Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Morphological
Uploaded by
Aaron TrevorOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Morphological
Uploaded by
Aaron TrevorCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction:
Acute inflammation is a rapid response to tissue injury that occurs within minutes to hours
after the injury. The morphological types of acute inflammation refer to the different patterns
of inflammation that can be observed under a microscope. There are three main types of
acute inflammation: serous, fibrinous, and suppurative.
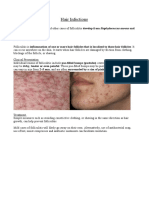
1. Serous inflammation:
Serous inflammation is characterized by the exudation of a watery, protein-rich fluid. This type
of inflammation is typically seen in mild cases of injury, such as a blister or sunburn. The fluid
that is exuded is clear and straw-colored. Microscopically, serous inflammation is
characterized by the presence of fluid-filled spaces within the tissue. Macroscopically, the
affected area appears swollen, shiny, and red.
2. Fibrinous inflammation:
Fibrinous inflammation is characterized by the exudation of a fibrin-rich fluid. Fibrin is a
protein that is involved in blood clotting and wound healing. This type of inflammation is
typically seen in more severe cases of injury, such as pneumonia or pericarditis.
Microscopically, fibrinous inflammation is characterized by the presence of fibrin deposits
within the tissue. Macroscopically, the affected area appears yellowish-white and may be
covered with a fibrinous membrane.
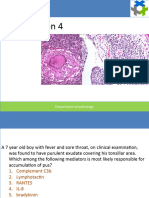
3. Suppurative inflammation:
Suppurative inflammation is characterized by the exudation of pus. Pus is a thick, opaque
fluid that contains dead cells, debris, and bacteria. This type of inflammation is typically seen
in cases of bacterial infection, such as an abscess or cellulitis. Microscopically, suppurative
inflammation is characterized by the presence of large numbers of neutrophils (a type of white
blood cell) within the tissue. Macroscopically, the affected area appears swollen, red, and
may be discharging pus.
In conclusion, the morphological types of acute inflammation reflect the severity of tissue
injury and the resulting response of the immune system. Serous inflammation is the mildest
form and is characterized by a watery exudate, fibrinous inflammation is more severe and is
characterized by a fibrin-rich exudate, while suppurative inflammation is the most severe and
is characterized by the presence of pus.
You might also like
- Pathology Lec 7Document63 pagesPathology Lec 7ahmadNo ratings yet
- Folliculitis, A Simple Guide To the Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandFolliculitis, A Simple Guide To the Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- INFLAMMATIONDocument2 pagesINFLAMMATIONАнастасия ПащенкоNo ratings yet
- Pathology Lecture 11 Scientific TeamDocument34 pagesPathology Lecture 11 Scientific TeammikiyaskayleNo ratings yet
- Inflammation ContiDocument2 pagesInflammation ContiKiranNo ratings yet
- Pathology 2018-2019 Dr. Hanan Nasib: Faculty of Public HealthDocument10 pagesPathology 2018-2019 Dr. Hanan Nasib: Faculty of Public HealthSon AbdoNo ratings yet
- Inflammation DetailedDocument12 pagesInflammation Detailedsimi yNo ratings yet
- Inflammation 3Document12 pagesInflammation 3Bhavya KakkarNo ratings yet
- 2 InflammationDocument91 pages2 InflammationDesta BelachewNo ratings yet
- Eksudativne UpaleDocument2 pagesEksudativne UpaleTarik GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Integumentary DisorderDocument6 pagesIntegumentary Disorderhxqf25mbvvNo ratings yet
- Chronic InflDocument31 pagesChronic InflAmany SaifNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument8 pagesInflammationHarjot RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and RepairDocument38 pagesInflammation and RepairIsaac Nsiah Acheampong100% (1)
- InflammationsDocument68 pagesInflammationsAnand GuptaNo ratings yet
- Inflammation: Bocharova TetianaDocument79 pagesInflammation: Bocharova Tetianaсветлый поповNo ratings yet
- Short Notes InflammationDocument3 pagesShort Notes InflammationDr-Rukhshanda RamzanNo ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument12 pagesAcute InflammationEslam NassarNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument17 pagesInflammationNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- The Agents Causing Inflammation May BeDocument3 pagesThe Agents Causing Inflammation May BemidoNo ratings yet
- 04.inflammation 4-ChronicInflammationDocument34 pages04.inflammation 4-ChronicInflammationShameena KnNo ratings yet
- PatternsDocument1 pagePatternsAaron TrevorNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Different Organ System SKINDocument102 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Different Organ System SKINBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- Inflamation: Drh. M. Arfan Lesmana, M.Sc. Fakultas Kedokteran Hewan, Universitas Brawijaya EmailDocument55 pagesInflamation: Drh. M. Arfan Lesmana, M.Sc. Fakultas Kedokteran Hewan, Universitas Brawijaya EmailalrezaNo ratings yet
- Subject XXVI. Quarantine Infections. SepsisDocument2 pagesSubject XXVI. Quarantine Infections. SepsisIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis:: - Classification - Morphology - Clinical FeaturesDocument28 pagesTuberculosis:: - Classification - Morphology - Clinical FeaturesRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNo ratings yet
- 3.acute InflammationDocument38 pages3.acute Inflammationyaqeenallawi23No ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis: InflammationDocument3 pagesAcute Appendicitis: Inflammationshahidkhan 654321654321No ratings yet
- Surgical Infection PDFDocument20 pagesSurgical Infection PDFosaNo ratings yet
- Granuloma Is Defined As A Circumscribed, Tiny Lesion, About 1 MM in Diameter, Composed PredominantlyDocument6 pagesGranuloma Is Defined As A Circumscribed, Tiny Lesion, About 1 MM in Diameter, Composed PredominantlyIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Manella Joseph Senior Lecturer/Consultant PathologistDocument41 pagesDr. Manella Joseph Senior Lecturer/Consultant PathologistNipun Shamika100% (1)
- InflammationDocument48 pagesInflammationTewodros TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Mikosis Dalam-Kel 7Document22 pagesMikosis Dalam-Kel 7Faizal BardanNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and HealingDocument23 pagesInflammation and Healingatiqullah tarmiziNo ratings yet
- Inflammation - Oral Maxillofacial Pathology - IUPDocument36 pagesInflammation - Oral Maxillofacial Pathology - IUPExnon RdXNo ratings yet
- 11 - Drobnoustroje Skóra ChorobyDocument6 pages11 - Drobnoustroje Skóra Choroby123No ratings yet
- Infection CTRL Ans To Study GuideDocument15 pagesInfection CTRL Ans To Study GuidegarvitaNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument60 pagesInflammationОлексій ПрилуцькийNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Immunology NotesDocument52 pagesUnit-1 Immunology NoteschitraNo ratings yet
- Pathology IDocument98 pagesPathology ICICATRIX ONSENo ratings yet
- CHR InflammationDocument33 pagesCHR InflammationAlnzeer6No ratings yet
- Inflammation and Healing ReportDocument48 pagesInflammation and Healing Reportks75q5w94yNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Sciences: Morphological Pattern of Acute InflammationDocument4 pagesLaboratory Sciences: Morphological Pattern of Acute Inflammationعلا باسم عبد الكاظم جابر (تعليم موازي)No ratings yet
- 6 TBDocument45 pages6 TBsamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Exp - No 6 Chronic InflammationDocument13 pagesExp - No 6 Chronic InflammationNatasha BalochNo ratings yet
- Infections of The Skin 2Document42 pagesInfections of The Skin 2Kathleen Daban RagudoNo ratings yet
- Skin InfectionsDocument5 pagesSkin InfectionsKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- Healing of Oral WoundsDocument73 pagesHealing of Oral WoundsMadhvendra Singh80% (5)
- Presenation Fibrous Cavernous Tuberculois Teachers VersionDocument49 pagesPresenation Fibrous Cavernous Tuberculois Teachers VersionĆux 天主好 OkereNo ratings yet
- Mycotic Diseases Histoplasmosis (Final)Document33 pagesMycotic Diseases Histoplasmosis (Final)hhes8116No ratings yet
- Cell Death: Apoptotic Bodies Which Are Phagocytised by Neighbouring Phagocytes. Apoptosis Is Not AssociatedDocument5 pagesCell Death: Apoptotic Bodies Which Are Phagocytised by Neighbouring Phagocytes. Apoptosis Is Not AssociatedIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion-Severe Thermal Burn InjuryDocument9 pagesCase Discussion-Severe Thermal Burn InjuryTrixNo ratings yet
- Inflammation & Healing of Soft & Hard TissueDocument3 pagesInflammation & Healing of Soft & Hard TissueLakshita PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic InflammationDocument8 pagesAcute and Chronic Inflammationsurfina87No ratings yet
- 1.inflammation & Repair: Cardinal Signs of InflammationDocument47 pages1.inflammation & Repair: Cardinal Signs of Inflammationsharu4291No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Inflammation, Tissue Repair & FeverDocument8 pagesChapter 6 - Inflammation, Tissue Repair & FeverChrista CastorNo ratings yet
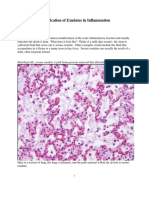
- Identification of Exudates in Inflammation PDFDocument5 pagesIdentification of Exudates in Inflammation PDFlourdes kusumadiNo ratings yet
- Identification of Exudates in InflammationDocument5 pagesIdentification of Exudates in InflammationAnna AzukiNo ratings yet
- Identification of Exudates in Inflammation...Document5 pagesIdentification of Exudates in Inflammation...Ivana Aginta GintingNo ratings yet