Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impression 1
Uploaded by
eslamezzat21061990Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impression 1
Uploaded by
eslamezzat21061990Copyright:
Available Formats
Applied material Level 2
Impression Materials
Dental Impressions: are negative reproductions of oral structures.
impression material is a substance used for recording the form and
dimensions of the oral tissues.
Cast(model): is a positive reproduction of oral structure made from a stone or
plaster.
Impression material is inserted into the mouth in a plastic condition to set
against oral tissues & removed from the mouth when hardened
• The set impression is a negative reproduction of the oral tissues & a positive
reproduction is obtained by pouring a suitable model or die
• Classification of impression:
1. It may be partial (part of oral tissues) or complete (the entire dental arch)
2. According to type:
a) Preliminary Impression is used for: Diagnostic models & Custom trays
b) Final Impression: used to produce the most accurate reproduction of the teeth and
surrounding tissue
• Objectives of making impression material:
1. Crown &bridge
2. Removable prosthodontics (partial or complete)
3. Study cast of orthodontic cases
4. Study presurgical cases as in implant cases
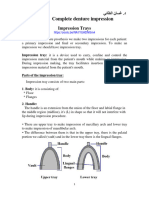
• impression is soft material, so we use tray to hold & support it.
• Impression tray: is a device used to hold & carry & support
impression material in oral cavity
• Trays may be (readymade) stock tray or custom(special) tray.
Ideal requirements of impression materials:
1. Accuracy:
▪ Definition: ability of impression to replicate the intraoral surface details
▪ the impression should be accurate as accuracy of restoration depends on accuracy of
impression.
▪ The restoration cant be more accurate than impression
1|Page Dr. eslam ezzat
Applied material Level 2
2. Biologically acceptable: non toxic, non irritant & non carcinogenic & of acceptable odor & taste
3.not affected by the oral fluids.
4. It should have a suitable working time to allow for placement of the impression material in the tray
and then insertion of the tray into the mouth before beginning of hardening.
Working time: time elapsed from beginning of mixing till insertion in pt. mouth
Initial setting time: time elapsed from mixing till beginning of setting
Final setting time: time elapsed from mixing till complete setting
6. It should have a suitable setting time to avoid fatigue to both operator and patient. Three
minutes is considered reasonable time for setting.
7 It should accept addition and correction after taking the impression.
8. Readily disinfected without loss of accuracy.
9. It should have a good shelf life.
Factors affecting accuracy of the impression material:
1. should have high flow at the beginning, i.e. the material must be in a fluid or plastic state on
insertion into the mouth, in order to have the ability to record fine details.
2. Dimensionally accurate: The dimensional changes associated
with its setting reaction should be negligible i.e. should not expand,
contract or warp during setting.
3. Dimensionally stable: There should be negligible dimensional
changes on storage(after setting) of the impression in the dental
laboratory before pouring the cast i.e. it should be dimensionally
stable after removal from the mouth
4. Should be elastic on removal from the mouth so that
undercuts can be recorded without distortion of the impression.
N.B: undercut is high is dentulous pt. compared to Edentulous pt.
5. During removal from the mouth, it should be adherent to the
tray.
Or it will be separated during removal from oral cavity.
So we need to use perforated tray with some impression material as alginate
6. should be compatible with the gypsum products:
o Should not need a separating medium when poured (it would occupy a space or may affect
the accuracy).
o Should not affect the setting or surface qualities of the model e.g. should not react with
the cast material or material which affects the surface of the model.
N.B.There is no impression material that can fulfill all these requisites however, these
requisites is useful to evaluate an impression material.
2|Page Dr. eslam ezzat
Applied material Level 2
Classifications of impression materials:
a) The manner of setting :
1. chemical reaction(irreversible):
▪ Harden through a chemical reaction
▪ e.g. Plaster of Paris, ZOE, alginates, rubber impression materials etc.
2.physical (reversible):
▪ set as a result of change of temperature without chemical changes.
▪ Thermoplastic substances e.g. wax, impression compound and agar agar
b) Their Behavior after setting:
▪ Depending on their ability to regain their original shape after removal from the undercuts
1. Inelastic impression materials(rigid|)
▪ They are used only when no undercut exists (edentulous pt.)
e.g. wax, Plaster of Paris, ZnO/eugenol and impression compound.
2. Elastic impression materials
▪ They can be used when undercut exists e.g. hydrocolloids and rubber impression materials.
c) Their use:
1. Impression materials used in completely edentulous pt.: Plaster, impression compound
and Zinc oxide and eugenol, hydrocolloids, rubbers
2. Impression materials used in partially edentulous pt.: Hydrocolloids, Rubbers
d) According to the Accuracy:
1. 1ry Impression (stock tray): Compound impression material, Alginate impression material
2.2ry Impression (special tray): Plaster impression material (not used now) , Zinc
oxide/eugenol, Agar -Agar, Rubbers impression materials , Alginate impression material
e) According to viscosity:
1) High: compound, putty elastomers
2) Medium: regular elastomers
3) Low: plaster, ZOE,
hydrocolloids, light body
elastomers
3|Page Dr. eslam ezzat
Applied material Level 2
Inelastic impression materials
1) Plaster of Paris:
• Application:
1. 2ry impression for completely edentulous patients in
non-perforated special tray(shellac or acrylic).
2. used in wash impression over compound.
Composition: supplied in the form of powder, to which
water is added, composed of:
1. CaSO4.1/2H2O. not alpha
The Ca sulfate is used rather than α and/or improved stone because:
a)weaker: So break during removal from undercut avoiding injury to the patient
and the fractured part can be reassembled accurately.
b)requires higher W/P ratio, which increases the flow at the beginning and thus records fine details.
c)The higher W/P ratio will reduce the exothermic heat evolved during taking of the impression.
2. Modifiers: Chemicals used to regulate the setting time & setting expansion:
accelerator: 4% potassium sulphate : decreases the setting expansion(anti expansion) and the
setting time.
retarder; 1% borax : decrease the setting expansion.
Setting mechanism: (chemical reaction)
• On mixing the powder with water, calcium sulfate hemihydrate reacts with water to produce
calcium sulfate dihydrate and setting occurs in the mouth.
CaSO4.1/2H2O + H2O CaSO4.2H2O + Heat
• Properties of plaster impression materials:
1. Accuracy of plaster impression materials:
a) semi-fluid → excellent recording of the fine details.
b) dimensional changes on setting are negligible due to anti-expansion additives.
c) A small degree of drying shrinkage during storage of the impression in the laboratory may occur
and may induce small dimensional changes
d) A plaster impression fractures on removal from undercuts and can be reassembled.
e)When pouring a plaster impression in plaster or in stone, a separating medium should be
used, otherwise, the pores of the impression will be filled with the cast material, and both will
be interlocked and become inseparable.
The film of separation should be as thin as possible, in order to avoid the inaccuracies.
The use of separating medium is disadvantage as it may obliterate the fine details.
f) taste and consistency are unpleasant to the patient
g) it dehydrates the Patient mouth
h) due to its fluidity, it runs through the throat.
2)Impression compound: (modeling composition)
Form : 1)sheets(round or square 4-5
mm),
2)stick ,cylinder or cones
Application :
1)full jaw primary impression for
completely edentulous patient
2)peripheral molding of impression trays
4|Page Dr. eslam ezzat
Applied material Level 2
3)single tooth impression in copper band for inlay & crowns
4) act as a tray for 2ny impression material (wash impression tech.)
Composition:
1. Thermoplastic material: Natural resins & wax soften by heating & harden by cooling…it and give
the qualities of flow and cohesion.
2. Fillers: Talc or diatomaceous earth(add body & ↑ strength &↓ thermal contraction &give a
suitable working consistency).
3. 3 %Plasticizers(lubricant): Stearic acid or stearin, act as lubricant and with fillers control
the flow and consistency of the material
4.coloring agent : e.g. Rouge. It produces characteristic reddish-brown color most commonly
used. Black and green colors are also available.
Types:
1)impression compound (type 1)( lower fusing materials)
a)For primary impressions (preliminary impression) for
edentulous patient supplied as sheets
b)stick form or cone shape for copper band impression for inlays
& crown.
c)sticks used in tracing (recording vestibule)
2)impression trays (type II) higher fusing used as an
impression trays to support another impression (wash
impression)
(Wash impression): the aluminum stock tray
containing the impression of the dental compound is
used to hold a second impression material as zinc
oxide-eugenol, which will record the final impression (corrective wash)
Setting mechanism:
*thermoplastic,warmed at 45ºC & cooled to mouth temperature 37ºC → rigid. *reversible physical
process rather than a chemical reaction. Hard Heating Soft
Cooling
Manipulation:
1) For completely edentulous cases:
a) Heating: over a flame or in water bath. For impressions it is heated in water bath at 55-60ºC. water
bath should be lined with napkin or it will adhere to the bath.
*it has a low thermal conductivity so it must be immersed in the water bath for sufficient time to
ensure complete softening & should be kneaded to obtain homogenous soft mass. but, if it is left too
5|Page Dr. eslam ezzat
Applied material Level 2
long some of the ingredients may be leached out into the water bath → sticky material.
Properties:
1. Accuracy of impression compound:
a)Flow: not sufficiently fluid to record all the fine details.
45ºC 37ºC
type I 85% less than 6%
typeII 70% less than 2%.
b) Dimensional accuracy and dimensional stability:
Dimensional changes during hardening are great why ??
1- High coefficient of thermal expansion.
*On cooling during setting, there is considerable cooling shrinkage.
*Shrinkage occurs on cooling from mouth to room temperature (0.3-0.4%)
2. Distortion: when it occurs?
a) During removal from undercut: Internal stresses occur on removal from undercuts as it is plastic
material & has low flow (deformation)
b) during storage: as internal stresses will be relieve leading to distortion
▪ 3 factors are responsible for these internal stresses:
a.The high value of coefficient of thermal expansion.
b. The poor thermal conductivity
c.The relatively large temperature drop from the softening temperature to room temperature.
Therefore, the impression should be cast maximum within an hour
2. The material is non-elastic : the most serious drawback of this material is that it distorts when
being removed from
an undercut area
3. Compatible with model and die materials and do not need a separating medium
4. Conductivity:
▪ Compound has poor thermal conductivity.
▪ so when softened, its outside will soften first & inside will soften later
▪ so Time must be allowed during either heating or cooling to allow the dental compound to come
to a uniform temperature
5. These impression can be removed from the mouth, re-softened and reinserted for any corrections
required..
6. Accept additions to the impression
7. Can be electroplated with copper.
8. Disinfection by different materials affects its properties
3) Zinc oxide/ eugenol:
• Applications: 2ry impressions for completely edentulous patient .
• Form: two pastes in two metallic collapsible tubes
• Composition
Base accelerator
a))Zinc oxide 80%: Reactive a)Oil of cloves or eugenol: 12-15%
ingredient which takes in ▪ Reactive ingredient takes part in setting reaction.
setting reaction. ▪ Oil of cloves: Sometimes used instead of the eugenol,
b)inert oil 15% → form a since it is less irritant than eugenol
paste with zinc-oxide powder b)Gum rosin and oils 65% (Gives body & cohesion &
6|Page Dr. eslam ezzat
Applied material Level 2
c)hydrogenated resin. thermoplastic properties for easy removal from the cast by
softening it in hot water.
c)Filler talk or kaolin or diatomaceous earth →form a paste.
d) Moisture: A very slight amount of moisture water is added to
the zinc oxide parts or accelerator?? Since it is essential for
the hydrolysis of the zinc oxide to its hydroxide
N.B. Water is essential since the dehydrated ZnO can’t react
with eugenol and the reaction is called chelation reaction.
e) zinc acetate: act as accelerator
Manipulation and setting mechanism:
• Two paste: provided in contrasting colors & equal lengths of two are mixed over a glass slab or
special oil-resistant paper pad, until a homogenous color is obtained.
▪ Zinc-oxide in the presence of moisture reacts with eugenol to form a chelate of zinc eugenolate,
which forms an amorphous matrix holding the unreacted particles of zinc oxide
▪ Zn O + H2O → Zn (OH)2
Zn (OH)2 + 2 Eugenol → Zn Eugenolate +H2O (salt)
Acid) (base) Chelation Reaction
▪ Water is essential for the reaction since the dehydrated ZnO cannot react with eugenol.
Properties:
1. Accuracy of zinc oxide and eugenol:
a. Flow: Very accurate (sufficiently fluid to record fine detail).
b. Dimensional accuracy and stability:
1)no or very little dimensional change on setting (0.1% Shrinkage).
2)no change during storage but ↑temp→distortion due to thermoplastic part.
c.Inelastic so use in completely edentulous patient with no undercut(fracture).
d.Compatibility with gypsum : removed by softening in hot water 60ºC.
2. Other properties:
a. Eugenol can be irritant →tingling or burning sensation to patient & leaving a persistent taste
(unpleasant ).
N.B. Non-eugenol zinc oxide impressions are now available to avoid this.
b. adhere to tissues, so the lips of the patient are usually coated with petroleum jelly (Vaseline) before
making the impression.
7|Page Dr. eslam ezzat
You might also like
- Analisys and application of dry cleaning materials on unvarnished pain surfacesFrom EverandAnalisys and application of dry cleaning materials on unvarnished pain surfacesNo ratings yet
- Impression PDFDocument11 pagesImpression PDFHany wahyuningrumNo ratings yet
- Creative Resin: Easy techniques for contemporary resin artFrom EverandCreative Resin: Easy techniques for contemporary resin artNo ratings yet
- Impression Materials and Impression Techniques: ClassificationDocument7 pagesImpression Materials and Impression Techniques: ClassificationruchikaNo ratings yet
- Impression in FPDDocument9 pagesImpression in FPDAmar Bhochhibhoya100% (1)
- Impressions For FPDDocument53 pagesImpressions For FPDpragatiNo ratings yet
- Lec.14 OperDocument32 pagesLec.14 Operبكر الدوريNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 Imp. MaterialDocument6 pagesLec 5 Imp. Materialمحمد جاسم محمد عجاجNo ratings yet
- Impression Tech in FPDDocument50 pagesImpression Tech in FPDDrGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb MCQsDocument65 pagesLower Limb MCQsabq90No ratings yet
- Impression Tech in FPDDocument51 pagesImpression Tech in FPDDrGagandeep Singh100% (3)
- Impresssion Mat-Rigid FinalDocument86 pagesImpresssion Mat-Rigid Finaldrsumit2002No ratings yet
- Complete 3Document17 pagesComplete 3Mohammed HassanNo ratings yet
- Final Impression: Objectives and MaterialsDocument28 pagesFinal Impression: Objectives and Materialsمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- DM Lec 3Document10 pagesDM Lec 3jqqy2487qnNo ratings yet
- Pros Lec4 638067499724273620Document8 pagesPros Lec4 638067499724273620hassan 3No ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document8 pagesLecture 4saleh alawdiNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontics: Criteria For Special Tray ConstructionDocument6 pagesProsthodontics: Criteria For Special Tray Constructionزهراء فاضل اجبير فعيلNo ratings yet
- Steps of Construction Complete DentureDocument31 pagesSteps of Construction Complete DentureShanna Hosein0% (1)
- DM - Impression MaterialsDocument12 pagesDM - Impression MaterialsambiliNo ratings yet
- Impression MaterialsDocument212 pagesImpression MaterialsSai Kumar100% (1)
- Impression Materials: Mohammed AdelDocument5 pagesImpression Materials: Mohammed Adelعلاء البناءNo ratings yet
- Impression Taking - Fabrication of Special Trays & Secondary Impressions - Session 4Document11 pagesImpression Taking - Fabrication of Special Trays & Secondary Impressions - Session 4baraa.abdulrahman.23No ratings yet
- Lec 4Document29 pagesLec 4Khalat RezanNo ratings yet
- Chapter I-Impressions (2021)Document15 pagesChapter I-Impressions (2021)Hany NassifNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٣-٠٦-٠٢ في ٥.٢١.٤٨ مDocument15 pagesلقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٣-٠٦-٠٢ في ٥.٢١.٤٨ ممنتظر منشد دعاشNo ratings yet
- Relining and RebasingDocument3 pagesRelining and RebasingMuhammad SdiqNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 Prosthodontics PDFDocument8 pagesLec 5 Prosthodontics PDFmustafa7calligrapherNo ratings yet
- Dental MaterialsDocument33 pagesDental Materialskevin1678No ratings yet
- Fabrication of Model: General Rules For Pouring, Trimming and Handling CastsDocument47 pagesFabrication of Model: General Rules For Pouring, Trimming and Handling CastsRachel BenitezNo ratings yet
- Impression Materials Techniques Procedures For Complete Dentures ProsthoDocument30 pagesImpression Materials Techniques Procedures For Complete Dentures ProsthoMaha Lakshmi100% (1)
- Lec 3,2nd StageDocument7 pagesLec 3,2nd Stageperlam.eoesNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 Impression 2020 1Document9 pagesLec 5 Impression 2020 1bf28215No ratings yet
- Impression Materials NsDocument4 pagesImpression Materials NsStanislavNemtanuNo ratings yet
- Impression Materials and Techniques For RPD: 1. Rigid Materials: 2. Thermoplastics Materials: 3. Elastic MaterialsDocument12 pagesImpression Materials and Techniques For RPD: 1. Rigid Materials: 2. Thermoplastics Materials: 3. Elastic Materialsفاطمه محمد فاضلNo ratings yet
- Stock Impression Trays and Construction of Diagnostic Casts LC 3Document10 pagesStock Impression Trays and Construction of Diagnostic Casts LC 3Rihan RihanNo ratings yet
- Lec. 4 D. M.Document5 pagesLec. 4 D. M.زهراء فاضل اجبير فعيلNo ratings yet
- Reline Rebase and Repairing DenturesDocument7 pagesReline Rebase and Repairing DenturesSam ChengNo ratings yet
- Review PDFDocument4 pagesReview PDFSonali KinikarNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument4 pagesReviewSonali KinikarNo ratings yet
- Impression MakingDocument14 pagesImpression MakingVincent SerNo ratings yet
- Primary ImpressionDocument17 pagesPrimary ImpressionJewana J. GhazalNo ratings yet
- Impression For Complete Denture1Document94 pagesImpression For Complete Denture1samar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Elastomeric Impression TechniquesDocument60 pagesElastomeric Impression TechniquesAnupriya SinghNo ratings yet
- 29 55 1 SMDocument6 pages29 55 1 SM1738Aufa LAVNo ratings yet
- Tissue Management and Impression MakingDocument55 pagesTissue Management and Impression MakingRamya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Impression Materials For Partial DentureDocument40 pagesImpression Materials For Partial Dentureyunie0959No ratings yet
- Impression Techniques in Fixed Prosthodontics: By: Assist. Prof. Dr. Nadia Hameed HasanDocument38 pagesImpression Techniques in Fixed Prosthodontics: By: Assist. Prof. Dr. Nadia Hameed HasanAseelNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Complete Denture ImpressionDocument8 pagesLec 4 Complete Denture Impressionحارث احمد فتاح قصاب باشيNo ratings yet
- Considerations For Adhesion of Impression Materials To Impression TraysDocument4 pagesConsiderations For Adhesion of Impression Materials To Impression TraysPhoebe DavidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Impression MaterialsDocument44 pagesLecture 4 - Impression MaterialsMichelle Lorraine Bayan TanNo ratings yet
- Alginate. Impression PasteDocument10 pagesAlginate. Impression PasteCRISTIAN FURDUINo ratings yet
- 2 5262829886866723249Document29 pages2 5262829886866723249علي محمدNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Prosthodontics PDFDocument7 pagesLec 4 Prosthodontics PDFmustafa7calligrapherNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document8 pagesLec 5Dr.Haider Saleem AbdullahNo ratings yet
- RPD Final ImpressionDocument52 pagesRPD Final Impressiondalal19996No ratings yet
- Non Elastic ImpressionDocument65 pagesNon Elastic ImpressionAbdelruhman SobhyNo ratings yet
- All Groups F2F and OnlineDocument3 pagesAll Groups F2F and OnlineNicole Dumrique100% (1)
- ImpressionsDocument87 pagesImpressionsmanoNo ratings yet
- Impression Partial DentureDocument29 pagesImpression Partial Dentureمؤمل رياض سعد كاظمNo ratings yet
- FullDocument20 pagesFullSai GowthamNo ratings yet
- Quartz Lumps Suppliers - Quartz Manufacturers in India - Tanvi Mines & MineralsDocument3 pagesQuartz Lumps Suppliers - Quartz Manufacturers in India - Tanvi Mines & MineralsnithiyNo ratings yet
- Automatic Door SystemsDocument4 pagesAutomatic Door Systemsjack.simpson.changNo ratings yet
- Narrative ConcretingDocument3 pagesNarrative ConcretingJune Mark AwingNo ratings yet
- Material Selection For Rocket Motor CasesDocument11 pagesMaterial Selection For Rocket Motor CasesArif Saadilah Nawawi0% (1)
- Installation and Operation Manual: Models SHPF and SHPMDocument24 pagesInstallation and Operation Manual: Models SHPF and SHPMROYALNo ratings yet
- Jseam 2018 32Document12 pagesJseam 2018 32Hatef SardariNo ratings yet
- Bole Sub CityDocument11 pagesBole Sub CityAbel BerhanemeskelNo ratings yet
- FTS018 MT3 Class 3 Machinery SpacesDocument4 pagesFTS018 MT3 Class 3 Machinery SpacesWissam JarmakNo ratings yet
- Pm-Drg-Ly26 11092-M-01 Isometric Drawing Rev. D 2010 - Internal Painting Option - A3 Discharge LineDocument1 pagePm-Drg-Ly26 11092-M-01 Isometric Drawing Rev. D 2010 - Internal Painting Option - A3 Discharge LineLEE JHONNo ratings yet
- Question and Answers For Introduction To TextilesDocument7 pagesQuestion and Answers For Introduction To TextilesProf Dr Md Saifur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Section 1, Seat No.4: Product Box CompanyDocument106 pagesSection 1, Seat No.4: Product Box CompanyKoy'z Vilailuk RadchakidNo ratings yet
- European Accumulator Catalogue 050613 Final VersionDocument60 pagesEuropean Accumulator Catalogue 050613 Final Versionscibduser001100% (1)
- ACTUAL COST OF 4 INCHES JACKBILT 300PSI CHB WALL Vs BLOCKTEC 4 INCHES AAC WALLDocument1 pageACTUAL COST OF 4 INCHES JACKBILT 300PSI CHB WALL Vs BLOCKTEC 4 INCHES AAC WALLTian Gatlabayan AlaNo ratings yet
- Rotameter Calibration SetDocument5 pagesRotameter Calibration SetnidhidarklordNo ratings yet
- Tariq PHD Thesis 13-08Document168 pagesTariq PHD Thesis 13-08unaialapontNo ratings yet
- 95-03097 Ballvlv300350 WCB PDFDocument26 pages95-03097 Ballvlv300350 WCB PDFasitdeyNo ratings yet
- Clock Spring Diamond Wrap BrochureDocument2 pagesClock Spring Diamond Wrap BrochuremuhammadxpNo ratings yet
- Control Plan For Zinc Flake CoatingDocument3 pagesControl Plan For Zinc Flake Coatingx y100% (1)
- BHEL - PresentationDocument32 pagesBHEL - Presentationsenthil031277No ratings yet
- 3d Panel SystemDocument25 pages3d Panel Systemprobir100% (2)
- UL Standards For SafetyDocument109 pagesUL Standards For Safetyoarriesgado100% (2)
- Paper Making ProcessDocument16 pagesPaper Making ProcessWinwin07No ratings yet
- FLS-Controlled Flow Storage SiloDocument4 pagesFLS-Controlled Flow Storage SilophitokrioNo ratings yet
- AISC Seismic Design-ModuleUG-Brief OverviewDocument86 pagesAISC Seismic Design-ModuleUG-Brief OverviewDemçe Florjan100% (1)
- ANPC - Unit 1-PPT-1 PDFDocument36 pagesANPC - Unit 1-PPT-1 PDFAkash YadavNo ratings yet
- Conductor Dimensioning For HV Surge ArrestersDocument3 pagesConductor Dimensioning For HV Surge ArrestersmartinpellsNo ratings yet
- CCCRCxToolkit-Sequence Operation Template 2007Document6 pagesCCCRCxToolkit-Sequence Operation Template 2007Humpy DumpyNo ratings yet
- Ncma Tek: Compressive Strength Testing Variables For Concrete Masonry Units TEK 18-7Document4 pagesNcma Tek: Compressive Strength Testing Variables For Concrete Masonry Units TEK 18-7williamptyNo ratings yet
- Fugato Full MetalDocument3 pagesFugato Full MetalDaniel KozoraNo ratings yet
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignFrom EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (137)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansFrom EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Cable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignFrom EverandCable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary of Neil Postman's Amusing Ourselves to DeathFrom EverandSummary of Neil Postman's Amusing Ourselves to DeathRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Crossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetFrom EverandCrossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansFrom EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansNo ratings yet
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- The Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element AnalysisFrom EverandThe Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeFrom EverandThe Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (59)
- Troubleshooting and Repair of Diesel EnginesFrom EverandTroubleshooting and Repair of Diesel EnginesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Construction Innovation and Process ImprovementFrom EverandConstruction Innovation and Process ImprovementAkintola AkintoyeNo ratings yet
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Pile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbFrom EverandPile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Engineering Rock Mass Classification: Tunnelling, Foundations and LandslidesFrom EverandEngineering Rock Mass Classification: Tunnelling, Foundations and LandslidesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Skyway: The True Story of Tampa Bay's Signature Bridge and the Man Who Brought It DownFrom EverandSkyway: The True Story of Tampa Bay's Signature Bridge and the Man Who Brought It DownNo ratings yet
- Bridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsFrom EverandBridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Transportation Decision Making: Principles of Project Evaluation and ProgrammingFrom EverandTransportation Decision Making: Principles of Project Evaluation and ProgrammingNo ratings yet