Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gas Laws Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
John Cailen Barceñas IIOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gas Laws Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
John Cailen Barceñas IICopyright:
Available Formats
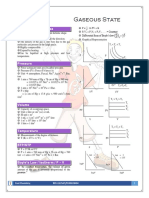
GAS LAWS CHEAT SHEET
Gas Variables and Common Units
Pressure (P) Equivalent
• atm (atmosphere)
1atm = 760torr
• torr or mmHg
1atm = 101325Pa
• Pa
1bar = 105Pa
• bar
Volume (V) Equivalent
• L (dm3)
1L = 1000mL
• kL (m3)
1kL = 1000L
• mL (cm3)
Temperature (T) Conversion
• °C (Celsius) 9
°C = ( °F + 32)
• °F (Fahrenheit) 5
• K (Kelvin)* K = °C + 273.15
*all calculations involving temperature must use K
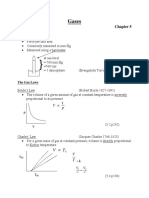
Gas Laws
Ideal Gas Eq’n (IGE) IGE, Rewritten
PV
PV = nRT =R
nT
Boyle’s Law Charles’ Law
V1 V2
P1 V1 = P2 V2 =
T1 T2
Gay-Lussac’s Law Avogadro’s Law
P1 P2 V1 V2
= =
T1 T2 n1 n2
Combined Gas Law
P1 V1 P2 V2
=
T1 T2
Dalton’s Law Amagat’s Law
PT = P1 + P2 + ⋯ + Pn VT = V1 + V2 + ⋯ + Vn
Important Quantities
• Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP):
0°C, 1 atm (pre-1984) 0°C, 1 bar (1984 onward)
• Volume of 1 mole of gas at STP (molar volume):
22.414 (0°C, 1 atm) 22.711L (0°C, 1 bar)
• Ideal Gas Constant (R):
L ⋅ atm L ⋅ mmHg L ⋅ kPa
0.08206 or 62.36 or 8.314
mol ⋅ K mol ⋅ K mol ⋅ K
You might also like
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- GAS LAWS Powerpoint Good OneDocument45 pagesGAS LAWS Powerpoint Good OneLerie Lou R. Penarroyo60% (5)
- CHM 121 - Lecture Note 7 - Kinetic Theory of Gases, Gas Laws, EquationsDocument35 pagesCHM 121 - Lecture Note 7 - Kinetic Theory of Gases, Gas Laws, Equationssomide kayodeNo ratings yet
- Atkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaDocument36 pagesAtkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaIvy JoyceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Technician Review GasesDocument53 pagesChemical Technician Review GasesJasonTenebrosoNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 4 ReviewerDocument8 pagesScience Quarter 4 Reviewercali anna75% (4)
- GasesDocument34 pagesGasesPaul Jeremiah Serrano NarvaezNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument101 pagesGASESdwyquishNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Cheat SheetDocument1 pageGas Laws Cheat SheetWeljun GallardoNo ratings yet
- 1-Ideal Gas LectureDocument60 pages1-Ideal Gas LecturemahmoudNo ratings yet
- Gas (3 Files Merged)Document76 pagesGas (3 Files Merged)Mashael 7No ratings yet
- 6 - ch5 Aa 0Document49 pages6 - ch5 Aa 0Edlyn RamirezNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document50 pagesCH 5Paul ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 GasesDocument30 pagesChapter 13 GasesGwen100% (1)
- Ch. 12 - Gases: II. The Gas Laws Boyles Charles Gay-LussacDocument22 pagesCh. 12 - Gases: II. The Gas Laws Boyles Charles Gay-LussacEmmie Denisse ApistarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08 GasesDocument42 pagesLecture 08 GasesDuy Do MinhNo ratings yet
- Gas Law: Ref: Basic Chemistry, TimberlakeDocument22 pagesGas Law: Ref: Basic Chemistry, TimberlakeSofeaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Gases PDFDocument49 pagesChapter 5 Gases PDFAbou WalidNo ratings yet
- Chem0861 GasLawProblemsDocument3 pagesChem0861 GasLawProblemsHavenNo ratings yet
- GAS LAWS Markup PDFDocument30 pagesGAS LAWS Markup PDFIsmaNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument65 pagesGasesjNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips - Chapter 5 The Gaseous StateDocument18 pagesSilo - Tips - Chapter 5 The Gaseous StateJerich Ivan PaalisboNo ratings yet
- Gases: 5/75 Questions in Multiple Choice Almost Every Year in Free Response SectionDocument53 pagesGases: 5/75 Questions in Multiple Choice Almost Every Year in Free Response SectionZenobia Joy VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Kimia Teknik TS Ke-5 (07102013)Document28 pagesKimia Teknik TS Ke-5 (07102013)Radja NurNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Cheat Sheet 2012Document1 pageGas Laws Cheat Sheet 2012Judy Ann Binguan PahayacNo ratings yet
- Gas LawDocument14 pagesGas LawRoszelan Majid100% (1)
- Atkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaDocument37 pagesAtkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaAmalia AnggreiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 (Shorten Version) Fall 2022Document3 pagesChapter 11 (Shorten Version) Fall 2022Nguyễn Đức ÝNo ratings yet
- 5.0 States of MatterDocument106 pages5.0 States of MatterTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- Gases: Course Name: Chemistry 101 Course CodeDocument28 pagesGases: Course Name: Chemistry 101 Course CodeHeartcheNo ratings yet
- ChE ThermodynamicsDocument49 pagesChE ThermodynamicsMiguel FelisildaNo ratings yet
- Chap 6: States of Matter:: Gases, Liquids, and Solids in Your WorldDocument22 pagesChap 6: States of Matter:: Gases, Liquids, and Solids in Your WorldyogurtkumarNo ratings yet
- Kimia Dasar Bab 5 GasDocument42 pagesKimia Dasar Bab 5 GasRiko KedikNo ratings yet
- Mjfa - Chemistry Reviewer (Q2 Exams)Document4 pagesMjfa - Chemistry Reviewer (Q2 Exams)who am iNo ratings yet
- Student CH 13 GasesDocument51 pagesStudent CH 13 GasesFernando Hernández VenegasNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Measurable Properties of Gases: CompositionDocument4 pagesAtmosphere Measurable Properties of Gases: CompositionjenduekieNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 States of MatterDocument43 pagesTopic 4 States of MatterJowyn SeetNo ratings yet
- Student CH 13 GasesDocument51 pagesStudent CH 13 GasesMichael MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws PPTDocument41 pagesGas Laws PPTIsabelle OdenbachNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 GasessamNo ratings yet
- BSG 104 Gas LawsDocument35 pagesBSG 104 Gas LawsCJ DRBNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 The Properties of Gases SP23Document56 pagesChap 1 The Properties of Gases SP23iB13eNo ratings yet
- Chem 110, Chapter 5 PDFDocument61 pagesChem 110, Chapter 5 PDFنواف السلميNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Gas LawsDocument1 pageFormula Sheet Gas LawskhbaltazarrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesDocument42 pagesChapter 5 GasesPerlita MorongNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument6 pagesGas LawskimNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law: PVNRT - Notebook November 02, 2015Document8 pagesIdeal Gas Law: PVNRT - Notebook November 02, 2015Faith AsdfNo ratings yet
- CHM131 - Chapter 5 - The Gases StateDocument54 pagesCHM131 - Chapter 5 - The Gases StateLeo PietroNo ratings yet
- 12 GasesDocument34 pages12 Gasesmuhamadhuzaifa1754No ratings yet
- Gas Laws Ws PDFDocument6 pagesGas Laws Ws PDFJulia Franchesca BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 - Ideal - GasDocument26 pagesModule 3.1 - Ideal - GasMax100% (1)
- CH 10 Gas Math Summary (p8)Document1 pageCH 10 Gas Math Summary (p8)Edison UsmaNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesScience ReviewerPamee BautistaNo ratings yet
- Gaseous State: Characteristics of GasDocument10 pagesGaseous State: Characteristics of GasAYUSH GOSWAMINo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 560982adad40bDocument5 pagesChapter 3 560982adad40bJimson MasculinoNo ratings yet
- Reaksi GasDocument19 pagesReaksi Gaszainal mustaqimNo ratings yet
- Chm131 - Chapter 5 - The Gases State 2Document50 pagesChm131 - Chapter 5 - The Gases State 2asyhqnaNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument24 pagesIdeal Gastechno studioNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Interview QuesDocument2 pagesInterview QuesJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- Self Regulated Learning HAND OUTDocument4 pagesSelf Regulated Learning HAND OUTJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- Ace Mil Q4Document1 pageAce Mil Q4John Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- GAS LawDocument50 pagesGAS LawJohn Cailen Barceñas II100% (1)
- Kant's Core IdeasDocument4 pagesKant's Core IdeasJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- Types of RocksDocument19 pagesTypes of RocksJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- NSTP001 M6 Drug Education 2022 RevisionDocument31 pagesNSTP001 M6 Drug Education 2022 RevisionJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet