Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit Test-2 11th NEET BIO
Uploaded by
reilyshawnOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit Test-2 11th NEET BIO
Uploaded by
reilyshawnCopyright:
Available Formats
Jijamata Education Society's
PREETISUDHAJI JUNIOR COLLEGE
At: Pimplas, Post: Rahata, Taluka: Rahata, Dist: Ahmednagar, Maharashtra . .
Pin Code – 423107.
ACADEMIC YEAR: 2023-2024
UNIT TEST- II
CLASS: XI NEET TIME: 1 Hrs
SUB: BIOLOGY
STREAM.: SCI MARKS- 25
STUDENT’S NAME:
SECTION-A
Multiple Choice Question 4 - marks
1. In photosynthesis, oxygen is produced during which stage?
2. a. Light-dependent reactions b. Calvin cycle c. Glycolysis d. Krebs cycle
3. Which type of root system is characteristic of monocots?
a. Taproot system b. Fibrous root system c. Adventitious root system d. Storage root system
4. During photosynthesis, where does the light-independent (Calvin cycle) reaction occur? a. Thylakoid
membrane b. Stroma c. Granum d. Outer membrane
Very short Answer Question 3 – marks
1. Define photosynthesis and state its overall chemical equation.
2. Differentiate between the transverse sections of monocot and dicot roots.
3. Name the cells responsible for photosynthesis in plant leaves and describe their structure.
SECTION-B
Short Answer Questions (Any 4 ) 8 - marks
1. Define photosynthesis, detailing the cyclic phosphorylation.
2. Compare and contrast the transverse sections of monocot and dicot stems.
3. Describe the adaptations in the leaves of plants for efficient photosynthesis.
4. Discuss the importance of the vascular bundles in plant roots.
5. Explain how the structure of chloroplasts is related to their function in photosynthesis.
SECTION-C
Short Answer Questions (Any 2 ) 6 - marks
1. Describe the kranz anatomy and explain its significance.
2. Explain non-cyclic phosphorylation with its diagram.
3. Explain the steps involved in C3 Cycle.
SECTION-D
Short Answer Questions (Any 1 ) 4 - marks
1. Provide an overview of the C4 Cycle and Photorespiration.
OR
2. Compare the structural features of monocot and dicot leaves, highlighting their adaptations for
photosynthesis.
You might also like
- DLL MitosisDocument6 pagesDLL MitosisMaica RamirezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine, USMLE ENDPOINTDocument73 pagesEndocrine, USMLE ENDPOINTDaNy Chiriac50% (2)
- Microbiology 1st Edition Wessner Test BankDocument19 pagesMicrobiology 1st Edition Wessner Test BankLatoya Capers100% (44)
- LP1 The Cell TheoryDocument3 pagesLP1 The Cell TheoryPaulus VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 5 Steps To A 5 AP BiologyDocument210 pages5 Steps To A 5 AP BiologyYingfang LiNo ratings yet
- General Biology-Q2-Week 2Document15 pagesGeneral Biology-Q2-Week 2ALFREDO CALEDANo ratings yet
- Checklist For Evaluation of Potential Airway & Breathing DisordersDocument7 pagesChecklist For Evaluation of Potential Airway & Breathing DisordersSaran BNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science MELCsDocument5 pagesGrade 10 Science MELCsMark Chris TanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Absorption Spectra and Geometry of Organic Molecules: An Application of Molecular Orbital TheoryFrom EverandElectronic Absorption Spectra and Geometry of Organic Molecules: An Application of Molecular Orbital TheoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bio 150 Syllabus 2011Document3 pagesBio 150 Syllabus 2011Jolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine - Minimally Invasive and Open SurgeryDocument338 pagesCervical Spine - Minimally Invasive and Open Surgerymohamed lamrana jallohNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE MELCs Grade 10Document3 pagesSCIENCE MELCs Grade 10Ciza Rhea Amigo Osoteo100% (5)
- Dll-Physical Science-Week 5-Alpha Pia v. RivasDocument6 pagesDll-Physical Science-Week 5-Alpha Pia v. RivasPia Vila RivasNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry PDFDocument144 pagesBiochemistry PDFIon BarboiNo ratings yet
- Template DLP BioenergeticsDocument9 pagesTemplate DLP Bioenergeticsargie joy marie100% (1)
- Final DLPDocument3 pagesFinal DLPԱբրենիկա ՖերլինNo ratings yet
- Cus3101 Course WorkDocument6 pagesCus3101 Course WorkMukbsNo ratings yet
- CELL BIO - 101 - THEORY - June 2019Document7 pagesCELL BIO - 101 - THEORY - June 2019Lucas LuluNo ratings yet
- Sci 101Document5 pagesSci 101Xenia Mae FloresNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment SB015 Session 20232024 - StudentsDocument7 pagesBiology Assignment SB015 Session 20232024 - StudentsMuhd AzreenNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 First QuarterDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1 First QuarterAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Department Curriculum MapDocument5 pagesSenior High School Department Curriculum MapCamille Sison-AlmirolNo ratings yet
- 2017 11 Sample Paper Biology 01 QPDocument2 pages2017 11 Sample Paper Biology 01 QPAlokNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 Course Objectives Sp23Document6 pagesBIO 101 Course Objectives Sp23begush015No ratings yet
- General InstructionsDocument4 pagesGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- General InstructionsDocument4 pagesGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- August 20-24, 2018Document5 pagesAugust 20-24, 2018Maria Virginia Fernandez100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry III 2022Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry III 2022Silvia AngelinaNo ratings yet
- Bixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, Quezon: Science and Technology 8Document3 pagesBixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, Quezon: Science and Technology 8Oliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- CM - GEN BIO Written Work 2Document4 pagesCM - GEN BIO Written Work 2Camille Sison-AlmirolNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentDocument5 pagesAP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentHannah ParkerNo ratings yet
- Ph.D. Entrance Examination, October 2013Document10 pagesPh.D. Entrance Examination, October 2013NikhilUdinurNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 1105 Midterm DivisionsDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 1105 Midterm DivisionsmahadasdfghjklNo ratings yet
- Unit Test Term-Ii (Xi 2021-22)Document1 pageUnit Test Term-Ii (Xi 2021-22)AdityaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline FUNCORE 102 General Zoology 1st Sem 2022-2023Document5 pagesCourse Outline FUNCORE 102 General Zoology 1st Sem 2022-2023Gracia NicolaiNo ratings yet
- MSC Biotechnology Assignment QuestionpapersDocument1 pageMSC Biotechnology Assignment QuestionpapersAISHA MUHAMMADNo ratings yet
- 9th Papers New PattrenDocument122 pages9th Papers New PattrenGul ZahraNo ratings yet
- CHY351 MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesCHY351 MacromoleculesKrrish BosamiaNo ratings yet
- Nuguid, Rochelle D - Assessment InstrumentDocument16 pagesNuguid, Rochelle D - Assessment InstrumentRochelle NuguidNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 MelcDocument3 pagesGrade 10 MelcKAREN SALLESNo ratings yet
- Vasquez, Angelica, Bio30lL, Activity 3,2020Document6 pagesVasquez, Angelica, Bio30lL, Activity 3,2020Angelica VasquezNo ratings yet
- BIO122 Histology of Cell and Tissue Tutorial Chapter 4.2: Lecturer: Date: GroupDocument2 pagesBIO122 Histology of Cell and Tissue Tutorial Chapter 4.2: Lecturer: Date: GroupAHMAD ZARIF ZAFRI BIN AHMAD FAUZI -No ratings yet
- Test 2 Review SheetDocument1 pageTest 2 Review Sheet10026722No ratings yet
- BIO 1401 Module Prof. C. Katongo-1Document79 pagesBIO 1401 Module Prof. C. Katongo-1OliverNo ratings yet
- GenBio1 Module1Document10 pagesGenBio1 Module1Alexander DontonNo ratings yet
- Science: Whole Brain Learning SystemDocument16 pagesScience: Whole Brain Learning SystemKayrell AquinoNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Q1 W7Document11 pages9 Science Q1 W7Mark Ivan AbrizaNo ratings yet
- BIOZONE IB Biology 2nd Edition Sample PacketDocument11 pagesBIOZONE IB Biology 2nd Edition Sample Packetvf5ctjknk6No ratings yet
- ZoologyDocument4 pagesZoologyMunna KumarNo ratings yet
- Budget-of-Work-General Biology 1Document2 pagesBudget-of-Work-General Biology 1joei ArqueroNo ratings yet
- 216 SyllabusDocument15 pages216 Syllabusapi-395433114No ratings yet
- SCH 102 Lecture 2 (2024) Functional Groups, Atomic Structure and Chemical BondingDocument51 pagesSCH 102 Lecture 2 (2024) Functional Groups, Atomic Structure and Chemical BondingmwendwagladwelNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Exam RevisionDocument3 pagesBiomolecules Exam RevisionCarmen CheahNo ratings yet
- Biology: M.B:shamsDocument9 pagesBiology: M.B:shamsmohamed sabryNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument2 pagesCell StructureEva GarciaNo ratings yet
- Test Review - Cells, Cell Transportation and Communication: Unit ObjectivesDocument5 pagesTest Review - Cells, Cell Transportation and Communication: Unit ObjectivesCole McFarlandNo ratings yet
- BIO111 Principles of Biology Course Outline 2022Document5 pagesBIO111 Principles of Biology Course Outline 2022Resego lentsweNo ratings yet
- Csir Net Colored SyllabusDocument40 pagesCsir Net Colored SyllabusSATYARANJAN SETHINo ratings yet
- Examination-2017 Chapter Test-Heredity & Evolution CBSE X-BiologyDocument2 pagesExamination-2017 Chapter Test-Heredity & Evolution CBSE X-BiologyIshvaryaNo ratings yet
- A16 Bio 101-Nya-05 BiologyDocument10 pagesA16 Bio 101-Nya-05 BiologyUmehabibah RehmanNo ratings yet
- Course Outline General Biology II: Course Code (S) and Mesrs Objectives Science (200.B0), Registered in 101-LCU-05Document12 pagesCourse Outline General Biology II: Course Code (S) and Mesrs Objectives Science (200.B0), Registered in 101-LCU-05Nicole GuNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Biological MembranesFrom EverandStructure and Function of Biological MembranesLawrence I. RothfieldNo ratings yet
- Structural Biology Using Electrons and X-rays: An Introduction for BiologistsFrom EverandStructural Biology Using Electrons and X-rays: An Introduction for BiologistsMichael F MoodyNo ratings yet
- As - Bride Copy Final ADocument4 pagesAs - Bride Copy Final AreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- 8 DevDocument2 pages8 DevreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Ex04 ExDocument3 pagesEx04 ExreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- 11th Biology BookDocument150 pages11th Biology BookreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology NotesDocument150 pagesClass 11 Biology NotesreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Active and Emerging Methodologies For Ubiquitous Education Potentials of Flipped Learning and GamificationDocument11 pagesActive and Emerging Methodologies For Ubiquitous Education Potentials of Flipped Learning and GamificationreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- 9 DevDocument1 page9 DevreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- A Framework To Evaluate The Interoperability of Information SystemsDocument13 pagesA Framework To Evaluate The Interoperability of Information SystemsreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Annex ADocument2 pagesAnnex AreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Butadiene Rubber-BRDocument20 pagesButadiene Rubber-BRreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Butyl Rubber-IIRDocument26 pagesButyl Rubber-IIRreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- EPDMDocument13 pagesEPDMreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Nitrile rubber-NBRDocument16 pagesNitrile rubber-NBRreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Rubber Lec-1 - 2Document51 pagesSynthetic Rubber Lec-1 - 2reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Chloropene Rubber-CRDocument9 pagesChloropene Rubber-CRreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Chem218 HW 6Document5 pagesChem218 HW 6reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Chem218 Essay 6Document4 pagesChem218 Essay 6reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Matrix COSEC TAM PresentationDocument90 pagesMatrix COSEC TAM PresentationreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- CHEM218 Questions 7Document4 pagesCHEM218 Questions 7reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Matrix COSEC Face Recognition V1R1 PresentationDocument44 pagesMatrix COSEC Face Recognition V1R1 PresentationreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- CHEM218 Summary 3Document4 pagesCHEM218 Summary 3reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- CHEM218 Progress Report 3Document4 pagesCHEM218 Progress Report 3reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- CHEM218 Exercise 9Document4 pagesCHEM218 Exercise 9reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- CHEM218 Report 9Document4 pagesCHEM218 Report 9reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Chem218 Notes 6Document4 pagesChem218 Notes 6reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- CHEM218 Homework Help 3Document5 pagesCHEM218 Homework Help 3reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- CHEM218 Summary 8Document5 pagesCHEM218 Summary 8reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Chem218 HW 2Document4 pagesChem218 HW 2reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Chem218 Notes 8Document4 pagesChem218 Notes 8reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Hema Lec Week 16 Leukocyte Disorders Part 2Document4 pagesHema Lec Week 16 Leukocyte Disorders Part 2Max RuideraNo ratings yet
- 1472 - Practical 2 - Total RBC Count by Hemocytometer - Hematology PracticalsDocument8 pages1472 - Practical 2 - Total RBC Count by Hemocytometer - Hematology PracticalsnihaNo ratings yet
- Monobind Reagent CatalogDocument40 pagesMonobind Reagent Catalogthuy dinhNo ratings yet
- Dose Response Relations Assignment PhysiologyDocument5 pagesDose Response Relations Assignment PhysiologyitsybitsyNo ratings yet
- NRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANDocument14 pagesNRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANEllen Mynelle MabulacNo ratings yet
- Sleep PhysiologyDocument23 pagesSleep PhysiologyPeter BockarieNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Drug Action and Dose Response Relationship (First Part)Document138 pagesMechanism of Drug Action and Dose Response Relationship (First Part)geniousmasud721No ratings yet
- Plant Embryogenesis (Zygotic and Somatic) : Introductory ArticleDocument10 pagesPlant Embryogenesis (Zygotic and Somatic) : Introductory ArticleJessica Asitimbay ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Disorders (Final Draft)Document17 pagesPituitary Disorders (Final Draft)Kiprono Keitany TimothyNo ratings yet
- EALS Q2 Week 1 Concept of LifeDocument18 pagesEALS Q2 Week 1 Concept of LifeMarylyn MirandaNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document33 pagesPart 1Ankit YadavNo ratings yet
- Medical Cannabis For Children Evidence and Recommendations Canadian Paediatric SocietyDocument22 pagesMedical Cannabis For Children Evidence and Recommendations Canadian Paediatric SocietyRegina de AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- P9mi9p6lx - Lesson 3.3-The Integumentary System 3Document23 pagesP9mi9p6lx - Lesson 3.3-The Integumentary System 3Precious RoxasNo ratings yet
- Ramos - Pathophysiology PCOSDocument1 pageRamos - Pathophysiology PCOSLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Jim Bidlack - BIO 1304Document1 pageJim Bidlack - BIO 1304Vashist mohanNo ratings yet
- Excretory System: Instruction: Complete The Table BelowDocument4 pagesExcretory System: Instruction: Complete The Table BelowChrista Villanueva MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics - A Treatise - Brahmankar, Jaiswal - Pharma DostDocument206 pagesBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics - A Treatise - Brahmankar, Jaiswal - Pharma DostmihirrupadhyayNo ratings yet
- P.B. TELEFO, Ph.D. Senior Lecturer of Biochemistry University of Dschang, CameroonDocument59 pagesP.B. TELEFO, Ph.D. Senior Lecturer of Biochemistry University of Dschang, CameroonTabe AndersonNo ratings yet
- Vagus Cranial NerveDocument6 pagesVagus Cranial NervedimiNo ratings yet
- DopplerDocument56 pagesDopplerEsraa AlmassriNo ratings yet
- Placentation in MammalsDocument261 pagesPlacentation in Mammalsjabeenjaveria98No ratings yet
- Central Nervous System CROSSWORDDocument2 pagesCentral Nervous System CROSSWORDJULIO CANIPASNo ratings yet
- Dillard - 2021 - Mechanistic Models of Microbial Community MetabolismDocument11 pagesDillard - 2021 - Mechanistic Models of Microbial Community MetabolismBGENo ratings yet
- Spa PPT - FinalDocument45 pagesSpa PPT - FinalShivam DwivediNo ratings yet
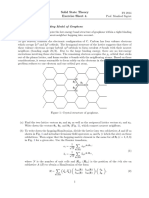
- BT3020 Jan-May 2023 Structural Biology Problem Set 1Document1 pageBT3020 Jan-May 2023 Structural Biology Problem Set 1Ahire Ganesh Ravindra bs20b004No ratings yet
- Week 3 - Basic Human Anatomy, Physiology & Fitness ConceptsDocument30 pagesWeek 3 - Basic Human Anatomy, Physiology & Fitness ConceptsJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet