Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formula Sheet Gas Laws
Uploaded by
khbaltazarr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThis document lists several gas laws and their equations, including Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, Gay-Lussac's Law, the Combined Gas Law, Avogadro's Law, the Ideal Gas Law, Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure, and Graham's Law. It also provides conversion factors between different pressure and temperature units. The gas laws describe the behavior of gases like pressure, volume, temperature, number of moles, and mass.
Original Description:
Original Title
FORMULA-SHEET-GAS-LAWS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document lists several gas laws and their equations, including Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, Gay-Lussac's Law, the Combined Gas Law, Avogadro's Law, the Ideal Gas Law, Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure, and Graham's Law. It also provides conversion factors between different pressure and temperature units. The gas laws describe the behavior of gases like pressure, volume, temperature, number of moles, and mass.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageFormula Sheet Gas Laws
Uploaded by
khbaltazarrThis document lists several gas laws and their equations, including Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, Gay-Lussac's Law, the Combined Gas Law, Avogadro's Law, the Ideal Gas Law, Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure, and Graham's Law. It also provides conversion factors between different pressure and temperature units. The gas laws describe the behavior of gases like pressure, volume, temperature, number of moles, and mass.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
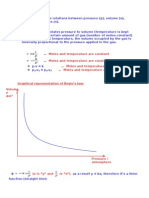
Gas Law Equations Conversion Factors
Boyle’s Law: P1V1 = P2V2 1.00 atm = 101.325 kPa
Charles’ Law: V1T2 = V2T1 1.00 atm = 760 mmHg
Gay-Lussac’s Law: P1T2 = P2T1 1 mL = 1 cm3
Combined Gas Law: P1V1T2 = P2V2T1 9
TF = (5 𝑇𝑐) + 32
Avogadro’s Law: V1n2 = V2n1 5
TC = 9(TF – 32)
Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT
STP Values
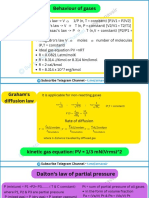
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure:
P = 1.00 atm
- Ptotal = PA + PB + PC
- Ppartial = X(Ptotal) T = 273.15 K
- X = mole of gas/total mole of gases V = 22.4 L
Gas Stoich: (1) Mass Relation → (2) PV = nRT
𝑅1 𝑀𝑀2
Graham’s Law: 𝑅2 = √𝑀𝑀1
Gas Law Equations Conversion Factors
Boyle’s Law: P1V1 = P2V2 1.00 atm = 101.325 kPa
Charles’ Law: V1T2 = V2T1 1.00 atm = 760 mmHg
Gay-Lussac’s Law: P1T2 = P2T1 1 mL = 1 cm3
Combined Gas Law: P1V1T2 = P2V2T1 9
TF = (5 𝑇𝑐) + 32
Avogadro’s Law: V1n2 = V2n1 5
TC = 9(TF – 32)
Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT
STP Values
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure:
P = 1.00 atm
- Ptotal = PA + PB + PC
- Ppartial = X(Ptotal) T = 273.15 K
- X = mole of gas/total mole of gases V = 22.4 L
Gas Stoich: (1) Mass Relation → (2) PV = nRT
𝑅1 𝑀𝑀2
Graham’s Law: 𝑅2 = √𝑀𝑀1
You might also like
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesThermodynamics Cheat SheetNitin Sharma0% (1)
- Gas LawsDocument31 pagesGas Lawsapi-546066323No ratings yet
- Atkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaDocument36 pagesAtkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaIvy JoyceNo ratings yet
- Gas Behaviour EOSDocument59 pagesGas Behaviour EOSMurugavel ChandranNo ratings yet
- Compressor Handbook 2Document7 pagesCompressor Handbook 2mssj87No ratings yet
- Study Guide Gas LawsDocument3 pagesStudy Guide Gas LawsAdamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Technician Review GasesDocument53 pagesChemical Technician Review GasesJasonTenebrosoNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument34 pagesGasesPaul Jeremiah Serrano NarvaezNo ratings yet
- 5.0 States of MatterDocument106 pages5.0 States of MatterTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Cheat SheetDocument1 pageGas Laws Cheat SheetJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- Gases and Their Properties: Exercises, Examples, and BOLD Numbered ProblemsDocument106 pagesGases and Their Properties: Exercises, Examples, and BOLD Numbered ProblemsMia YukimuraNo ratings yet
- 1-Ideal Gas LectureDocument60 pages1-Ideal Gas LecturemahmoudNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 GasesDocument78 pagesLecture 5 GasesHiep NguyenNo ratings yet
- Atkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaDocument37 pagesAtkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaAmalia AnggreiniNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Cheat SheetDocument1 pageGas Laws Cheat SheetWeljun GallardoNo ratings yet
- Aula 5Document46 pagesAula 5hannibal_12No ratings yet
- Gaseous StateDocument51 pagesGaseous StateSal Sabeela RahmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 States of MatterDocument43 pagesTopic 4 States of MatterJowyn SeetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Gases PDFDocument49 pagesChapter 5 Gases PDFAbou WalidNo ratings yet
- ChapterII - GasesDocument40 pagesChapterII - Gasesjumanahelmy12No ratings yet
- 12 GasesDocument34 pages12 Gasesmuhamadhuzaifa1754No ratings yet
- Chapter10 NotesDocument33 pagesChapter10 NotesHeather WrightNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips - Chapter 5 The Gaseous StateDocument18 pagesSilo - Tips - Chapter 5 The Gaseous StateJerich Ivan PaalisboNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws:: P V K VDocument18 pagesGas Laws:: P V K VFarah Zu'biNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: CHEM140 February 2, 2005Document33 pagesGas Laws: CHEM140 February 2, 2005elokflhNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws PPTDocument41 pagesGas Laws PPTIsabelle OdenbachNo ratings yet
- Gas LawDocument14 pagesGas LawRoszelan Majid100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3Joshua EspirituNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Without AudioDocument17 pagesLecture 2 Without AudioMahmoud shendyNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Gases StudentDocument48 pagesCH 10 Gases StudentTrọng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CHM131 - Chapter 6 - The Gaseous StateDocument37 pagesCHM131 - Chapter 6 - The Gaseous StateNotes NotesNo ratings yet
- Gas LawDocument37 pagesGas LawSupasinee RNo ratings yet
- Gases: Course Name: Chemistry 101 Course CodeDocument28 pagesGases: Course Name: Chemistry 101 Course CodeHeartcheNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas Law 12-3 FFF 09Document9 pagesCombined Gas Law 12-3 FFF 09FFF100% (2)
- Sifat-Sifat Gas (Properties of Gases) : Kimia Dasar I (CH1101)Document67 pagesSifat-Sifat Gas (Properties of Gases) : Kimia Dasar I (CH1101)abid naufalNo ratings yet
- 6 - ch5 Aa 0Document49 pages6 - ch5 Aa 0Edlyn RamirezNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Measurable Properties of Gases: CompositionDocument4 pagesAtmosphere Measurable Properties of Gases: CompositionjenduekieNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08 GasesDocument42 pagesLecture 08 GasesDuy Do MinhNo ratings yet
- Gaseous StateDocument3 pagesGaseous StateSiya ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Notes Solutions Chapter 05Document22 pagesNotes Solutions Chapter 05steveislaryNo ratings yet
- 1st Law of ThermodynamicsDocument95 pages1st Law of ThermodynamicsMARUMO_LEVYNo ratings yet
- Lecture28 f05Document30 pagesLecture28 f05Awaawa D orianoNo ratings yet
- Module 11 - The Gas PhaseDocument15 pagesModule 11 - The Gas PhaseAna Maria Millan RinconNo ratings yet
- GAS LAWS Markup PDFDocument30 pagesGAS LAWS Markup PDFIsmaNo ratings yet
- Kimia Teknik TS Ke-5 (07102013)Document28 pagesKimia Teknik TS Ke-5 (07102013)Radja NurNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document50 pagesCH 5Paul ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Reaksi GasDocument19 pagesReaksi Gaszainal mustaqimNo ratings yet
- Che 254 (Midsem)Document6 pagesChe 254 (Midsem)obumaradonaNo ratings yet
- Chap 03 - Gaseous State MindNote Class 11th by Arnav SirDocument5 pagesChap 03 - Gaseous State MindNote Class 11th by Arnav SirSmeet MehtaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Cheat Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesThermodynamics Cheat Sheet PDFImranzo HsnNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesThermodynamics Cheat SheetBrian TeaNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry EquationsDocument2 pagesPhysical Chemistry Equationsvixi_hNo ratings yet
- Gases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783Document34 pagesGases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783ade dosmariaNo ratings yet
- Gases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783Document34 pagesGases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783ade dosmariaNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Cheat Sheet 2012Document1 pageGas Laws Cheat Sheet 2012Judy Ann Binguan PahayacNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument11 pagesProperties of GasessalasineNo ratings yet
- Gas TheoryDocument65 pagesGas TheoryNicole OssaNo ratings yet
- Extra Information For Chem 340 Exams:: Transport Temperature (T), Activity/concentration (A) W RT JDocument4 pagesExtra Information For Chem 340 Exams:: Transport Temperature (T), Activity/concentration (A) W RT JZevano C. SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsNo ratings yet