Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3 Topic Header
Chapter 3 Topic Header
Uploaded by
woyabayoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3 Topic Header
Chapter 3 Topic Header
Uploaded by
woyabayoCopyright:
Available Formats
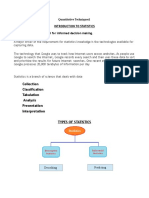
Topic: Chapter 3 Interpreting and Representing Data
Prior Knowledge:
Know how to find Mean, Mode, Median and Range from a data set.
Ability to read data from a table. e.g. Train Timetable.
Familiarity with plotting and coordinate axes
What we will be learning: Red Amber Green Hegarty Tasks Date Reviewed
Stem and Leaf Diagrams 430, 431, 432, 433
Pie Charts 427, 428, 429
Frequency Polygons 441
Time Series 450, 451, 452
Scatter Graphs 453, 454
Line of Best Fit 454
Averages and Range 404, 405, 406, 407, 408,
409, 410, 411, 417, 418,
419, 420, 421
Two-way Tables 422, 423, 424
Key words:
Where it leads:
Real-life graphs, Sampling, Cumulative Frequency, Box Plots, Histograms
Diagrams provide a quick way of comparing data quickly and easily. Scientist can use trends to predict the future
and changes in patterns. Data can also help identify if there is a connection between two sets of data. You can also
use the line of best to predict variables. Recognising misleading graphs can help you avoid being conned by
misleading diagrams or adverts.
Assessment Score:
Summary of assessment and what I need to focus on:
You might also like
- Radiographic Image Analysis e Book 5th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesRadiographic Image Analysis e Book 5th Edition Ebook PDFroy.mula62298% (46)
- Business Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making 9th Edition Black Solutions ManualDocument54 pagesBusiness Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making 9th Edition Black Solutions Manuallokesh verma0% (1)
- Answer - Topic 1.3 Collecting and Describing Data 3Document3 pagesAnswer - Topic 1.3 Collecting and Describing Data 3beepNo ratings yet
- Research II Q4 M2Document14 pagesResearch II Q4 M2dayshara9No ratings yet
- 4.3 Frequency DistributionDocument5 pages4.3 Frequency DistributionNosheen RamzanNo ratings yet
- Standard Text of Standard Primary Citations Supporting CitationsDocument1 pageStandard Text of Standard Primary Citations Supporting Citationssosan khanjaniNo ratings yet
- Wigderson Et Al. - Expander Graphs and Their ApplicationsDocument123 pagesWigderson Et Al. - Expander Graphs and Their ApplicationsPedoPopeNo ratings yet
- Algebra: More Equations and Inequalities: ApterDocument1 pageAlgebra: More Equations and Inequalities: Aptersosan khanjaniNo ratings yet
- Operation Management HomeworkDocument3 pagesOperation Management HomeworkI love JesusNo ratings yet
- Monte Carlo Analysis in Excel A Design Tool For The Component Engineer Chuck Johnson 24 January 2014Document11 pagesMonte Carlo Analysis in Excel A Design Tool For The Component Engineer Chuck Johnson 24 January 2014AMB SpainNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - Result and DiscussionDocument16 pagesGroup 7 - Result and DiscussionTari AftariniNo ratings yet
- PP Ix Unit 2 Chap 7 Trigo and 8Document1 pagePP Ix Unit 2 Chap 7 Trigo and 8Daniel M. MartinNo ratings yet
- Front Page Report CorrectDocument9 pagesFront Page Report CorrectselbalNo ratings yet
- Book 2.0 - PythonDocument143 pagesBook 2.0 - PythonShiva YadandlaNo ratings yet
- JuliaPro v0.6.4.1 Package API ManualDocument497 pagesJuliaPro v0.6.4.1 Package API ManualEduardo Henrique de Sousa SalvinoNo ratings yet
- Guide To Maths For ScientistsDocument67 pagesGuide To Maths For ScientistsWisdom PhanganNo ratings yet
- Robust Motion Estimation Using Trajectory Spectrum Learning: Application To Aortic and Mitral Valve Modeling From 4D TEEDocument9 pagesRobust Motion Estimation Using Trajectory Spectrum Learning: Application To Aortic and Mitral Valve Modeling From 4D TEEherusyahputraNo ratings yet
- Business Research - Chap 1 (Cont)Document2 pagesBusiness Research - Chap 1 (Cont)Nhi HoNo ratings yet
- 21 Ejs1881Document42 pages21 Ejs1881Leonardo MeloNo ratings yet
- NITK-Unit-1-Lecture-1-Graphical Method and Data RepresentationDocument10 pagesNITK-Unit-1-Lecture-1-Graphical Method and Data RepresentationAvinash RNo ratings yet
- Unit 8D Draft 1Document7 pagesUnit 8D Draft 1Shamsul ArifinNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 2: Analytical Methods of Data RepresentationDocument27 pagesLecture # 2: Analytical Methods of Data Representationmuhammad aifNo ratings yet
- 4 Research Findings: 4.1frequency AnalysisDocument12 pages4 Research Findings: 4.1frequency AnalysisHaseeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Course Name Course Description Number of Units (Lec/Lab) Pre-Requisite Co-RequisiteDocument5 pagesCourse Name Course Description Number of Units (Lec/Lab) Pre-Requisite Co-RequisiteShane NakhuiNo ratings yet
- Result and Discussion Group 7Document15 pagesResult and Discussion Group 7Tari AftariniNo ratings yet
- Analisa Dan Interpretasi DataDocument108 pagesAnalisa Dan Interpretasi Datagunawan sadhewoNo ratings yet
- S2 Math ReadingDocument17 pagesS2 Math ReadingG WNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Raster Data Model: Box 4.1 Rules in Determining A Categorical Cell ValueDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Raster Data Model: Box 4.1 Rules in Determining A Categorical Cell ValueMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Measures of PositionDocument18 pagesMeasures of PositionEMILL ASUNCIONNo ratings yet
- Stat Lesson 2 Presentation of DataDocument8 pagesStat Lesson 2 Presentation of DataPrecious CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Time SeriesDocument50 pagesTime Seriesmkalidas2006No ratings yet
- Stellar Data Classification Using SVM With Wavelet TransformatioDocument6 pagesStellar Data Classification Using SVM With Wavelet TransformatioDRScienceNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Frequency Distribution and Graphical Presentation: StructureDocument21 pagesUnit 4 Frequency Distribution and Graphical Presentation: StructuremanishNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Sample PagesDocument35 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Sample Pagesdeepti goelNo ratings yet
- Matrix Methods MainDocument156 pagesMatrix Methods MainMelissa Marie HernandezNo ratings yet
- 3... A Multi-Objective ILP Formulation For WDM NetworksDocument67 pages3... A Multi-Objective ILP Formulation For WDM NetworksnabinNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH METHODOLOGY - Processing and Analysis of DataDocument21 pagesRESEARCH METHODOLOGY - Processing and Analysis of DataMathematics StatisticsNo ratings yet
- 8 The Role of Aperiodic Order in Science and TechnologyDocument46 pages8 The Role of Aperiodic Order in Science and TechnologyCarlinhos Queda D'águaNo ratings yet
- Web Search Algorithms and PageRankDocument101 pagesWeb Search Algorithms and PageRankCeornea Paula100% (1)
- Gene FindingDocument5 pagesGene FindingVineetha Mary IpeNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry - 1Document15 pagesCoordinate Geometry - 1BHANUNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making 9th Edition Black Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesBusiness Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making 9th Edition Black Solutions ManualKevinSandovalitreNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2Hitarth ChughNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document30 pagesUnit 2brm1shubhaNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-006Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-006dr.kungNo ratings yet
- 2DataGrouping CentralTendencyDocument49 pages2DataGrouping CentralTendencySONALI MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Table: Joint Coordinates Joint Coordsys Coordtype Xorr Y Z SpecialjtDocument5 pagesTable: Joint Coordinates Joint Coordsys Coordtype Xorr Y Z SpecialjterikavasquezNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1: Abhishek ShringiDocument19 pagesAssignment-1: Abhishek ShringiFranklin GarysonNo ratings yet
- MODULE IN STATISTICS Frequency Distribution and GraphDocument13 pagesMODULE IN STATISTICS Frequency Distribution and GraphFarah Mae Mosquite-GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Easy Statistics For Food Science With R PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Easy Statistics For Food Science With R PDFjuan.starkey551100% (21)
- Offline Sorter Data SheetDocument2 pagesOffline Sorter Data SheetjhaebioNo ratings yet
- JuliaPro v0.6.2.1 Package API ManualDocument480 pagesJuliaPro v0.6.2.1 Package API ManualCapitan TorpedoNo ratings yet
- QT1 Pre MidDocument30 pagesQT1 Pre MidmatharajeshNo ratings yet
- 2 Frequency Distribution and GraphsDocument4 pages2 Frequency Distribution and GraphsJay SerdonNo ratings yet
- Kla Maths Investigation PatternDocument6 pagesKla Maths Investigation PatternOliver Gabaon GalimbaNo ratings yet
- Probability, Statistics and Queuing Theory: January 2009Document3 pagesProbability, Statistics and Queuing Theory: January 2009sajiczNo ratings yet
- © CFA Institute. For Candidate Use Only. Not For DistributionDocument1 page© CFA Institute. For Candidate Use Only. Not For DistributionhbwdfebdeguNo ratings yet
- Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics The Mcgraw Hill Irwin Series in Operations and Decision Sciences 17th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesStatistical Techniques in Business and Economics The Mcgraw Hill Irwin Series in Operations and Decision Sciences 17th Edition Ebook PDFjoseph.shinn208100% (44)