Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CONTRACTS - Tondo
Uploaded by
Tondo JericaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CONTRACTS - Tondo
Uploaded by
Tondo JericaCopyright:
Available Formats
CONTRACTS
What is a contract?
A contract is a meeting of minds between two parties
whereby one binds himself, with respect to the other, to give
something or to render some service.
Contract vs Obligation
CONTRACTS OBLIGATION
One of the sources of Juridical necessity to give to
obligation. do or not to do.
Contract vs Other Sources Obligations
CONTRACT OTHER SOURCES OF
OBLIGATIONS (law, quasi-
contracts, delict, quasi-delict)
Will of the parties Laws
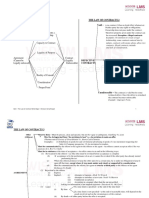
Essential Elements of a Contract
1. Object
2. Cause or consideration
3. Consent
Object - GENERAL RULE: All things and services may be
the object of contract.
EXCEPTIONS:
Things outside the commerce of man (inalienable lands)
In transmissible rights (right to vote)
Future inheritance
Services which are contrary to law, morals, good customs,
public order or public policy (dangerous drugs,
endangered species)
Impossible things or services (ability to fly)
Cause or Consideration - is the essential or more proximate
purpose which moves the contracting parties to enter into the
contract.
What would I get in return?
• Contract of sale – Goods, Payment
• Donation – liberality of the donor
Characteristics of a Contract Consent - is manifested by the meeting of the offer and the
acceptance upon the object and the consideration.
1. Obligatory
2. Mutuality • Consent is essential in a contract. No consent = no
3. Autonomy contract.
4. Relativity
First Requisite of Consent
Obligatory - A contract has the force of law between the The OFFER must be:
contracting parties and should be complied with in good faith.
a) It must be definite (e.g., not negotiable)
Mutuality - The validity and compliance of a contract cannot
b) It must be intentional (not a joke)
be left to the will of one of them. c) It must be complete (all conditions)
Autonomy - Parties may establish such agreements as they d) It must be directed to a person or persons with whom the
offeror intends to enter into a contract except definite
may deem convenient, provided they are not contrary to law,
offers which are not directed to a particular person but to
morals, good customs, public order or public policy.
the public in general
Example of a lawful provision
Counter-Offer - Acceptance of the offer must be definite and
A and B entered into a contract of lease of a 2-story building absolute in character. A qualified acceptance constitutes a
for a period of 5 years. During the duration of the contract, A counter-offer.
will pay B 100,000 per month.
Implied Acceptance - may arise from acts or facts which
Par. 9 of the contract provides for a penalty clause which reveal the intent to accept, such as the consumption of things
states that in case of breach, the breaching party will pay sent to the offeree, or the fact of immediately carrying out the
Php50,000 pesos as liquidated damages. contract offered.
After 3 years, A no longer wanted to continue the lease Withdrawal of offer - Offer may be withdrawn so long as the
agreement. A may does so, provided that she pays B the offeror has no knowledge of the acceptance by the offeree.
amount of Php50,000 as liquidated damages.
Relativity - A contract binds ONLY the contracting parties,
their assigns and heirs.
General Rule: Contracts shall be obligatory, in whatever form
they may have been entered into, provided that all the essential
requisites for their validity are present.
Exceptions:
Offer made to 2 or more persons
1) When law requires that the contract be in a certain
General Rule: Pending acceptance of the offer, the offeror form to be valid;
may perfect a contract over the same thing with another 2) When law requires that the contract be in a certain
form to be enforceable;
person
3) When required to make the contract effective as
Exception: against third parties
Option Contract – one-person (the offeror/promisors) grants Contracts which must appear in WRITING to be VALID.
to another person (the offeree/promisee) the right or privilege
to buy (or to sell) a determinate thing at a fixed price, if he or 1. Donation of real property.
she chooses to do so within an agreed period. 2. Donation of personal property with value exceeding
Php 5,000
Business Advertisements - They are mere invitations to make 3. Sale of piece of land or any interest therein through
an offer, and not definite offers, unless it appears otherwise. an agent
4. Agreements regarding payment of interest in
Advertisements for bidders - are simply invitations to make contracts of loan
proposals, and the advertiser is not bound to accept the highest
and lowest bidder, unless the contrary appears. Contracts which must appear in a PUBLIC
INSTRUMENT (notarized) to be VALID.
Second Requisite of Consent
1. Donation of real property.
2. Parties must possess the necessary legal capacity
2. Partnership where real rights are contributed to the
I. Who are persons incapacitated to give consent?
common fund.
No legal capacity to give consent
a) Minors
Defective Contracts
Exceptions:
1. When the contract is entered into by a minor who VOID OR VOIDABLE RESCISSIBLE UNENFORCEABLE
actively misrepresents his age, not merely INEXISTENT
constructive misrepresentation
2. When it involves sale and delivery of necessities to Do not Valid and Valid and Cannot be enforced
minors produce any enforceable enforceable by a proper action
3. Contracts entered into in behalf of the minor by legal effect until until in court
annulled by rescinded by a
guardians or legal representatives a competent
4. When upon reaching the age of majority, the minor competent court
ratifies the contract. court
b) Insane or demented persons, unless the contract was
entered into during lucid interval. Defect is Defect is Defect is Defect is caused by
It is not necessary that there be a previous declaration of caused by cause by caused by lack of form,
mental incapacity in order that a contract entered into may be lack of vice of injury/damage authority, or
annulled. essential consent; or to either one capacity of both
• Contracts entered into in state of drunkenness or requisites or one of the of the parties parties
illegality or parties to a or to a third
hypnotic spell may be voidable provided that it must impossibility contract is person
be of a degree that obscures completely the faculties a minor
and almost extinguishes the conscious of acts.
Cannot be Can be Need not be Can be ratified
c) Deaf-mute who do not know how to read and write. ratified ratified ratified
Third Requisite of Consent
3. Consent must be intelligent, free, spontaneous and real. Examples:
Vices of consent (Third requisite is not present if consent is
Minor entered into a contract with a person of legal age
vitiated)
- voidable; one of the parties is incapable of giving consent
1. violence
Minor entered into a contract with a person of legal age
2. intimidation
but the object of the contract is food
3. mistake of fact – must be substantial
- valid; the contract involves sale and delivery of necessities to
4. fraud
minors
5. undue influence
Minors entered into a contract.
- unenforceable; both parties are incapable of giving a consent
Forms of a contract
The parent of the minors ratified the contract.
- valid; the defect is cured by ratification
You might also like
- Contracts To LeaseDocument91 pagesContracts To LeaseFCNo ratings yet
- Contracts: General ProvisionsDocument8 pagesContracts: General ProvisionsVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Law On ContractsDocument4 pagesLaw On ContractsRizza OlanoNo ratings yet
- Contracts Basic ConceptsDocument14 pagesContracts Basic ConceptsCory RitaNo ratings yet
- Contract Law Crash CourseDocument9 pagesContract Law Crash CourseJane NgNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ObliconDocument5 pagesReviewer ObliconDion AdalaNo ratings yet
- RFBT 02 - Law On ContractsDocument6 pagesRFBT 02 - Law On ContractsAndrea BannisterNo ratings yet
- Contracts: Definition, Classification, and DistinctionsDocument20 pagesContracts: Definition, Classification, and DistinctionsKyle BandolaNo ratings yet
- General Provisions of ContractsDocument42 pagesGeneral Provisions of ContractsShan Marie RusianaNo ratings yet
- Contracts ObliDocument32 pagesContracts ObliAnsherina FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Obl IconDocument5 pagesObl IconAndrea BathanNo ratings yet
- Sales Week 5 Cases PDFDocument146 pagesSales Week 5 Cases PDFMikee AngelesNo ratings yet
- C. All Contracts Are Agreements But Not All Agreements Are ContractsDocument12 pagesC. All Contracts Are Agreements But Not All Agreements Are ContractsElla Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Essential Requisites of ContractsDocument10 pagesEssential Requisites of ContractsJessica AlbaracinNo ratings yet
- Law of Contract 1 PDFDocument62 pagesLaw of Contract 1 PDFNitesh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Contracts Because They Have To ComplyDocument6 pagesContracts Because They Have To ComplyAnna Biella Dacaymat PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Contracts Ch1 2Document30 pagesContracts Ch1 2Zenna WongNo ratings yet
- RFBT.3602 ContractsDocument13 pagesRFBT.3602 ContractsGrezel Mae ProvidoNo ratings yet
- Contracts OutlineDocument39 pagesContracts OutlinesienaNo ratings yet
- Memory Aid in Contracts PDFDocument9 pagesMemory Aid in Contracts PDFbabyjamskieNo ratings yet
- Law On ContractsDocument21 pagesLaw On ContractsHannah SyNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTSDocument3 pagesCONTRACTSsweetestcitrus13No ratings yet
- Real Estate Law of ContractsDocument3 pagesReal Estate Law of ContractsADRES CUSTCARENo ratings yet
- MGMT 260 CH 9 SLDocument11 pagesMGMT 260 CH 9 SLqhaweseithNo ratings yet
- DisadvantagesDocument6 pagesDisadvantagesAlex MichaelNo ratings yet
- Business LawDocument3 pagesBusiness LawMaria Anselma MuerongNo ratings yet
- PRELIMSDocument8 pagesPRELIMSMay MayNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Notes ContractsDocument10 pagesOblicon Notes ContractskikoNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid-19 On Commercial ContractDocument6 pagesImpact of Covid-19 On Commercial ContractDarshan DhawareNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Notes Business Environment & Legal Aspect of BusinessDocument117 pagesUnit 3 Notes Business Environment & Legal Aspect of BusinesskamaltechnolkoNo ratings yet
- Article 1305: Title Ii. - Contracts Chapter 1 - Contracts, General ProvisionsDocument15 pagesArticle 1305: Title Ii. - Contracts Chapter 1 - Contracts, General ProvisionsBryne SarillanaNo ratings yet
- Unit I: The Indian Contract Act: Introduction To Law & Establishing Contractual RelationshipDocument24 pagesUnit I: The Indian Contract Act: Introduction To Law & Establishing Contractual RelationshipMegha NaNo ratings yet
- Contracts - Chapter 1Document7 pagesContracts - Chapter 1Anne Marieline BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Contracts (Oblicon Reviewer)Document15 pagesContracts (Oblicon Reviewer)Bryan AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Bus. Law SummaryDocument8 pagesBus. Law SummaryJhonalyn MaraonNo ratings yet
- The Law of Contract Mind MapsDocument8 pagesThe Law of Contract Mind MapsSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Contract Is A Meeting of The Minds Between Two Persons Whereby One Binds HimselfDocument8 pagesContract Is A Meeting of The Minds Between Two Persons Whereby One Binds Himselfanon-904259100% (1)
- Contracts I OutlineDocument33 pagesContracts I OutlineSteven FinkNo ratings yet
- Law On ContractDocument14 pagesLaw On ContractcarabaldovinoNo ratings yet
- Sales ReviewerDocument13 pagesSales ReviewerJica GulaNo ratings yet
- Handouts For The Law On ContractsDocument5 pagesHandouts For The Law On ContractsHannah Jane UmbayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3iñigo molineroNo ratings yet
- Objective Theory of Contracts - "An Intention To Enter IntoDocument4 pagesObjective Theory of Contracts - "An Intention To Enter IntoJenny ShenNo ratings yet
- MACALINODocument11 pagesMACALINOChelsea MacalinoNo ratings yet
- RFBT.O 1602.law On Contracts WithanswersDocument42 pagesRFBT.O 1602.law On Contracts WithanswersDanielle Nicole Marquez0% (1)
- Chapter 1. General ProvisionsDocument9 pagesChapter 1. General ProvisionsRose Anne CaringalNo ratings yet
- Sales JMLim 29052020Document96 pagesSales JMLim 29052020Lex TalionisNo ratings yet
- 02 Contracts Contracts Notes Oct 2021 PDFDocument11 pages02 Contracts Contracts Notes Oct 2021 PDFhswjushdjwkwNo ratings yet
- Law On Contracts-1-7Document7 pagesLaw On Contracts-1-7Althea RubinNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Construction ContractDocument109 pagesChapter Three Construction ContractHayelom Tadesse GebreNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Construction ContractDocument109 pagesChapter Three Construction ContractHayelom Tadesse GebreNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS Chapter 1Document17 pagesCONTRACTS Chapter 1LabLab ChattoNo ratings yet
- RFBT.2902 ContractsDocument9 pagesRFBT.2902 Contractslgcainglet07No ratings yet
- Module 6 - ContractsDocument7 pagesModule 6 - ContractsalfortegwenNo ratings yet
- Acbn Task 1+2Document21 pagesAcbn Task 1+2AdelinaPredescuNo ratings yet
- All CL 1-15 Merged With PPT (Vijay)Document685 pagesAll CL 1-15 Merged With PPT (Vijay)kaviyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1brian duelaNo ratings yet
- Pointers For FinalsDocument28 pagesPointers For FinalsJOCIEL JOYCE DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Handout-Pointers in Contracts 1Document13 pagesHandout-Pointers in Contracts 1Janina Frances RuideraNo ratings yet
- Advisory Board ResearchDocument6 pagesAdvisory Board Researcheaw12No ratings yet
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights - United NationsDocument12 pagesUniversal Declaration of Human Rights - United NationsSafdar HussainNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Assessment of Literature Studies and CA LitDocument9 pagesTeaching and Assessment of Literature Studies and CA LitjoshuaalimnayNo ratings yet
- BuildingBotWithWatson PDFDocument248 pagesBuildingBotWithWatson PDFjavaarchNo ratings yet
- 02 - Nature and Role of Science in SocietyDocument10 pages02 - Nature and Role of Science in SocietyMarcos Jose AveNo ratings yet
- Persuasive SpeechDocument2 pagesPersuasive SpeechAngel Zachary RayyanNo ratings yet
- Shalini NaagarDocument2 pagesShalini NaagarAazam AdtechiesNo ratings yet
- Mein Leben Und Streben by May, Karl Friedrich, 1842-1912Document129 pagesMein Leben Und Streben by May, Karl Friedrich, 1842-1912Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- BTCTL 17Document5 pagesBTCTL 17Alvin BenaventeNo ratings yet
- Schemes and Tropes HandoutDocument6 pagesSchemes and Tropes HandoutJohn LukezicNo ratings yet
- Sample DCCM, DLHTM and DCLRDocument38 pagesSample DCCM, DLHTM and DCLREagle100% (5)
- Lista Alumnos Julio 2019123Document74 pagesLista Alumnos Julio 2019123Mateo RomeroNo ratings yet
- SakalDocument33 pagesSakalKaran AsnaniNo ratings yet
- Erotic Massage MasteryDocument61 pagesErotic Massage MasteryChristian Omar Marroquin75% (4)
- Seerat Mujaddid Alf-e-Sani (Urdu)Document518 pagesSeerat Mujaddid Alf-e-Sani (Urdu)Talib Ghaffari100% (12)
- Cns Spectrums: The Clinical Challenges of Akathisia CME Review ArticleDocument16 pagesCns Spectrums: The Clinical Challenges of Akathisia CME Review Articledzakiyah nurul israNo ratings yet
- Overpressure Prediction From PS Seismic DataDocument10 pagesOverpressure Prediction From PS Seismic DataSevinj HumbatovaNo ratings yet
- Rule Against Multiplicity and Child PornoDocument3 pagesRule Against Multiplicity and Child PornoHouston Criminal Lawyer John T. FloydNo ratings yet
- How Death Came To The CityDocument3 pagesHow Death Came To The City789863No ratings yet
- PHNCDocument6 pagesPHNCAmit MangaonkarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1session 2 Performance MGMTDocument38 pagesUnit 1session 2 Performance MGMTMayank TrivediNo ratings yet
- Soal Respi 2010Document41 pagesSoal Respi 2010Joseph ThanaNo ratings yet
- Aswini Expert SystemsDocument37 pagesAswini Expert SystemsKarishma Satheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- PM-KISAN: Details of Eligible and Ineligible FarmersDocument2 pagesPM-KISAN: Details of Eligible and Ineligible Farmerspoun kumarNo ratings yet
- JKSSB Panchayat Secretary Adfar NabiDocument3 pagesJKSSB Panchayat Secretary Adfar NabiSHEIKHXUNINo ratings yet
- Resume - General Manager - Mohit - IIM BDocument3 pagesResume - General Manager - Mohit - IIM BBrexa ManagementNo ratings yet
- Iver Brevik, Olesya Gorbunova and Diego Saez-Gomez - Casimir Effects Near The Big Rip Singularity in Viscous CosmologyDocument7 pagesIver Brevik, Olesya Gorbunova and Diego Saez-Gomez - Casimir Effects Near The Big Rip Singularity in Viscous CosmologyDex30KMNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps PDFDocument208 pagesMind Maps PDFAnonymous 9uu04elNo ratings yet
- What Is Mathematical InvestigationDocument1 pageWhat Is Mathematical Investigationbj mandia100% (1)
- Father Saturnino Urios University Engineering and Technology Program Butuan CityDocument16 pagesFather Saturnino Urios University Engineering and Technology Program Butuan CityTalal SultanNo ratings yet
- Learn the Essentials of Business Law in 15 DaysFrom EverandLearn the Essentials of Business Law in 15 DaysRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Contracts: The Essential Business Desk ReferenceFrom EverandContracts: The Essential Business Desk ReferenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (15)
- The Certified Master Contract AdministratorFrom EverandThe Certified Master Contract AdministratorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Small-Business Guide to Government Contracts: How to Comply with the Key Rules and Regulations . . . and Avoid Terminated Agreements, Fines, or WorseFrom EverandThe Small-Business Guide to Government Contracts: How to Comply with the Key Rules and Regulations . . . and Avoid Terminated Agreements, Fines, or WorseNo ratings yet
- How to Win Your Case In Traffic Court Without a LawyerFrom EverandHow to Win Your Case In Traffic Court Without a LawyerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Digital Technical Theater Simplified: High Tech Lighting, Audio, Video and More on a Low BudgetFrom EverandDigital Technical Theater Simplified: High Tech Lighting, Audio, Video and More on a Low BudgetNo ratings yet
- The Business of Broadway: An Insider's Guide to Working, Producing, and Investing in the World's Greatest Theatre CommunityFrom EverandThe Business of Broadway: An Insider's Guide to Working, Producing, and Investing in the World's Greatest Theatre CommunityNo ratings yet
- Crash Course Business Agreements and ContractsFrom EverandCrash Course Business Agreements and ContractsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Law of Contract Made Simple for LaymenFrom EverandLaw of Contract Made Simple for LaymenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Starting Your Career as a Photo Stylist: A Comprehensive Guide to Photo Shoots, Marketing, Business, Fashion, Wardrobe, Off Figure, Product, Prop, Room Sets, and Food StylingFrom EverandStarting Your Career as a Photo Stylist: A Comprehensive Guide to Photo Shoots, Marketing, Business, Fashion, Wardrobe, Off Figure, Product, Prop, Room Sets, and Food StylingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Win Your Case in Small Claims Court Without a LawyerFrom EverandHow to Win Your Case in Small Claims Court Without a LawyerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Theatrical Design: A Guide to the Basics of Scenic, Costume, and Lighting DesignFrom EverandFundamentals of Theatrical Design: A Guide to the Basics of Scenic, Costume, and Lighting DesignRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Contract Law for Serious Entrepreneurs: Know What the Attorneys KnowFrom EverandContract Law for Serious Entrepreneurs: Know What the Attorneys KnowRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)