep123No ratings yet
- 1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in SomeDocument20 pages1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in Somekadilobari100% (3)
- Css MOTHERBOARD - TRANSESDocument7 pagesCss MOTHERBOARD - TRANSESRonalyn SiaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorDocument12 pages1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorTuesept Anne Vargas UrgenteNo ratings yet
- CPH Microproject PDFDocument12 pagesCPH Microproject PDFRohanNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument12 pagesClass NotesHeart WeyganNo ratings yet
- Ece018 - Digital Electronics 2 - Reflection Paper 1Document2 pagesEce018 - Digital Electronics 2 - Reflection Paper 1John Wilfredd CurimoNo ratings yet
- Motherboards & ChipsetsDocument51 pagesMotherboards & ChipsetsRamesh Gandla PadmashaliNo ratings yet
- TESDA Assestment Review (Motherboard) 2015Document77 pagesTESDA Assestment Review (Motherboard) 2015Sharalyn P. SiaNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardDocument5 pagesComputer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardErickson JavonitallaNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-10: Discuss The System Maintains and Troubleshooting ToolsDocument5 pagesExperiment:-10: Discuss The System Maintains and Troubleshooting ToolsVishv PatelNo ratings yet
- CMT Ex-13Document2 pagesCMT Ex-13Vishv PatelNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-12: Removing Unwanted SoftwareDocument7 pagesExperiment:-12: Removing Unwanted SoftwareVishv PatelNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-11: Step:1 Know That If You Are Not Using Microsoft Windows, Seek Instructions Other Than TheDocument4 pagesExperiment:-11: Step:1 Know That If You Are Not Using Microsoft Windows, Seek Instructions Other Than TheVishv PatelNo ratings yet
- CMT Ex-2Document7 pagesCMT Ex-2Vishv PatelNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-8: Installing Driver and Set Up The ConnectionDocument4 pagesExperiment:-8: Installing Driver and Set Up The ConnectionVishv PatelNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-7: Step 1. Insert The Windows 7 Operating System Disk Into Your DVD Drive, and ThenDocument8 pagesExperiment:-7: Step 1. Insert The Windows 7 Operating System Disk Into Your DVD Drive, and ThenVishv PatelNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-6: Standard CMOS FeaturesDocument4 pagesExperiment:-6: Standard CMOS FeaturesVishv PatelNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-3: Processor Sockets and SlotsDocument4 pagesExperiment:-3: Processor Sockets and SlotsVishv PatelNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-5: Sides or Heads - Drive With Three Platters One Can Read and Write On Six Sides. IfDocument5 pagesExperiment:-5: Sides or Heads - Drive With Three Platters One Can Read and Write On Six Sides. IfVishv PatelNo ratings yet
- NtbtlogDocument3 pagesNtbtlogutkarshthegeniu2288No ratings yet
- How To Update Bios enDocument5 pagesHow To Update Bios enJojo YlananNo ratings yet
- Typing KEYBOARD LMG-ARUN PDFDocument2 pagesTyping KEYBOARD LMG-ARUN PDFNaran Desai0% (1)
- Prepare UBS Bootable InstallerDocument5 pagesPrepare UBS Bootable InstallerronaldNo ratings yet
- A26361 D2581 Z110 MuliDocument44 pagesA26361 D2581 Z110 MuliIonut ViorelNo ratings yet
- Bios Le69kbDocument45 pagesBios Le69kbEugen SavcaNo ratings yet
- QwqwertyertyDocument6 pagesQwqwertyertyqwertyNo ratings yet
- Cosmo 270209Document152 pagesCosmo 270209AngelaViorel GheregTurcanuNo ratings yet
- Software KalDocument13 pagesSoftware Kalhanoun1987No ratings yet
- EXP8449 Motherboard Settings and ConfigurationDocument14 pagesEXP8449 Motherboard Settings and ConfigurationLabargarNo ratings yet
- Setupapi Dev LogDocument546 pagesSetupapi Dev LogFriedrich Kurniawan Moja100% (1)
- EPSTPLOGDocument64 pagesEPSTPLOGxyz-net-net1154No ratings yet
- Modbin45 PDFDocument22 pagesModbin45 PDFsjosjo-1No ratings yet
- UsbFix ReportDocument4 pagesUsbFix ReportRuben Ganchozo FNo ratings yet
- M61PMXDocument37 pagesM61PMXFlavianoSilvaNo ratings yet
- PC Analyzer Debug Card ManualDocument35 pagesPC Analyzer Debug Card ManualTania Segovia100% (2)
- Types of BusesDocument16 pagesTypes of BusesIan Conan JuanicoNo ratings yet
- How To Create A Virtual Floppy DiskDocument6 pagesHow To Create A Virtual Floppy DiskLupu DorinNo ratings yet
- PmlogDocument7 pagesPmlogDragos A. RozsnyaiNo ratings yet
- Emu LogDocument4 pagesEmu LogRendy KurosakiNo ratings yet
- Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8 Group Policy SettingsDocument414 pagesWindows Server 2012 and Windows 8 Group Policy Settingsdavidtan1230% (2)
- Intel I7 ArchitectureDocument29 pagesIntel I7 ArchitectureHithesh chNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentGab Worlanyo GodsonNo ratings yet
- Readme NS3FB enDocument3 pagesReadme NS3FB enKartik ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Windows 2000 Pro BR: Serial IDocument4 pagesWindows 2000 Pro BR: Serial IMuhammed YusupNo ratings yet
- LiveUpdate 6.2 ReleaseNoteDocument5 pagesLiveUpdate 6.2 ReleaseNoteMichael MellaNo ratings yet
- Post Bios CodeDocument3 pagesPost Bios CodechokNo ratings yet
- PLT-04543 A.2 - HID FARGO DTC5500LMX Windows Printer Driver Release NotesDocument5 pagesPLT-04543 A.2 - HID FARGO DTC5500LMX Windows Printer Driver Release Notesredd.xox93No ratings yet
- Gigabyte Ga-945gcm-S2l - Rev 1.0Document33 pagesGigabyte Ga-945gcm-S2l - Rev 1.0Everton Dorado100% (1)
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsFrom EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Digital Transformation: An Executive Guide to Survive and Thrive in the New EconomyFrom EverandDigital Transformation: An Executive Guide to Survive and Thrive in the New EconomyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (230)
- CompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)From EverandCompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]From EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- Computer Science: A Concise IntroductionFrom EverandComputer Science: A Concise IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Design Recipes for FPGAs: Using Verilog and VHDLFrom EverandDesign Recipes for FPGAs: Using Verilog and VHDLRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Cyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandCyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsHoubing H. SongNo ratings yet
- Arduino: A Beginner's Guide to Arduino ProgrammingFrom EverandArduino: A Beginner's Guide to Arduino ProgrammingRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XFrom EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Practice Tests: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Practice Tests: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102No ratings yet
- How To Market Mobile Apps: Your Step By Step Guide To Marketing Mobile AppsFrom EverandHow To Market Mobile Apps: Your Step By Step Guide To Marketing Mobile AppsNo ratings yet
- Cancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionFrom EverandCancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Creative Selection: Inside Apple's Design Process During the Golden Age of Steve JobsFrom EverandCreative Selection: Inside Apple's Design Process During the Golden Age of Steve JobsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- Raspberry PI: Learn Rasberry Pi Programming the Easy Way, A Beginner Friendly User GuideFrom EverandRaspberry PI: Learn Rasberry Pi Programming the Easy Way, A Beginner Friendly User GuideNo ratings yet
- iPhone Photography: A Ridiculously Simple Guide To Taking Photos With Your iPhoneFrom EverandiPhone Photography: A Ridiculously Simple Guide To Taking Photos With Your iPhoneNo ratings yet






































































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1715524978?v=1)