Professional Documents
Culture Documents
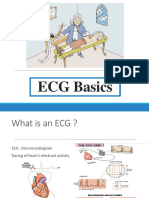
at The Blink of An Eye-Deconstructing The ECG Curve - Fact Sheet
Uploaded by
ddOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
at The Blink of An Eye-Deconstructing The ECG Curve - Fact Sheet
Uploaded by
ddCopyright:
Available Formats
Visit www.afratafreeh.
com for more
Level 1
Deconstructing the ECG curve–
the components of the tracing
In this first chapter, you will learn about the different
waves on the ECG and how to recognize them.
Key concepts
Your first step is to learn how to identify QRS complexes, T waves, and P waves on a tracing.
QRS
The isoelectric line is the baseline of the ECG.
A wave that is above the
By definition, it‘s the line on the ECG during isoelectric line is called “positive”
which electrical activity is absent—look for
the flat line that connects a T wave to the
following P wave. Anything above is positive, isoelectric line
anything below is negative. A wave that is below the
isoelectric line is called “negative”
T
QRS
Electrical depolarization of the ventricles leads to sharp
deflections in the ECG called QRS complexes. Every depolarizati-
on is followed by a phase of repolarization. Repolarization of the
ventricles is represented by the so-called T waves. The T wave can
be positive or negative.
QRS
Atrial depolarization is depicted by the P wave, which is steeper P
than the T wave but flatter than the QRS complex. We said that
every depolarization is followed by a phase of repolarization. But
since atrial repolarization happens at the same time as the QRS
P
complex, it cannot be recognized on the ECG.
Level 1 Deconstructing the ECG curve—the components of the tracing
Visit www.afratafreeh.com for more
Identifying the components of the QRS complex
There are five concepts that will help you to identify the different components of the QRS complex.
isoelectric line
Q Q
Concept #1 Concept #2 Concept #3
The first downward deflec- Any upward deflection is Any downward deflection
tion is called a Q wave. called an R wave.
S that comes after an R wave
and crosses the isoelectric
line is called an S wave.
R R wave
R′ R′ = R prime
isoelectric line
S
RSR′
Concept #4 Concept #5
A second upward deflection is called R prime (R′) If the entire QRS complex
consists of one large down-
QS ward deflection, then this is
called a QS complex.
Example: identifying P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves
Based on the concepts outlined above, we can now identify the P waves, QRS complexes, and T
waves in an example exercise. Notice that the second wave is steep and edgy; it has sharper
deflections than the other curves and therefore has to be the QRS complex.
P
QRS
T
Dotted vertical lines originate from the different waves of the ECG. They intersect with horizontal lines identifying P, QRS, and T.
In this example we have already identified the different waves for you.
Level 1 Deconstructing the ECG curve—the components of the tracing
You might also like
- 007 - Cardiovascular Physiology) MASTER ECGDocument8 pages007 - Cardiovascular Physiology) MASTER ECGSWATHIKA L100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For "Heart Failure Chronic"Document16 pagesNursing Care Plan For "Heart Failure Chronic"jhonroks97% (34)
- Electrical Conduction of The Heart and Ecg Interpretation: Prepared By: Suha Ballout, PHD, RNDocument22 pagesElectrical Conduction of The Heart and Ecg Interpretation: Prepared By: Suha Ballout, PHD, RNddNo ratings yet
- Simple Guide To Ecg InterpretationDocument53 pagesSimple Guide To Ecg Interpretationedy suyantoNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Pocket Guide ECG InterpretationDocument21 pages2017 - Pocket Guide ECG InterpretationmariaNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation TheoryDocument4 pagesECG Interpretation TheorySteph PiperNo ratings yet
- Rest and SleepDocument39 pagesRest and Sleepmesdejen50% (2)
- The Digestive System Summative Test - Q3 - M1Document2 pagesThe Digestive System Summative Test - Q3 - M1Metchel100% (1)
- Deconstructing The ECG Curve - The Components of The Tracing: Key ConceptsDocument117 pagesDeconstructing The ECG Curve - The Components of The Tracing: Key ConceptsdrynwhylNo ratings yet
- 1-Blood Composition and FunctionDocument43 pages1-Blood Composition and FunctionKaleem Mohammad100% (2)
- Electrocardiography: I. Leads A. Limb LeadsDocument11 pagesElectrocardiography: I. Leads A. Limb LeadsJoezelle0% (1)
- Yellow Belt Level 01 - Fact SheetDocument2 pagesYellow Belt Level 01 - Fact SheetJo Marie LeeNo ratings yet
- ECG in 100 StepsDocument38 pagesECG in 100 StepsAlok MishraNo ratings yet
- 118 Skills Lab-Week 2-ECG TakingDocument8 pages118 Skills Lab-Week 2-ECG TakingKeisha BartolataNo ratings yet
- Ecg 2Document106 pagesEcg 2hammad992No ratings yet
- 07 - Nomenclature of QRS ComplexDocument3 pages07 - Nomenclature of QRS ComplexSharan MurugaboopathyNo ratings yet
- LAB 1 - Station 6Document17 pagesLAB 1 - Station 6william atmadjiNo ratings yet
- 07 - Nomenclature of QRS Complex - 0Document3 pages07 - Nomenclature of QRS Complex - 0sk875970No ratings yet
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument62 pagesBasic ECG Interpretationmohannadalkwiese3No ratings yet
- Green Orange Blue Creative Healthcare Facility PresentationDocument31 pagesGreen Orange Blue Creative Healthcare Facility Presentationshreyamukherjee3009No ratings yet
- 02 - ECG - General Approach and Normal Aspects 2Document18 pages02 - ECG - General Approach and Normal Aspects 2hussain alkhrsanyNo ratings yet
- 5hypertrophy and MIDocument116 pages5hypertrophy and MIsamooanatenaNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument16 pagesElectrocardiogram12Klaire Therese CabigasNo ratings yet
- A Typical ECG Tracing of The Cardiac CycleDocument3 pagesA Typical ECG Tracing of The Cardiac CycleMhiyciel UyNo ratings yet
- ECG ReviewingDocument50 pagesECG ReviewingLutfir Rahman TarisNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument3 pagesElectrocardiogramgaratoh099No ratings yet
- Ecg in 100 Steps: Dr. S. Aswini Kumar MDDocument37 pagesEcg in 100 Steps: Dr. S. Aswini Kumar MDaprameyak_19915720No ratings yet
- AC Circuits Laboratory Report: Submitted By: Cancio, Gillian Claire GDocument3 pagesAC Circuits Laboratory Report: Submitted By: Cancio, Gillian Claire GMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Basics ECGDocument33 pagesBasics ECGFika IndahNo ratings yet
- 118 Rle Ecg PDFDocument5 pages118 Rle Ecg PDFclaire yowsNo ratings yet
- ECE131 Unit 1 Lecture 10Document30 pagesECE131 Unit 1 Lecture 10Gaurav JhaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: Procedure Used To Record Electrical Activity of The Human HeartDocument6 pagesElectrocardiography: Procedure Used To Record Electrical Activity of The Human HeartBanana PeachNo ratings yet
- Cardiologia - EletrocardiografiaDocument40 pagesCardiologia - EletrocardiografiaDANIEL ALEJANDRONo ratings yet
- Location Amplitude Duration Configuration P-Wave P-R Interval QRS COMPLEX Follows P-R Interval ST SegmentDocument2 pagesLocation Amplitude Duration Configuration P-Wave P-R Interval QRS COMPLEX Follows P-R Interval ST SegmentKaren Joyce LasimNo ratings yet
- ECG WaveformsDocument2 pagesECG Waveformscnshariff@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Click Here To View: Septal Infarction, Because The Septum Is Activated Early From TheDocument1 pageClick Here To View: Septal Infarction, Because The Septum Is Activated Early From TheLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Ecg MonitoringDocument26 pagesEcg Monitoringclaire yowsNo ratings yet
- THE Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document13 pagesTHE Electrocardiogram (ECG)Bander Binjabaan Al-QahtaniNo ratings yet
- DASAR KURSUS EKG - DR WiryawanDocument68 pagesDASAR KURSUS EKG - DR WiryawanElsa TjahyaNo ratings yet
- Section 1. ECG Basics 1. TP Segment.: ECG Reviews and Criteria Brugada SyndromeDocument183 pagesSection 1. ECG Basics 1. TP Segment.: ECG Reviews and Criteria Brugada SyndromeTiến HàNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document32 pagesLab 2AyeshaNo ratings yet
- 3 s2.0 B9780750671736500109 MainDocument32 pages3 s2.0 B9780750671736500109 MainEster shilumeNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg Interpretation & Procedure: BY: Ahmad Hafiz Bin Alias Universuty Lecturer UniszaDocument26 pagesBasic Ecg Interpretation & Procedure: BY: Ahmad Hafiz Bin Alias Universuty Lecturer UniszaLogadarshini VeerasamyNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi ElektrokardiogramDocument36 pagesInterpretasi ElektrokardiogramendahNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiology of The HeartDocument27 pagesElectrophysiology of The HeartTsegaye HailuNo ratings yet
- Normal Electrocardiogram: Lucia Kris Dinarti Cardiology Department Faculty of Medicine GMUDocument21 pagesNormal Electrocardiogram: Lucia Kris Dinarti Cardiology Department Faculty of Medicine GMUMuhammad Ricky RamadhianNo ratings yet
- How Procedure Is Performed: ElectrocardiogramDocument10 pagesHow Procedure Is Performed: ElectrocardiogramJonathan AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Pure Inductive Circuit AND L R Circuit: Nimisha Lonees K Ac Circuit-Electronics 2020-2021Document15 pagesPure Inductive Circuit AND L R Circuit: Nimisha Lonees K Ac Circuit-Electronics 2020-2021mahmoud yarahmadiNo ratings yet
- ECG PracticalDocument48 pagesECG PracticalbvkjtzrvnyNo ratings yet
- E Lectrocardiography ECG: Practical Physiology 2020-2021 LabDocument8 pagesE Lectrocardiography ECG: Practical Physiology 2020-2021 LabBushra AlkaqaniNo ratings yet
- ECG With ImageDocument7 pagesECG With ImagemathavanNo ratings yet
- Interpretion of EcgDocument17 pagesInterpretion of EcgAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ecgs: Terry White, RNDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Ecgs: Terry White, RNNourhanGamalNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: DR Uwanuruochi KelechukwuDocument50 pagesElectrocardiography: DR Uwanuruochi KelechukwuJake MillerNo ratings yet
- ECG InerpretitionDocument12 pagesECG InerpretitionMended_Heart100% (6)
- Basic ECGDocument14 pagesBasic ECGDexter TurlaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography Basics: Dr. Nagula PraveenDocument90 pagesElectrocardiography Basics: Dr. Nagula PraveenhendranatjNo ratings yet
- Cate NaryDocument1 pageCate NaryddNo ratings yet
- גסטרוDocument88 pagesגסטרוddNo ratings yet
- Improving Patient Care Under Fire: Tactical Casualty Care Simulation SuiteDocument11 pagesImproving Patient Care Under Fire: Tactical Casualty Care Simulation SuiteddNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions: Last Revised: February 28th, 2019Document29 pagesOperating Instructions: Last Revised: February 28th, 2019ddNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Circulatory SystemDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Circulatory SystemPrisha ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Evaluation For Pediatric PatientsDocument7 pagesBone Marrow Evaluation For Pediatric PatientssylvetriNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology: Lawrence A. Olatunji ReaderDocument46 pagesCardiovascular Physiology: Lawrence A. Olatunji ReaderMaryam Ogunade0% (1)
- Abnormal Breathing PatternsDocument5 pagesAbnormal Breathing PatternsJonalyn EtongNo ratings yet
- Excretion and OsmoregulationDocument48 pagesExcretion and OsmoregulationMiguel Roman Reloaded Kerr100% (1)
- Sleep Disordered Breathing and Anesthesia: DefinitionsDocument1 pageSleep Disordered Breathing and Anesthesia: DefinitionsMuhammad SyammNo ratings yet
- Alumnas Grissel Petra Garcia Paez Materia: Ingles Tecnico HomeworkDocument2 pagesAlumnas Grissel Petra Garcia Paez Materia: Ingles Tecnico HomeworkGrissel PaezNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pain: Methodical Manual For StudentsDocument71 pagesPhysiology of Pain: Methodical Manual For StudentsMelnic CristinaNo ratings yet
- COMFORT, PAIN, REST and SLEEPDocument11 pagesCOMFORT, PAIN, REST and SLEEPJanelle LasalaNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology & Bio-ChemistryDocument22 pagesHuman Physiology & Bio-ChemistryPranav PawarNo ratings yet
- ASV Intellivent ArticleDocument8 pagesASV Intellivent ArticleAnonymous KEAdr5Hd4No ratings yet
- 6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested FoodDocument13 pages6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested Foodkiongoc100% (1)
- Scale For Assessment of Pain in Infants, Neonates and ChildrenDocument4 pagesScale For Assessment of Pain in Infants, Neonates and Childrenfuka priesleyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Energy Systems: Pe&Health 11Document12 pagesLesson 2: Energy Systems: Pe&Health 11Gokotan ESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument5 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionNIKKI GRACE SANTILLANNo ratings yet
- ContDocument76 pagesContIola JaneNo ratings yet
- University of Patanjali: Haridwar, UttarakhandDocument11 pagesUniversity of Patanjali: Haridwar, UttarakhandAbhimanyu RanaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Excretory System ReviewDocument27 pagesRespiratory and Excretory System ReviewJoyce Catherine Buquing UysecoNo ratings yet
- The Value of Vocal Warm-Up and Cool-Down Exercises: Questions and ControversiesDocument3 pagesThe Value of Vocal Warm-Up and Cool-Down Exercises: Questions and ControversiesTayssa MarquesNo ratings yet
- Jacob Gutierrez - Virtual Bioman PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesJacob Gutierrez - Virtual Bioman PhotosynthesisJacob GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Life ProcessesDocument10 pagesChapter 6 Life ProcessesRiddhimaNo ratings yet
- Organ Dysfunction in SepsisDocument19 pagesOrgan Dysfunction in SepsisRossalia Yuliana100% (1)
- Infants ApneaDocument15 pagesInfants ApneaDEOGRA B PARDEDENo ratings yet
- Author: Section Editors: Deputy EditorDocument31 pagesAuthor: Section Editors: Deputy EditorAntenehNo ratings yet
- Prime The Line! A Case Report of Air Embolism From A Peripheral IV Line in The FieldDocument10 pagesPrime The Line! A Case Report of Air Embolism From A Peripheral IV Line in The FieldLisete NunesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet