Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation Topic (Electrolytic Cell)
Uploaded by
hansrajkukreja740 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views16 pagesVery good Presentation on Electrolytic Cell
Original Title
Presentation topic (Electrolytic Cell)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVery good Presentation on Electrolytic Cell
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views16 pagesPresentation Topic (Electrolytic Cell)
Uploaded by
hansrajkukreja74Very good Presentation on Electrolytic Cell
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Electrochemical Cells
Chap: Electrochemistry
(Presentation topic:Electrolytic Cell)
Table of contents.
• What is Electrolytic Cell?
•Working principle of Electrolytic Cell
• Types of Electrolytic Cells
• Applications of Electrolytic Cell Presented By: Mr.Naeem
Cells: Cells are the containers of liquid containing of
electrodes .
Liquid in Cells: Acts as an electrolyte
Electrolyte: The molten or aqueous solutions of acids ,
bases or salts having the capability to conduct electricity
Exp: NaCl(aq), NaCl(l), HCl(aq), NaOH(aq)
Electrodes: Piece of metals/non-metals having the
capability to conduct electricity
Introduction about Electrochemical Cells
Electrochemical Cells:
An apparatus which convert electrical Energy into
chemical energy or chemical energy into
Electrical energy via redox reaction
Electrochemical Cell : A) Electrolytic Cell
B) Galvanic or Voltaic Cell
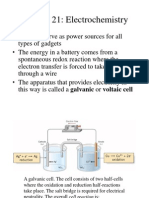
Electrolytic Cell: Electricity is used to force the chemicals to undergoe a redox
Rn
> Non spontaneous reaction occurs(Electrolysis)
> Endothermic redox reaction
> No salt Bridge is used Non-spontaneous Rn: The
reaction which is driven by an external source
but not itself
> Inert electrodes are used
> Uses battery source
> Exp: Electroplating, Electrolysis of water, purification of Na-metal from Molten NaCl,
Recharging of batteries
Non- Spontaneous Reaction
Non- Spontaneous Reaction
Working principle of an E.Cell
Electrical energy is used to drive the Non-spont reaction.
Electrolysis of Molten NaCl
°In molten state> Ions move freely.
° Battery> As an external source to drive a
non- Spontaneous reaction
° Anoins move towards the anode(+)
° Cations move towards the cathode(-)
° Oxidation (Removal of electrons) occurs at anode(+)
° Reduction ( Gaining of electrons) occurs at Cathode(-)
Migration of ions towards their respective
Electrodes in an Electrolytic Cell
Working principle of an E.Cell
2NaCl(s) + ∆H —----> 2Na+(g) + 2Cl-(g)
Reaction At Anode:
(Oxidation occurs) Anode: A piece of metal
connected to +ve terminal of battery.
2Cl-(g) —--> Cl2 (g) + 2e-
Reaction At Cathode:
(Reduction occurs ) Cathode: A piece of metal
2Na+(g) + 2e- —-> 2Na(g). Connected to the -ve terminal of battery..
Working principle of
Types of an Electrolytic Cell
Electrolytic Cell> Two types
1) : Down’s Cell 2) : Nelson's Cell
° Electrolyte > Molten NaCl ° Electrolyte > Aqueous NaCl
° Cathode> Iron(Fe) ° Cathode > may be same metal or different
° Anode > Graphite(C). Metal depends upon electrolytic
° Used to extract the metals( Na, Mg and Ca) process
° Used to prepare NaOH ,
Electrolysis of water and electroplating
Application of An E. Cell
→ To prepare caustic soda(NaOH) at commercial
Scale
→ To extract the sodium(Na), Magnesium(Mg)
and Calcium(Ca) metal.
→ To purify copper(Cu)
→ Electroplating of copper(Cu), Silver(Ag), Gold(Au) , Nickel(Ni)
and chromium(Cr).
→ Electrolysis of water
→ To prepare Chlorine gas
→ To Anodized Aluminium
Purification of copper
Extraction of Na-metal
You might also like
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chap 3 Signal Conditioning CircuitDocument26 pagesChap 3 Signal Conditioning CircuitMuhammed I'zwanNo ratings yet
- BYD Bus AmericaDocument213 pagesBYD Bus Americaunyuunyu00100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Electrolysis With Instructional LessonDocument15 pagesLesson Plan Electrolysis With Instructional LessonMichael Harris100% (1)
- Electrochemical Energy Systems: Batteries and Fuel CellsDocument42 pagesElectrochemical Energy Systems: Batteries and Fuel Cellsshubhika guptaNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument12 pagesDepartment of Chemical EngineeringSheikh AliNo ratings yet
- Voltaic and Electrolytic Cell ComparisonDocument32 pagesVoltaic and Electrolytic Cell Comparisonmamta2111No ratings yet
- ABB SACE Tmax XT Series - IEC - TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICSDocument412 pagesABB SACE Tmax XT Series - IEC - TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICSIoannis PerperisNo ratings yet
- 14.3 NotesDocument28 pages14.3 NotesCarmen PurewalNo ratings yet
- Chem G - 10 Reading Material - IIDocument5 pagesChem G - 10 Reading Material - IIYishakNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument32 pagesElectrochemistrylalla.lilli026No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Chm271Document63 pagesChapter 4 Chm271Amirah AdlinaNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Electrochemical CellsDocument31 pages9.2 Electrochemical Cells昊元No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Electro ChemistryDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Electro ChemistryKritika MishraNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3-Dr - HariDocument111 pagesMODULE 3-Dr - HariKartik KaushikNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument12 pagesElectrolysisFT Geeyah Tahir100% (1)
- Lecture 09. 28122020 E&MEDocument41 pagesLecture 09. 28122020 E&MEMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Voltaic Cells - Daniell Cell (S)Document22 pages2.2 Voltaic Cells - Daniell Cell (S)Guru temp id-03 for KPM-Guru-TempNo ratings yet
- 2 Electrochemistry (Electrolytic Cells)Document45 pages2 Electrochemistry (Electrolytic Cells)Gerald Paul SumagpaoNo ratings yet
- Electrochem 201516Document81 pagesElectrochem 201516Mohd AminudinNo ratings yet
- أ - اندي محمد تجربه مختبرDocument9 pagesأ - اندي محمد تجربه مختبرMmm 123No ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry (BCHY101L) : Energy DevicesDocument84 pagesEngineering Chemistry (BCHY101L) : Energy DevicesDeepali Mishra 21BCE3440No ratings yet
- Lab Report Corrosion-1Document10 pagesLab Report Corrosion-1areniqwardiah_918730100% (1)
- Module 4 - Trimmed FinalDocument93 pagesModule 4 - Trimmed FinalivanjaisonNo ratings yet
- Electrochem Power PointDocument14 pagesElectrochem Power PointSaba P.No ratings yet
- Cell PotentialDocument39 pagesCell Potentialellamae sanbuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- When A Non-Spontaneous Redox Reaction Is Made To Occur by Putting Electrical Energy Into The SystemDocument11 pagesWhen A Non-Spontaneous Redox Reaction Is Made To Occur by Putting Electrical Energy Into The SystemArdit QerimiNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument27 pagesElectrochemistry22cs103No ratings yet
- Chemi G 10 Chap 3 HanoutDocument5 pagesChemi G 10 Chap 3 HanoutYISHAK ABRHAMNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - Galvanic Cell NewDocument51 pagesElectrochemistry - Galvanic Cell NewPink WandererNo ratings yet
- Faraday'S LAW AND GALVANIC CELL LESSONDocument4 pagesFaraday'S LAW AND GALVANIC CELL LESSONmmmmmNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 1Document17 pagesElectrochemistry 1dwijsaidwhatNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument12 pagesElectrolysissaeikipNo ratings yet
- Ăn MònDocument52 pagesĂn MònLam CuongNo ratings yet
- BatteriesDocument30 pagesBatteriesBrotinNo ratings yet
- TSSM Topic 5Document18 pagesTSSM Topic 5sudotesterNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 2019 HANDOUTDocument50 pagesElectrochemistry 2019 HANDOUTAndrearose Ivy FietasNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument21 pagesOxidation and ReductionKaroline UhlemannNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument68 pagesElectrochemistryAlpha HoNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document64 pagesChap 2Swe Zin Zaw MyintNo ratings yet
- ENCHML130 Energy 4 - Part 2Document29 pagesENCHML130 Energy 4 - Part 2G7 SJ-01 Cabataña, MichailaNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Chapter 4 - ElectrochemistryDocument36 pagesPhysical Chemistry Chapter 4 - Electrochemistryjatropos6810No ratings yet
- Chapter 21: ElectrochemistryDocument55 pagesChapter 21: ElectrochemistryrendipinemNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic CellDocument4 pagesElectrolytic Cellanuj devatwalNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument76 pagesElectrochemistryRatna ThakurNo ratings yet
- 1.ElectrochemistryPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae SheetDocument4 pages1.ElectrochemistryPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae SheetArbab MazharNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 9th CLASS Long QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 7 9th CLASS Long Questionssomerakhan2023No ratings yet
- 2nd Chem CH 03Document26 pages2nd Chem CH 03Dushyanth S JNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 7Document11 pagesKelompok 7Anes OctavianiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Electro ChemistryDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Electro ChemistryKritika MishraNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY - Electrolytic CellsDocument5 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY - Electrolytic CellsCherry EmbateNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Class 12 - Chemistry Chapter 3:electrochemistryDocument9 pagesDelhi Public School Class 12 - Chemistry Chapter 3:electrochemistryAvishi OjNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Galvanic Cell NewDocument48 pagesElectrochemistry Galvanic Cell Newralphkirby.felicitaNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectrochemistryDocument36 pagesBasics of ElectrochemistryNaveed JanjuaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY Chapter 7 NOTES IIDocument46 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY Chapter 7 NOTES IIWandisile ezileNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical ProcessesDocument19 pagesElectrochemical Processeshrishikeshdeka18No ratings yet
- Chem Notes Merged MergedDocument721 pagesChem Notes Merged Mergedmaxrenson2002No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry (Compatibility Mode)Document9 pagesElectrochemistry (Compatibility Mode)Kim Ivan MendozaNo ratings yet
- Design Process in ElectrochemistryDocument92 pagesDesign Process in ElectrochemistryWulan SariNo ratings yet
- Analisis ElektrokimiaDocument108 pagesAnalisis ElektrokimiaIntan CahyasariNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Chemical Change and Electrical WorkDocument68 pagesElectrochemistry: Chemical Change and Electrical WorkJoshua AeronNo ratings yet
- Viva-Voce Electrical MachinesDocument2 pagesViva-Voce Electrical MachinesjishnusajiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Representation of Power System ComponentsDocument24 pagesChapter Two: Representation of Power System ComponentsBonsaNo ratings yet
- Radio Reloj Aiwa Fr-A300Document20 pagesRadio Reloj Aiwa Fr-A300Roderick Lenhardt FontanNo ratings yet
- Radiated, RF Immunity TestDocument42 pagesRadiated, RF Immunity TestAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Merlin Gerin Multi 9 CT Modular Contactors Technical PDFDocument2 pagesMerlin Gerin Multi 9 CT Modular Contactors Technical PDFiedmondNo ratings yet
- NCP81253 5 V MOSFET Driver Compatible With Single-Phase IMVP8 ControllersDocument11 pagesNCP81253 5 V MOSFET Driver Compatible With Single-Phase IMVP8 ControllersTom TomNo ratings yet
- DC/DC Converter: FeaturesDocument5 pagesDC/DC Converter: FeaturescesarNo ratings yet
- Xylem Hydrovar Variable Speed Drive IEM Seminar Agent CS PowerDocument41 pagesXylem Hydrovar Variable Speed Drive IEM Seminar Agent CS PowerAnonymous IGtWHoi0No ratings yet
- Network Theorems - Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFDocument7 pagesNetwork Theorems - Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFMahesh sNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - WeldingDocument42 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - WeldingGOBLIN XXXNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller AT89C2051Document4 pagesMicrocontroller AT89C2051aditya6adityaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Preliminary Report: ELEC3307 Electronics LaboratoryDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 Preliminary Report: ELEC3307 Electronics LaboratoryArda Deniz EryiğitNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Project ReportDocument22 pagesSummer Training Project ReportAnkit Sharma50% (2)
- Jint-G1C R8-Frame 380-500V Coated Main Circuit Board Jint: Product-DetailsDocument4 pagesJint-G1C R8-Frame 380-500V Coated Main Circuit Board Jint: Product-DetailsAlessandro DamascenoNo ratings yet
- Aiml Bee Lab Manual I Yr II Sem 2023-24Document102 pagesAiml Bee Lab Manual I Yr II Sem 2023-24holagoogolNo ratings yet
- High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Installations - Systems TestDocument77 pagesHigh-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Installations - Systems TestChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- DI+ Technical Reference Manual - 1.2.3Document27 pagesDI+ Technical Reference Manual - 1.2.3EdgardsoteloNo ratings yet
- USI FullCatalog 2018Document96 pagesUSI FullCatalog 2018Nguyễn Thị HườngNo ratings yet
- Panimalar Institute of Technology Set A: Jaisakthi Educational Trust, Chennai - 600 123Document4 pagesPanimalar Institute of Technology Set A: Jaisakthi Educational Trust, Chennai - 600 123DINAKARANNo ratings yet
- HICO 72kV Gas Circuit Breaker CatalogDocument2 pagesHICO 72kV Gas Circuit Breaker Catalogsubidubi99No ratings yet
- Harmony XALD XALD03Document3 pagesHarmony XALD XALD03Hansen LaMessiah SaputraNo ratings yet
- Dta 100 CDocument92 pagesDta 100 CAndrew SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Tetra TR EngDocument42 pagesCatalogue Tetra TR EngArun KumarNo ratings yet
- BYV95A - BYV96E: PRV: 200 - 1000 Volts Io: 1.5 AmperesDocument3 pagesBYV95A - BYV96E: PRV: 200 - 1000 Volts Io: 1.5 AmperesMostafa El SayedNo ratings yet
- Model P4480 Kill A Watt Graphic Timer Operation Manual: Safety InstructionsDocument9 pagesModel P4480 Kill A Watt Graphic Timer Operation Manual: Safety Instructionspulse59No ratings yet
- LSQ5 - B - Bedienungsanleitung - V1 5 - ENDocument36 pagesLSQ5 - B - Bedienungsanleitung - V1 5 - ENDiego MondragonNo ratings yet
- Underground CablesDocument9 pagesUnderground CablesphaniputtaNo ratings yet