Professional Documents
Culture Documents
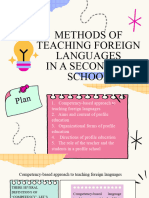
Colorful Clean Project Planning Concept Map Graph
Colorful Clean Project Planning Concept Map Graph
Uploaded by
Yasmin Nava MerinoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Colorful Clean Project Planning Concept Map Graph
Colorful Clean Project Planning Concept Map Graph
Uploaded by
Yasmin Nava MerinoCopyright:
Available Formats
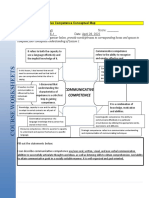
COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE
AND LINGUISTIC COMPETENCE
LINGUISTIC COMMUNICATIVE
COMPETENCE
RELATIONSHIPS
COMPETENCE
System of linguistic Individual’s ability to
knowledge possessed undrestand and use the
SECONDARY SECONDARY
by native speakers IDEA IDEA appropiately language
Linguistic Competence is a Communicative Competence
Component of Communicative Builds Upon Linguistic
Competence: Competence:
Description: Linguistic
competence (grammar, syntax, Description: Being proficient in
etc.) is essential within the speaking, listening, reading,
FOCUS broader scope of and writing relies on a strong
communicative competence. linguistic competence. COMPONENTS CONCEPTS
Implication: To communicate Implication: Linguistic
effectively, understanding
competence provides the
linguistic structures is
foundation for effective Combination of
Indiviual’s knowledge Linguistic communication. knowledge, judgment, Focused solely on
necessary.
and understanding of competence are and skills in connected grammatical
a language grammar, focused in Speaking, Integration of Both Competences:
areas. knowledge.
Description: In practice, effective writing and speaking require both linguistic accuracy
vocabulary and rules. listening, reading, and communicative skills.
Linguistic competence Take pragmatic
Implication: The combination of both competences is crucial in various language
writing and non- applications.
Operational competence
Improving Linguistic Competence through Interaction: aspects of language
verbal cues. Description: Conversations and discussions contribute to refining and applying
Social competence
linguistic competence.
use.
Implication: Real-life practice helps strengthen linguistic competence.
Practical Application of Linguistic Competence: Strategic competence.
Description: Linguistic competence is used in communicative contexts to express oneself
clearly and meaningfully.
Implication: The ultimate purpose is effective communication in everyday situations.
APPLICATIONS: APLICATIONS
EXAMPLE Real-Life Communication: Communicative competence is essential in
Language Learning: Linguistic competence is fundamental for everyday interactions, whether in personal relationships, professional
those learning a new language. It provides the foundation to settings, or social situations.
comprehend the structure and rules of the language. In summary, linguistic and communicative competence are
Language Proficiency Assessment: Testing individuals' ability to use
Translation: It is crucial for the accurate translation of written interconnected, with linguistic competence serving as the
language effectively in various contexts, evaluating both verbal and
content, maintaining grammatical integrity and conveying essential foundation for effective communication and
written communication skills.
the intended meaning. evolving alongside the needs of contemporary
Cross-Cultural Communication: In globalized settings, individuals with
communication.
Language Teaching: Educators use linguistic competence to communicative competence navigate cultural differences to
explain grammatical concepts and language rules to communicate successfully in diverse environments.
students. Four areas: Words and rules, appropriacy, cohesion and coherence
use of communication strategies.
You might also like
- G 19-1 Iep Meeting Notes TemplateDocument3 pagesG 19-1 Iep Meeting Notes Templateapi-333679610100% (4)
- Oral Communication SyllabusDocument12 pagesOral Communication SyllabusRebekah Mambiar100% (3)
- методика 10Document13 pagesметодика 10dilrabosaidikramova4No ratings yet
- Communicative Language TeachingDocument1 pageCommunicative Language TeachingGabriela GómezNo ratings yet
- PCOM Manual (Mid)Document50 pagesPCOM Manual (Mid)ZAIL JEFF ALDEA DALENo ratings yet
- CHAPTER5Document16 pagesCHAPTER5fadylahasyimNo ratings yet
- College of Arts, Social Sciences & Education: Assessment Task #1Document3 pagesCollege of Arts, Social Sciences & Education: Assessment Task #1Wey MagsinoNo ratings yet
- PCOM Manual MidtermDocument50 pagesPCOM Manual MidtermViezca Francine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Novelyn Hencianos - Activity 5Document5 pagesNovelyn Hencianos - Activity 5Jey GencianosNo ratings yet
- Teaching Intercultural Communicative Competence Through The Four SkillsDocument11 pagesTeaching Intercultural Communicative Competence Through The Four SkillsJHON MNo ratings yet
- Compétence 1 - Anglais Langue SecondeDocument1 pageCompétence 1 - Anglais Langue Secondemaudecrepeau14No ratings yet
- Module Reference OutlineDocument6 pagesModule Reference OutlineMary Joy PaldezNo ratings yet
- Communicative Competence: Brown, H.D (1994) Principles of Language Teaching andDocument16 pagesCommunicative Competence: Brown, H.D (1994) Principles of Language Teaching andLuciaNo ratings yet
- ALL - MetodDocument114 pagesALL - MetodAlper AslanNo ratings yet
- Lamp Bow Grade 5Document196 pagesLamp Bow Grade 5Maryjane LattaoNo ratings yet
- ManualPCOM Module 1& Module 2Document45 pagesManualPCOM Module 1& Module 2GersonNo ratings yet
- PCOM NotesDocument27 pagesPCOM NotesAndrea Elizabeth SottoNo ratings yet
- ELT Teaching Approaches HWDocument1 pageELT Teaching Approaches HWgigaleaderNo ratings yet
- Theories of Language and Learning (Based On Richards & Rodgers, 2014)Document1 pageTheories of Language and Learning (Based On Richards & Rodgers, 2014)scintillamx100% (1)
- Grade 6 Q1 W1-4Document12 pagesGrade 6 Q1 W1-4Marco MedurandaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Rationale: K12 CurriculumDocument1 pagePhilosophy and Rationale: K12 CurriculumElitiea KwonNo ratings yet
- Rubrics PCK 5 - The Teacher and The School Curriculum: Developing Student'S Communicative CompetenceDocument10 pagesRubrics PCK 5 - The Teacher and The School Curriculum: Developing Student'S Communicative CompetenceJalen PizarraNo ratings yet
- English 6 q1w1-4 Lamp v3Document12 pagesEnglish 6 q1w1-4 Lamp v3Ricca OtidaNo ratings yet
- Didactica FolletoDocument2 pagesDidactica FolletoTatiana LemusNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Q1 W1-4Document20 pagesGrade 5 Q1 W1-4Marco MedurandaNo ratings yet
- Features of The Formation of Grammatical CompetenceDocument5 pagesFeatures of The Formation of Grammatical CompetenceElisa Medina AlbinoNo ratings yet
- 13.0 PP 181 186 Approaches and Methods An OverviewDocument6 pages13.0 PP 181 186 Approaches and Methods An OverviewvietdungnhuthaoNo ratings yet
- Scripta+XXII+Bielak enDocument17 pagesScripta+XXII+Bielak ensmoczyowoc123No ratings yet
- TOPIC 4 Communicative-CompetenceDocument4 pagesTOPIC 4 Communicative-CompetenceKris LMNo ratings yet
- in Oral Com - eDocument10 pagesin Oral Com - eSofia Aizel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- COMUNICATIVE LEARNING HOMEWORK 1 Unidad 2 - en GrupoDocument3 pagesCOMUNICATIVE LEARNING HOMEWORK 1 Unidad 2 - en Grupovictoria puycan romeroNo ratings yet
- Exploring Communicative Competence 2024 2 15 10 15 51Document8 pagesExploring Communicative Competence 2024 2 15 10 15 51dimo.mridNo ratings yet
- OBTLP Macro SkillsDocument6 pagesOBTLP Macro SkillsJojie BatoonNo ratings yet
- English12 Q4 W2 DebbiedelossantosDocument37 pagesEnglish12 Q4 W2 DebbiedelossantosJuliusSarmientoNo ratings yet
- Communicative CompetenceDocument1 pageCommunicative CompetenceJesaiah HiganaNo ratings yet
- Translation BaganDocument1 pageTranslation BaganLidwynna GuloNo ratings yet
- Actividad 5 - DIGITAL POSTER ABOUT THE TEACHERS BASIC SKILLSDocument1 pageActividad 5 - DIGITAL POSTER ABOUT THE TEACHERS BASIC SKILLSjohannasalcedo95No ratings yet
- Group 3 - Week 7 Homework: Language Competence, Strategic Competence, PsychophysiologicalDocument7 pagesGroup 3 - Week 7 Homework: Language Competence, Strategic Competence, Psychophysiologicaltrung Hieu BuiNo ratings yet
- Universidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco: Lic. en IdiomasDocument5 pagesUniversidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco: Lic. en IdiomasRubén ZapataNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument10 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Fridayelizea mojicaNo ratings yet
- What Is TEFL 2Document10 pagesWhat Is TEFL 2Nora RomeraNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 5 - Q2 - W6Document11 pagesDLL - English 5 - Q2 - W6JOECEL MAR AMBIDNo ratings yet
- ELT Teaching Approaches HWDocument13 pagesELT Teaching Approaches HWgigaleaderNo ratings yet
- Avt HM 2Document3 pagesAvt HM 2Оксана ТрапезунNo ratings yet
- Teaching ReadingDocument12 pagesTeaching ReadingRosalina Rodríguez100% (1)
- DLL - English 5 - Q2 - W6Document9 pagesDLL - English 5 - Q2 - W6Benedicto AntonioNo ratings yet
- Overview On The Teaching of MacroskillsDocument5 pagesOverview On The Teaching of MacroskillsZarahJoyceSegoviaNo ratings yet
- Derek Bickerton (1981) : Teaching and Assessment in GrammarDocument4 pagesDerek Bickerton (1981) : Teaching and Assessment in GrammarRachel AlveroNo ratings yet
- Lamp E5Document196 pagesLamp E5Jayson Dawal RodriguezNo ratings yet
- DLL - MTB 3 - Q3 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - MTB 3 - Q3 - W5Kristel CañeteNo ratings yet
- Assessing Speaking Level C1 PDFDocument14 pagesAssessing Speaking Level C1 PDFphantom26No ratings yet
- DLL - English 5 - Q2 - W6Document10 pagesDLL - English 5 - Q2 - W6vickydelacruz19754No ratings yet
- Habilidad Linguistica CommunicativaDocument6 pagesHabilidad Linguistica CommunicativaAntonio MontanaNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 5 - Q3 - W5Document9 pagesDLL - English 5 - Q3 - W5Benedick BuendiaNo ratings yet
- Appl DidacticsM2Document14 pagesAppl DidacticsM2Teyebi SlimaneNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 5 - Q2 - W6Document10 pagesDLL - English 5 - Q2 - W6Leceil Oril PelpinosasNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument10 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogJay Lord BacaniNo ratings yet
- App Eval Rubric - BusuuDocument2 pagesApp Eval Rubric - Busuuapi-379364409No ratings yet
- Communicative CompetenceDocument1 pageCommunicative CompetenceAlejandra De La CruzNo ratings yet
- John Dewey and the Artful Life: Pragmatism, Aesthetics, and MoralityFrom EverandJohn Dewey and the Artful Life: Pragmatism, Aesthetics, and MoralityNo ratings yet
- LAS For Summative Assessment Written Work Performance TaskDocument4 pagesLAS For Summative Assessment Written Work Performance TaskMalenkov Lyndon Torres100% (1)
- Gender Etc.Document3 pagesGender Etc.Lucky EsportsNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Ii Review of LiteratureDocument49 pagesChapter - Ii Review of Literaturepooja shandilyaNo ratings yet
- Recommendations and Curricular Foundations of PRONI and The Use of Project Based LearningDocument2 pagesRecommendations and Curricular Foundations of PRONI and The Use of Project Based LearningAngelus AnimarumNo ratings yet
- Pedagogy QuizDocument8 pagesPedagogy QuizUsman MariNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The Community School Culture and Organizational Leadership Week 12Document4 pagesThe Teacher and The Community School Culture and Organizational Leadership Week 12Shiera GannabanNo ratings yet
- Sample Learner Centered Teaching PhilosophyDocument6 pagesSample Learner Centered Teaching PhilosophyMacreene MacallaNo ratings yet
- Sandeep Second SemDocument2 pagesSandeep Second SemPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Delft Design GuideDocument176 pagesDelft Design GuideAhmed Zawad ShovonNo ratings yet
- Reading PlanDocument31 pagesReading PlanAleixs miraplesNo ratings yet
- Modern College of Arts, Science and Commerce (Autonomous) : Arts Faculty T.Y.B.A Sem ViDocument2 pagesModern College of Arts, Science and Commerce (Autonomous) : Arts Faculty T.Y.B.A Sem ViAniket SalveNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet Gen. Math m1Document3 pagesAnswer Sheet Gen. Math m1Rohainah MalawadNo ratings yet
- Toefl PDFDocument2 pagesToefl PDFfarisiNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Flexible Learning On The Academic Performance of StudentsDocument6 pagesEffectiveness of Flexible Learning On The Academic Performance of StudentsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Resume GustiDocument1 pageResume GustiMariska Tri IsnantoNo ratings yet
- Importance of StatisticsDocument2 pagesImportance of StatisticsJonah Garcia TevesNo ratings yet
- Literature Review PresentationDocument11 pagesLiterature Review PresentationJINKYMarie ABELLANo ratings yet
- Reflection 1Document12 pagesReflection 1danilo miguelNo ratings yet
- Sales Salise BelgiraDocument30 pagesSales Salise BelgiraManilyn Villarey100% (1)
- Sean KutzlerDocument2 pagesSean Kutzlerapi-469029790No ratings yet
- Concept Note of The Train The Trainers ProgramDocument5 pagesConcept Note of The Train The Trainers ProgramCloudFarmInnovations IncorporatedNo ratings yet
- Conditioning Lesson 1Document4 pagesConditioning Lesson 1Jake ElliottNo ratings yet
- Bell Ringer Instructions s1 19Document2 pagesBell Ringer Instructions s1 19api-327965506No ratings yet
- DISS DLL Week 4Document6 pagesDISS DLL Week 4Rheena-Ann Dupale PadillaNo ratings yet
- Women in Pakistan by DR BariDocument67 pagesWomen in Pakistan by DR BariSadam LashariNo ratings yet
- The Problem of Education of Backward Classes in MaharashtraDocument11 pagesThe Problem of Education of Backward Classes in MaharashtraAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Stem Training Survey Questionnaire Docx 1477920457417Document6 pagesStem Training Survey Questionnaire Docx 1477920457417api-336954866No ratings yet
- Special Checking Is Handed A Loss Background Information Sammy Benson Supervised The Special Check Sorting Unit of The Greater DownDocument3 pagesSpecial Checking Is Handed A Loss Background Information Sammy Benson Supervised The Special Check Sorting Unit of The Greater DownSumerah SaeedNo ratings yet
- The Use of Non - Verbal Communication in The Teaching of English LanguageDocument6 pagesThe Use of Non - Verbal Communication in The Teaching of English LanguageJOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN LINGUISTICSNo ratings yet