Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FR Presentation 2.1
FR Presentation 2.1
Uploaded by
Juan carlos Mora Tores0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views17 pagesThis document discusses the urban environment and building collapses during disasters. It covers:
- How disasters impact the urban environment, causing casualties, damage, and disruptions.
- Common building types found in cities and how they typically collapse in different patterns like lean-to, cantilever, or pancake, each creating different rescue challenges.
- The importance of first responders understanding building construction and collapse patterns to locate survivors trapped in voids or unstable debris. Coordination between response teams is critical to saving lives during urban disasters.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the urban environment and building collapses during disasters. It covers:
- How disasters impact the urban environment, causing casualties, damage, and disruptions.
- Common building types found in cities and how they typically collapse in different patterns like lean-to, cantilever, or pancake, each creating different rescue challenges.
- The importance of first responders understanding building construction and collapse patterns to locate survivors trapped in voids or unstable debris. Coordination between response teams is critical to saving lives during urban disasters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views17 pagesFR Presentation 2.1
FR Presentation 2.1
Uploaded by
Juan carlos Mora ToresThis document discusses the urban environment and building collapses during disasters. It covers:
- How disasters impact the urban environment, causing casualties, damage, and disruptions.
- Common building types found in cities and how they typically collapse in different patterns like lean-to, cantilever, or pancake, each creating different rescue challenges.
- The importance of first responders understanding building construction and collapse patterns to locate survivors trapped in voids or unstable debris. Coordination between response teams is critical to saving lives during urban disasters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
First
Responder
Presentation Title: The Disaster Environment
Module: 2.1
Presenter/Instructor: Add presenters name here
Coordination Saves Lives
First
Responder
The Disaster
Environment
Introduction to the
Disaster Environment
Coordination Saves Lives
Introduction to the Disaster Environment
Learning Outcomes
§ Understand the consequences of disaster
upon the urban environment
§ Identify main building types and
characteristics when involved in collapse
§ Identify basic types of collapse
Introduction to the Disaster Environment
Brief Facts:
§ The urban environment is growing
§ More people around the globe live in cities and
towns
§ Threat levels are increasing
§ Cannot prevent or minimise incidents
§ Larger numbers of casualties and more damage
Examples of disasters affecting the urban
environment:
Natural Accidental Deliberate
Earthquake Train crash Explosion
Flood Collapsed building Terrorism
Tsunami Plane crash
Fire - forest Fire - urban
Landslide Chemical release
Volcano
Typhoon or
Hurricane
Impact of disasters on the urban environment:
§ Casualties – dead and injured
§ Damage and destruction to the infrastructure
§ Disruption of the public utilities
§ Environmental damage
§ Economic damage
§ Sociological damage
§ Disruption to normal life
What is the urban environment:
§ Buildings
§ Bridges, tunnels and viaducts
§ Roads, railways and airports
§ Dams, canals, water treatment facilities
§ Powerlines, pipelines and over-ground utilities
§ Underground railways and utilities
§ Ports, piers and dock facilities
What is the urban environment:
Building Construction
² Un-reinforced masonry, mud brick
² Light timber or bamboo frame
² Reinforced masonry
² Concrete framed
² Monolithic concrete – precast sections
Each type of construction often collapses in
predicted ways, leaving recognised patterns of
hazards and opportunities for survival
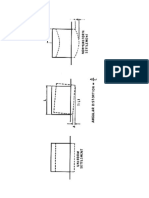
Collapse Patterns:
§ Lean-to
§ Cantilever
§ Pancake
§ V-type
§ A-frame
Lean-to or supported:
§ Floor/wall connection
at one end fails
§ Debris supported by
the remaining wall
§ Large but unstable
voids
§ Victims in voids
Cantilever or hanging:
§ Floor is supported at
one end only
§ Strongest part next to
the remaining wall
§ Debris are very
unstable
§ Victims may be
uninjured but not able
to get down
Pancake or total collapse:
§ Floor/wall connections
fail at both ends
§ Debris impact onto
floors below causing
further collapse
§ Fairly stable
§ No or few voids
§ Not very survivable
V-type collapse:
§ Floor fails in the
centre – mid-span
§ Fairly stable
§ Victims found in small
voids below the floor
§ Victims found in the
debris on top of the
floor
A-frame or tent collapse:
§ Floor/wall connections
fail at both ends
§ Interior load bearing
wall or girder remains
intact
§ Fairly stable
§ Victims found in small
voids below the floor
Structural collapse realities:
§ It is common for more than one type of collapse
pattern to be present
§ Often, walls and floors fail catastrophically
§ Often, there is both lateral and vertical
displacement
?
问题
вопросов La question
domande
Fragen
vragen
सवालों के जवाब perguntas kysymykset
Questions األسئلة
Cuestión
въпроси 質問 otázky sorular
pertanyaan küsimused spørgsmål
1
7
You might also like
- Building Repair and Maintenance From CracksDocument3 pagesBuilding Repair and Maintenance From Cracksmayur1985febNo ratings yet
- 4.10 - APPENDIX-3J - Basic Engineering Design DataDocument21 pages4.10 - APPENDIX-3J - Basic Engineering Design DataSubrata DasNo ratings yet
- Structural Building Defects - Crack in FoundationDocument4 pagesStructural Building Defects - Crack in Foundationmyrayaya100% (1)
- PDAField Guide 2008Document28 pagesPDAField Guide 2008richardong lauNo ratings yet
- The Property Doctor: WWW - Brianlindley.co - UkDocument8 pagesThe Property Doctor: WWW - Brianlindley.co - Uklrk2006No ratings yet
- Eq StrengthenhouseDocument23 pagesEq StrengthenhouseTuroyNo ratings yet
- Cracks Phenomenonon HousesDocument22 pagesCracks Phenomenonon HousesSarah MendezNo ratings yet
- LandslidDocument2 pagesLandslidAli AmranNo ratings yet
- Building Consrucion: Submitted byDocument15 pagesBuilding Consrucion: Submitted byAmit BharatiNo ratings yet
- Wall Crack and Methodology of RepairDocument6 pagesWall Crack and Methodology of RepairMohamed Raffik Bagha100% (1)
- Safeconspractices 090722081145 Phpapp02Document29 pagesSafeconspractices 090722081145 Phpapp02Chandan BagaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four - Slope Stability AnalysisDocument23 pagesChapter Four - Slope Stability AnalysisEebbisaa AddaamuuNo ratings yet
- What Is A Landslide?Document6 pagesWhat Is A Landslide?Luna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Earthquake HazardsDocument34 pagesEarthquake HazardsrosejuliannapaetNo ratings yet
- Inspection Checklist For Older BuildingsDocument4 pagesInspection Checklist For Older BuildingsForbes KambaNo ratings yet
- Sinking & Settling Foundation Repair PDFDocument11 pagesSinking & Settling Foundation Repair PDFAlejandra VelasquezNo ratings yet
- How To Repair Cracks in WallsDocument8 pagesHow To Repair Cracks in WallsAbdNo ratings yet
- RT Reading MaterialDocument6 pagesRT Reading Materialxjsddjwef100% (1)
- DefectsDocument16 pagesDefectsDIVYANSH MISHRANo ratings yet
- Understanding CracksDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Cracksbrian1mugadza100% (2)
- Civil Engineering Cracks Types and CausesDocument8 pagesCivil Engineering Cracks Types and Causeskatia diaNo ratings yet
- Tech Notes: Cracking in Concrete WallsDocument4 pagesTech Notes: Cracking in Concrete WallsNarate MeesookNo ratings yet
- EarthquakesDocument7 pagesEarthquakescharmaineNo ratings yet
- DRRR Q1 M 12Document30 pagesDRRR Q1 M 12miradornathaniel71No ratings yet
- Framing - House ConstructionDocument64 pagesFraming - House Construction오상진100% (1)
- BLDG Construction Philippines Handbook 4Document2 pagesBLDG Construction Philippines Handbook 4mknightNo ratings yet
- Building DefectsDocument40 pagesBuilding DefectsVeereshNo ratings yet
- Retainingwall 140712100253 Phpapp02 PDFDocument67 pagesRetainingwall 140712100253 Phpapp02 PDFDr-Hany HashishNo ratings yet
- Teach Yourself Body LanguageDocument67 pagesTeach Yourself Body LanguageMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Geological and Meteorological HazardsDocument60 pagesGeological and Meteorological HazardsIris Camille GabrielNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument52 pagesUnit Vsai keerthiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 EarthquakeDocument34 pagesChapter 7 EarthquakeJayc ChantengcoNo ratings yet
- Brick MasonaryDocument42 pagesBrick MasonarySaddam HossainNo ratings yet
- Settlement Part 3Document20 pagesSettlement Part 3Wong Chee LoongNo ratings yet
- Department of Interior & Furniture Design Lsad: Lecture-3 Detail of Junctions in Brick WallDocument19 pagesDepartment of Interior & Furniture Design Lsad: Lecture-3 Detail of Junctions in Brick WallAnmol MehanNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 Junctions PDFDocument19 pagesLecture-3 Junctions PDFAnmol Mehan100% (3)
- Department of Interior & Furniture Design Lsad: Lecture-3 Detail of Junctions in Brick WallDocument19 pagesDepartment of Interior & Furniture Design Lsad: Lecture-3 Detail of Junctions in Brick WallAnmol MehanNo ratings yet
- Department of Interior & Furniture Design Lsad: Lecture-3 Detail of Junctions in Brick WallDocument19 pagesDepartment of Interior & Furniture Design Lsad: Lecture-3 Detail of Junctions in Brick WallAnmol MehanNo ratings yet
- Foundation FailureDocument7 pagesFoundation FailureIzwan BujNo ratings yet
- Stay Safe During Land SlidesDocument5 pagesStay Safe During Land SlidesSarina ZeenatNo ratings yet
- Defects in Buildings: Construction & Materials - IxDocument15 pagesDefects in Buildings: Construction & Materials - IxSHIVANI GUPTANo ratings yet
- Repair and Rehabilitation of Structures: CIV18R428Document8 pagesRepair and Rehabilitation of Structures: CIV18R428saravana kumarNo ratings yet
- U U U UDocument9 pagesU U U UDennise DavidNo ratings yet
- Retaining Walls LectureDocument23 pagesRetaining Walls LectureWan Sya100% (2)
- Waterproofing Problems: A Simple Explanation, A Simple SolutionDocument5 pagesWaterproofing Problems: A Simple Explanation, A Simple Solutionwaterproofing_bestNo ratings yet
- Diagonal CracksDocument18 pagesDiagonal CracksNaveen Kumar Nil100% (1)
- Unit 2 Brick MasonryDocument20 pagesUnit 2 Brick MasonryNivashini VindhyaNo ratings yet
- Brickbond 160527160054Document19 pagesBrickbond 160527160054Dipti AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Construction DefectsDocument33 pagesConstruction DefectsShivamTomarNo ratings yet
- Building DefectsDocument41 pagesBuilding DefectsVaibhav HireraddiNo ratings yet
- Inspection Checklist For Historic BuildingsDocument7 pagesInspection Checklist For Historic BuildingsHen8No ratings yet
- Construction DefectsDocument41 pagesConstruction DefectsItchater Paz100% (2)
- 15.8 What Are The Impacts of Earthquakes and Tsunamis?Document26 pages15.8 What Are The Impacts of Earthquakes and Tsunamis?blueblue7978No ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Diagnosing Structural Movement in BuildingDocument29 pagesPractical Guide To Diagnosing Structural Movement in Buildingzaman musaNo ratings yet
- Survival For EarthquakeDocument3 pagesSurvival For EarthquakeallanNo ratings yet
- 298 Hands FaultsDocument3 pages298 Hands FaultsDe MurielNo ratings yet
- Steeper Slopes Permeable Sands Above Impermeable Layers: A) Natural FactorsDocument18 pagesSteeper Slopes Permeable Sands Above Impermeable Layers: A) Natural FactorsDivyagarapatiNo ratings yet
- AD15PM Property Management: Building DefectsDocument47 pagesAD15PM Property Management: Building Defectschauhansukant52No ratings yet
- Flexible Pavements Failures (Types, Causes & Treatments)Document26 pagesFlexible Pavements Failures (Types, Causes & Treatments)Baseer BaigNo ratings yet
- Practical hints to builders and those contemplating buildingFrom EverandPractical hints to builders and those contemplating buildingNo ratings yet
- FR Presentation 1.2Document10 pagesFR Presentation 1.2Juan carlos Mora ToresNo ratings yet
- FR Presentation 1.2Document10 pagesFR Presentation 1.2Juan carlos Mora ToresNo ratings yet
- FR-Presentation-1.1 v2Document13 pagesFR-Presentation-1.1 v2Juan carlos Mora ToresNo ratings yet
- Causalidad ROTHMANDocument8 pagesCausalidad ROTHMANJuan carlos Mora ToresNo ratings yet
- Van Duyn May 11, 2021 InspectionDocument12 pagesVan Duyn May 11, 2021 InspectionJames MulderNo ratings yet
- Vietnam Studies Base Development in South Vietnam 1965-1970Document175 pagesVietnam Studies Base Development in South Vietnam 1965-1970Bob Andrepont100% (2)
- Case Study-Le Meredian, DelhiDocument9 pagesCase Study-Le Meredian, DelhiKUMAR NAVNITNo ratings yet
- Visual C 2012 How To Program 5th Edition Deitel Solutions ManualDocument9 pagesVisual C 2012 How To Program 5th Edition Deitel Solutions Manualtammypearsonyowsrgnpfi100% (26)
- Lemuel Ticman Clarif Meeting No. 1Document3 pagesLemuel Ticman Clarif Meeting No. 1Vholts Villa VitugNo ratings yet
- Jigs and Fixtures: GATE - 1999Document7 pagesJigs and Fixtures: GATE - 1999aditya rastogiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Pricing Forwards and Futures (S.V.)Document39 pagesChapter 5 - Pricing Forwards and Futures (S.V.)flippy23No ratings yet
- Is Iso 105 A05 1996Document12 pagesIs Iso 105 A05 1996tramy1413No ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Arch Bridge PDFDocument7 pagesDesign and Construction of Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Arch Bridge PDFnishantsky1990No ratings yet
- Thermoanalytical Methods-1Document19 pagesThermoanalytical Methods-1Namish ManchandaNo ratings yet
- CRSP ManualDocument140 pagesCRSP ManualCarlos Andrés Buenahora BallesterosNo ratings yet
- BS en 12385-1-2002+a1 - 2009Document24 pagesBS en 12385-1-2002+a1 - 2009Qiu RitaNo ratings yet
- TM 2 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry 7th Edition by John McMurryDocument15 pagesTM 2 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry 7th Edition by John McMurrysukma AsaNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Rx-V800 Service ManualDocument75 pagesYamaha Rx-V800 Service ManualTheoniusNo ratings yet
- Parkway Shenton Health Screening PackagesDocument14 pagesParkway Shenton Health Screening Packagesseptira amNo ratings yet
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.2 - 2014 - IndexDocument53 pagesEuropean Pharmacopoeia 8.2 - 2014 - IndexRoger (Sisfarma)100% (3)
- ADB Report DISCO Tranche 1Document261 pagesADB Report DISCO Tranche 1Javed RashidNo ratings yet
- My First Inspiration By: Jose RizalDocument5 pagesMy First Inspiration By: Jose RizalMavic Jaictin Bagondol SemaNo ratings yet
- Poster PrzntationDocument1 pagePoster PrzntationSakshiKoulNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Oxidized and Unoxidized Filtrate On Oxygen DelignificationDocument40 pagesThe Effect of Oxidized and Unoxidized Filtrate On Oxygen DelignificationAria DarmawanNo ratings yet
- SreeDocument105 pagesSreeAravind PothinaNo ratings yet
- ch-2 Petruzella PDFDocument26 pagesch-2 Petruzella PDFozzaapriodede100% (2)
- The Borehole Environment (Compatibility Mode)Document29 pagesThe Borehole Environment (Compatibility Mode)Adian AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Iron Ore Amp Iron Ore Mining Revision 1 PDFDocument140 pagesIntroduction To Iron Ore Amp Iron Ore Mining Revision 1 PDFravi00098No ratings yet
- 2.4W Stereo Audio Amplifier - Yd2025H: Youda Integrated CircuitDocument4 pages2.4W Stereo Audio Amplifier - Yd2025H: Youda Integrated CircuitMarceloNo ratings yet
- Solutions To The 83rd William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 3, 2022Document7 pagesSolutions To The 83rd William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 3, 2022Lyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) - Instrument - BritannicaDocument2 pagesTransmission Electron Microscope (TEM) - Instrument - BritannicaSabareesan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- What Are The Symptoms of Bulimia?: Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia SymptomsDocument13 pagesWhat Are The Symptoms of Bulimia?: Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia SymptomsMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- VibrioDocument20 pagesVibrioDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet