Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TC Material - 634
Uploaded by
Mouse LALA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageOriginal Title
TC material - 634
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageTC Material - 634
Uploaded by
Mouse LALACopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
from NDBs, radials from VHF/UHF aids, centre lines of designated airways, air
routes, localizers and DME distances.
Deviation. The angle through which the compass needle is deflected from magnetic
north due to the influence of magnetic fields in the airplane.
Discrete Frequency. A separate radio frequency for use in direct pilot/controller
communications in ATC which reduces frequency congestion by controlling the
number of aircraft operating on the frequency at any one time.
Displaced Threshold. A threshold that is located at a point on the runway other than
the designated beginning of the runway.
Distance Measuring Equipment (DME). Equipment used to measure in nautical
miles the slant range distance of an aircraft from the DME navigation aid.
Doppler Navigation System. A self contained area navigation system that fixes the
position of an airplane and determines groundspeed by means of radar beams
directed from the aircraft to the ground that measure “Doppler Shift”.
DUATS (Direct User Access Terminal System). A computer based system provided
by a vendor to pilots and other operational personnel. It supplies aviation weather
and NOTAM information and provides flight plan filing capability.
Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT). A radio transmitter which operates from
its own power source on 121.5 MHz, or on 121.5 MHz and 243.0 MHz, and is
activated automatically by the g forces experienced in a crash landing.
Empennage. The tail section of an airplane (vertical stabilizer, or fm, horizontal
stabilizer or tail plane, rudder, elevators, and all trimming and control devices).
Equivalent Airspeed (EAS). Calibrated airspeed corrected for compressibility factor.
Expected Further Clearance Time. The time at which it is expected that further
clearance will be issued to an aircraft.
Feathered Propeller. A propeller whose blades have been rotated so that the leading
and trailing edges are nearly parallel with the aircraft flight path to minimize drag
and engine rotation.
Final. Commonly used to mean an aircraft is on the final approach course or is
aligned with a landing area.
Final Approach. That part of an instrument approach procedure from the time an
aircraft has completed the last procedure turn or base turn, or crossed the final
approach fix or point, or intercepted the last track specified for the procedure
until it reaches the missed approach point. In this portion of the procedure,
alignment and descent for landing are accomplished.
Fix. A geographical position determined by visual reference to the surface, or by
reference to one or more radio navaids, or by celestial plotting or by another
navigational device.
Flag/Flag Alarm. A warning device incorporated in certain airborne navigation and
flight instruments to indicate that the instrument is inoperative or that signal
strength is below acceptable values.
Flaps Down Speed. The maximum speed at which the airplane may be flown with
the flaps lowered.
Flight Information Region (FIR). An airspace of defined dimensions extending
upwards from the surface of the earth within which flight information service and
alerting service is provided.
Flight Itinerary. Specified information relating to the intended flight of an aircraft,
that is filed with a responsible person.
Flight Level (FL). An altitude expressed in hundreds of feet indicated on an altimeter
set to 29.92” Hg or 1013.2 hectopascals/ millibars.
You might also like
- Architecture After Modernism - Diane GhirardoDocument10 pagesArchitecture After Modernism - Diane GhirardoCebo DharuNo ratings yet
- APMP Certification Syllabus and Program V3.1 March 2019 PDFDocument20 pagesAPMP Certification Syllabus and Program V3.1 March 2019 PDFMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Aviation - Glossary of TermsDocument36 pagesAviation - Glossary of TermsRoberto Alejandro100% (1)
- Air Navigation FacilitiesDocument8 pagesAir Navigation FacilitiesrutherenceNo ratings yet
- SAP MM ReportsDocument59 pagesSAP MM Reportssaprajpal95% (21)
- Radiotelephony ConspectusDocument61 pagesRadiotelephony ConspectusEmilia EivNo ratings yet
- UNA Phraseology Radiotelephony GlossaryDocument4 pagesUNA Phraseology Radiotelephony GlossaryJackson XavierNo ratings yet
- TC Material - 639Document1 pageTC Material - 639Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- TC Material - 635Document1 pageTC Material - 635Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- TC Material - 631Document1 pageTC Material - 631Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- Air Traffic Control Important DefinitionsDocument4 pagesAir Traffic Control Important DefinitionsNithya MohanNo ratings yet
- Acrobatic Flight. Manoeuvres: DefinitionsDocument27 pagesAcrobatic Flight. Manoeuvres: DefinitionsArslanKhanNo ratings yet
- TC Material - 637Document1 pageTC Material - 637Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- TC Material - 630Document1 pageTC Material - 630Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- TC Material - 641Document1 pageTC Material - 641Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- TC Material - 633Document1 pageTC Material - 633Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- OpDocument29 pagesOpGhino San DiegoNo ratings yet
- Aviation GlossariesDocument11 pagesAviation GlossariesramiiijavedNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrical & Electronic Systems What Is Avionics?: ADF DME EAT EfisDocument8 pagesAircraft Electrical & Electronic Systems What Is Avionics?: ADF DME EAT EfisArslanKhanNo ratings yet
- Avionics Systems Drive Military Aircraft Cost and CapabilityDocument73 pagesAvionics Systems Drive Military Aircraft Cost and CapabilityArif Abdul Rahman100% (1)
- General Definitions and Terms for AerodromesDocument8 pagesGeneral Definitions and Terms for AerodromesChandra SekaranNo ratings yet
- The Instrument Landing System (ILS) Is ADocument10 pagesThe Instrument Landing System (ILS) Is Ahareeshraj100% (1)
- Glossary: REF REF SODocument12 pagesGlossary: REF REF SOWachirarat Ton ChomchomeNo ratings yet
- FAA H 8083 16B GlossaryDocument12 pagesFAA H 8083 16B GlossaryVilmaNo ratings yet
- TC Material - 642Document1 pageTC Material - 642Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- I. AircraftDocument120 pagesI. AircraftMaria KristianiNo ratings yet
- Classifying Airspace and Understanding Navigation AidsDocument31 pagesClassifying Airspace and Understanding Navigation AidsLolaNo ratings yet
- Control Definitions for ApproachDocument10 pagesControl Definitions for ApproachRochelle Mirasol AquinoNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Aeronautical TermsDocument4 pagesGlossary of Aeronautical Termsapi-321359763No ratings yet
- Fom Lec 03Document12 pagesFom Lec 03Uswa FiazNo ratings yet
- Instrument Approach: ILS MLS PAR Military GPS Waas Egnos Laas Jpals GCADocument8 pagesInstrument Approach: ILS MLS PAR Military GPS Waas Egnos Laas Jpals GCASheikh Mahmud HabibNo ratings yet
- Avionics - Afzal SirDocument29 pagesAvionics - Afzal SirgultusundoriNo ratings yet
- ATCDocument11 pagesATCAbdullah Attie100% (2)
- Aircraft Navigation Equipment GuideDocument30 pagesAircraft Navigation Equipment GuideSahala Rgk50% (2)
- Communications 1delDocument80 pagesCommunications 1deljkranjc34No ratings yet
- TC Material - 638Document1 pageTC Material - 638Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- Flight Rules: Orderly ExpeditiousDocument8 pagesFlight Rules: Orderly ExpeditiousJobelle Gonzales De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Navigation Ppt 2Document19 pagesNavigation Ppt 2Ethan PintoNo ratings yet
- Aviation Electronics Acronyms and TermsDocument13 pagesAviation Electronics Acronyms and TermsCarlos Peroni Jr.No ratings yet
- D M E DME: Istance Easuring QuipmentDocument17 pagesD M E DME: Istance Easuring QuipmentIan Edianel MagdaugNo ratings yet
- Approach ManualDocument15 pagesApproach ManualMircea PopNo ratings yet
- TC Material - 636Document1 pageTC Material - 636Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- Aviation TerminologisDocument12 pagesAviation Terminologisdionicio perezNo ratings yet
- Air Traffic Control Common PhraseologyDocument8 pagesAir Traffic Control Common PhraseologycharlesmatosNo ratings yet
- Air Traffic Control Lecture-1Document37 pagesAir Traffic Control Lecture-1azhar ishaq100% (1)
- Airport Engineering - 6 - Air Traffic Control (ATC)Document35 pagesAirport Engineering - 6 - Air Traffic Control (ATC)raghav VarmaNo ratings yet
- PARDocument3 pagesPAREugenia Gina FerminNo ratings yet
- Terminal Procedures PublicationDocument18 pagesTerminal Procedures PublicationAlejandro PattNo ratings yet
- Avionics LectureDocument29 pagesAvionics LecturegultusundoriNo ratings yet
- TC Material - 632Document1 pageTC Material - 632Mouse LALANo ratings yet
- DME (Distance Measuring Equipment) : Dme Components and OperationsDocument2 pagesDME (Distance Measuring Equipment) : Dme Components and Operationsmuhammad hassan sheikh100% (2)
- Distance Measuring EquipmentDocument13 pagesDistance Measuring EquipmentJb Basco100% (1)
- UNIT 2 - Mac - VocabularyDocument2 pagesUNIT 2 - Mac - VocabularyfasadpifpafNo ratings yet
- Capt. S R Meena's guide to all weather operationsDocument86 pagesCapt. S R Meena's guide to all weather operationsOmshree PatelNo ratings yet
- 1988 and Regulation 11.245 of The Civil Aviation Safety Regulations 1998 and SubsectionDocument103 pages1988 and Regulation 11.245 of The Civil Aviation Safety Regulations 1998 and Subsectiongreg mNo ratings yet
- Internship at AAI BarodaDocument24 pagesInternship at AAI BarodaShubham Sehrawat100% (1)
- Automatic Dependent Surveillance - BroadcastDocument7 pagesAutomatic Dependent Surveillance - Broadcastgrae16No ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument18 pagesDefinitionsabdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Avionics: - Unit IV: Electronic Flight Instrument System - Deepak Gaur - Assistant Professor - MvjceDocument66 pagesAvionics: - Unit IV: Electronic Flight Instrument System - Deepak Gaur - Assistant Professor - MvjceNagaraja BhagavNo ratings yet
- The Samora Machel and Helderberg Conspiracies and Other South African Air AccidentsFrom EverandThe Samora Machel and Helderberg Conspiracies and Other South African Air AccidentsNo ratings yet
- VFR and IFR Flight Training: Need to Know AcronymsFrom EverandVFR and IFR Flight Training: Need to Know AcronymsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- SAP HCM - Default Wage Types - Info Type 0008Document6 pagesSAP HCM - Default Wage Types - Info Type 0008cjherrera2No ratings yet
- Hps40 Tech Doc ScreenDocument20 pagesHps40 Tech Doc ScreenAnonymous oyUAtpKNo ratings yet
- Al-Jahiz (781-869) : ZoologyDocument25 pagesAl-Jahiz (781-869) : ZoologyJA QuibzNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog Encoders en IM0038143Document788 pagesProduct Catalog Encoders en IM0038143Eric GarciaNo ratings yet
- Business English 2, (ML, PI, U6, C3)Document2 pagesBusiness English 2, (ML, PI, U6, C3)Ben RhysNo ratings yet
- Teaching English as a Second Language in Four PhasesDocument18 pagesTeaching English as a Second Language in Four PhasesVia Johnson100% (1)
- Organic Vapour List PDFDocument1 pageOrganic Vapour List PDFDrGurkirpal Singh MarwahNo ratings yet
- Abbadvant 800 XaDocument9 pagesAbbadvant 800 XaAlexNo ratings yet
- Arnica The Miracle Remedy - Case RecordsDocument4 pagesArnica The Miracle Remedy - Case Recordskaravi schiniasNo ratings yet
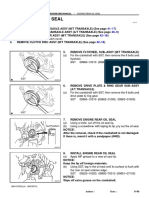
- Engine Rear Oil Seal PDFDocument3 pagesEngine Rear Oil Seal PDFDIEGONo ratings yet
- Reference Interval For CeruloplasminDocument3 pagesReference Interval For CeruloplasminGawri AbeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Research and DesignDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Research and Designalvin salesNo ratings yet
- Dimension ReductionDocument15 pagesDimension ReductionShreyas VaradkarNo ratings yet
- Samsung (UH5003-SEA) BN68-06750E-01ENG-0812Document2 pagesSamsung (UH5003-SEA) BN68-06750E-01ENG-0812asohas77No ratings yet
- Calendula EbookDocument12 pagesCalendula EbookCeciliaNo ratings yet
- Nad C541iDocument37 pagesNad C541iapi-3837207No ratings yet
- 00001Document20 pages00001Maggie ZhuNo ratings yet
- Panasonic SA-HT878Document82 pagesPanasonic SA-HT878immortalwombatNo ratings yet
- Applsci 13 13339Document25 pagesApplsci 13 13339ambroseoryem1No ratings yet
- Ebola Research ProposalDocument10 pagesEbola Research ProposalChege AmbroseNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes 501-601Document27 pagesManual de Partes 501-601camilo bautista100% (2)
- 12 Orpic Safety Rules Managers May 17 RevDocument36 pages12 Orpic Safety Rules Managers May 17 RevGordon Longforgan100% (3)
- H2 Physic 2010 A Level SolutionsDocument32 pagesH2 Physic 2010 A Level Solutionsonnoez50% (4)
- YearBook2016 2017Document212 pagesYearBook2016 2017Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Decision Flow Chart: For Suspicious PackagesDocument2 pagesDecision Flow Chart: For Suspicious PackagesHervian LanangNo ratings yet
- Trailers Parts - Rocket Trailers - Suspension & FastenersDocument24 pagesTrailers Parts - Rocket Trailers - Suspension & FastenersRocket TrailersNo ratings yet
- Confidentiality Agreement With Undertaking and WaiverDocument1 pageConfidentiality Agreement With Undertaking and WaiverreddNo ratings yet