Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Applying Basic Operation in Mathematics. Valuing Income From Profits of Sales
Uploaded by
canoydexeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Applying Basic Operation in Mathematics. Valuing Income From Profits of Sales
Uploaded by
canoydexeeCopyright:
Available Formats
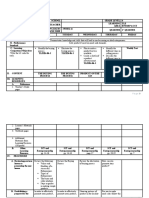
School BAGOR ELEMENTARY SCHOOL Grade Level VI
Teacher DEXEE GIEL C. CANOY Learning Area TLE-IA
Time & Date FEBRUARY 27, 2024 Quarter 3rd Quarter
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content The learners demonstrate an understanding of knowledge and skills in
Standards enhancing/decorating products as an alternative source of income.
B. Performance
Standards performs necessary skill in enhancing/ decorating finished products
C. Learning
Competencies 1.7.1 applies creative packaging and labeling techniques
/Objectives 1.7.2 applies technology-assisted and other means of product
marketing
Write the LC code 1.7.3 computes income from sales
for each 1.7.4 prepares plans for mass production or creating new product
TLE6IA- 1.7.3 0e-7
D. Specific Objective 1. Discuss the proper procedure in computing the selling price.
2. Compute income from sales.
3. Appreciate the importance of proper computing of income from sales.
E. Integration of Applying Basic operation in mathematics.
Content Within Valuing income from profits of sales.
and Across
Curriculum
II. CONTENT COMPUTING INCOME FROM SALES
III. LEARNING CG Pages
RESOURCES
IV. A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide NONE
pages
2. Learner’s Material NONE
pages
3. Textbook pages NONE
4. Additional NONE
Materials from
Learning
Resource (LR)
portal
5. Other Learning NONE
Resources
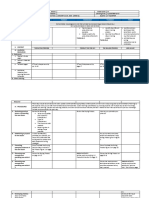
IV. PROCEDURES Teacher’s Activity/ies Learner’s Expected
Response/s
A. Reviewing Have pupils recall the meaning of:
previous lesson or Capital
Expenses
presenting the new Gain
lesson
B. Establishing a A. Have you tried to earn money by selling a
purpose for the product?
lesson
B. What is that product?
Proje Piec Cost of Lab Selli Possib Bracelet
C. Presenting ct es Materi or ng le 90 Php
examples/instances of als Price Incom
the new lesson e
Brace 10 Php Php
let 60.00 30.0
0
What is the item/listed in the chart?
If you were to sell the item, what will be the price
per piece?
D. Discussing new What are the steps in computing the selling
concepts and price?
practicing new skills Discuss the proper procedure in computing the
selling price.
#1
Steps on how to get the selling price and the
possible income.
Project: Beaded bracelet
1. Add all the cost of materials
plus cost labor to get the unit
cost for each bracelet.
Materials -------------------- Php 60.00
Labor (Php 30.00/bracelet)---- Php 30.00
Php 90.00
2. Count how many beaded
bracelets were made. Multiply
this with total cost of
materials plus labor to get
your capital.
Php 90.00 x 10 bracelets
= Php 900.00 (capital)
3. Multiply Php 90.00 x 20% for
mark-up purposes.
Php 90.00
X 20% (.20)
Php 18.00 mark-up price
4. Add the mark-up to your
capital. The sum will be the
selling price.
Php 90.00
+ 18.00
Php 108.00 selling price
Define Business income, Revenue &
Expense
Business Income
is the amount of gain
earned from a sale of a
service and/ or product
after deducting all
incidental expenses
incurred by the business.
Revenue is the
amount of money
received (or to be
received) in exchange for
product and/or services
provided and sold.
Revenue includes gross
receipts on the sale of
service – or gross sale of
product.
Expense is the
amount of money paid (or
to be paid) in exchange
for product and/ or service
received and purchased.
Sample expenses include
inventory purchases,
salary and wages,
transportation,
advertising, electric and
water bills,
communication,
professional fees, etc.
Steps in Computing Business Income
1. Identify all the products and/or services sold
in a given period and then total the amount. The
total represents the revenue.
2. Identify all the cost you pay in order to
operate your business in the same given period.
The total represents your total expenses.
3. To compute your business income, subtract
your total expenses against your total revenue.
E. new concepts and Group Activity:
practicing new skills Compute the selling price & possible income
#2 use 20% as mark-up price
Group 1
Proj Piec Cost Lab Selli Possi
ect es of or ng ble
Materi per Pric Incom
als piec e e
e
Php
Key Php
50 20.0
chain 420.00
0
Group 2
Proj Pie Cost Labor Sellin Possib
ect ce of per g le
s Materi piece Price Incom
als e
Pen
Php Php
Hold 30
250.00 25.00
er
Group 3
Proj Pie Cost Labor Sellin Possib
ect ces of per g le
Materi piece Price Income
als
Pap
er Php Php
42
Wei 385.00 18.00
ghts
F. Developing Seat work: Compute the selling price & possible
mastery income
(Leads to
**use 20% as mark-up price
Formative
Assessment)
Project: Shoe Rack
Pieces: 4
Cost of Materials: Php 2000
Labor: Php 180
What is the selling price?
What is the possible income?
G. Finding practical Your uncle put up a bracelet business, he’s just (Answers Vary)
applications of guessing the price for each item. What will be
concepts and the consequence of his action? What will you
do?
skills in daily
living
H. Making In order to get the selling price of your selected
generalizations project, what are you going to do?
and abstractions
about the lesson
I. Evaluating Multiple Choices. Write the letter of the correct
learning answer.
1. To compute the unit ______ of each finished
article, add the cost of materials and cost of
labor.
a. Cost b. Earned c. Gain
d. Revenue
2. The sum of mark-up price and capital is
the_____________.
a. Revenue b. Selling price c. Expenses
d. Inventory
3. This refers to the amount of gain earned from
a sale or servcice/product sold.
a. Revenue b. Selling price c. Expenses
d. Income
4. Refers to the amount of money received in
exchanged for the product sold.
a. Revenue b. Selling price c. Expenses
d. Income
5. Refers to the amount of money paid in
exchanged for product received and purchased.
a. Revenue b. Selling price c. Expenses
d. Income
J. Additional 4-5 Think of a project. List down your capital,
activities for labor needed and possible expenses. Compute
application or your profit and report to the class.
0-3 Compute the selling price & possible
remediation
income
**use 20% as mark-up price
Project: BAMBOO LAMPSHADE
Pieces: 3
Cost of Materials: Php 2400
Labor: Php 200
What is the selling price?
What is the possible income?
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of ___Lesson carried. Move on to the next objective.
learners ___Lesson not carried.
who ___% of the pupils got 80% mastery
earned
80% in
the
evaluatio
n
B. No. of learners who ___Pupils did not find difficulties in answering their lesson.
require additional ___Pupils found difficulties in answering their lesson.
activities for ___Pupils did not enjoy the lesson because of lack of knowledge, skills and
remediation who interest about the lesson.
scored below 80% ___Pupils were interested on the lesson, despite of some difficulties
encountered in answering the questions asked by the teacher.
___Pupils mastered the lesson despite of limited resources used by the teacher.
___Majority of the pupils finished their work on time.
___Some pupils did not finish their work on time due to unnecessary behavior.
C. Did the remedial ___ of Learners who earned 80% above
lessons work? No. of
learners who have
caught up with the
lesson
D. No. of learners who ___ of Learners who require additional activities for remediation
continue to require
remediation
E. Which of my teaching ___Yes ___No
strategies worked ____ of Learners who caught up the lesson
well? Why did these
work?
F. What difficulties did I ___ of Learners who continue to require remediation
encounter which my
principal or
supervisor can help
me solve?
G. What innovation or Strategies used that work well:
localized materials ___Metacognitive Development: Examples: Self assessments, note taking and
did I use/discover studying techniques, and vocabulary assignments.
which I wish to share ___Bridging: Examples: Think-pair-share, quick-writes, and anticipatory charts.
with other teachers?
___Schema-Building: Examples: Compare and contrast, jigsaw learning, peer
teaching, and projects.
___Contextualization:
Examples: Demonstrations, media, manipulatives, repetition, and local
opportunities.
___Text Representation:
Examples: Student created drawings, videos, and games.
___Modeling: Examples: Speaking slowly and clearly, modeling the language
you want students to use, and providing samples of student work.
Other Techniques and Strategies used:
___ Explicit Teaching
___ Group collaboration
___Gamification/Learning throuh play
___ Answering preliminary
activities/exercises
___ Carousel
___ Diads
___ Differentiated Instruction
___ Role Playing/Drama
___ Discovery Method
___ Lecture Method
Why?
___ Complete IMs
___ Availability of Materials
___ Pupils’ eagerness to learn
___ Group member’s
collaboration/cooperation
in doing their tasks
___ Audio Visual Presentation
of the lesson
Prepared by:
Teacher Demonstrator
Reviewed by:
Master Teacher
Approved by:
Education Program Supervisor- TLE
You might also like
- LESSON PLAN IN INDUSTRIAL ARTS 6 For COTDocument3 pagesLESSON PLAN IN INDUSTRIAL ARTS 6 For COTjopeth92% (36)
- BUSINESS MATH-IDEA EXEMPLAR-DLP - FinalDocument4 pagesBUSINESS MATH-IDEA EXEMPLAR-DLP - FinalSharon May Javier100% (2)
- BUSiness Math LessonsDocument40 pagesBUSiness Math LessonsDaniel Brown100% (9)
- Dll-4th-Week - EntrepreneurshipDocument15 pagesDll-4th-Week - EntrepreneurshipJose A. Leuterio Jr.100% (2)
- TLE 6 - Industrial ArtsDocument10 pagesTLE 6 - Industrial ArtsJoseph R. Galleno100% (4)
- Introduction To Management Accounting 16th Edition Horngren Solutions Manual 1Document58 pagesIntroduction To Management Accounting 16th Edition Horngren Solutions Manual 1andrea100% (48)
- DLL-entrep Q2 w6Document4 pagesDLL-entrep Q2 w6windell arth Mercado100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 13Th Edition by RomneyDocument18 pagesSolution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 13Th Edition by Romneyyebegashet100% (1)
- Louis Vuitton Case StudyDocument27 pagesLouis Vuitton Case StudyUry Suryanti Rahayu AdzaniNo ratings yet
- TLE Feb11Document2 pagesTLE Feb11Vangie Daguinotas Ferrer100% (1)
- Enhancing Decorating Products As An Alternative Source of IncomeDocument26 pagesEnhancing Decorating Products As An Alternative Source of IncomeJulie Julz67% (3)
- Business Mathematics Module 8 Break Even AnalysisDocument12 pagesBusiness Mathematics Module 8 Break Even AnalysisDavid DueNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF ABM - BM11BS-Ih-2 (Week Eight-Day One)Document3 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG OF ABM - BM11BS-Ih-2 (Week Eight-Day One)Aileen Joyce EscasinasNo ratings yet
- Dll-5th-Week - EntrepreneurshipDocument8 pagesDll-5th-Week - EntrepreneurshipJose A. Leuterio Jr.No ratings yet
- SDO-Imus City-LeaP-ABM-Business Math-3RD-Quarter-Week6Document3 pagesSDO-Imus City-LeaP-ABM-Business Math-3RD-Quarter-Week6Gerlie SaligaoNo ratings yet
- Abm 11 Business Mathematics q1 w6 Mod6Document17 pagesAbm 11 Business Mathematics q1 w6 Mod6Jenette D CervantesNo ratings yet
- DLL For Observation EntrepreneurshipDocument3 pagesDLL For Observation EntrepreneurshipEmarilyn BayotNo ratings yet
- Buss-Math W6Document3 pagesBuss-Math W6Erica AmolarNo ratings yet
- TLE-IA6 q0 Mod7 Market-Products EditedDocument11 pagesTLE-IA6 q0 Mod7 Market-Products Editedsam yoongNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDaily Lesson PlanApril Rose BondadNo ratings yet
- Profit, Loss, and Break-EvenDocument20 pagesProfit, Loss, and Break-EvenMarc Angel VicenteNo ratings yet
- As Q2 ENTREP AS2 Week 3 and 4 Approved 12-7-21Document6 pagesAs Q2 ENTREP AS2 Week 3 and 4 Approved 12-7-21Shiela Mae CeredonNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Value Method - LascanoDocument2 pagesReproduction Value Method - LascanoCha DumpyNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF ABM - BM11BS-Ih-5 (Week Eight-Day Four)Document3 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG OF ABM - BM11BS-Ih-5 (Week Eight-Day Four)Aileen Joyce EscasinasNo ratings yet
- The Statement of Comprehensive Income of A Merchandising BusinessDocument6 pagesThe Statement of Comprehensive Income of A Merchandising BusinessMichael MangahasNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Public Technical - Vocational High SchoolsDocument28 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Public Technical - Vocational High SchoolsAira Mae PeñaNo ratings yet
- Entrep 10 Q2 Week 1 7 NEW FINAL FinalDocument51 pagesEntrep 10 Q2 Week 1 7 NEW FINAL Finaltaylorsheesh64No ratings yet
- Pricing and Costing Reporting QuizshitDocument2 pagesPricing and Costing Reporting QuizshitJan Marc ConcioNo ratings yet
- OCT 8 How To Calculate Percentage MarkupDocument3 pagesOCT 8 How To Calculate Percentage MarkupMaria Jobelle Borja AlbiaNo ratings yet
- Profits and LossDocument9 pagesProfits and LossSandra Milena GallegoNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Format NDCDocument8 pagesBusiness Plan Format NDCKristoffer AngNo ratings yet
- Entrep 10 WK 7Document3 pagesEntrep 10 WK 7Kanon NakanoNo ratings yet
- CH1 CH7解答Document72 pagesCH1 CH7解答Koushik ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Packaging and Marketing Household Linens II GRADE 6 DLPDocument5 pagesPackaging and Marketing Household Linens II GRADE 6 DLPElizabeth Tausa100% (1)
- Joint and by Products Supplementary MaterialDocument4 pagesJoint and by Products Supplementary Materials.gallur.gwynethNo ratings yet
- Dll. Busmath1 Week 5Document11 pagesDll. Busmath1 Week 5Mariz Bolongaita AñiroNo ratings yet
- SDO Imus City LeaP ABM Business Math 3RD Quarter Week8Document5 pagesSDO Imus City LeaP ABM Business Math 3RD Quarter Week8Joseph QuizanaNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Abm-11-Business-Mathematics-Q1-W8-Mod1pdfDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Abm-11-Business-Mathematics-Q1-W8-Mod1pdfApril Rose BondadNo ratings yet
- TLE-ICT-WEEK-2-DLL Done Page 9-15Document6 pagesTLE-ICT-WEEK-2-DLL Done Page 9-15Sta. Rita Elementary SchoolNo ratings yet
- DLL Tle Ia W5Document4 pagesDLL Tle Ia W5benz cadiong100% (2)
- DLLweek 5Document4 pagesDLLweek 5Wilmar MondidoNo ratings yet
- DLL G6 Q4 Week3 Tle EntrepDocument3 pagesDLL G6 Q4 Week3 Tle EntrepferlousheenNo ratings yet
- Entrep12 - Q2 - M7 - Forecasting Revenues and CostsDocument35 pagesEntrep12 - Q2 - M7 - Forecasting Revenues and CostsMariekitty JohnbertNo ratings yet
- Second 7 Quarter 1Document7 pagesSecond 7 Quarter 1Princess AnnNo ratings yet
- LAS Principles of Marketing (Price)Document3 pagesLAS Principles of Marketing (Price)Franciz PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Q2 WK4 Las Entrep Graciel Ann C. SolatorioDocument8 pagesQ2 WK4 Las Entrep Graciel Ann C. SolatorioMalouiesa ManalastasNo ratings yet
- TG - FundaofABM-Lesson 2Document9 pagesTG - FundaofABM-Lesson 2HLeigh Nietes-Gabutan60% (5)
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Public Technical - Vocationalhigh SchoolsDocument26 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Public Technical - Vocationalhigh SchoolsAshMere Montesines100% (5)
- Lesson - BuyingsellingDocument94 pagesLesson - BuyingsellingEllaine joy DariaNo ratings yet
- Q1 LAS FABM2 12 5 Week 3Document9 pagesQ1 LAS FABM2 12 5 Week 3Flare ColterizoNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Uts ZquuDocument10 pagesJawaban Uts ZquuKattyNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan (Cost of Production)Document2 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan (Cost of Production)Glenda Javier100% (1)
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan Tle CookeryDocument4 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan Tle CookeryJane Anson GambrajoNo ratings yet
- Business Math - GuideDocument10 pagesBusiness Math - GuideAva Barrameda67% (6)
- G6 K-12 DLL Q4 Week 2 2018-2019 Epp Entrep IctDocument4 pagesG6 K-12 DLL Q4 Week 2 2018-2019 Epp Entrep IctGia AlvarezNo ratings yet
- S.M.A.R.T Smoke Detector: Financial PlanDocument8 pagesS.M.A.R.T Smoke Detector: Financial PlanIvan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting and CostManagementDocument35 pagesCost Accounting and CostManagementLiza Magat MatadlingNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: San Sebastian College - RecoletosDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: San Sebastian College - RecoletosNhel AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Profit or Loss For A Business: Let's Explore and DiscoverDocument8 pagesLesson 1 Profit or Loss For A Business: Let's Explore and DiscoverScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Lecture SlidesDocument16 pagesWeek 2 Lecture SlidesfinastefanNo ratings yet
- Fabm2 Mod3Document10 pagesFabm2 Mod3Margaret Pagdilao MaliksiNo ratings yet
- Cover Page-Portfolio BPADocument1 pageCover Page-Portfolio BPAcanoydexeeNo ratings yet
- Inbound 661890188Document3 pagesInbound 661890188canoydexeeNo ratings yet
- ST-industrial ArtsDocument1 pageST-industrial ArtscanoydexeeNo ratings yet
- CATCHDocument7 pagesCATCHcanoydexee100% (1)
- Classroom MGT 2023Document15 pagesClassroom MGT 2023canoydexeeNo ratings yet
- Woodbois Annual Report 2022Document61 pagesWoodbois Annual Report 2022Suresh PoojariNo ratings yet
- PremiumReceipt 03128410 1638813565Document1 pagePremiumReceipt 03128410 1638813565Arpit GulhaneNo ratings yet
- Asia Const & Dev Corp Vs CADocument8 pagesAsia Const & Dev Corp Vs CADeo DaclesNo ratings yet
- National Law Institute University, Bhopal: Basics of E-BankingDocument21 pagesNational Law Institute University, Bhopal: Basics of E-BankingDikshaNo ratings yet
- HWAWELLTEX 2021-2022 Annual PDFDocument146 pagesHWAWELLTEX 2021-2022 Annual PDFCAL ResearchNo ratings yet
- M/S Best Sellers Retail (I) P.Ltdvs M/S Aditya Birla Nuvo Ltd.&Ors (2012) 6 SCC 792Document20 pagesM/S Best Sellers Retail (I) P.Ltdvs M/S Aditya Birla Nuvo Ltd.&Ors (2012) 6 SCC 792sai kiran gudisevaNo ratings yet
- Technical Cleanless Articles - Bought-In Parts (External Use)Document19 pagesTechnical Cleanless Articles - Bought-In Parts (External Use)Gonzalo de LuisNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin To PaypalDocument10 pagesBitcoin To PaypalRobiulNo ratings yet
- Arsalan Mid LogisticsDocument3 pagesArsalan Mid LogisticsHassan Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- alashankri-Bangalore-3ST Road, Phase.: WXIN2106250004345 4th 7th Banashankn User Type: End UserDocument2 pagesalashankri-Bangalore-3ST Road, Phase.: WXIN2106250004345 4th 7th Banashankn User Type: End UserKaushal RaghuNo ratings yet
- Solved Richie Is A Wealthy Rancher in Texas He Operates HisDocument1 pageSolved Richie Is A Wealthy Rancher in Texas He Operates HisAnbu jaromiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Business Studies 0450/11Document23 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Business Studies 0450/11eulalialamNo ratings yet
- Participate in Workplace Health and SafetyDocument38 pagesParticipate in Workplace Health and SafetyDemisachew TenaNo ratings yet
- Service Organization Controls - SOCDocument3 pagesService Organization Controls - SOCrrponkshe5060No ratings yet
- Security Officer Resume ObjectiveDocument5 pagesSecurity Officer Resume Objectivekzwfvmfgf100% (1)
- Notes - FAR - InvestmentDocument7 pagesNotes - FAR - InvestmentElaineJrV-IgotNo ratings yet
- Spousal Support PDFDocument107 pagesSpousal Support PDFemxn100% (1)
- ACCA AAA (UK) Past Papers - B1bf. Typical Threats - ACOWtancy TextbookDocument9 pagesACCA AAA (UK) Past Papers - B1bf. Typical Threats - ACOWtancy TextbookDavid JohnNo ratings yet
- Abuja Alternate Festival ProposalDocument10 pagesAbuja Alternate Festival ProposalFemi AmorinNo ratings yet
- Solicitud Programa de C-Innovacion 2021 - Nutri Shot enDocument9 pagesSolicitud Programa de C-Innovacion 2021 - Nutri Shot enMELANIENo ratings yet
- Perancangan Konsep Pengukuran Kinerja POADocument11 pagesPerancangan Konsep Pengukuran Kinerja POAJawikencono 03No ratings yet
- Ethiopia's KAIZEN Has Now A Manual: ContentsDocument5 pagesEthiopia's KAIZEN Has Now A Manual: ContentszigaNo ratings yet
- 6 Untapped Traffic Sources in 2020 That Convert With ANY NicheDocument22 pages6 Untapped Traffic Sources in 2020 That Convert With ANY Nichehamza driouchNo ratings yet
- Preliminary ExaminationDocument6 pagesPreliminary ExaminationRozel MontevirgenNo ratings yet
- Maize, Wheat, Soya Beans, Sugar Beans, Cowpeas, Sorghum, Groundnuts and VegetablesDocument2 pagesMaize, Wheat, Soya Beans, Sugar Beans, Cowpeas, Sorghum, Groundnuts and Vegetablescretu gabiNo ratings yet
- Iris Tower - Business BayDocument15 pagesIris Tower - Business Bayahmed hussienNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Student'S Name: IdDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 Student'S Name: IdHAFIZ MUHAMMAD ARSLAN MUNIRNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Part 2 Performance EvaluationDocument3 pagesLecture 9 Part 2 Performance EvaluationAryaman JunejaNo ratings yet