Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orange Photo Clean & Corporate Organization History Timeline Infographic
Uploaded by
Zara AzamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orange Photo Clean & Corporate Organization History Timeline Infographic
Uploaded by
Zara AzamCopyright:
Available Formats
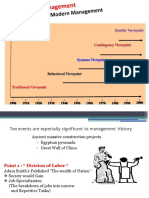
Management Theory
Timeline
Classical Theory
• Scientifically, he reduced each task to a series of physical movements.
Fredrick
1. Develop specific procedures for every job.
Select workers carefully. Make sure they have the right abilities for
Taylor
the job.
Train workers to do the job and give them incentives to carefully
follow the specific procedures designed for their jobs.
father of scientific
Support workers by carefully planning their work and removing
management.
obstacles
Henri
Scalar Chain – there should be a clear and unbroken line of
communication from top to bottom in the organization
Fayol
Unity of Command – each person should receive orders from only one
boss
Unity of Direction – one person should be in charge of all activities
developed and
that have the same performance objectives (one leader with one
implemented an
plan)
administrative model
1. Planning 2. Organization 3. Command 4. Coordination & Control
Mary diverse individuals could combine their talents for the
Parker
greater good
managers and workers should work in harmony
Follet
1. Negotiation
2. Conflict Resolution
3. Power Sharing
Administrative Principle
Max Bureaucracy is a rational and efficient form of an
organization founded on logic, order, and legitimate
Weber
Bureaucratic
authority
1. Clear division of labour 2. Clear hierarchy of authority
3. Formal rules and procedures 4. Impersonality
Organization
Behavioral Approach
concluded that gains in worker productivity had more to do with human
relations and the social needs of workers than the lighting conditions.
Elton Factors that account for increased productivity include group atmosphere,
one with high trust and low fear
Mayo Work conditions or wages could be sources of satisfaction or
dissatisfaction
Hawthorne Effect: the tendency of persons singled out for special attention
to perform as expected
Maslow created a pyramid of needs that every human seeks to
satisfy.
Maslow Need: a physiological or psychological deficiency a person feels
Deficit Principle: people act to satisfy “deprived” needs
Progression Principle: needs exist in a hierarchy – need at any
level is only activated when the lower level need is satisfied
Mcgregor
McGregor’s Theory X assumes that McGregor’s Theory Y assumes that
workers: workers:
• Generally dislike work • Are willing to work
• Lack ambition • Are capable of self-control
• Are irresponsible • Are willing to accept responsibility
• Are resistant to change • Are imaginative and creative
• Prefer to be led than lead • Are capable of self-directio
“Management Science” and “Operations Research” are both terms used to
Quotative
describe the use of mathematical techniques to analyze and solve
management problems.
(1) The focus is on rational decision making that leads to specific action
Approach plans.
(2) The techniques are based on “money” issues (ex. cost and profit)
(3) Mathematical models with sophisticated rules and formulas are used.
Learn m
ore at w
ww.rea
Modern Management Theory llygrea
tsite.co
m Important aspects:
Total Total Quality is a description of the culture, attitude, and
operation of an organization that works to provide its
customer-driven quality, top
management leadership
Quality customers with goods and services that satisfy their and commitment, continuous
needs. The culture requires quality in all aspects of the improvement, fast response,
Theory company's operations, with the emphasis on things being actions based on facts, and
done right the first time. employee participation.
open systems which means they interact with their
System
environment – transforming resource inputs, into outputs.
Good managers understand that organizations must
Theory
successfully integrate the contributions of many
individuals. Managers must ensure that each part of
the system works well in cooperation with the others.
You might also like
- Chapter-2: Development of Management ThoughtDocument59 pagesChapter-2: Development of Management Thoughtnatnael haileNo ratings yet
- Social Work and Management TheoriesDocument6 pagesSocial Work and Management TheoriesMechisedec BalacuitNo ratings yet
- Social Work and Management TheoriesDocument6 pagesSocial Work and Management TheoriesMechisedec BalacuitNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Emerging of Management ThoughtDocument52 pagesChapter Two Emerging of Management ThoughtmichaelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management: History of Management ThoughtDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Management: History of Management ThoughtWynn LeongNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Historical Perspectives On ManagementDocument3 pagesModule 2 Historical Perspectives On ManagementJohn Carlo CortezNo ratings yet
- Summary Buku Introduction To Management - John SchermerhornDocument5 pagesSummary Buku Introduction To Management - John SchermerhornElyana BiringNo ratings yet
- Management: Chapter 2: The Evolution of Management TheoryDocument29 pagesManagement: Chapter 2: The Evolution of Management TheoryTrương Phúc NguyênNo ratings yet
- PA 203 2nd Sem 2020 2021Document105 pagesPA 203 2nd Sem 2020 2021inshiraNo ratings yet
- Org. & Mgt. ReviewerDocument7 pagesOrg. & Mgt. ReviewerlapNo ratings yet
- Теороия Менеджмента PDFDocument70 pagesТеороия Менеджмента PDFWill HalloNo ratings yet
- Dmiec & JP - 03 (27.7.20)Document36 pagesDmiec & JP - 03 (27.7.20)srisuji14No ratings yet
- MGT CH 2Document24 pagesMGT CH 2besedegefub9131No ratings yet
- Management - Historical PerspectivesDocument6 pagesManagement - Historical PerspectivesTesfaye OlanaNo ratings yet
- Ana 201 ManagementDocument20 pagesAna 201 ManagementRoche Dela Cruz CaroNo ratings yet
- Orgweek1 5wpicDocument7 pagesOrgweek1 5wpicjasmineotapNo ratings yet
- Intelligence, Passion, A Strong Work Ethic, and A Genuine Concern For PeopleDocument5 pagesIntelligence, Passion, A Strong Work Ethic, and A Genuine Concern For PeopleChelsea Anne VidalloNo ratings yet
- Managing in Turbulent Times: Page - 1Document24 pagesManaging in Turbulent Times: Page - 1Lydia ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Evolution-of-ManagementDocument75 pagesEvolution-of-ManagementRaynil LadjamatliNo ratings yet
- Handouts Org. and MangamentDocument8 pagesHandouts Org. and MangamentBrian Omaña Deconlay EmhayNo ratings yet
- ThoghtDocument73 pagesThoghtwondimu getachewNo ratings yet
- LMGT IntroDocument4 pagesLMGT IntroKEZIA GERONIMONo ratings yet
- 1.1 Meaning and Function of ManagementDocument4 pages1.1 Meaning and Function of ManagementHannah Denise BatallangNo ratings yet
- Organization & Management - 1ST Semi-Quarterly - Grade 11 - AbmDocument7 pagesOrganization & Management - 1ST Semi-Quarterly - Grade 11 - AbmJullianaNo ratings yet
- L2-Basic Management TheoriesDocument24 pagesL2-Basic Management Theoriesguga neshNo ratings yet
- Teaching Slides - Management History A202Document49 pagesTeaching Slides - Management History A202Fikrah OthmanNo ratings yet
- Sess 5 6 Evolution of ManagementDocument47 pagesSess 5 6 Evolution of Managementparth moreNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument8 pagesIlovepdf MergedWilliam GonzalesNo ratings yet
- IntroductionToOrgBehavior ModifiedDocument64 pagesIntroductionToOrgBehavior ModifiedAdwik RajeshNo ratings yet
- General Management: Mng2601: Chapter 1: The Evolution of The Management TheoryDocument25 pagesGeneral Management: Mng2601: Chapter 1: The Evolution of The Management TheoryAndile Charity DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Management Theories 2018Document16 pagesManagement Theories 2018Anusha KVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Management Yesterday and TodayDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Management Yesterday and Todaybiancag_9175% (4)
- 01 Org&Manage ReviewerDocument10 pages01 Org&Manage Reviewerortega.johnrhonlieNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management Engg. EconomyDocument67 pagesIndustrial Management Engg. Economyagergizat girmaNo ratings yet
- Brown Doodle Company Profile PresentationDocument31 pagesBrown Doodle Company Profile PresentationMarvin PameNo ratings yet
- Overview of Organization ManagementDocument2 pagesOverview of Organization ManagementJuan Miguel Sto. DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Definition and Functions of ManagementDocument39 pagesLesson 1 Definition and Functions of ManagementSiopau GalosoNo ratings yet
- OM ReviewerDocument18 pagesOM ReviewerJAVELOSA, YUAN ALDRICH M.No ratings yet
- Classical Management TheoryDocument22 pagesClassical Management Theorysabyasachibosu0% (1)
- Environmental Factors Influencing Management Thought: Economic InfluencesDocument58 pagesEnvironmental Factors Influencing Management Thought: Economic Influencesjanagyrama1No ratings yet
- ManagementDocument134 pagesManagementaemon05No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The History and Evaluation of ManagementDocument25 pagesChapter 2 - The History and Evaluation of ManagementMisbah QayyumNo ratings yet
- Overview of Organization ManagementDocument3 pagesOverview of Organization ManagementJuan Miguel Sto. DomingoNo ratings yet
- Business Syllabus Notes (Marketing)Document79 pagesBusiness Syllabus Notes (Marketing)Preet OberaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Past To PresentDocument40 pagesChapter 2 - Past To PresentNgoc Hai PhanNo ratings yet
- Management Theories or SchoolsDocument4 pagesManagement Theories or SchoolsJason DurdenNo ratings yet
- Nature and Concepts of ManagementDocument46 pagesNature and Concepts of ManagementKevin T. OnaroNo ratings yet
- Fsu 2402 Session 4Document10 pagesFsu 2402 Session 4malcomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. IntroductionDocument55 pagesChapter 1. Introductionsheil.cogayNo ratings yet
- MGMT Theory CH 2Document48 pagesMGMT Theory CH 2habatmuNo ratings yet
- mng2601 Notes Best SummaryDocument25 pagesmng2601 Notes Best Summarydrahlaga1No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Part IiDocument24 pagesLesson 1 - Part IiLizbethHazelRiveraNo ratings yet
- Evolution of ManagementDocument30 pagesEvolution of Managementaditi kushwahaNo ratings yet
- A. Definition of Management: Harold Koontz Frederick W. Taylor Henry FayolDocument5 pagesA. Definition of Management: Harold Koontz Frederick W. Taylor Henry Fayolanon_487132184No ratings yet
- Mamonova MamonovaMOB Lecture Notes PPIntroduction To OBDocument35 pagesMamonova MamonovaMOB Lecture Notes PPIntroduction To OBTai WcNo ratings yet
- Om Unit 1 NotesDocument7 pagesOm Unit 1 NotesRonaldine Julie PunongNo ratings yet
- Managemnent Thoughts (Ses 5 6)Document34 pagesManagemnent Thoughts (Ses 5 6)Hemant SoniNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Evolution of Organizational Behaviour: ObjectivesDocument20 pagesUnit 3 Evolution of Organizational Behaviour: ObjectivesHari om SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of oDocument8 pagesEvolution of oPrincessNo ratings yet
- Product Costing Design Document - BusinessDocument18 pagesProduct Costing Design Document - Businesshemanthreganti81100% (1)
- Bus ModDocument2 pagesBus ModdmadhavanurNo ratings yet
- Management: Paper: 09, Entrepreneurship Development & Project ManagementDocument11 pagesManagement: Paper: 09, Entrepreneurship Development & Project ManagementDeepak Kumar PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- JSA 03 To Do Work On Concrete Mixer, Concrete Pump, Vibrator, De-Watering Pump.Document3 pagesJSA 03 To Do Work On Concrete Mixer, Concrete Pump, Vibrator, De-Watering Pump.mehtab uddinNo ratings yet
- Penggunaan Sistem Pembayaran E-Money Berbasis Server Untuk Mendukung Gerakan Cashless Society Pada Generasi MilenialDocument8 pagesPenggunaan Sistem Pembayaran E-Money Berbasis Server Untuk Mendukung Gerakan Cashless Society Pada Generasi MilenialSyahrakansa PutraNo ratings yet
- Project Integration ManagementDocument21 pagesProject Integration ManagementNurul IbrahNo ratings yet
- Holiday PermitDocument1 pageHoliday PermitToha Hilpan HamimNo ratings yet
- (Rev.1) Si - 121 - Tb. Karya Pacific 2203-Bg. Pacific Star 7803 - Mv. Chang Yang Jin An - TpuDocument1 page(Rev.1) Si - 121 - Tb. Karya Pacific 2203-Bg. Pacific Star 7803 - Mv. Chang Yang Jin An - TpuGamaliel ChiodaniNo ratings yet
- Week 013-Understanding The 4M's of OperationDocument4 pagesWeek 013-Understanding The 4M's of OperationKat MoliNo ratings yet
- Just in 10 Minutes: A Case Study On Zepto: Keywords: Zepto, Start-Up, E-Commerce, Business Model, Post-CovidDocument4 pagesJust in 10 Minutes: A Case Study On Zepto: Keywords: Zepto, Start-Up, E-Commerce, Business Model, Post-CovidAlisha ShwetaNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 - Setting Up A New Enterprise - UpdatedDocument33 pagesCHP 1 - Setting Up A New Enterprise - UpdatedAbdullah :No ratings yet
- Trout Inc. Prepared The Following Production Report-Weighted AverageDocument4 pagesTrout Inc. Prepared The Following Production Report-Weighted AverageJalaj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gallagherbrandguidelines 01-2022Document72 pagesGallagherbrandguidelines 01-2022Amol TiwariNo ratings yet
- 1 MANU 3318 Engineering Economics and Management PDFDocument47 pages1 MANU 3318 Engineering Economics and Management PDFAmirul HakimNo ratings yet
- Explain The Difference in Attitude To Risk Between European and US CompaniesDocument3 pagesExplain The Difference in Attitude To Risk Between European and US CompaniesJomer FernandezNo ratings yet
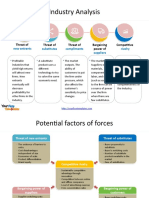
- Industry Analysis: Threat of Threat of Threat of Bargaining Power of CompetitiveDocument2 pagesIndustry Analysis: Threat of Threat of Threat of Bargaining Power of Competitivevasuca2007No ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2Jerome Eziekel Posada PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Rural EntrepreneurshipDocument37 pagesRural EntrepreneurshipRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Descriptive Solve 2Document8 pagesCase Descriptive Solve 2rocken samiunNo ratings yet
- Elements of BusinessDocument6 pagesElements of BusinessetfregtrgNo ratings yet
- Component Seals: and Machine Specific Plug in SealsDocument72 pagesComponent Seals: and Machine Specific Plug in SealsDamonNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1 by Yerbol Bolat-CapstoneDocument10 pagesPresentation 1 by Yerbol Bolat-CapstoneYerbol BolatNo ratings yet
- BSBWOR203 - Complaint Handling Policy and Procedures.v1.0Document2 pagesBSBWOR203 - Complaint Handling Policy and Procedures.v1.0মাহমুদুল হাসান0% (1)
- Software Project Management: Activity PlanningDocument56 pagesSoftware Project Management: Activity PlanningAhmed Nasir Haji HassanNo ratings yet
- IC364 Total Quality ManagementDocument2 pagesIC364 Total Quality ManagementAKSHAY KRISHNA K RNo ratings yet
- Vega Helmet Project 2010Document82 pagesVega Helmet Project 2010kittya135748988% (8)
- Business StrategyDocument18 pagesBusiness StrategyValeria CostoNo ratings yet
- Accurate Industrial Controls PVT LTD: Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesAccurate Industrial Controls PVT LTD: Job DescriptionANIRBAN BISWASNo ratings yet
- Five Aspects of Feasibility AnalysisDocument24 pagesFive Aspects of Feasibility AnalysisLovelyn Bunda-Palomo100% (2)
- ISO 13053-2 2011 (E) PDF DocumentDocument56 pagesISO 13053-2 2011 (E) PDF DocumentmacprorababNo ratings yet