Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch. 1
Uploaded by
abibiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch. 1
Uploaded by
abibiCopyright:
Available Formats
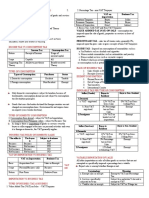
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMPTION TAXES CONSUMPTION ABROAD are not subject to
consumption tax.
The Concept of Consumption and Consumption Taxes Cross-boarder doctrine- goods that cross the boarder
Consumption- acquisition or utilization of goods or services by destined for foreign countries are not charged
any person. consumption taxes. THEREFORE, THE NIRC EITHER
EXEMPTS EXPORTS OR SUBJECT THEM TO A 0% TAX
Utilization of goods or services- may be through purchase, RATE.
exchange, or other means. This is subject to a tax called
consumption tax. Types of Domestic Consumption AS TO SOURCE
Rationale of Consumption Tax 1. Domestic sales- purchases from resident sellers
2. Importation- purchases from abroad by non-
1. Savings formation residents
Savings- income less consumption. 1. Consumption tax on DOMESTIC SALES
- A capital that is useful in funding projects crucial to purchase- domestic consumptions of RESIDENT BUYERS TO
economic activites that could spur further economic RESIDENT SELLERS.
development.
- Subject to a consumption tax called BUSINESS TAX.
Tax on consumption promotes savings formation BY LIMITING - Business tax is an INDIRECT TAX because the
THE LEVEL OF CONSUMPTION. consumption tax is indirectly imposed upon sellers
which are businesses.
2. Rationalization of the Benefit Received Theory - Object of taxation: purchase of buyers. Obligation to
Benefit received theory- those who receive more benefit from pay: sellers.
the govt. should pay more taxes. 2. Consumption tax on IMPORTATION
Every person consumes goods and services as a normal part Importation- domestic consumption of goods or services from
of life, even if they do not earn income. A tax on consumption non-resident sellers.
will effectively render everybody taxable. Therefore,
consumption tax is a practical rationalization of the Benefit - Subject to a consumption tax called VAT on
Received Theory in taxation. importation.
- DIRECT TAX because VAT is directly levied upon the
3. Wealth distribution to society buyer-importer. Because the seller is non-resident
Redistribute wealth to society so everyone in the State could and is out of reach of the PH’s taxing power.
enjoy the same. Business Tax vs. VAT on IMPORTATION
Rich people buy or spend more than poor people. A tax on VAT on Importation Business Tax
consumption will effectively make the rich pay more taxes for Scope of tax Imports from BUSINESS or
NON-BUSINESS
Purchases from BUSINESSES
ONLY
the govt. Type of consumption tax Pure form Relative form
Statutory taxpayer Buyer Seller
Economic taxpayer Buyer Buyer
A Caveat to Consumption Tax (limitation) Nature of imposition Direct Indirect
Basis of tax Total purchase cost Sales or receipts
Consumption tax shall not be levied upon BASIC NECESSITIES Business- habitual engagement in a commercial activity.
such as food, education, health and shelter.
The VAT on importation is not impasse to
Income Tax vs. Consumption Tax administrative feasibility as the govt. has placed a
Income tax Consumption Tax border control managed by the Bureau of Customs
Nature Tax upon RECEIPT of income Tax upon USAGE of income or
capital.
(BOC).
Scope/ average A tax to the CAPABLE A tax to ALL
Theoretical basis Ability to pay theory Benefit received theory Bureau of Customs (BOC)- tasked to collect tax in behalf of
Types of Consumption the BIR. Thus, the VAT on importation is conveniently
Types of Consumption Purchaser Status
collectible through this.
1. Domestic consumption Resident Taxable
2. Foreign consumption Non-resident Exempt/ effectively non- Being a business is very essential to business taxation
taxable
while it is not the case with importation. So long as
Because taxation is INHERENTLY TERRITORIAL, the
there is importation of goods or service, the VAT
govt. can only impose tax upon DOMESTIC
generally applies.
CONSUMPTION.
Destination principle- only goods and services Types of Consumption Taxes
destined for CONSUMPTION IN THE PH are subject to
CONSUMPTION TAX while those destined for
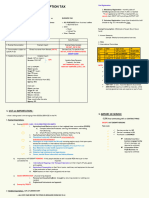
1. Percentage Tax- a tax of various rates from .60% to - services specifically subject to percentage tax
30% are taxable consumption of services but subject only to
2. Value Added Tax- a consumption tax of 12%
a specific percentage tax rate set by NIRC. Not subject to
3. Excise Tax- an ad valorem or specific tax, which is
imposed in addition to VAT or percentage tax, only in VAT.
certain goods or services.
3. VATABLE IMPORTATION OR SALES
Types of Domestic Consumption as to Taxability
- all other importation or sales of either goods
1. Exempt consumption- consumption of or services that are not exempted or specifically
goods/services not subject to consumption taxes. imposed a percentage tax is vatable.
2. Consumptions specifically subject to percentage
tax- consumption of services that are not subject to The Structure of the VAT on Importation
VAT but are imposed with a specific percentage tax.
3. Vatable consumption- consumption that are neither Import of service
VAT on Importation
Import of goods
exempted or subject to percentage tax. Exempt Exempt Exempt
% tax Percentage tax -
Importation Domestic sales/receipts VAT Final withholding VAT VAT on importation
Exempt consumption
Services subject to a % tax
exempt importation
Service specifically subject
Exempt sales/receipt
Services specifically subject
Import of services
to a % tax to a % tax
Vatable consumption Vatable importation Vatable sales or receipt The import of service is either:
1. EXEMPT CONSUMPTION
a. Exempt
- neither subject to percentage tax nor VAT.
b. Subject to percentage tax
-sourced from abroad- exempt from VAT c. Subject to final withholding VAT
The import of services by certain VAT-exempt
-sourced from within- exempt from business tax
person is exempt from VAT.
Basis of exemption from consumption tax
Basis of exemption
Human necessity
VAT on Importation
Goods imported is a
Business Tax
The goods, services or
Import of goods
HUMANA NECESSITY property sold is a HUMAN
Out of scope of tax The importation DOES NOT
NECESSITY
The seller is NOT engaged in
The import of goods is either:
constitute a domestic business.
consumption a. Exempt
Tax incentive The importation is exempted The sales or receipt is
as a tax incentive to CERTAIN exempted as a tax incentive b. Subject to VAT importation
IMPORTERS. to CERTAIN SELLERS.
International comity The importation is exempted The sales or receipt is
by treaty exempted by treaty. The Structure of the Business Tax
Human necessity- certain basic necessities such as natural Business Tax
agricultural or marine food products, agricultural inputs, Sales of services sales of goods
Exempt Exempt receipt Exempt
books, newspapers and magazines, residential properties; and % tax Receipts specifically subject -
essential services. These consumables are not taxable. to a % tax
VAT Vatable receipts Vatable sales
Out of scope of the consumption tax- Sales of services
VAT on Importation
The bringing of goods to the Ph which
Business Tax
Domestic consumption from businesses only.
The receipt from the sale of service is either:
represents current domestic consumption.
Scope of the VAT on importation- applies to current purchase a. Exempt
or acquisition of goods and services by a resident person from b. Specifically subject to a percentage taxe
non-resident persons. Importation that do not reflect c. Vatable
CURRENT acquisition are exempt.
Sales of goods
Scope of business taxes- only sales or persons engaged in
business is subject to business tax. The sales from the sale of goods is either:
Tax incentives- certain institutions and objects are not subject a. Exempt
to business taxes to encourage actions that are beneficial to b. Vatable
the country.
VAT on Importation vs. VAT on Sales in Business Tax
International comity- importation or sales of goods/service
that are agreed to be exempted in an international VAT on importation- is directly computed on the landed
agreement. costs of importation without any deduction or tax
credit.
2. SERVICES SPECIFICALLY SUBJECT TO PERCENTAGE TAX
VAT on Sales in Business Tax- is unique as it is
theoretically imposed on the value added (the amount
of mark-up imposed by sellers on their purchase costs).
It follows a tax credit method wherein a VAT of 12% is
imposed on sales and is reduced by VAT paid by the
business on its purchases.
The tax due is computed as:
Output VAT (12% of sales & receipts) xxx
Less: Input VAT (12% VAT paid on xxx
purchases
VAT due xxx
Input VAT- tax credit against output VAT when due or
paid not when goods are sold.
- Not imposed on the gross profit.
This feature of the VAT on sales and receipt is
unique compared to the percentage taxes which
is merely computes as a fixed percentage of
sales or receipts.
The Excise Tax
Excise tax- an additional imposition to VAT or
percentage tax.
- Is normally imposed before the goods are sold
by domestic producers or upon their
importation by importers.
It is imposed on the consumption commodities such as:
a. Sin products such as alcohol and cigarettes
b. Non-essential commodities such as automobile
and jewelry
c. Non-essential services, such as cosmetic surgery
d. Products which are environmentally degrading
in their production or consumption, such as
petroleum and minerals.
You might also like
- Imf Quiz 1 - MaduraDocument4 pagesImf Quiz 1 - MaduraTheSupaDupa100% (3)
- Case Study China To Float or Not To FloatDocument6 pagesCase Study China To Float or Not To FloatShaniah IturraldeNo ratings yet
- Credit ManagementDocument75 pagesCredit ManagementYurih Khei Jham AluminumNo ratings yet
- Consumption Taxes: Business Tax Is A Form of Consumption TaxDocument8 pagesConsumption Taxes: Business Tax Is A Form of Consumption TaxDenvyl MangsatNo ratings yet
- History of Giant HypermarketDocument2 pagesHistory of Giant HypermarketAudreyTeoNo ratings yet
- Rationale of Consumption TaxDocument3 pagesRationale of Consumption Taxmy miNo ratings yet
- BUSTAX MidtermsDocument32 pagesBUSTAX Midtermssilverjez1801No ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Business TaxDocument9 pagesTopic 1 - Business Taxalexissosing.cpaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and 2 BUSTAXDocument6 pagesChapter 1 and 2 BUSTAXCory RitaNo ratings yet
- Business and Transfer TaxationDocument9 pagesBusiness and Transfer Taxationcj8kim8maggayNo ratings yet
- Tax 2 NotesDocument2 pagesTax 2 NotesMark LapidNo ratings yet
- Importation by Importers) : Income Tax Vs Consumption TaxDocument2 pagesImportation by Importers) : Income Tax Vs Consumption TaxMark LapidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Consumption Taxes: Prepared By: Mrs. Nelia I. Tomas, CPA, LPTDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Consumption Taxes: Prepared By: Mrs. Nelia I. Tomas, CPA, LPTTokis SabaNo ratings yet
- Tax 202 - Chapter 1 Consumption TaxDocument4 pagesTax 202 - Chapter 1 Consumption TaxLizandraArceoBarteNo ratings yet
- TAX2Document6 pagesTAX2DeyNo ratings yet
- Jpia-Hau: Business and Transfer TaxationDocument12 pagesJpia-Hau: Business and Transfer Taxationronniel tiglaoNo ratings yet
- Business Tax Chapter 1Document3 pagesBusiness Tax Chapter 1Mamin ChanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Consumption TaxesDocument9 pagesIntro To Consumption TaxesAnna CynNo ratings yet
- Tax 01 Introduction To Consumption TaxesDocument3 pagesTax 01 Introduction To Consumption TaxesShiela LlenaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Consumption and Consumption Taxes and Vat On ImportationDocument4 pagesConcept of Consumption and Consumption Taxes and Vat On ImportationJamaica DavidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document6 pagesLesson 6Iris Lavigne RojoNo ratings yet
- Business and Transfer Taxation: TO Consumption TaxesDocument40 pagesBusiness and Transfer Taxation: TO Consumption TaxesKC GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesJason MablesNo ratings yet
- M7 - Intro To Consumption Tax & VAT On Importation Students'Document54 pagesM7 - Intro To Consumption Tax & VAT On Importation Students'Elaiza RegaladoNo ratings yet
- 01 BustaxDocument10 pages01 BustaxJake Raphael Cruz CalaguasNo ratings yet
- Business and Transfer Taxes: An Introduction To Consumption TaxesDocument16 pagesBusiness and Transfer Taxes: An Introduction To Consumption TaxesAngelo Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Business TaxesDocument20 pagesBusiness TaxesAnime ScreenshotsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Consumption Taxes NotesDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Consumption Taxes NotesSelene DimlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesDocument1 pageChapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesMicko LagundinoNo ratings yet
- Bustax Chapter 1Document9 pagesBustax Chapter 1Pineda, Paula MarieNo ratings yet
- Bustax Chapters 1 4Document6 pagesBustax Chapters 1 4Naruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bttax BanggawanDocument21 pagesChapter 1 Bttax Banggawanlaythejoylunas21No ratings yet
- Introduction To Consumption Tax PDFDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Consumption Tax PDFShamae Duma-anNo ratings yet
- TAX 221-AVP (Atillo, Cañete, Dejan, Manlimos, Hortellano)Document50 pagesTAX 221-AVP (Atillo, Cañete, Dejan, Manlimos, Hortellano)reymardicoNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument198 pagesCombine PDFliamdrlnNo ratings yet
- Tax 2 - BanggawanDocument175 pagesTax 2 - BanggawanJessica IslaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Tax 2Document5 pagesChapter 1 Tax 2Hazel Jane EsclamadaNo ratings yet
- TAXATION II KMA PREFINALS VAT EditedDocument14 pagesTAXATION II KMA PREFINALS VAT Editedethel hyuga0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesDocument21 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesNacpil, Alyssa JesseNo ratings yet
- At A GlanceDocument22 pagesAt A GlanceThakur RinkiNo ratings yet
- Kjaefncl (Complete)Document42 pagesKjaefncl (Complete)Kenzo RodisNo ratings yet
- BSTX Reviewer (Midterm)Document7 pagesBSTX Reviewer (Midterm)alaine daphneNo ratings yet
- Consumption TaxDocument6 pagesConsumption TaxSha MagondacanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Consumption and Business TaxDocument4 pagesTopic 1 - Consumption and Business TaxNicole Daphne FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Reviewerrrr Tax 2 PDFDocument11 pagesReviewerrrr Tax 2 PDFAnthony EboraNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Consumption TaxesDocument3 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Consumption TaxesMonica MonicaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 & 2: at The End of This Topic, We Should Be Able To Learn The FollowingDocument33 pagesModule 1 & 2: at The End of This Topic, We Should Be Able To Learn The FollowingAlicia FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Module 6. Nature and Concepts of Business TaxesDocument6 pagesModule 6. Nature and Concepts of Business TaxesYolly DiazNo ratings yet
- Tax Direct IndirectDocument2 pagesTax Direct IndirectSukram HembromNo ratings yet
- Value Added TaxDocument29 pagesValue Added TaxSNLTNo ratings yet
- Gruba Tax 2 NotesDocument13 pagesGruba Tax 2 NotesPJezrael Arreza FrondozoNo ratings yet
- Value Added Tax NotesDocument12 pagesValue Added Tax NotesAimeeNo ratings yet
- Business Tax Reviewer IDocument5 pagesBusiness Tax Reviewer IMariefel Irish Jimenez KhuNo ratings yet
- Indirect Tax DefinitionDocument9 pagesIndirect Tax DefinitionSuhas SalehittalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document37 pagesChapter 4Christine Anne ValdezNo ratings yet
- Business Taxation Intro To Consumption Taxes: Anie P. Martinez, Cpa, MbaDocument32 pagesBusiness Taxation Intro To Consumption Taxes: Anie P. Martinez, Cpa, MbaAnie MartinezNo ratings yet
- What Is The Nature of Value Added Taxes?: MB AgunoyDocument11 pagesWhat Is The Nature of Value Added Taxes?: MB AgunoyhbcgNo ratings yet
- Part 4Document17 pagesPart 4Marc Lester Hernandez-Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- EH403 TAXATION MIDTERMS VAT - EditedDocument12 pagesEH403 TAXATION MIDTERMS VAT - Editedethel hyugaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ConsumptionDocument41 pagesChapter 1 ConsumptionBeatrix Domingo SampangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document6 pagesChapter 8my miNo ratings yet
- CTT Examination Reviewer (Notes) Page A - 30Document13 pagesCTT Examination Reviewer (Notes) Page A - 30Seneca GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Tax Savings Strategies for Small Businesses: A Comprehensive Guide For 2024From EverandTax Savings Strategies for Small Businesses: A Comprehensive Guide For 2024No ratings yet
- Tatasteel Inclass DiscusionDocument6 pagesTatasteel Inclass DiscusionADAMYA VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- 07 - Chapter 1 PDFDocument26 pages07 - Chapter 1 PDFJAI SHANKAR 2No ratings yet
- ECO201 - SP23 - IB1702 - Group Assignment - Group 4Document15 pagesECO201 - SP23 - IB1702 - Group Assignment - Group 4JinyNo ratings yet
- Online Financial Services3Document1 pageOnline Financial Services3Rebel 8No ratings yet
- This Line Is Only For CommerceDocument23 pagesThis Line Is Only For CommerceSourav SsinghNo ratings yet
- The Promissory Note As A Substitute For MoneyDocument30 pagesThe Promissory Note As A Substitute For MoneyricetechNo ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoicemayank jeevnaniNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Brazil and US - CottonDocument7 pagesCase Study - Brazil and US - CottonDISHA MALHOTRANo ratings yet
- Super Savings Account: Common Service ChargesDocument2 pagesSuper Savings Account: Common Service ChargesSantosh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Hlcubo1221091769 TDocument2 pagesHlcubo1221091769 TJeson RamjiteNo ratings yet
- Azure InvoiceDocument1 pageAzure InvoiceAnkit SambhareNo ratings yet
- International Trade Organizations Rachit Gupta FinalDocument17 pagesInternational Trade Organizations Rachit Gupta FinalUjjwal MishraNo ratings yet
- Midterm - Shariah IVDocument15 pagesMidterm - Shariah IVchaeny limNo ratings yet
- Badla (Stock Trading)Document2 pagesBadla (Stock Trading)BOBBY212No ratings yet
- Statement 09apr2023Document8 pagesStatement 09apr2023Daia SorinNo ratings yet
- FM I Note - Chapter Three (TVM)Document15 pagesFM I Note - Chapter Three (TVM)zewdieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business LawDocument1 pageIntroduction To Business LawAaryan RautNo ratings yet
- Ifm - 5Document17 pagesIfm - 5Tường LinhNo ratings yet
- PDF Chapter 16 30 Valix Practical Accounting 2011 DLDocument429 pagesPDF Chapter 16 30 Valix Practical Accounting 2011 DLChristabel Lecita PuigNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Why Did Europeans Want To Enter The Indian Ocean Trade NetworkDocument2 pagesLesson 4 - Why Did Europeans Want To Enter The Indian Ocean Trade NetworktokteacherNo ratings yet
- The World Bank: DPL To Reform The Indonesian Maritime Logistics Sector (P158140)Document8 pagesThe World Bank: DPL To Reform The Indonesian Maritime Logistics Sector (P158140)Octadian PNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of India (Rbi)Document27 pagesReserve Bank of India (Rbi)monika0827100% (1)
- Related Titles: Search DocumentDocument90 pagesRelated Titles: Search DocumentNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Regional TradeDocument1 pageRegional TradeK.QNo ratings yet
- USPADocument18 pagesUSPAtayyebaNo ratings yet
- Ups InvoiceDocument3 pagesUps InvoiceDoina FrunzareanuNo ratings yet