Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 11
Uploaded by
moviezonyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 11
Uploaded by
moviezonyCopyright:
Available Formats
~
LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
Important Questions for Class 10
Science
Chapter 11- Human Eye and Colourful World
Very Short Answer Questions 1 Mark
1. When a person is myopic, he/ she can clearly see
a. Both nearby and far off objects
b. Only nearby objects
c. Only far off objects
d. Neither nearby nor far off objects
Ans: b. Only nearby objects
2. The defect of myopia can be corrected by using
a. Concave lens
b. Convex lens
c. Either concave or convex
d. A complicated combination of lenses.
Ans: a. Concave lens
3. The colour that is scattered the least by the tiny particles and the atoms/
molecules of the atmosphere is
a. Violet
b. Green
c. Yellow
d. Red
Ans. d. Red
4. Which of the following phenomenon contributes significantly to the
reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise or sunset?
a. Dispersion of light
b. Scattering of light
c. Total internal Reflection
d. Reflection of light from the earth
Ans: b. Scattering of light
5. The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles.
a. are relaxed and lens becomes thinner
b. contract and lens becomes thicker
c. are relaxed and lens becomes thicker
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 1
~LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
d. Contract and lens becomes thinner.
Ans: a. are relaxed and lens becomes thinner
6. Define power of accommodation?
Ans: The power of the eye lens to focus on objects near or far from the retina by
adjusting its focal length is called power of accommodation.
7. Which part of the human eye provides most of the refraction for the light
rays entering the eye?
Ans: Cornea and Aqueous humour provides most of the refraction for the light
rays entering the eye.
8. What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the
distance of an object from the eye?
Ans: When the distance of an object from the eye is increased, the image distance
remains the same and image is formed on the retina of the eye.
9. What happens to the pupil of the eye when the light is very bright?
Ans: When the light is very bright, the pupil’s size becomes smaller and limits
the extent of light entering the eye.
10. Which part of the human eye conveys the electrical signals generated by
the light sensitive cells of the retina to the brain?
Ans: Optic nerves convey the electrical signals generated by the light sensitive
cells of the retina to the brain.
11. The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the
focal length of the eye lens. This is due to
a. Presbyopia
b. Accommodation
c. Near-sightedness
d. Far-sightedness
Ans: b. Accommodation
12. The human eye forms the image of an object at its
a. Cornea
b. Iris
c. Pupil
d. Retina
Ans: d. Retina
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 2
~LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
13. The least distance of distinct vision for an eye lens is caused by the action
of the
a. 25 m
b. 2.5 cm
c. 25 cm
d. 2.5 m
Ans: c. 25 cm
14. The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of the
a. Pupil
b. Retina
c. Ciliary muscles
d. Iris
Ans: c. Ciliary muscles
15. What would have been the colour of the sky if there had not been any
atmosphere around the earth?
Ans: The colour of the sky would be black if there had not been any atmosphere
around the earth.
16. For dispersion of light through a prism which colour has maximum
deviation?
Ans: Violet has the maximum deviation for dispersion of light through a prism.
17. What is the least distance of distinct vision of a normal human eye?
Ans: The least distance of distinct vision of a normal human eye is 25 cm.
18. Name the muscle responsible for bringing change in the focal length of
the eye lens?
Ans: Ciliary muscles are responsible for bringing change in the focal length of
the eye lens.
19. Name one defect of vision which cannot be corrected by any type of
spectacle lenses?
Ans: Cataract, clouding of the lens of the eyes is a vision defect that cannot be
corrected by any type of spectacle lenses.
20. State one effect produced by the scattering of light by the atmosphere?
Ans: Tyndall effect is produced by the scattering of light by the atmosphere.
21. What is the nature of image formed on the retina of the eye?
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 3
~LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
Ans: The image formed on the retina of the eye is real and inverted.
22. What type of lens is used for correcting hypermetropia?
Ans: Convex lens is used to rectify hypermetropia or long-sightedness.
23. Who was the first person to obtain the spectrum of sunlight?
Ans: Sir Isaac Newton was the first person to obtain the spectrum of sunlight.
24. As light rays pass from air into glass prism, are they refracted towards
or away from the normal?
Ans: As light rays pass from air into a glass prism they are refracted towards the
normal as glass is denser than air.
25. Which colour has largest wavelength?
Ans: Red colour of light has the longest wavelength in the visible spectrum of
light.
26. Which defect of vision can be rectified using a concave lens?
Ans: Myopia (short-sightedness) can be rectified using a concave lens.
27. What phenomenon causes twinkling of star on a clear night?
Ans: Atmospheric refraction is the phenomenon that causes twinkling of star on
a clear night.
28. What is meant by scattering of light?
Ans: Scattering of light is defined as the change in the direction of light on striking
an obstacle such as dust, water vapour, etc.
Short Answer Questions 2 Marks
1. The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the
nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem.
Ans: The far point of a myopic person is given as 80 cm.
Since the person is Myopic, the lens would be concave and the focal length will
be negative.
f 80 cm 0.8 m
We know, power of a lens is equal to the reciprocal of the focal length.
1
P
f
1
P 1.25D
0.8
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 4
~LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
The nature of the lens is concave and its power is 1.25D .
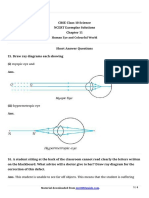
2. Draw a diagram to show the dispersion of white light by a glass prism.
Ans: Diagram depicting the dispersion of white light by a glass prism is drawn
below.
Ray of white light
3. Name the phenomenon responsible for the observed twinkling of stars.
Will this twinkling be observed by an observer on the moon.
Ans: The phenomenon responsible for the twinkling of stars is atmospheric
refraction.
Since the moon has no atmosphere, the observer on the moon will not be able to
observe the twinkling of stars.
4. Name the part of the eye that
a. determines the colour of a person’s eye
Ans: Iris
b. Controls the amount of light entering the eye
Ans: Iris
5. What is the role of the ciliary muscles?
Ans: The main role of the ciliary muscles is to hold the eye lens in its position.
The ciliary muscles contract and relax to focus on near or far away objects by
changing the shape of the eye lens which in turn increases or decreases the focal
length of the eye lens.
6. Why convex lens is called as converging lens?
Ans: A convex lens focuses all the parallel light rays at its focus after refraction.
Hence, it is called as a converging lens.
7. State the role of eye lens in the human eye?
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 5
~LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
Ans: The eye lens focuses the light rays entering the eye on the retina forming a
real and an inverted image of the object on the retina.
8. A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly.
What should be the corrective lens used to restore proper vision?
Ans: Since the person is myopic and cannot see objects clearly beyond 1.2 m, he
should use a concave lens having focal length 1.2 m to restore his normal vision.
9. What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
Ans: For a human eye with proper vision, the near point is 25 cm from the eye
and the far point is at infinity.
10. A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last
row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from? How can it be
corrected?
Ans: Since, the student has difficulty reading the blackboard, sitting in the last
row, he is suffering from myopia or short sightedness. A concave lens of suitable
power should be used to correct his vision defect.
11. Why is a normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than
25 cm?
Ans: The normal eye is not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25
cm because at a distance of 25 cm power of accommodation gets exhausted.
Hence, the eye is unable to focus the light rays on the retina, when the object is
placed closer than 25 cm, .
12. Why does the Sun appear reddish early in the morning?
Ans: During sunrise, the sun is at the farthest distance from the earth’s surface.
The light rays travel a large distance in the Earth’s atmosphere before reaching
our eyes.
While passing through atmosphere, the light rays with shorter wavelengths get
scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere and the red colour light with the longest
wavelength is able to reach our eyes. Hence, the Sun appears reddish early in the
morning.
13. A person wears eye glass of focal length 70 cm what is the far point of the
person?
Ans: The focal length of the eye glass is given as,
f 70 cm
u
From the lens formula, we have:
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 6
~LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
1 1 1
f v u
1 1 1
70 v
1 1
70 v
v 70 cm
Hence, the far point of the person will be 70 cm.
14. If your eye glasses have focal length 60 cm what is your near point?
Ans: The focal length of the eye glass is given as,
f 60 cm
u 25 cm
From the lens formula, we have:
1 1 1
f v u
1 1 1
60 v 25
1 1 1
60 25 v
v 43 cm
Hence, the near point will be 43 cm.
15. Why do we observe random wavering or flicking of the objects near a
fire or on a very hot day?
Ans: We observe random wavering or flicking of the objects near a fire or on a
very hot day because of atmospheric refraction. Area above the fire is hot and is
lighter than cool air above it due to which its refractive index is low and density
also does not remain the same. Therefore, apparent position of the object flickers.
16. Why are we not able to see the things clearly when we come out of a
darkroom?
Ans: In a dark room, the iris expands the pupil which allows more light to enter
the eye. As we come out of dark room, a large amount of light enters our eye and
because of glare feeling, we are not able to see things clearly.
17. What is the function of optic nerve in human eye?
Ans: Optic nerve carries the visual information from the retina to the brain in the
form of electrical signals.
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 7
~LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
18. Why do different colours deviate though different angles on passing
through a prism?
Ans: Different colours deviate though different angles on passing through a prism
because different colours with different wavelengths travel through glass with
different speeds and the glass has different refractive index for different colours.
19. Name the defect of vision in person
a. Whose near point is more than 25 cm away?
Ans: Hypermetropia
b. Whose far point is less than infinity.
Ans: Myopia
20. What is a spectrum?
Ans: A continuum of colour obtained by dispersion of white light by passing
through a prism is called a spectrum.
21. Why does clear sky look blue?
Ans: As white light passes through the atmosphere, the tiny particles held in the
atmosphere scatter the light of shorter wavelength. Therefore, blue light having
the shortest wavelength is scattered the most and the clear sky appears blue.
22. Can visible light be scattered by atoms/molecules in earth’s atmosphere?
Ans: Yes, visible light be scattered by atoms/molecules in earth’s atmosphere as
size of molecules/atoms is much less than the wavelength of visible light.
23. Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
Ans: The outer space do not have atmosphere. As a result, the light does not
scatter into its constituent colours in the outer space and hence the sky appears
dark instead of blue to an astronaut.
24. What is the basic cause of atmospheric refraction?
Ans: Atmospheric refraction is caused by the bending of light when it passes
through the layers of the Earth’s atmosphere with different optical densities.
25. What is range of vision?
Ans: Range of vision of a normal human eye is the distance between the near
point and far point of the human eye. Hence, for a normal human eye it ranges
from 25 cm to infinity.
Short Answer Questions 3 Marks
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 8
~LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
1. Explain in brief:
a. What is hypermetropia?
Ans: Hypermetropia (long-sightedness) is a vision defect where nearby objects
appear blurred but the distant objects can be seen clearly.
b. What are the two causes of this defect of vision?
Ans: The two possible causes of this defect are:
i. Increase is the focal length of the eye lens or the power of eye lens decreases
ii. Size of the eye ball decreases
2. Explain the following:
a. What is scattering of light?
Ans: Scattering of light is defined as the change in the direction of light on striking
an obstacle such as dust, water vapour, etc.
3. A person is known to use a lens of power
i. 5.5 D for his distant vision
ii. 1.5 D for his near vision
Calculate the focal length of the lens used for correcting his
a. Distant vision
Ans: For distant vision, the power of lens is given to be 5.5 D.
The focal length is given by,
1
f
P
1
f m
5.5
f 18.2 cm
b. Near vision problems.
Ans: For near vision, the power of lens is given to be 1.5 D.
The focal length is given by,
1
f
P
1
f m
1.5
f 66.7 cm
4. What is presbyopia? State the causes of this defect? How is presbyopia of
a person corrected?
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 9
~
LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
Ans: Presbyopia is a visual impairment mainly due to ageing when a person is
unable to see the near and far off objects clearly.
The main causes of presbyopia are as follows:
1) Stiffness of the eye lens
2) Due to ageing, the power of accommodation of the eye may decrease.
3) The ciliary muscles become weak.
Presbyopia is corrected using a bifocal lens whose upper half has a concave nature
and the lower half a convex nature.
5. The rainbow is a natural spectrum appearing in the sky after a rain
shower.
a. Is it correct to say that a rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite
to sun?
Ans: Yes, a rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to sun as a rainbow
is just the sunlight which has been refracted and reflected.
b. Can it be seen on a sunny day?
Ans: Yes, a rainbow can be seen on a sunny day if the Sun’s beam passing through
the droplets of water suspended in the atmosphere, reaches the observer’s eye.
c. Arrange the sequence in correct sequential order Refraction, Internal
Reflection, Refraction & Dispersion.
Ans: The correct sequential order is:
Refraction & Dispersion, Internal Reflection, Refraction.
6. Explain in detail:
a. Write two causes of hypermetropia?
Ans: The two causes of hypermetropia are:
i. Increase is the focal length of the eye lens or the power of eye lens decreases
ii. Size of the eye ball decreases
b. Show diagram to show the correctness of hypermetropia?
Ans: Diagram to show correctness of hypermetropia is shown below,
Correction for Hypermetrovic eye
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 10
~LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
7. A reporter records the following observations of an astronaut from his
space ship. Justify each statement.
a. The length of the day is same as observed on the earth.
Ans: This statement is not true as the length of the day in space can be four
minutes shorter than on Earth.
b. Sky appears black in colour.
Ans: The statement is correct because in space there is no atmosphere. Hence,
there is no scattering of light.
c. The star appears to twinkle while the planets do not do so as they do on
the earth.
Ans: The statement is incorrect since we know that the twinkling of stars is due
to atmospheric refraction and the space has no atmosphere. Hence, the stars do
not appear to twinkle in space.
8. Why do stars twinkle?
Ans: Twinkling of stars is due to the atmospheric refraction of light. Stars behave
as point sources of light since they are present far away. The path of the light rays
from the star experiences atmospheric refraction and the position of the star
appears to change. Also, the amount of light entering the eye flickers, so
sometimes the star appear brighter and at some other time, fainter. Thus, the stars
twinkle.
9. Explain why the planets do not twinkle.
Ans: The planets are much closer to the earth than the stars. A planet can be
considered a collection of a large number of limited light sources. Although light
comes from individual point sources flicker, the total amount of light that enters
our eye from all of the individual point sources will be the same. Thus, the planets
appear equally brighter and there are no planetary blinks.
10. A certain person has minimum distance of distinct vision of 150 cm. He
wishes to read at a distance of 25 cm. What focal length glass should he
use? What is the nature of eye defect?
Ans: Given,
v 150 cm
u 25 cm
From the lens formula, we have:
1 1 1
f v u
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 11
LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
1 1 1
f 150 25
1 1
f 30
f 30 cm
Since the focal length is positive, the lens used is a convex lens.
Hence, the eye defect is Hypermetropia.
Long Answer Questions 5 Marks
1. A 14 -year-old student is not able to see clearly the questions written of the
blackboard placed at a distance of 5 m from him.
a. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from?
Ans: The student is suffering from myopia.
b. Draw the diagram to show this defect?
Ans: The diagram showing myopic defect is drawn below.
__________________.,....,_,_~
Myopic eye
c. Name the type of lens used to correct this defect?
Ans: A concave lens is used to correct myopia.
d. Name two possible cause of this defect.
Ans: The two possible causes of myopia are:
i. Elongation of the eyeball
ii. Decrease in the focal length of the eye lens
e. Draw the diagram to show how this defect can be corrected.
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 12
LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
Ans: The diagram showing how myopic defect is corrected is drawn below.
--------------+--,1---7-'+~-
o'·-------•-----------------►
0
2. Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point
of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to
correct this defect? Assume that near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.
Ans: The diagram showing the correction of hypermetropia is drawn below.
Correction .for l-Iypennetropic eye
Near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m and that of normal eye is 25 cm.
Given,
v 1 m = 100 cm
u 25 cm
From the lens formula, we have:
1 1 1
f v u
1 1 1
f 100 25
100 1
f cm = m
3 3
The focal length is given by,
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 13
~
LIVE ONLINE TUTORING
1
f
P
1
P D
1
3
P 3.0 D
Class X Science www.vedantu.com 14
You might also like
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Important Questions 2022-23Document14 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Important Questions 2022-23Rohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colorfull WorldDocument16 pagesHuman Eye and The Colorfull Worldanushanashi362No ratings yet
- C10SCh11 Human Eye Colourful World PDFDocument12 pagesC10SCh11 Human Eye Colourful World PDFPieNo ratings yet
- 11-2 (1)Document5 pages11-2 (1)paparaoNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solution of Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument8 pagesExercise Solution of Human Eye and Colourful WorldiTutor Classes BapiNo ratings yet
- EN1 Us 8 CM 9 D5 WLL2 R RfytDocument18 pagesEN1 Us 8 CM 9 D5 WLL2 R RfytMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- 11.human Eye and Colorful World SolutionsDocument6 pages11.human Eye and Colorful World SolutionsMuzafar ahmadNo ratings yet
- HUMAN EYE AND COLOURFUL WORLD Very Short Answer PDFDocument3 pagesHUMAN EYE AND COLOURFUL WORLD Very Short Answer PDFAkash ManiNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument5 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful WorldOlajuwonNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper on Human Eye and VisionDocument5 pagesCBSE Test Paper on Human Eye and VisionTanmay KatyalNo ratings yet
- 10th Human Eye and The Colourful World Very Short QuestionsDocument2 pages10th Human Eye and The Colourful World Very Short QuestionshsmannNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Imp Ch11 HotsDocument2 pages10 Science Imp Ch11 HotsUday JoshiNo ratings yet
- 10th The Human Eye and The Colourful World Solved QuestionsDocument4 pages10th The Human Eye and The Colourful World Solved QuestionsJit AggNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument25 pagesHuman Eye and The Colourful WorldjituNo ratings yet
- HumanEye and Colourful World 7Document26 pagesHumanEye and Colourful World 7VinodKumarTummalurNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and ColourfuDocument2 pagesHuman Eye and Colourfumohammadgajini8No ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 11 2017Document13 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 11 2017satishNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Imp ch11 2Document6 pages10 Science Imp ch11 2Jagpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Light-The Human and The Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesLight-The Human and The Colourful WorldTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Power and Lens CorrectionDocument14 pagesHuman Eye Power and Lens CorrectionGaurav SethiNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Adhyasa Deepika 2022-2023Document7 pagesHuman Eye Adhyasa Deepika 2022-2023prakashNo ratings yet
- 06 Human Eye and Colourful World Chapter Wise Important Questions PDFDocument12 pages06 Human Eye and Colourful World Chapter Wise Important Questions PDFTannu KaurNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesHuman Eye Chapter SummaryHarshit bhaveNo ratings yet
- 05 - Human Eye & The Colourful WorldDocument26 pages05 - Human Eye & The Colourful WorldAmogh Suman100% (2)
- Physics Worksheet Class X The Human Eye and Its Colourful WorldDocument2 pagesPhysics Worksheet Class X The Human Eye and Its Colourful WorldNamratha BalajeeNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colorful World NotesDocument17 pagesHuman Eye and The Colorful World NotesSourav MaityNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-05 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument7 pagesCbse Test Paper-05 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldTanmay KatyalNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye and Colour VisionDocument6 pagesThe Human Eye and Colour VisionChetan BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Exemplar Chapter 11 SQDocument4 pages10 Science Exemplar Chapter 11 SQPoojitha kamarajNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument12 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful Worldapi-246793885100% (1)
- Human Eye AssignmentDocument6 pagesHuman Eye Assignmentrishabhsharma94163No ratings yet
- 8 Light - SolutionDocument7 pages8 Light - Solutionsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16Document7 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16JollyNo ratings yet
- F.Sc. Part-1 Physics-PTBDocument1 pageF.Sc. Part-1 Physics-PTBgarrisonian96No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument8 pagesChapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful Worldapi-246793885No ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 11 Human Eye and Colourful World 1Document11 pages10 Science Notes 11 Human Eye and Colourful World 1Koustav BiswasNo ratings yet
- Class - X - Physics - Revison Worksheet 2 - Human Eye and Colourful World - 2018-19Document3 pagesClass - X - Physics - Revison Worksheet 2 - Human Eye and Colourful World - 2018-19aayush619_com3918No ratings yet
- Class X Physics Question Bank - HUMAN EYE and The COLOURFUL WORLDDocument5 pagesClass X Physics Question Bank - HUMAN EYE and The COLOURFUL WORLDNitish UnniNo ratings yet
- Human Eye 2023Document5 pagesHuman Eye 2023arpitashekhawat2No ratings yet
- Notebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Document9 pagesNotebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Adhya MisraNo ratings yet
- Physics U2Document6 pagesPhysics U2Alima IqbalNo ratings yet
- Human Eye SpiralDocument9 pagesHuman Eye SpiralPravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - HUMAN EYE and COLOURFUL WORLD-1Document23 pagesChapter 11 - HUMAN EYE and COLOURFUL WORLD-1Sriramulu JaichandarNo ratings yet
- RS - X - Physics - July - Notes of Human Eye - 2022-23Document6 pagesRS - X - Physics - July - Notes of Human Eye - 2022-23RishikaNo ratings yet
- Physics 10th Human Eye and Colourful World - 082934Document5 pagesPhysics 10th Human Eye and Colourful World - 082934defalter090No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions, CBSE Sample Papers, Textbook SolutionsDocument27 pagesNCERT Solutions, CBSE Sample Papers, Textbook SolutionsSreejith SurendranNo ratings yet
- Notes of 10th Cbse Human EyeDocument7 pagesNotes of 10th Cbse Human EyeAvichal TatuNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument11 pagesHuman EyeblehblehdadaNo ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Solutions Physics Chapter 6Document72 pagesLakhmir Singh Class 10 Solutions Physics Chapter 6Aishwaria MurthyNo ratings yet
- Lens Maker Equation and Eye Optics GuideDocument59 pagesLens Maker Equation and Eye Optics GuidePrincess Dianna SulitNo ratings yet
- Class VIII LightDocument2 pagesClass VIII Lightbose baraniNo ratings yet
- Human Eye WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Eye Worksheetcartooncompany73No ratings yet
- 12 Physics Imp Ch9 2Document9 pages12 Physics Imp Ch9 2Amar PandeyNo ratings yet
- 11-1Document5 pages11-1paparaoNo ratings yet
- Humam EyeDocument7 pagesHumam EyeMahamNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseNo ratings yet
- The Cure of Imperfect Sight by Treatment Without Glasses: IllustratedFrom EverandThe Cure of Imperfect Sight by Treatment Without Glasses: IllustratedNo ratings yet
- 13.1-Charactics of Light: Physics Revision Worksheet Name: ..Grade: 11 Section: . DateDocument6 pages13.1-Charactics of Light: Physics Revision Worksheet Name: ..Grade: 11 Section: . DatefgdhNo ratings yet
- Idarat Lwa9tDocument218 pagesIdarat Lwa9tmedingrNo ratings yet
- Types of EMWaves & Their UsesDocument3 pagesTypes of EMWaves & Their UsesPallika DhingraNo ratings yet
- Test YourselfDocument7 pagesTest Yourselfhien thuyNo ratings yet
- Zonal Cavity & Lumen MethodDocument36 pagesZonal Cavity & Lumen MethodAnanda DuttaNo ratings yet
- Solar Radiation & Photosynthetically Active Radiation - Environmental Measurement SystemsDocument1 pageSolar Radiation & Photosynthetically Active Radiation - Environmental Measurement SystemsRobert StagnittoNo ratings yet
- The Biomedical Effects of Laser ApplicationDocument9 pagesThe Biomedical Effects of Laser ApplicationSam SonNo ratings yet
- ImagePROGRAF Color Management Systems GuideDocument41 pagesImagePROGRAF Color Management Systems GuidearrowheadcorpNo ratings yet
- Badminton Court Lighting Design GuideDocument9 pagesBadminton Court Lighting Design GuideVedant HingmireNo ratings yet
- Tree Wall Design Concept Explores Meaning and Effects of Colors Like Green and BrownDocument26 pagesTree Wall Design Concept Explores Meaning and Effects of Colors Like Green and BrownDimple LalwaniNo ratings yet
- Physics Range NvisDocument26 pagesPhysics Range NvisMuhammed SultanNo ratings yet
- Duplicate of An 1005 Hunterlab Vs Cie Lab PDFDocument4 pagesDuplicate of An 1005 Hunterlab Vs Cie Lab PDFRomeu NataleNo ratings yet
- Continuation of Colour TheoryDocument9 pagesContinuation of Colour Theoryapi-335210893No ratings yet
- Commercial Luminaires Product ExplorerDocument87 pagesCommercial Luminaires Product ExplorerMukesh PanwarNo ratings yet
- Dracast Led1000 Fresnel Series Info SheetDocument2 pagesDracast Led1000 Fresnel Series Info SheetJohnNo ratings yet
- Westinghouse 1938 Mazda Lamp CatalogDocument40 pagesWestinghouse 1938 Mazda Lamp CatalogAlan MastersNo ratings yet
- Fusional Vergence Measures and Their Significance in Clinical Assessment 2010Document10 pagesFusional Vergence Measures and Their Significance in Clinical Assessment 2010Estefania GuerreroNo ratings yet
- p94-1634 Diagram - Headlamps W DRL PDFDocument2 pagesp94-1634 Diagram - Headlamps W DRL PDFDiego LiraNo ratings yet
- How A Color CRT TV WorksDocument3 pagesHow A Color CRT TV WorksehabNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Eltron 04-01-2017 PDFDocument140 pagesCatalogue Eltron 04-01-2017 PDFemmaobasiNo ratings yet
- 2.laser Optics +LTIDocument28 pages2.laser Optics +LTIDr: Mary BitewNo ratings yet
- Download Physics Formula ListDocument19 pagesDownload Physics Formula Listanwar9602020No ratings yet
- ITT American Electric HPS Cutoff Luminaire Series 53-54-153-154 Spec Sheet 5-80Document8 pagesITT American Electric HPS Cutoff Luminaire Series 53-54-153-154 Spec Sheet 5-80Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Class Xii PhysicsDocument4 pagesClass Xii PhysicsBiswajit BeheraNo ratings yet
- IBM Colors PANTONE v2.1 REFERENCEDocument2 pagesIBM Colors PANTONE v2.1 REFERENCETaka TomoNo ratings yet
- All Pantone C colors with HEX, RGB codes in one placeDocument57 pagesAll Pantone C colors with HEX, RGB codes in one placeHector Fabio Vega EspinelNo ratings yet
- Cadmium, Prussian Blue & Phthalo Green PigmentsDocument1 pageCadmium, Prussian Blue & Phthalo Green PigmentsLudmila MocanNo ratings yet
- RFQ Cables, Lamps & SwitchesDocument18 pagesRFQ Cables, Lamps & SwitchesAndile NtuliNo ratings yet
- Sylvania Batwing Series Floodlight Spec Sheet 3-72Document4 pagesSylvania Batwing Series Floodlight Spec Sheet 3-72Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph Academy of Dasmariñas, Inc.: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesSaint Joseph Academy of Dasmariñas, Inc.: Republic of The Philippinesdarwin armadoNo ratings yet