Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ramos - Pathophysiology PCOS
Uploaded by
Louwella Ramos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pageOriginal Title
Ramos_Pathophysiology PCOS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pageRamos - Pathophysiology PCOS
Uploaded by
Louwella RamosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Ramos, Louwella Faith M.
2-BN Gynaecology Ward RLE
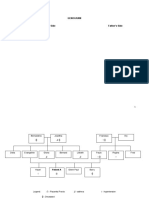
Pathophysiology of Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Modifiable risk factors
-Diet Non Modifiable risk factors
-environmental -genetics
-lifestyle -hormones
-immune system -age
Intrinsic ovarian factors
The body produced more androgen in the
adrenal gland and ovaries.
Excessive androgen disturbed the production of
gonadotropin releasing hormones levels
Excessive gonadotropin releasing hormones levels travels to
the ovaries to the thecal cell and granulosa cell
Signs and
symptoms
This generates disproportion in LH and FSH productions,
increasing LH and decreasing FSH Menstrual
Irregularity
Increase in LH causes increases
Produce big the
but Androgen
non-mature follicles
hormones release and production
Hormonal imbalance signal hypothalamus to
release more hormone to try to correct it.
This create effect called insulin sensitivity
This causes the pancreas to stimulate more
insulin
You might also like
- Nursing Lab 3 Skill Performance Checklist Administering A Blood Transfusion S U NP CommentsDocument2 pagesNursing Lab 3 Skill Performance Checklist Administering A Blood Transfusion S U NP CommentsCandice Cheng88% (8)
- Case Study, Chapter 70, Management of Patients WithOncologic or Degenerative Neurologic DisordersDocument1 pageCase Study, Chapter 70, Management of Patients WithOncologic or Degenerative Neurologic Disordersclyde i am100% (1)
- TMC Dosing ChartDocument6 pagesTMC Dosing ChartScott100% (1)
- Spina Bifida Concept Map PDFDocument1 pageSpina Bifida Concept Map PDFnot realNo ratings yet
- 2Document4 pages2Emmyr JohnNo ratings yet
- Date Performed: August 18, 2015 Group No. and Section: Group 5 WCDE-A Date Submitted: September 1, 2015 Group MembersDocument28 pagesDate Performed: August 18, 2015 Group No. and Section: Group 5 WCDE-A Date Submitted: September 1, 2015 Group MembersCm MacaliaNo ratings yet
- Extra CasesDocument1 pageExtra CasesE.J. PelayoNo ratings yet
- Wilhelm Wundt - 1896 - Outlines of PsychologyDocument367 pagesWilhelm Wundt - 1896 - Outlines of Psychologysamanthaacl100% (2)
- Uti in ChildrenDocument20 pagesUti in ChildrenNovina FirliaNo ratings yet
- Agn PDFDocument6 pagesAgn PDFMohamed ZiadaNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument9 pagesNCP Impaired Physical MobilityChristian Apelo SerquillosNo ratings yet
- Case Study EvaluationDocument6 pagesCase Study EvaluationKristy HimmlerNo ratings yet
- ALTERED POST PARTUM Complications Nursing Lecture and Care PlanDocument13 pagesALTERED POST PARTUM Complications Nursing Lecture and Care PlanKristelle Joy Capili SicatNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument6 pagesDrugs StudyMark_Rebibis_8528No ratings yet
- Dhan Chan NCPDocument3 pagesDhan Chan NCPDhaneanne Marie ChanNo ratings yet
- Kardex: Diet: Interventions IVF (Indicate Date and Time Started) Room Number: 313Document2 pagesKardex: Diet: Interventions IVF (Indicate Date and Time Started) Room Number: 313kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin (Pitocin) : Slide 1Document16 pagesOxytocin (Pitocin) : Slide 1Kalesha JonesNo ratings yet
- NCP For HYPERTHERMIADocument3 pagesNCP For HYPERTHERMIAGil Ganiban0% (1)
- HANDOUT Chapter 11 Promoting Fetal and Maternal HealthDocument7 pagesHANDOUT Chapter 11 Promoting Fetal and Maternal HealthClouiseNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing Care PlanDocument12 pagesObstetric Nursing Care PlanJass Mira Bueno100% (1)
- Status AsthmaticusDocument6 pagesStatus AsthmaticusMae Azores100% (1)
- Vincristine (OncovinDocument4 pagesVincristine (Oncovin9959101161No ratings yet
- EthicsDocument1 pageEthicsNadineNo ratings yet
- Patho DHFDocument2 pagesPatho DHFPhillip GoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #1 Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Independent Short TermDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan #1 Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Independent Short TermAlmer OstreaNo ratings yet
- De Guzman NCP GDMDocument4 pagesDe Guzman NCP GDMCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Document3 pagesZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- Obstructed Labor-Bandl's RingDocument43 pagesObstructed Labor-Bandl's RingJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- EndometriosisDocument6 pagesEndometriosissalamredNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug AnaDocument4 pagesCefuroxime Drug AnaCarpz DarpzNo ratings yet
- MicrocephalyDocument4 pagesMicrocephalykurei_bluflamedNo ratings yet
- Determine The Gestational AgeDocument18 pagesDetermine The Gestational AgeMomshie Felaih Binasoy Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Fetal Distress: Dr. Moses KayungiDocument41 pagesFetal Distress: Dr. Moses Kayungimarco luenaNo ratings yet
- Ob MaternityDocument46 pagesOb MaternityJohanna Erazo Padilla100% (1)
- Intake & Output Monitoring Sheet: 11 PM 11-7 1000 ML 0 550 ML 0 0Document2 pagesIntake & Output Monitoring Sheet: 11 PM 11-7 1000 ML 0 550 ML 0 0Renea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Pathophysiology and ManagementDocument7 pagesPreeclampsia Pathophysiology and ManagementAuliaNo ratings yet
- Inguinal Hernia MinicaseDocument13 pagesInguinal Hernia MinicaseGerold Chua100% (1)
- GonorrheaDocument9 pagesGonorrheaWulan DayuNo ratings yet
- Sheehan's SyndromeDocument12 pagesSheehan's SyndromePawpaw ChanNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid Med CardDocument3 pagesFolic Acid Med CardDadybooboo2013No ratings yet
- Missed AbortionDocument5 pagesMissed AbortionDesta MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Concept Map 2Document3 pagesConcept Map 2John DoeNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Abruptio Placentae Revised Case StudyDocument87 pagesGroup 3 Abruptio Placentae Revised Case StudyXena IngalNo ratings yet
- NCP NCM 109 Post Partum PeritonitisDocument2 pagesNCP NCM 109 Post Partum PeritonitisHoney MacabuhayNo ratings yet
- EINC ReviewDocument14 pagesEINC ReviewRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Post Test 30 Items OBDocument5 pagesPost Test 30 Items OBJohnasse Sebastian NavalNo ratings yet
- PLMNursing - StudyMaterial - The Growing FetusDocument11 pagesPLMNursing - StudyMaterial - The Growing FetusGwyneth ManioNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics MALNUTRITION - Dra. Garcia's Lecture: Primum Non NocereDocument8 pagesPediatrics MALNUTRITION - Dra. Garcia's Lecture: Primum Non NocerekrishNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Management: BleomycinDocument1 pagePharmacologic Management: BleomycinKim ApuradoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Fetal Well BeingDocument22 pagesEvaluation of Fetal Well BeingJoanah Mae AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Pre and Post PregnancyDocument23 pagesPre and Post PregnancyJitendra ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- A Review On Otitis Media (Karnapaka) : Ayurvedic Aspects and TreatmentDocument4 pagesA Review On Otitis Media (Karnapaka) : Ayurvedic Aspects and TreatmentEditor_IAIMNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH) : Case Scenario 4Document4 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH) : Case Scenario 4Mae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- Availability: Classifications: Antihistamine Antipruritic Pregnancy Category: CDocument4 pagesAvailability: Classifications: Antihistamine Antipruritic Pregnancy Category: CCay SevillaNo ratings yet
- OB Case StudyDocument20 pagesOB Case Studylms93093No ratings yet
- Care Plan FaringitisDocument63 pagesCare Plan FaringitisEnerolisa ParedesNo ratings yet
- GRP 4 CLO 2 Concept Map PT 1 PDFDocument14 pagesGRP 4 CLO 2 Concept Map PT 1 PDFMaria Lyn Ocariza ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice: Miriti M.D Master of Clinical Medicine:Accidents and Emerrgency MAY 2018Document25 pagesNeonatal Jaundice: Miriti M.D Master of Clinical Medicine:Accidents and Emerrgency MAY 2018Dennis MiritiNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous AbortionDocument8 pagesSpontaneous Abortionsaber_fate_11No ratings yet
- Ramos-2bn NCP Delivery RoomDocument2 pagesRamos-2bn NCP Delivery RoomLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- AtivanDocument1 pageAtivanSheri490No ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- HSB The Endocrine System Csec NotesDocument4 pagesHSB The Endocrine System Csec NotesGiaaNo ratings yet
- Ramos, LF - 2BN - LFDDocument1 pageRamos, LF - 2BN - LFDLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis GyneDocument2 pagesCase Analysis GyneLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Program Proposal FinalDocument5 pagesProgram Proposal FinalLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Ramos PathophysiologyDocument1 pageRamos PathophysiologyLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Survey Questionnaire Pacheckk 4444Document11 pagesSurvey Questionnaire Pacheckk 4444Louwella RamosNo ratings yet
- KrystelDocument11 pagesKrystelLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Standing Order SheetDocument1 pageStanding Order SheetLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Batang Malusog? END Malnourishment Now para NO MORE SANA ALL!Document2 pagesBatang Malusog? END Malnourishment Now para NO MORE SANA ALL!Louwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Ramos PathophysiologyDocument1 pageRamos PathophysiologyLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- COPAR Chapter 10Document2 pagesCOPAR Chapter 10Louwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument5 pagesProject ProposalLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- RAMOS, LOUWELLA 2 BN International Health Information Regulatory BodiesDocument2 pagesRAMOS, LOUWELLA 2 BN International Health Information Regulatory BodiesLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Ramos CASE ANALYSIS GYNEDocument3 pagesRamos CASE ANALYSIS GYNELouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Ramos NCP RevisionDocument3 pagesRamos NCP RevisionLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- KrystelDocument11 pagesKrystelLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Ramos NCP RevisionDocument3 pagesRamos NCP RevisionLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- PRIODocument7 pagesPRIOLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Ramos - Cervical-DysplasiaDocument1 pageRamos - Cervical-DysplasiaLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Ramos - Genogram-PathophysioDocument5 pagesRamos - Genogram-PathophysioLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Bryan Beran: Barangay Captain, RizalDocument1 pageBryan Beran: Barangay Captain, RizalLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Breasts and AxillaeDocument2 pagesBreasts and AxillaemadamcloudnineNo ratings yet
- Coahs Medical Center: Date/Tim E Focus Data, Action, ResponseDocument4 pagesCoahs Medical Center: Date/Tim E Focus Data, Action, ResponseLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Ramos CASE ANALYSIS GYNEDocument3 pagesRamos CASE ANALYSIS GYNELouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Coahs Medical Center: Date/Time Focus Data, Action, ResponseDocument4 pagesCoahs Medical Center: Date/Time Focus Data, Action, ResponseLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Activity-5 K 2BNDocument3 pagesActivity-5 K 2BNLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Coahs Medical Center: Date/Tim E Focus Data, Action, ResponseDocument4 pagesCoahs Medical Center: Date/Tim E Focus Data, Action, ResponseLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- PCOSDocument1 pagePCOSLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Cycling: Ramos, Louwella Faith M. 2-BNDocument7 pagesCycling: Ramos, Louwella Faith M. 2-BNLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- The Windmill Technique Avoids Manual Removal of The RetainedDocument6 pagesThe Windmill Technique Avoids Manual Removal of The RetainedEndrianus Jaya PutraNo ratings yet
- 01 Lecture Animation PPTDocument47 pages01 Lecture Animation PPTMary JewelNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Imperforated HymenDocument133 pagesCase Pres Imperforated Hymenpongiyalabs50% (2)
- Food Microbiology Quality Control Nov 14Document36 pagesFood Microbiology Quality Control Nov 14Harith AtrisNo ratings yet
- Poster ApmlDocument1 pagePoster Apmlkuel1511No ratings yet
- PUB - NEWater - Quality 1Document1 pagePUB - NEWater - Quality 1Weijin LeowNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Science TestDocument2 pagesGrade 4 Science Testnakeshia.stapletonNo ratings yet
- Volume 21 Opt Compressed ADocument205 pagesVolume 21 Opt Compressed AJeff TaylorNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Agents in Periodontal Treatment 2Document5 pagesChemotherapy Agents in Periodontal Treatment 2shathaNo ratings yet
- Small Ruminant Research: Amanda K. Jones, Sarah A. ReedDocument9 pagesSmall Ruminant Research: Amanda K. Jones, Sarah A. ReedIngrid MachadoNo ratings yet
- 56 4 Article01Document14 pages56 4 Article01Thiago GomezNo ratings yet
- A Relative Difference EVAU ExamenDocument1 pageA Relative Difference EVAU ExamenDA MANo ratings yet
- Weathering of RocksDocument2 pagesWeathering of Rocksvee propagandaNo ratings yet
- STRA65Document6 pagesSTRA65SUJITH232323No ratings yet
- Z+blood TransfusionDocument16 pagesZ+blood TransfusionilhamaminsyaputraNo ratings yet
- How Do The Parts of The Integumentary System Work?: LessonDocument4 pagesHow Do The Parts of The Integumentary System Work?: LessonSyrill EsperoNo ratings yet
- Markeri MereDocument6 pagesMarkeri MereGigiPetreaNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To WOUNDDocument22 pages2 Introduction To WOUNDkat garciaNo ratings yet
- Ce - 332 Ee Lab ManualDocument105 pagesCe - 332 Ee Lab ManualShanihaKKNo ratings yet
- Week 15 16 Module Biochem Lec EndocrinologyDocument19 pagesWeek 15 16 Module Biochem Lec EndocrinologyLy xyNo ratings yet
- Cactus Explorer 09 - Complete PDFDocument56 pagesCactus Explorer 09 - Complete PDFkhun sakNo ratings yet
- FA CPR Workbook 0001Document56 pagesFA CPR Workbook 0001Shawn KimballNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Science 2013 Elodea and Photosynthesis Lab Report PROBLEM: How Does The Color of Light (Blue, Red) Affect The Rate of PhotosynthesisDocument4 pages7th Grade Science 2013 Elodea and Photosynthesis Lab Report PROBLEM: How Does The Color of Light (Blue, Red) Affect The Rate of Photosynthesisapi-194649051No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledMarande LisaNo ratings yet
- Talasemia de HB S y Talasemia de HB CDocument10 pagesTalasemia de HB S y Talasemia de HB CAlejandra NúñezNo ratings yet
- Rat AnatomyDocument4 pagesRat AnatomySophia Ho100% (1)
- 2024 Microbiology Hons Booklet - FINALDocument54 pages2024 Microbiology Hons Booklet - FINALchand198No ratings yet