Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mind Map On Ecological Succession 2-2-53 Watermark 56
Uploaded by
krishuchavda310320030 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Mind Map on Ecological Succession 2-2-53 Watermark 56
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesMind Map On Ecological Succession 2-2-53 Watermark 56
Uploaded by
krishuchavda31032003Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
www.byjusexamprep.
com
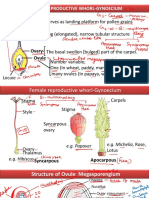
ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION
HYDRARCH SUCCESSION XERARCH SUCCESSION
Process of succession ini ated in a wet area is termed hydrarch succession and the The process of succession ini ated in dry areas is
successional stages are known as hydrosere. This is of two types: termed xerarch succession and successional stages
HYDROSERE: Succession taking place in freshwater ecosystems (ponds, lakes, pools, known as xerosere. This is of two types:
marshes). LITHOSERE: Succession taking place on bare rocks
HALOSERE: Succession taking place in saline water habitats (mangroves, estuaries, coral (shown below)
PSAMMOSERE: Succession taking place in a sandy
reefs). area (like sand dunes)
PHYTOPLANKTON
Pioneer The water is poor in nutrient and incapable of suppor ng
larger lifeforms, phytoplanktons consis ng of microscopic
Community blue green algae, green algae, diatoms and bacteria etc. BARE ROCK
are the first organism to colonise the primi ve medium of
the pond (the pioneer community). Phytoplankton
followed by zooplankton.
SUBMERGED ROOTED PLANT STAGE LICHEN-MOSS STAGE (Pioneer
E As a result of death and decomposi on of phytoplanktons, Species)
a muddy layer at the bo om of pond develops. The now
C shallower and richer in nutrients habitat, with some light
Colonisa on by pioneer species;
Crustose lichen followed by Foliose
availability upto a certain depth becomes amiable for the
O growth of rooted submerged hydrophytes like, Hydrilla,
lichen and then moss stage.
Vallisneria, Ceratophyllum etc.
L
O ROOTED FLOATING STAGE
At this stage the pond is colonised by the plant species which are
G rooted in mud with their large leaves floa ng on the water surface. ANNUAL HERB STAGE (Pioneer)
Small annual plants start establishing
These include species of Nymphaea, Trapa, Monochoria etc. Some
I free floa ng species as Azolla, Lemma, Wolffia, etc, also become themselves on the barren land.
associated with the rooted plants. Water depth is almost 2-5 feet
C now; floa ng species sooner or later disappear from the area.
A
REED-SWAMP STAGE PERENNIAL HERB STAGE (Pioneer)
L Also termed the "Amphibious Stage", as the plants are rooted but Decomposi on creates a layer of top
majority parts of their shoots remain exposed to air. Species of soil; grasses grow and displace the
Typha, Sagi aria and Phragmites etc, are the chief plants of this pioneer species. Grasses, weed, and
P stage. Plants in this stage have well- developed rhizomes and form
dense vegeta on over the area which prevent light penetra on to
mixed herbaceous plants become
prominent.
R the lower por on.
O MARSH (SEDGE)-MEDOW STAGE SHRUB STAGE (Intermediate
Successive decrease in water level and further changes in the species)
G substratum, paves way for Cyperaceae and Gramineae species More nutrients in soil pave way
such as Carex, Cyperus, Eleocharis, Juncus to colonize the area.
R They form a mat like vegeta on courtesy of their heavily branched
for shrub growth. Grasses, shrub
and shade-intolerant tress like
E rhizomatous system. Owing to high transpira on rates, rapid loss
of water, and sooner or later, the mud becomes exposed to air,
pine establish themselves.
S causing nutrients such as ammonia, sulphides etc, to oxidize. The
condi on in the area gradually changes from marshy to mesic and
S marshy vegeta on disappears gradually.
FOREST STAGE (Climax Community)
I WOODLAND STAGE Increase in soil depth allows for
Disappearance of marshy vegeta on, soil becoming drier over me growth of shade-tolerant trees like
O favours development of wet woodland. Area is now invaded by the oak.
terrestrial plants, like some shrubs (Salix, Cornus) and trees
N (Populus, Alnus). The mineraliza on of the soil (humus
accumula on) supports the arrival of new tree species in the area
leading to the climax stages.
FOREST STAGE
The woodland community is invaded by a variety of large tree
forms which soon develops into climax community. The nature of
the climax community (forest) depends upon the climate of the
Climax region. In tropical climates with heavy rainfall, tropical rain forest
Community develop, while in temperate regions mixed forests of Acer, Ulmus ,
Quercus develop. In regions of moderate rainfall, tropical
deciduous forest or monsoon forest develops.
You might also like
- American Horticultural Society - The Fully Illustrated Plant-ByDocument322 pagesAmerican Horticultural Society - The Fully Illustrated Plant-ByAja AS67% (6)
- Training and Pruning Fruit Trees in North Carolina PDFDocument16 pagesTraining and Pruning Fruit Trees in North Carolina PDFJohn Xoán100% (1)
- Effect of Plant Biostimulants On Flowering, Fruit Drop, Yield and Return Bloom of Pomegranate CVDocument5 pagesEffect of Plant Biostimulants On Flowering, Fruit Drop, Yield and Return Bloom of Pomegranate CVAbhinav ShendageNo ratings yet
- Cowie A Survey of Flora Timor LesteDocument68 pagesCowie A Survey of Flora Timor LestetheoNo ratings yet
- Field Trip Report, 2010Document12 pagesField Trip Report, 2010raoumair67% (3)
- Plant Succession XerosereDocument14 pagesPlant Succession Xerosereuqbasiddique.12No ratings yet
- SuccessionDocument11 pagesSuccessionbutterfilyNo ratings yet
- Stabilization or Climax: 3. Seral Community / Transitional CommunityDocument6 pagesStabilization or Climax: 3. Seral Community / Transitional CommunityRosy SorenNo ratings yet
- Hydro SereDocument4 pagesHydro SereAyanKhanNo ratings yet
- PSB 462 SuccessionDocument4 pagesPSB 462 Successiond.orreenselcouthNo ratings yet
- Ges RevieweDocument6 pagesGes Reviewefor extraNo ratings yet
- Plant SuccessionDocument13 pagesPlant SuccessionKhandoker mariatul IslamNo ratings yet
- Ecological Succession Deepak SainiDocument64 pagesEcological Succession Deepak Sainid.orreenselcouthNo ratings yet
- Zonation & Primary SuccessionDocument20 pagesZonation & Primary Successionmuh4mm4d167No ratings yet
- Brugiera Sp. Lastly, at The Inland Zone, Bruguiera Sp. Which Have Buttress Roots To Trap More Mud andDocument1 pageBrugiera Sp. Lastly, at The Inland Zone, Bruguiera Sp. Which Have Buttress Roots To Trap More Mud andRuthrahini RavichandranNo ratings yet
- BOT GE202 - HydrosereDocument13 pagesBOT GE202 - Hydroseresoumya vermaNo ratings yet
- Stages of HydrosereDocument9 pagesStages of HydroserenilaNo ratings yet
- Colonisation and SuccessionDocument2 pagesColonisation and SuccessionreenaarumugamNo ratings yet
- Ecological SuccessionDocument37 pagesEcological SuccessionKenneth DomasianNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 8Document52 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 8Gaya GayaNo ratings yet
- Cikgu S. Murali: Biology 4 44 Colonisation & SuccessionDocument18 pagesCikgu S. Murali: Biology 4 44 Colonisation & SuccessionmuraliMuNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem: A Community of Living Organisms Interacting With Each Other and With The Non-Living EnvironmentDocument26 pagesEcosystem: A Community of Living Organisms Interacting With Each Other and With The Non-Living EnvironmentIra MunirahNo ratings yet
- Hydrach Succession 1Document14 pagesHydrach Succession 1Sylvia RohillaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Ecological Succession-2Document7 pages1.5 Ecological Succession-2Patrick batemenNo ratings yet
- MangroveDocument12 pagesMangrovesitizafirahNo ratings yet
- Wastelands - Rocky Outcrops and Land Affected by SalinityDocument16 pagesWastelands - Rocky Outcrops and Land Affected by SalinityRohan patilNo ratings yet
- Lichen Structure: A) Algal Part (Chlorophyt Aor Cyanophyta) B) Fungus Part (Ascomycot Aor Basidiomyc Ota)Document10 pagesLichen Structure: A) Algal Part (Chlorophyt Aor Cyanophyta) B) Fungus Part (Ascomycot Aor Basidiomyc Ota)Aleine Leilanie OroNo ratings yet
- Ecoli GiaDocument49 pagesEcoli Giadiana cuaranNo ratings yet
- Mangrove EcosystemDocument42 pagesMangrove EcosystemMernie Grace DionesioNo ratings yet
- Final For Lms Ecological SuccessionDocument5 pagesFinal For Lms Ecological SuccessionVarun BhandariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 REVIEWERDocument6 pagesChapter 4 REVIEWERROSETHEL PEDROSANo ratings yet
- Population and Community Development and StructureDocument45 pagesPopulation and Community Development and StructureXernick Marquez FelipeNo ratings yet
- Lec 7, 8 - Ecological SuccessionDocument20 pagesLec 7, 8 - Ecological SuccessionTanishka SainiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Ed. Chapter 7 EcologyDocument38 pages2nd Ed. Chapter 7 EcologyYeny MiluskaNo ratings yet
- Ecological SuccessionDocument4 pagesEcological SuccessionChristine ShellyNo ratings yet
- Los Osos Garden Science Program - Background Research On Dunes and Coastal Dune ScrubDocument4 pagesLos Osos Garden Science Program - Background Research On Dunes and Coastal Dune ScrubZafiriou MavrogianniNo ratings yet
- My How Ecosystem Change PRDocument9 pagesMy How Ecosystem Change PRMckayren VossNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document1 pageDocument 1SunilNo ratings yet
- Colonisation and Succession in A Mangrove SwampDocument23 pagesColonisation and Succession in A Mangrove Swampmiadi95% (22)
- Ion and Succession in A MangroveDocument7 pagesIon and Succession in A Mangrovenaniey_ayobNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Chapter 9.1 BIODocument14 pagesPart 2 Chapter 9.1 BIOYue Kee LeeNo ratings yet
- Urban EcosystemsDocument4 pagesUrban EcosystemsChristineNo ratings yet
- 4wetland 16-02-19Document6 pages4wetland 16-02-19Ar Deepti ManojNo ratings yet
- Ecological Succession-HerbertDocument3 pagesEcological Succession-HerbertRuno OmughelliNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial HabitatDocument4 pagesTerrestrial HabitatmadzNo ratings yet
- Hemi EpiphytesDocument9 pagesHemi EpiphytesLana MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Mangroves: EnvironmentDocument2 pagesMangroves: EnvironmentTrexie Claire Say HisonaNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument3 pagesBiomesReysheleParalNo ratings yet
- 184 Inv Sand DuesDocument5 pages184 Inv Sand DuespopeyeNo ratings yet
- Audur - An Introduction To The Mezozoic Paleobotany PDFDocument9 pagesAudur - An Introduction To The Mezozoic Paleobotany PDFVasilică-Dănuţ HorodnicNo ratings yet
- Marine Ecology - Mangrove - Dr. Mustafiz - BSMRMU - OCN 06Document52 pagesMarine Ecology - Mangrove - Dr. Mustafiz - BSMRMU - OCN 06you knowNo ratings yet
- The Dancer's HemDocument15 pagesThe Dancer's Hemmutton$$No ratings yet
- Wetland Ecology Basic Principles 111418 MoseleyDocument41 pagesWetland Ecology Basic Principles 111418 Moseleysomnathmandal89No ratings yet
- Mangrove EcosystemDocument6 pagesMangrove EcosystemMark Dave Damgo AguillonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 Coastal Principles of EcologyDocument6 pagesChapter 25 Coastal Principles of EcologyKarmina SantosNo ratings yet
- 36-Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular PlantsDocument21 pages36-Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular PlantsJan Leo QuinioNo ratings yet
- Water & Forests: The Role Trees Play in Water QualityDocument6 pagesWater & Forests: The Role Trees Play in Water QualityJexNo ratings yet
- 1953 EconomicBiologyCollembolaDocument4 pages1953 EconomicBiologyCollembolabrandon arredondoNo ratings yet
- Eduart Zimer - The Adventive Crassulaceae of Rangitoto Island (2010)Document26 pagesEduart Zimer - The Adventive Crassulaceae of Rangitoto Island (2010)eduartzimerNo ratings yet
- Dunares PDFDocument8 pagesDunares PDFbelenNo ratings yet
- Nigerian VegetationDocument24 pagesNigerian VegetationAlabi FauziatBulala100% (1)
- Tree Species As Indicators of Ground Water Recharge and DischargeDocument9 pagesTree Species As Indicators of Ground Water Recharge and DischargeerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Major Biomes of The WorldDocument3 pagesMajor Biomes of The WorldStephine DizonNo ratings yet
- ROSEDocument3 pagesROSE190030049cseNo ratings yet
- JCR 2021 Impact Factor PDF ListDocument322 pagesJCR 2021 Impact Factor PDF ListJuliana Cassol SpanembergNo ratings yet
- Gibberellins Signalling: DELLA Motif (Aspartate-Glutamate-Leucine-Leucine-AlanineDocument11 pagesGibberellins Signalling: DELLA Motif (Aspartate-Glutamate-Leucine-Leucine-AlanineTauseef AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ch.8 Plantae ModuleDocument3 pagesCh.8 Plantae ModuleEMIL SALNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson in TleDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson in TleNiña Edrienne JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Produce Organic Vegetables UpdatedDocument11 pagesProduce Organic Vegetables UpdatedHONEY JYL DUCUSINNo ratings yet
- The Typification and Status of Phymatolithon Corallinaceae RhodophytaDocument27 pagesThe Typification and Status of Phymatolithon Corallinaceae RhodophytaJamesNo ratings yet
- Winter Semester 2022-23 Digital Assessment-3 Pink-Pigmented Facultative Methylotrophs (PPFM) and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR)Document7 pagesWinter Semester 2022-23 Digital Assessment-3 Pink-Pigmented Facultative Methylotrophs (PPFM) and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR)Kaviyashri.S 20BAG0086No ratings yet
- HilverdaKooij SnijbloemenDocument52 pagesHilverdaKooij Snijbloemengabrielm_33No ratings yet
- 3.11.20-Plants and Their FoodDocument3 pages3.11.20-Plants and Their FoodMilliNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Production Technology of Safed MusliDocument63 pagesPresentation On: Production Technology of Safed MuslijagatividyasagarNo ratings yet
- A Revised Survey of The Forest Types of PDFDocument609 pagesA Revised Survey of The Forest Types of PDFGaurang TawdeNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Planting Depth On Germination and Seedling Vigoursity of Maize (Zea Mays L.)Document7 pagesThe Effect of Planting Depth On Germination and Seedling Vigoursity of Maize (Zea Mays L.)ReddyNo ratings yet
- PomegranateDocument27 pagesPomegranateShreya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Hydroponics Background Research PDFDocument4 pagesHydroponics Background Research PDFHarsh RajNo ratings yet
- Chinese Vegetables: Department of HorticultureDocument5 pagesChinese Vegetables: Department of HorticultureKwok Chung ChuNo ratings yet
- Propagation Methods in PlantsDocument36 pagesPropagation Methods in PlantsThea PadlanNo ratings yet
- Agro Estate Jurnal Budidaya Perkebunan Kelapa Sawit Dan KaretDocument10 pagesAgro Estate Jurnal Budidaya Perkebunan Kelapa Sawit Dan KaretAnggita Lusi Tania TurnipNo ratings yet
- 23 Nov A5 Life Cycle of Angiosperm - EnglishDocument21 pages23 Nov A5 Life Cycle of Angiosperm - EnglishAyush bhadaniNo ratings yet
- Radley Miguel Adarlo - PERFORMANCE TASK - URBAN GARDENING USING RECYCLABLE MATERIALSDocument8 pagesRadley Miguel Adarlo - PERFORMANCE TASK - URBAN GARDENING USING RECYCLABLE MATERIALSJK De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Medicinally Potential Aromatic Plants of The Lamiaceae Family in Bangladesh Agricultural University Botanical GardenDocument12 pagesDiversity of Medicinally Potential Aromatic Plants of The Lamiaceae Family in Bangladesh Agricultural University Botanical GardenMD. Jahid Hasan JoneNo ratings yet
- Translokasi FotoasimilatDocument15 pagesTranslokasi FotoasimilatsophiaNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s00344 015 9541 6Document28 pages10.1007@s00344 015 9541 6gofruNo ratings yet
- (1920) Rennie's Seed Annual & Garden Guide For 1920 (Catalogue)Document88 pages(1920) Rennie's Seed Annual & Garden Guide For 1920 (Catalogue)Herbert Hillary Booker 2ndNo ratings yet
- Tissue Culture AcclimatizationDocument9 pagesTissue Culture AcclimatizationLaxman KumarNo ratings yet