Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 02 1
Uploaded by
ahmedmansurr98Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 02 1
Uploaded by
ahmedmansurr98Copyright:
Available Formats
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, GPRA CAMPUS, HYD–32
SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM (2019-20)
SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS
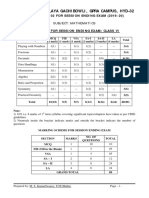
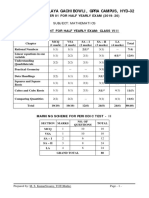
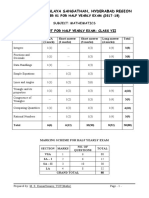
BLUE PRINT FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM: CLASS VII
MCQ FIB VSA SA-I SA-II LA
Unit/Topic Total
(1 mark) (1 mark) (1 mark) (2 marks) (3 marks) (4 marks)
Integers 1(1) 1(1) -- 1(2) -- -- 3(4)
Congruence of
-- -- -- 1(2) 1(3) -- 2(5)
Triangles
Comparing Quantities 1(1) 1(1) -- 1(2) 1(3) -- 4(7)
Rational Numbers 1(1) -- -- 1(2) 1(3) 1(4) 4(10)
Practical Geometry -- -- -- -- 2(6) 1(4) 3(10)
Perimeter and Area 2(2) 1(1) 1(1) -- 1(3) 1(4) 6(11)
Algebraic Expressions 2(2) -- 1(1) -- 1(3) 1(4) 5(10)
Exponents and Powers 1(1) 1(1) 1(1) 1(2) -- 1(4) 5(9)
Symmetry 2(2) 1(1) 1(1) -- 1(3) -- 5(7)
Visualizing Solid
-- -- 1(1) 1(2) -- 1(4) 3(7)
Shapes
Total 10(10) 5(5) 5(5) 6(12) 8(24) 6(24) 40(80)
Note:
1) 20% i.e. 16 marks of 1st term syllabus covering significant topics/chapters have taken as per
CBSE guidelines.
2) Numerals inside the bracket indicate marks and outside the bracket indicate the number of
questions
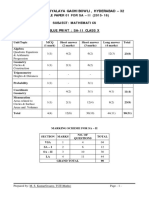
MARKING SCHEME FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM
NO. OF
SECTION MARKS TOTAL
QUESTIONS
MCQ 1 10 10
FIB (Fill in the Blank) 1 5 05
VSA 1 5 05
SA – I 2 6 12
SA – II 3 8 24
LA 4 6 24
GRAND TOTAL 80
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, GPRA CAMPUS, HYD–32
SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM (2019-20)
SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS MAX. MARKS : 80
CLASS : VII DURATION : 3 HRS
General Instruction:
(i) All the questions are compulsory.
(ii) The question paper consists of 40 questions divided into 4 sections A, B, C, and D.
(iii) Section A comprises of 20 questions of 1 mark each. Section B comprises of 6 questions of 2
marks each. Section C comprises of 8 questions of 3 marks each. Section D comprises of 6
questions of 4 marks each.
(iv) Use of calculators is not permitted.
SECTION – A
7 4
1. What number should be added to to get ?
12 15
19 11 51 1
(a) (b) (c) (d)
60 30 60 20
2. 7 steps to the left of 4 on number line gives:
(a) 3 (b) 11 (c) - 11 (d) - 3
3. The ratio of 90 cm to 1.5 m is
(a) 2 : 5 b) 3 : 5 c) 4 : 5 d) none of these
4. On decreasing the radius of the circle by 30%, its area is decreased by
(a) 30% (b) 60% (c) 45% (d) none of these
5. The order of the rotational symmetry of the below left figure about the point marked ‘x’
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3
6. The order of the rotational symmetry of the above sided right figure about the point marked ‘x’
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3
7. In simplified form ( 30 + 40 + 50 )0 is equals to
(a) 12 (b) 3 (c) 12 (d) 1
8. The area of the square is the same as the area of the circle. Their perimeter are in the ratio
(a) 1 : 1 (b) : 2 (c) 2 : (d) none of these
9. The expression xyz is
(a) Monomial (b) Binomial (c) Trinomial (d) Zero polynomial
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2 -
10. From the following expressions 10pq, 7p, 8q, -p2q2, -7pq, -23, ab,3a,b.The like terms are
(a) 3,7p (b) 10 pq, –7pq (c) ab,3a,b (d)10pq,7p,8q
11. 5 added to the – 1 gives ______
12. In a computer lab, there are 3 computers for every 6 students. The computers will be needed for
24 students is _____
13. 648 expressed as a product of powers of prime factors is ______
14. Find the area of a circle of radius 30 cm (use π = 3.14) is _____
15. Letter ‘M’ of the English alphabet have reflectional symmetry (i.e., symmetry related to mirror
reflection) about is _______
16. Express 729 as a power 3.
17. If p = – 2, find the value of –3p2 + 4p + 7
18. What is the circumference of a circle of diameter 10 cm (Take π = 3.14)?
19. What cross-sections do you get when you give a vertical cut to the brick?
20. Find the number of lines of symmetry of the given figure:
SECTION – B
21. Using laws of exponents, simplify and write the answer in exponential form: (220 ÷ 215 )× 23
22. The temperature at 12 noon was 10°C above zero. If it decreases at the rate of 2°C per hour until
midnight, at what time would the temperature be 8°C below zero? What would be the
temperature at mid-night?
23. In the below figure, it is given that LM = ON and NL = MO
(a) State the three pairs of equal parts in the triangles NOM and MLN.
(b) Is NOM MLN. Give reason?
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3 -
24. The number of illiterate persons in a country decreased from 150 lakhs to 100 lakhs in 10 years.
What is the percentage of decrease?
7 2
25. Find the value of
12 13
26. Two dice are placed side by side as shown in below figure. What the total would be on the face
opposite to (a) 5 + 6 (b) 4 + 3
SECTION – C
27. In the below Fig, BD and CE are altitudes of ABC such that BD = CE.
(i) State the three pairs of equal parts in CBD and BCE.
(ii) Is CBD BCE? Why or why not?
(iii) Is DCB = EBC? Why or why not?
1 1
28. Find any three rational numbers between and .
4 2
29. Draw, wherever possible, a rough sketch of
(i) a triangle with both line and rotational symmetries of order more than 1.
(ii) a triangle with only line symmetry and no rotational symmetry of order more than 1.
30. Add:
(i) 14x + 10y – 12xy – 13, 18 – 7x – 10y + 8xy, 4xy
(ii) 3p2q2 – 4pq + 5, – 10 p2q2, 15 + 9pq + 7p2q2
31. In an examination, there are three papers each of 100 marks. A candidate obtained 53 marks in
the first and 75 marks in the second paper. How many marks must the candidate obtain in the
third paper to get an overall of 70 per cent marks?
32. Construct ΔLMN, right-angled at M, given that LN = 5 cm and MN = 3 cm.
33. A verandah of width 2.25 m is constructed all along outside a room which is 5.5 m long and 4 m
wide. Find: (i) the area of the verandah.
(ii) the cost of cementing the floor of the verandah at the rate of Rs 200 per m2.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4 -
SECTION – D
34. A square tile of length 20 cm has four quarter circles at each corner as shown in below Fig. (i).
Find the area of shaded portion. Another tile with same dimensions has a circle in the centre of
the tile [see below Fig. (ii)]. If the circle touches all the four sides of the square tile, find the area
of the shaded portion. In which tile, area of shaded portion will be more? (Take = 3.14)
8 (2) 6 7
35. Find: (i ) (ii )
19 57 13 15
36. A light year is the distance that light can travel in one year.
1 light year = 9,460,000,000,000 km.
(a) Express one light year in scientific notation.
(b) The average distance between Earth and Sun is 1.496 × 108 km. Express the distance in
normal form.
(c) Is the distance between Earth and the Sun greater than, less than or equal to one light year?
(d) Find the difference between the distance between Earth & the Sun and one light year.
37. Complete the following table:
Shape Centre of Rotation Order of Rotation Angle of Rotation
Rectangle
Rhombus
Equilateral Triangle
Semi-circle
38. From the sum of 2y2 + 3yz, – y2 – yz – z2 and yz + 2z2, subtract the sum of 3y2 – z2 and –y2 + yz
+ z2.
39. Three cubes each with 2 cm edge are placed side by side to form a cuboid. Make an oblique
sketch and find its length, breadth and height.
40. Construct ΔPQR if PQ = 5 cm, m PQR = 105° and m QRP = 40°.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 5 -
You might also like
- Maths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 01 1Document5 pagesMaths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 01 1ahmedmansurr98No ratings yet
- Maths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03 1Document5 pagesMaths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03 1ahmedmansurr98No ratings yet
- Maths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 02Document6 pagesMaths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 02Sonali SinghNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Viii Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 01 1Document6 pagesMaths Class Viii Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 01 1Volety Sai SudheerNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper 02 For Session Ending Exam (2019-20)Document5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper 02 For Session Ending Exam (2019-20)FRESH BOWLNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI SAMPLE PAPER 03 FOR HALF YEARLY EXAMDocument5 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI SAMPLE PAPER 03 FOR HALF YEARLY EXAMLatha RajaiyanNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Vi Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesMaths Class Vi Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 02AfsanaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 03Document6 pagesMaths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 03Bhavya JangidNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 02Document6 pagesMaths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 02Bhavya JangidNo ratings yet
- Periodic Test 2 Paper 1Document4 pagesPeriodic Test 2 Paper 1Bhavya JangidNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 02Document6 pagesMaths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 02Latha RajaiyanNo ratings yet
- KV GACHIBOWLI CLASS 8 MATH SAMPLE PAPERDocument6 pagesKV GACHIBOWLI CLASS 8 MATH SAMPLE PAPERBhavya JangidNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01Document4 pagesMaths Class VII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01nseeker19No ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM (2017-18Document4 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM (2017-18Suman DesarkerNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Document6 pagesMaths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Latha RajaiyanNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01Document4 pagesMaths Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01Nooman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SAMPLE PAPER FOR HALF YEARLY EXAMDocument5 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SAMPLE PAPER FOR HALF YEARLY EXAMGAUTAMNo ratings yet
- Math and Geometry Sample Paper QuestionsDocument4 pagesMath and Geometry Sample Paper QuestionsJITENDRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VII Paper 03Document3 pagesMaths Class VII Paper 03Keerti Kiran BommuNo ratings yet
- Maths Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesMaths Practice QuestionsKiyotakaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Periodic Test II 40 Marks Sample Paper 03 PDFDocument3 pagesMaths Class X Periodic Test II 40 Marks Sample Paper 03 PDFK VaralakshmiNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesMaths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Nashra KhanamNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesMaths Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02PauraviNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesMaths Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Geade 9 MathDocument5 pagesGeade 9 Mathgaikwadmanish1976No ratings yet
- 6 Maths SQP 5Document4 pages6 Maths SQP 5Saahithi DharavathNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 2Document6 pagesSample Paper 2samarth.c.patelNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Periodic Test II 40 Marks Sample Paper 02Document3 pagesMaths Class X Periodic Test II 40 Marks Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesMaths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Areeb GamingNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Periodic Test II Revised Sample Paper 01Document4 pagesMaths Class X Periodic Test II Revised Sample Paper 01hweta173No ratings yet
- Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesMaths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- 1731915719maths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Document5 pages1731915719maths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01sonu kumarNo ratings yet
- Junior Olympiad: Marathon SessionsDocument27 pagesJunior Olympiad: Marathon SessionsLalitha KNo ratings yet
- VMC National Admission Test 2018-19Document7 pagesVMC National Admission Test 2018-19Samvid Pundir83% (6)
- Maths Class VII Sample Paper Test 03 For See 2023 1Document3 pagesMaths Class VII Sample Paper Test 03 For See 2023 1Tanvi Doshi ViraNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VII Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesMaths Class VII Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Shib Shankar PalNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X SA-II Sample Paper 01Document4 pagesMaths Class X SA-II Sample Paper 01pranitNo ratings yet
- Viii Nstse Level-1 Mock Test-2-5Document15 pagesViii Nstse Level-1 Mock Test-2-5puneet manglaNo ratings yet
- Viii Nstse Level-1 Mock Test-2-6Document16 pagesViii Nstse Level-1 Mock Test-2-6puneet mangla100% (1)
- Half Yearly Exam - QPDocument5 pagesHalf Yearly Exam - QPDe SebNo ratings yet
- rsbm.5 2010Document10 pagesrsbm.5 2010Kavita Jain0% (1)
- SQP - 1 IX 23-24 MathsDocument6 pagesSQP - 1 IX 23-24 Mathsadhikarigautam696No ratings yet
- X NSTSE Level-1 Mock Test-2-5Document15 pagesX NSTSE Level-1 Mock Test-2-5puneet manglaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VII Sample Paper Test 02 For See 2023Document3 pagesMaths Class VII Sample Paper Test 02 For See 2023anita lokareNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02 2020 21Document9 pagesMaths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02 2020 21Psy KoTeaYenNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths Mid Term PaperDocument4 pages10 Maths Mid Term PaperAnishikaNo ratings yet
- Sol of MathsDocument6 pagesSol of MathskidzeekondapurNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesMaths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Anonymous TvppppNo ratings yet
- ipmat-indore-2021-paperDocument8 pagesipmat-indore-2021-paperdivyanshjoshidpsjkpNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesMaths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01hweta173No ratings yet
- Test of MathDocument13 pagesTest of Mathdixitkavita02No ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI MATHS SAMPLE PAPERDocument3 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI MATHS SAMPLE PAPERShyvam RajputNo ratings yet
- Math-Class X - CPBE 2023 QPDocument7 pagesMath-Class X - CPBE 2023 QPkubusisgreatNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 6 Maths Half Yearly Set 4Document4 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 6 Maths Half Yearly Set 4bshnbaNo ratings yet
- X Math Sample Paper 23-24-2Document6 pagesX Math Sample Paper 23-24-2mandalankan2No ratings yet
- Series I - QuestionsDocument16 pagesSeries I - Questionsintekhab ahmedNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths AecsDocument27 pages8 Maths Aecsjollysakshamgupta25No ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAM CLASS IX MATHEMATICSDocument4 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAM CLASS IX MATHEMATICSriyas babuNo ratings yet
- Maths Class 6 Annual-2Document4 pagesMaths Class 6 Annual-2Satpreet DhanjalNo ratings yet
- Inovasi Kurikulum Berdasarkan Komponen Kurikulum Strategi Dan Evaluasi Oleh: Sri MaryatiDocument16 pagesInovasi Kurikulum Berdasarkan Komponen Kurikulum Strategi Dan Evaluasi Oleh: Sri MaryatiFitroh NailulNo ratings yet
- Visual Division-1Document3 pagesVisual Division-1Jumran BaharNo ratings yet
- Exam 2020-2021Document8 pagesExam 2020-2021Rawan ToubarNo ratings yet
- Stress Distribution in The Temporomandibular Joint After Mandibular Protraction A Three-Dimensional Finite Element StudyDocument10 pagesStress Distribution in The Temporomandibular Joint After Mandibular Protraction A Three-Dimensional Finite Element StudySelvaNo ratings yet
- 199 - R.O. Burt - C. Mills - Gravity Concentration 1000 Years Old and Still OmprovingDocument10 pages199 - R.O. Burt - C. Mills - Gravity Concentration 1000 Years Old and Still OmprovingMaría Alejandra Vera BurauNo ratings yet
- Watching TV ads or internet ads? Pros, cons and preferencesDocument5 pagesWatching TV ads or internet ads? Pros, cons and preferencesJiaqi LiNo ratings yet
- Louis Kahn's Insights on Architectural Design for Glare and Breeze in AngolaDocument21 pagesLouis Kahn's Insights on Architectural Design for Glare and Breeze in AngolaBeatriz OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Zinc Clad II (85) : Inorganic Zinc Rich CoatingDocument2 pagesZinc Clad II (85) : Inorganic Zinc Rich CoatingKatherine Marimón JiménezNo ratings yet
- Group 4 (Ap229d 3c)Document11 pagesGroup 4 (Ap229d 3c)aremyulNo ratings yet
- An Ecological Approach For Social Work PracticeDocument11 pagesAn Ecological Approach For Social Work PracticeJona MempinNo ratings yet
- Clamper and ClipperDocument16 pagesClamper and ClipperSouvik ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- M5 - Freedom of The Human PersonDocument8 pagesM5 - Freedom of The Human PersonMarisol OtidaNo ratings yet
- Prompt Engineering Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesPrompt Engineering Cheat SheetJuan Pablo Dell'OroNo ratings yet
- Garlic As Mosquito RepellentDocument18 pagesGarlic As Mosquito Repellentagnes80% (5)
- PGDM-IIPR Final Research Based ReportDocument9 pagesPGDM-IIPR Final Research Based Reportnavneet dubeyNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management - Module 7Document18 pagesMarketing Management - Module 7SnehaNo ratings yet
- Pioneers of Modern Architecture: Maseana ProjectDocument86 pagesPioneers of Modern Architecture: Maseana ProjectEriNo ratings yet
- Brochure - DT - SO - SORTEX B MultiVision - BSBDDocument12 pagesBrochure - DT - SO - SORTEX B MultiVision - BSBDAlexandruNo ratings yet
- AD IBS Assignment-1Document6 pagesAD IBS Assignment-1anvesha raoNo ratings yet
- Early Childhood Physical DevelopmentDocument34 pagesEarly Childhood Physical DevelopmentEditha100% (1)
- Nuig Lander1Document21 pagesNuig Lander1diana meriakri100% (1)
- Ultra Low Dose CT Vs Chest X Ray in Non Traumatic Emergency D 2023 EClinicaDocument14 pagesUltra Low Dose CT Vs Chest X Ray in Non Traumatic Emergency D 2023 EClinicaronaldquezada038No ratings yet
- TSO TSI Fiber OrientationDocument6 pagesTSO TSI Fiber OrientationEngsiang Yimrutai0% (1)
- Introduction to Capacitors and DielectricsDocument55 pagesIntroduction to Capacitors and DielectricsParthuNo ratings yet
- DD Cen TS 14425-1-2003Document16 pagesDD Cen TS 14425-1-2003mossamorrisNo ratings yet
- 2018A4PS0580P Arpan Sharma: Experiment 7 Heat Exchanger - Shell and Tube ObjectiveDocument4 pages2018A4PS0580P Arpan Sharma: Experiment 7 Heat Exchanger - Shell and Tube ObjectiveArpanNo ratings yet
- J1 - Today 1 - First Test 2022 (KEY)Document3 pagesJ1 - Today 1 - First Test 2022 (KEY)EmanuelBriosoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Organs of Speech and Phonemic SymbolsDocument5 pagesLesson 1: Organs of Speech and Phonemic Symbolsnoah granja2No ratings yet
- The De-Urbanisation of Bihar: by Mohan Guruswamy Jeevan Prakash MohantyDocument20 pagesThe De-Urbanisation of Bihar: by Mohan Guruswamy Jeevan Prakash MohantyD KNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For The CFA Exam - QuoraDocument10 pagesHow To Prepare For The CFA Exam - QuoraaduragbeNo ratings yet