Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mehebub Islam - Electronic Device (Ec-301)
Uploaded by
bniksmanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mehebub Islam - Electronic Device (Ec-301)
Uploaded by
bniksmanCopyright:
Available Formats
DREAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Campus: Thakurpukur, B. H. Road, Kolkata – 700 104.
A REPORT ON
(PN junction diode and its operation under NO-BIAS condition.)
FOR THE COURSE
SUBJECT NAME-ELECTRONICS DEVICE
SUBJECT CODE: - EC-301
SUBMITTED BY:
NAME- MEHEBUB ISLAM.
. COLLEGE ROLL NO. – EC/22L/10
DEPT.- ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
YEAR- 2ND (Lateral), SEMESTER- 3RD
DATE OF SUBMISSION: - 20/11/2022
What is a P-N junction Diode?
A P-N junction diode is a piece of silicon that has two terminals. One of the
terminals is doped with P-type material and the other with N-type material.
The P-N junction is the basic element for semiconductor diodes. A
Semiconductor diode facilitates the flow of electrons completely in one
direction only – which is the main function of semiconductor diode. It can
also be used as a Rectifier.
PN Junction Diode Theory
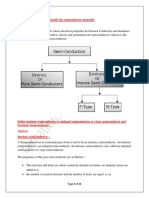
There are two operating regions: P-type and N-type. And based on
the applied voltage, there are three possible “biasing” conditions
for the P-N Junction Diode, which are as follows:
Zero Bias – No external voltage is applied to the PN junction diode.
Forward Bias– The voltage potential is connected positively to the
P-type terminal and negatively to the N-type terminal of the Diode.
Reverse Bias– The voltage potential is connected negatively to
the P-type terminal and positively to the N-type terminal of the
Diode.
Zero bias P-N junction
In n-type semiconductor materials, pentavalent impurities are
added while in p-type semiconductor materials, trivalent
impurities are added. If the impurities added to p-type and n-
type semiconductor materials are not uniform then at one
region large number of charge carriers are present while at
another region small number of charge carriers are present.
Due to this non uniform doping charge carriers at high
concentration region repel from each other and move towards
the low concentration region to achieve uniform concentration
all over the material.
Charge carriers crossing the junction
The p-n Junction in which no external voltage is applied is
called zero bias p-n junction. Zero bias p-n Junction is also
called as unbiased p-n junction.
Let us consider a zero bias p-n junction as shown in below
figure, at n-type semiconductor large number of free
electrons is present while at p-type semiconductor small
number of free electrons is present. Hence, the concentration
of electrons at n-type semiconductor is high while the
concentration of electrons at p-type semiconductor is low.
Due to this high concentration of electrons at n-side, they
get repelled from each other. Hence they try to move
towards the low concentration region. Also, since free
electrons and holes at the junction are very close to each
other. According to coulomb’s law there exist an
electrostatic force of attraction between the opposite
charges.
Hence, the free electrons from the n-side are attracted
towards the holes at the p-side. Thus, the free electrons
move from n-region (high concentration region) to p-region
(low concentration region).
At p-type semiconductor large number of holes is present
while at n-type semiconductor small number of holes is
present. Hence, the concentration of holes at p-type
semiconductor is high while the concentration of holes at n-
type semiconductor is low. Also, since electrons and holes at
the junction are very close to each other. According to
coulomb’s law there exist an electrostatic force of attraction
between the opposite charges.
Hence, the holes from the p-side are attracted towards the
free electrons at the n-side. Thus, the holes move from p-
region (high concentration region) to n-region (low
concentration region).
Formation of positive and negative ion
The free electrons crossing the junction provide the extra
electrons to the p-side atoms by filling the holes in the p-side
atoms. The atom which gains extra electron has more number
of electrons than protons. We know that, when the atom gains
an extra electron from the outside atom it will become a
negative ion. Negative ions are also called as acceptors because they accept
extra electrons from outside atoms.
Thus, each free electron that crosses the junction to fill the
holes in the p-side creates negative ions on the p-side.
Similarly each free electron that left the n-side atom to fill the
holes in the p-side atom creates a hole at n-side atom. The
atom which loses an electron has more number of protons
than electrons. We know that, when the atom loses an
electron it will becomes a positive ion. Positive ions are also
called as donors because they donate extra electrons to the
outside atoms.
Thus, each free electron that left the n-side parent atom and
crosses the junction to fill the holes in the p-side atom creates
positive ion at n-side.
You might also like
- Sem 2Document78 pagesSem 2Tech TeamNo ratings yet
- Properties of A P - N JunctionDocument6 pagesProperties of A P - N JunctionSharmistha JuiNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesP-N Junction - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaphaninderNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Bios Seminar ReportDocument14 pagesPN Junction Bios Seminar ReportDevendra PadalkarNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesP-N Junction: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediapratysweetyNo ratings yet
- Charge Carriers Crossing The JunctionDocument5 pagesCharge Carriers Crossing The Junctionhoangloc NgoNo ratings yet
- Ec8252 Electronicdevices 997787639 Ec8252 NotesDocument96 pagesEc8252 Electronicdevices 997787639 Ec8252 NoteschandanpgowdachandanpNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's Law: Application in Diodes: 3.electrical ChargeDocument3 pagesCoulomb's Law: Application in Diodes: 3.electrical ChargeRegidor PetilunaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics ProjectDimpySurya44% (25)
- ECE 212A: PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesECE 212A: PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsNiño John JaymeNo ratings yet
- EC6464 Electro Micro Proc Notes (Typed)Document77 pagesEC6464 Electro Micro Proc Notes (Typed)DolianNo ratings yet
- p-n Junction Diode OperationDocument6 pagesp-n Junction Diode OperationMuhamad Hanif RidhaNo ratings yet
- MODULE-I - PN Junction DiodeDocument17 pagesMODULE-I - PN Junction DiodeAnurag HodgeNo ratings yet
- Zero Bias P-N Junction: Charge Carriers Crossing The JunctionDocument62 pagesZero Bias P-N Junction: Charge Carriers Crossing The Junctionafifur rohmanNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics ProjectJayesh PandyaNo ratings yet
- SECA1101Document127 pagesSECA1101Anil MohiteNo ratings yet
- SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE - A Semiconductor Diode Is A P-N Junction With Metallic Contacts ProvidedDocument2 pagesSEMICONDUCTOR DIODE - A Semiconductor Diode Is A P-N Junction With Metallic Contacts ProvidedRAHUL KURMINo ratings yet
- ' Semiconductor Materials and Diodes: Rizal Technological UniversityDocument8 pages' Semiconductor Materials and Diodes: Rizal Technological UniversityVam ArmodiaNo ratings yet
- EDC Unit-1 (Semiconductor Diode) PDFDocument17 pagesEDC Unit-1 (Semiconductor Diode) PDFSaiKrishna81% (16)
- Beee-Unit 2Document79 pagesBeee-Unit 2thamizhan4341No ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode: A Guide to Its Structure and OperationDocument5 pagesPN Junction Diode: A Guide to Its Structure and OperationVickeyNo ratings yet
- UNIL PDocument3 pagesUNIL Psunil8080No ratings yet
- 21EES101T-EEE-Unit-2 NotesDocument35 pages21EES101T-EEE-Unit-2 Notessr1343No ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument3 pagesSemiconductorzubairwahidNo ratings yet
- Categories or Electric Materials P2Document33 pagesCategories or Electric Materials P2Zach VittoriNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 SlidesDocument67 pagesLecture-2 Slidestanisha guptaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 PN Junction Diode Complete Notes BEEDocument12 pagesUNIT 4 PN Junction Diode Complete Notes BEESomesh Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Theory of PN Junction-ModifiedDocument20 pages3.2 Theory of PN Junction-Modifiedraunak guptaNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronic Design Module E - Diode V-I CharacteristicsDocument50 pagesAnalogue Electronic Design Module E - Diode V-I CharacteristicsArvish RamseebaluckNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document56 pagesUnit 2Kamble RamNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction: See Also: andDocument11 pagesP-N Junction: See Also: andRupali SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document97 pagesUnit 2MOHAN RuttalaNo ratings yet
- Solids and Semi ConductorDocument11 pagesSolids and Semi ConductorGayatriNo ratings yet
- PN JunctionDocument10 pagesPN Junctionasdxws feNo ratings yet
- Experiment-01: Theory: P-N Junction DiodeDocument5 pagesExperiment-01: Theory: P-N Junction Diodevamsee007No ratings yet
- Diode Fundamentals Explained: Formation, Energy Bands & Junction PotentialDocument24 pagesDiode Fundamentals Explained: Formation, Energy Bands & Junction Potentialmuvin236No ratings yet
- Part 1-Semiconductor Devices SemiconductorDocument10 pagesPart 1-Semiconductor Devices SemiconductorBASIL KUMAR N.KNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Pn-Junction DiodeDocument48 pagesUnit-I Pn-Junction DiodeBabu GundlapallyNo ratings yet
- JUNCTION DIODE CHARACTERISTICSDocument55 pagesJUNCTION DIODE CHARACTERISTICSbalu56kvNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument2 pagesSemiconductorsNitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 PN JunctionDocument6 pages1 PN JunctionrameshNo ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument5 pagesPhy Projecteniyan.arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Name: K Sai Bhavana Class: Csit Roll No: 21951A3333 SubjectDocument12 pagesName: K Sai Bhavana Class: Csit Roll No: 21951A3333 SubjectK SAI BHAVANANo ratings yet
- Module - 1 18ELN14Document38 pagesModule - 1 18ELN14DaisyQueen100% (1)
- 3.3 IV Characteristics of PN Junction Diode-ModifiedDocument18 pages3.3 IV Characteristics of PN Junction Diode-Modifiedraunak guptaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Electronics - NNDocument6 pagesSemiconductor Electronics - NNBalaji Class-10thNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor NotesDocument8 pagesSemiconductor NotesAaryaNo ratings yet
- PN Junction DiodeDocument85 pagesPN Junction DiodesatyashopperNo ratings yet
- 2 - PN Junction TheoryDocument4 pages2 - PN Junction TheoryAdel RaweaNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Diode DefinitionDocument7 pagesTunnel Diode Definitiongulzar ahmadNo ratings yet
- Project NewDocument48 pagesProject NewAmritha SureshNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor and Electronic Devices TheoryDocument10 pagesSemiconductor and Electronic Devices TheoryAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Materials and TypesDocument33 pagesSemiconductor Materials and TypesSaidur Rahman SidNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON Semiconduct ORSDocument14 pagesPresentation ON Semiconduct ORSParagNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument23 pagesSemiconductormillinagi95No ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Electrochimica ActaDocument27 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Electrochimica ActakarthikNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Properties of FluidDocument15 pagesWeek 1 Properties of FluidJoquem PamesaNo ratings yet
- Cryoscopic Determination of Molar MassDocument15 pagesCryoscopic Determination of Molar MassFrances PaulineNo ratings yet
- Ar6303 - Climate and Built EnvironmentDocument1 pageAr6303 - Climate and Built Environmentdoss186No ratings yet
- AL-CHEM Chemistry of Carbon Compounds (03-06)Document24 pagesAL-CHEM Chemistry of Carbon Compounds (03-06)AmyLinNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) - 2019Document37 pagesAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) - 2019NishantNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledFelix YeboahNo ratings yet
- Bansal Classes Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEDocument824 pagesBansal Classes Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEHarshitShukla0% (1)
- SEAFARERS TRAINING CENTER FIRE PREVENTION AND FIRE FIGHTINGDocument106 pagesSEAFARERS TRAINING CENTER FIRE PREVENTION AND FIRE FIGHTINGTulia TapiaNo ratings yet
- Light ScatteringDocument10 pagesLight ScatteringAndri HanryansyahNo ratings yet
- DPPS-3 - Chemical KineticsDocument2 pagesDPPS-3 - Chemical KineticsShrish PratapNo ratings yet
- Free Mastic G 316Document5 pagesFree Mastic G 316Kelly RobertsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Salts: Flow Chart of Preparation of SaltsDocument7 pagesChapter 8: Salts: Flow Chart of Preparation of SaltsPrincess Ting TingNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Seal Face MaterialsDocument19 pagesMechanical Seal Face MaterialsKamlesh Kamlesh Etwaro100% (1)
- Assignment 7 SolutionsDocument11 pagesAssignment 7 SolutionsIsaiah Qe LiewNo ratings yet
- Kimia PolimerDocument44 pagesKimia PolimerMitaPermataSariNo ratings yet
- Prodrugs As Drug Delivery Systems Hydrolysis Oxazolidines-A Potential New Prodrug TypeDocument5 pagesProdrugs As Drug Delivery Systems Hydrolysis Oxazolidines-A Potential New Prodrug TypeDoc MartenzNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases & SaltDocument16 pagesAcid Bases & SaltKK patel0% (1)
- GR0177 SolutionsDocument143 pagesGR0177 SolutionsDavid LatchmanNo ratings yet
- Jones, 1964Document6 pagesJones, 1964andrea.cipagautaNo ratings yet
- Abuzahra2007 PDFDocument10 pagesAbuzahra2007 PDFplamtaNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab 6 Ideal Gas ConstantDocument8 pagesChem Lab 6 Ideal Gas Constantapi-317126154No ratings yet
- Es2008 54190Document6 pagesEs2008 54190Selvaraji MuthuNo ratings yet
- Ryerson CHE312 assignment on reactor engineeringDocument2 pagesRyerson CHE312 assignment on reactor engineeringAbdi Ahmed0% (1)
- MSE 321 Engineering Thermodynamics & Heat Transfer Assignment 4Document4 pagesMSE 321 Engineering Thermodynamics & Heat Transfer Assignment 4Indran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate The Temperature Rise in A Sealed EnclosureDocument20 pagesHow To Calculate The Temperature Rise in A Sealed EnclosureChandrashekhar SarafNo ratings yet
- HMT Answer 2 & 16 Marks HMTDocument85 pagesHMT Answer 2 & 16 Marks HMTChandra Sekar100% (3)
- Annotated Bibliography GiftedDocument3 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Giftedapi-298269450No ratings yet
- Sulfur DegassingDocument15 pagesSulfur DegassingAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Science-9 SLM Q2 W2 M2 V1.0-CC-released-25Dec2020Document16 pagesScience-9 SLM Q2 W2 M2 V1.0-CC-released-25Dec2020jan lawrence panganibanNo ratings yet