Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MathsStandard MS Class 10 2022 23
Uploaded by
methesmrtyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MathsStandard MS Class 10 2022 23
Uploaded by
methesmrtyCopyright:
Available Formats
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
MARKING SCHEME
SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS- STANDARD
CLASS X
SECTION - A
1 (c) 35 1
2 (b) x2–(p+1)x +p=0 1
3 (b) 2/3 1
4 (d) 2 1
5 (c) (2,-1) 1
6 (d) 2:3 1
7 (b) tan 30° 1
8 (b) 2 1
𝑎𝑦
9 (c) x= 𝑎+𝑏 1
10 (c) 8cm 1
11 (d) 3√3cm 1
12 (d) 9π cm2 1
13 (c) 96 cm2 1
14 (b) 12 1
15 (d) 7000 1
16 (b) 25 1
17 (c) 11/36 1
18 (a) 1/3 1
19 (b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is not the correct 1
explanation of assertion (A)
20. (a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct 1
explanation of assertion (A)
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
SECTION – B
21 Adding the two equations and dividing by 10, we get : x+y = 10 ½
Subtracting the two equations and dividing by -2, we get : x-y =1 ½
Solving these two new equations, we get, x = 11/2 ½
y = 9/2 ½
22 In ΔABC,
∠1 = ∠2
∴ AB = BD ………………………(i) ½
Given,
AD/AE = AC/BD
Using equation (i), we get ½
AD/AE = AC/AB ……………….(ii)
In ΔBAE and ΔCAD, by equation (ii),
AC/AB = AD/AE ½
∠A= ∠A (common)
∴ ΔBAE ~ ΔCAD [By SAS similarity criterion] ½
23 ∠PAO = ∠ PBO = 90° ( angle b/w radius and tangent) ½
∠AOB = 105° (By angle sum property of a triangle) ½
∠AQB = ½ x105° = 52.5° (Angle at the remaining part of the circle is half the 1
angle subtended by the arc at the centre)
24
We know that, in 60 minutes, the tip of minute hand moves 360°
In 1 minute, it will move =360°/60 = 6° ½
∴ From 7 : 05 pm to 7: 40 pm i.e. 35 min, it will move through = 35 × 6° = 210° ½
∴ Area of swept by the minute hand in 35 min = Area of sector with sectorial angle θ
of 210° and radius of 6 cm
210
= 360x π x 62 ½
7 22
= x x6x6
12 7
=66cm2 ½
OR
Let the measure of ∠A, ∠B, ∠C and ∠D be θ₁, θ₂, θ₃ and θ₄ respectively
Required area = Area of sector with centre A + Area of sector with centre B
½
+ Area of sector with centre C + Area of sector with centre D
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
𝛉₁ 𝛉₂ 𝛉₃ 𝛉₄
= x π x 72 + x π x 72 + x π x 72 + x π x 72
360 360 360 360 ½
(𝛉₁ + 𝛉₂ + 𝛉₃ + 𝛉₄)
= x π x 72
360
(𝟑𝟔𝟎) 𝟐𝟐
= x x 7x 7 ( By angle sum property of a triangle) ½
360 7
= 154 cm2 ½
25 sin(A+B) =1 = sin 90, so A+B = 90……………….(i) ½
cos(A-B)= √3/2 = cos 30, so A-B= 30……………(ii) ½
From (i) & (ii) ∠A = 60° ½
And ∠B = 30° ½
OR
cosθ − sin θ 1−√3
= 1+√3
cosθ+sin θ
Dividing the numerator and denominator of LHS by cosθ, we get ½
1 − tan θ 1−√3
= 1+√3 ½
1+tan θ
Which on simplification (or comparison) gives tanθ = √3
Or θ= 60° ½
½
SECTION - C
26 Let us assume 5 + 2√3 is rational, then it must be in the form of p/q where p and
1
q are co-prime integers and q ≠ 0
i.e 5 + 2√3 = p/q
½
𝑝−5𝑞
So √3 = ……………………(i)
2𝑞
½
Since p, q, 5 and 2 are integers and q ≠ 0, HS of equation (i) is rational. But
LHS of (i) is √3 which is irrational. This is not possible. ½
This contradiction has arisen due to our wrong assumption that 5 + 2√3 is
rational. So, 5 + 2√3 is irrational.
½
27 Let α and β be the zeros of the polynomial 2x2 -5x -3
Then α + β = 5/2 ½
And αβ = -3/2. ½
Let 2α and 2β be the zeros x2 + px +q
Then 2α + 2β = -p ½
2(α + β) = -p
2 x 5/2 =-p
So p = -5 ½
And 2α x 2β = q ½
4 αβ = q
So q = 4 x-3/2
= -6 ½
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
28
Let the actual speed of the train be x km/hr and let the actual time taken be y hours.
½
Distance covered is xy km
If the speed is increased by 6 km/hr, then time of journey is reduced by 4 hours i.e.,
when speed is (x+6)km/hr, time of journey is (y−4) hours.
∴ Distance covered =(x+6)(y−4)
⇒xy=(x+6)(y−4)
⇒−4x+6y−24=0 ½
⇒−2x+3y−12=0 …………………………….(i)
Similarly xy=(x−6)(y+6)
⇒6x−6y−36=0
⇒x−y−6=0 ………………………………………(ii) ½
Solving (i) and (ii) we get x=30 and y=24 1
Putting the values of x and y in equation (i), we obtain
Distance =(30×24)km =720km.
½
Hence, the length of the journey is 720km.
OR
Let the number of chocolates in lot A be x
½
And let the number of chocolates in lot B be y
∴ total number of chocolates =x+y
𝟐
Price of 1 chocolate = ₹ 2/3 , so for x chocolates = 𝟑x
and price of y chocolates at the rate of ₹ 1 per chocolate =y.
𝟐
∴ by the given condition 𝟑x +y=400
½
⇒2x+3y=1200 ..............(i)
𝟒
Similarly x+𝟓y = 460
½
⇒5x+4y=2300 ........ (ii)
Solving (i) and (ii) we get
x=300 and y=200
∴x+y=300+200=500 1
So, Anuj had 500 chocolates. ½
29 LHS : sin3θ/ cos3θ + cos3θ/ sin3θ ½
1+ sin2θ/cos2θ 1+ cos2θ/ sin2θ
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
= sin3θ/ cos3θ + cos3θ/ sin3θ
(cos2θ + sin2θ)/cos2θ (sin2θ + cos2θ)/ sin2θ
= sin3θ + cos3θ ½
cosθ sinθ
= sin4 θ + cos4 θ ½
cosθsinθ
= (sin2θ + cos2θ)2 – 2 sin2θcos2θ ½
cosθsinθ
= 1 - 2 sin2θcos2θ ½
cosθsinθ
= 1 - 2 sin2θcos2θ
cosθsinθ cosθsinθ
= secθcosecθ – 2sinθcosθ ½
= RHS
30
Let ABCD be the rhombus circumscribing the circle
with centre O, such that AB, BC, CD and DA touch
the circle at points P, Q, R and S respectively.
We know that the tangents drawn to a circle from an
exterior point are equal in length.
∴ AP = AS………….(1)
BP = BQ……………(2)
CR = CQ …………...(3) 1
DR = DS……………(4).
Adding (1), (2), (3) and (4) we get
AP+BP+CR+DR = AS+BQ+CQ+DS
(AP+BP) + (CR+DR) = (AS+DS) + (BQ+CQ)
∴ AB+CD=AD+BC-----------(5) 1
Since AB=DC and AD=BC (opposite sides of parallelogram ABCD) ½
putting in (5) we get, 2AB=2AD
or AB = AD.
∴ AB=BC=DC=AD
Since a parallelogram with equal adjacent sides is a rhombus, so ABCD is a ½
rhombus
OR
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
Join OC
In Δ OPA and Δ OCA
OP = OC (radii of same circle)
PA = CA (length of two tangents from an external point) 1
AO = AO (Common)
Therefore, Δ OPA ≅ Δ OCA (By SSS congruency criterion) ½
Hence, ∠ 1 = ∠ 2 (CPCT) ½
Similarly ∠ 3 = ∠ 4
∠PAB + ∠QBA =180°(co interior angles are supplementary as XY∥X’Y’) ½
2∠2 + 2∠4 = 180°
½
∠2 + ∠4 = 90°-------------------------(1)
∠2 + ∠4 +∠AOB = 180° (Angle sum property)
Using (1), we get, ∠AOB = 90°
31 3 1
(i) P (At least one head) = 4
3 1
(ii) P(At most one tail) = 4
2 1 1
(iii) P(A head and a tail) = 4 = 2
SECTION D
32 Let the time taken by larger pipe alone to fill the tank= x hours ½
Therefore, the time taken by the smaller pipe = x+10 hours
4
Water filled by larger pipe running for 4 hours = 𝑥 litres
9
Water filled by smaller pipe running for 9 hours = 𝑥+10 litres
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
We know that
4 9 1 1
+ 𝑥+10 = 2
𝑥
Which on simplification gives:
1
x2−16x−80=0
x2−20x + 4x−80=0
x(x-20) + 4(x-20)= 0
(x +4)(x-20)= 0
1
x=- 4, 20
x cannot be negative.
½
Thus, x=20
½
x+10= 30
Larger pipe would alone fill the tank in 20 hours and smaller pipe would fill the
½
tank alone in 30 hours.
OR
Let the usual speed of plane be x km/hr ½
and the reduced speed of the plane be (x-200) km/hr
Distance =600 km [Given]
According to the question,
(time taken at reduced speed) - (Schedule time) = 30 minutes = 0.5 hours.
1
600 600 1
− 𝑥 =2
𝑥−200
Which on simplification gives:
1
x2 - 200x−240000=0
x2 -600x + 400x −240000=0
x(x- 600) + 400( x-600) = 0
(x-600)(x+400) =0
1
x=600 or x=−400
½
But speed cannot be negative.
½
∴ The usual speed is 600 km/hr and
600 ½
the scheduled duration of the flight is 600 =1hour
33 For the Theorem :
Given, To prove, Construction and figure 1½
Proof
1½
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
Let ABCD be a trapezium DC∥AB and EF is a line parallel to AB and hence to DC.
𝐃𝐄 𝐂𝐅
To prove : 𝐄𝐀 =𝐅𝐁
Construction : Join AC, meeting EF in G.
Proof :
In △ABC, we have
GF∥AB
CG/GA=CF/FB [By BPT] ......(1) ½
In △ADC, we have
EG∥DC ( EF ∥AB & AB ∥DC)
½
DE/EA= CG/GA [By BPT] .....(2)
From (1) & (2), we get,
𝐃𝐄 𝐂𝐅 ½
=
𝐄𝐀 𝐅𝐁
34. Radius of the base of cylinder (r) = 2.8 m = Radius of the base of the cone (r)
Height of the cylinder (h)=3.5 m
Height of the cone (H)=2.1 m.
Slant height of conical part (l)=√r2+H2
= √(2.8)2+(2.1)2
1
= √7.84+4.41
= √12.25 = 3.5 m 1
Area of canvas used to make tent = CSA of cylinder + CSA of cone
1
= 2×π×2.8×3.5 + π×2.8×3.5
= 61.6+30.8
= 92.4m2 1
1
Cost of 1500 tents at ₹120 per sq.m
= 1500×120×92.4
= 16,632,000
Share of each school to set up the tents = 16632000/50 = ₹332,640
OR
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
First Solid Second Solid
(i) SA for first new solid (S₁):
6×7×7 + 2 π ×3.52 - π ×3.52 1
= 294 + 77 – 38.5
= 332.5cm2
SA for second new solid (S₂):
6×7×7 + 2 π ×3.52 - π ×3.52 1
= 294 + 77 – 38.5 1
= 332.5 cm2
So S₁: S₂ = 1:1
2
(ii) Volume for first new solid (V₁)= 7×7×7 - 3π ×3.53
539 1519
= 343 - = cm3 1
6 6
2
Volume for second new solid (V₂)= 7×7×7 + 3π ×3.5 3
539 2597
= 343 + = cm3 1
6 6
35 Median = 525, so Median Class = 500 – 600 ½
Class interval Frequency Cumulative Frequency
0−100 2 2
100−200 5 7
200−300 x 7+x
300−400 12 19+x
400−500 17 36+x 1½
500−600 20 56+x
600−700 y 56+x+y
700−800 9 65+x +y
800−900 7 72+x+y
900−1000 4 76+x+y
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
76+x+y=100⇒x+y=24 ….(i) 1
n
−cf
Median = l + 2
xh ½
f
Since, l=500, h=100, f=20, cf=36+x and n=100
Therefore, putting the value in the Median formula, we get;
50−(36+x)
525 = 500 + x 100
20 ½
so x = 9
y = 24 – x (from eq.i)
y = 24 – 9 = 15
Therefore, the value of x = 9 ½
and y = 15. ½
36 (i) B(1,2), F(-2,9)
BF² = ( -2-1)²+ ( 9-2)²
= ( -3)²+ ( 7)²
= 9 + 49
= 58
So, BF = √58 units 1
(ii)
W(-6,2), X(-4,0), O(5,9), P(3,11) ½
Clearly WXOP is a rectangle
Point of intersection of diagonals of a rectangle is the mid point of
the diagonals. So the required point is mid point of WO or XP
−6+5 2+9
=( 2 , 2 )
−1 11
½
=(2, )
2
(iii) A(-2,2), G(-4,7)
Let the point on y-axis be Z(0,y) ½
AZ² = GZ² ½
10
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
( 0+2)² + ( y-2)² = ( 0+4)² + ( y-7)²
( 2)² + y² + 4 -4y= (4)²+ y² + 49 -14y
8-4y = 65-14y
10y= 57
So, y= 5.7 ½
i.e. the required point is (0, 5.7) ½
OR
A(-2,2), F(-2,9), G(-4,7), H(-4,4)
Clearly GH = 7-4=3units ½
AF = 9-2=7 units ½
So, height of the trapezium AFGH = 2 units
1
So, area of AFGH = (AF + GH) x height
2
1
= 2(7+3) x 2
½
= 10 sq. units ½
37. (i) Since each row is increasing by 10 seats, so it is an AP with first term a= 30,
and common difference d=10. ½
So number of seats in 10th row = 𝑎10 = a+ 9d
= 30 + 9×10 = 120 ½
n
(ii) Sn = 2( 2a + (n-1)d)
n ½
1500 = 2( 2 × 30 + (n-1)10)
3000 = 50n + 10n2
n2 +5n -300 =0 ½
n2 + 20n -15n – 300 =0
(n+20) (n-15) =0 ½
Rejecting the negative value, n= 15 ½
OR
No. of seats already put up to the 10th row = S10 ½
10
S10 = 2 {2 × 30 + (10-1)10)} ½
11
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
= 5(60 + 90) = 750 ½
So, the number of seats still required to be put are 1500 -750 = 750 ½
(iii) If no. of rows =17
then the middle row is the 9th row ½
𝑎8 = a+ 8d
= 30 + 80
= 110 seats ½
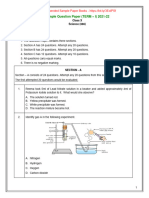
38 (i)
P and Q are the two positions of the plane flying at a height of 3000√3m.
A is the point of observation.
(ii) In △ PAB, tan60° =PB/AB
Or √3 = 3000√3/ AB
So AB=3000m 1
tan30°= QC/AC
1/√3= 3000√3 / AC
AC = 9000m ½
distance covered = 9000- 3000
= 6000 m. ½
OR
In △ PAB, tan60° =PB/AB
Or √3 = 3000√3/ AB
So AB=3000m ½
tan45° = RD/AD
1= 3000√3 / AD ½
12
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
AD = 3000√3 m
distance covered = 3000√3 - 3000 ½
= 3000(√3 -1)m.
(iii) speed = 6000/ 30 ½
= 200 m/s
= 200 x 3600/1000 ½
= 720km/hr
3000(√3 −1)
Alternatively: speed = 15(√3 −1) ½
= 200 m/s
= 200 x 3600/1000 ½
= 720km/hr
13
Buy Recommended Sample Paper Books - https://bit.ly/3EoIPSf
You might also like
- MathsStandard MSDocument13 pagesMathsStandard MSRaj YadavNo ratings yet
- Maths Standard MSDocument14 pagesMaths Standard MSAMAN RAJNo ratings yet
- MathsStandard MSDocument14 pagesMathsStandard MSAscendry OkNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - Sample Paper Math For Model Exam.Document8 pagesAnswer Key - Sample Paper Math For Model Exam.ashhhaabNo ratings yet
- T23 First Year 2nd Half Book Test MathDocument3 pagesT23 First Year 2nd Half Book Test MathMuzammil JuttNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class X Mathematics Basic 2023-24 Marking SchemeDocument12 pagesCBSE Class X Mathematics Basic 2023-24 Marking SchemeshailajamahadikNo ratings yet
- Math S Ans BasicDocument12 pagesMath S Ans BasicAyushman BeriaNo ratings yet
- SetA - 10 - Maths Basic Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesSetA - 10 - Maths Basic Marking SchemesamarthbadoniyaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PQMSDocument22 pagesMathematics PQMSHans rajNo ratings yet
- Math Practice Paper 4 MSDocument16 pagesMath Practice Paper 4 MSReeveNo ratings yet
- Ss 3 Mathematics First Term ExamDocument7 pagesSs 3 Mathematics First Term ExamElena SalvatoreNo ratings yet
- Math Club 22-23 F1 Mock Paper - SolDocument17 pagesMath Club 22-23 F1 Mock Paper - Soltrach88347No ratings yet
- PT2 MS X MathDocument5 pagesPT2 MS X MathAkNo ratings yet
- ss3 Furthermaths Mock1Document4 pagesss3 Furthermaths Mock1adegunloye temitopeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions MCQDocument2 pagesTrigonometric Functions MCQHinaud DdbNo ratings yet
- Maths BasicnotesDocument12 pagesMaths BasicnotesMoni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PQMS2Document7 pagesMathematics PQMS2penperfectionist150No ratings yet
- Maths - Tapasya - Complete PDFDocument11 pagesMaths - Tapasya - Complete PDFiNLUV WDuNo ratings yet
- Maths Pre Board Xii Ms Vi-X - Booklet - Part - 2Document20 pagesMaths Pre Board Xii Ms Vi-X - Booklet - Part - 2Abhinav ANo ratings yet
- Math Class X - ADocument7 pagesMath Class X - Asharmavarin72No ratings yet
- DSE 2021 Paper 1 SolutionsDocument9 pagesDSE 2021 Paper 1 SolutionslokNo ratings yet
- Ix Ro Kolkata 2022-2023Document15 pagesIx Ro Kolkata 2022-2023Ritam AichNo ratings yet
- MCQ - ProportionDocument3 pagesMCQ - Proportionbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Algebra For College Students 8th Edition Blitzer Test Bank DownloadDocument94 pagesAlgebra For College Students 8th Edition Blitzer Test Bank DownloadAlan Maxwell100% (23)
- 7th Kat Maths Level - I Work Sheet - 1Document2 pages7th Kat Maths Level - I Work Sheet - 1SahithiNo ratings yet
- Complete Paper 9-14 and 4,5Document4 pagesComplete Paper 9-14 and 4,5punjabcollegekwl5800No ratings yet
- Mathematics PRWDocument7 pagesMathematics PRWanandNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-PQ2 240115 085649Document8 pagesMathematics-PQ2 240115 085649bablubhai1993jsrNo ratings yet
- XII Pre-Board (Evening Shift) MS Directorate of Education, Delhi 2023-24Document18 pagesXII Pre-Board (Evening Shift) MS Directorate of Education, Delhi 2023-24SahilNo ratings yet
- Application of TrigonometryDocument2 pagesApplication of TrigonometryMaster MakingNo ratings yet
- In PS: Nimcet - 2022Document17 pagesIn PS: Nimcet - 2022Avishek JhaNo ratings yet
- Vectors and 3-D Geometry Test - XII (13.02.22) +2 Maths India (NCERT)Document3 pagesVectors and 3-D Geometry Test - XII (13.02.22) +2 Maths India (NCERT)Shivansh KatochNo ratings yet
- 1st Year MathsDocument3 pages1st Year MathskhurramNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE 2006 Mathematics Soutions: Time: 2 HoursDocument14 pagesIIT JEE 2006 Mathematics Soutions: Time: 2 HoursSohan PrajapafNo ratings yet
- CBSE-XII Applied Mathematics Board Paper 2023Document16 pagesCBSE-XII Applied Mathematics Board Paper 2023mohuldua07No ratings yet
- Ratio, Proportion, Indices & LogarithmsDocument7 pagesRatio, Proportion, Indices & LogarithmsTariq100% (1)
- 10 MathematicsBasic MSDocument10 pages10 MathematicsBasic MSAdhil AseemNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper-2 Years Course - XI Moving-EngineeringDocument10 pagesSample Paper-2 Years Course - XI Moving-EngineeringRamanujam SinghNo ratings yet
- Class IX VISTO - 1 MOCK TEST-1Document11 pagesClass IX VISTO - 1 MOCK TEST-1Augustine Joe JNo ratings yet
- Grade10PreboardExaminationMathematics SET2 MakingScheme 8722Document12 pagesGrade10PreboardExaminationMathematics SET2 MakingScheme 8722aadhikrish1357No ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 10 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 10 For Board Exam 2024Roses Are RosieNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Cbse Math 2nd Term Sample Paper 1Document2 pagesGrade 8 Cbse Math 2nd Term Sample Paper 1Dhana AryalNo ratings yet
- CL - 7 - UIMO-2024-Paper-9279 KeyDocument6 pagesCL - 7 - UIMO-2024-Paper-9279 KeySaralaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Maths Paper 2 (AP)Document15 pagesCBSE Maths Paper 2 (AP)Acharya Dronacharya Foundation CenterNo ratings yet
- Xii - Math 041 - MS - PB-1 - SS - Set-1Document8 pagesXii - Math 041 - MS - PB-1 - SS - Set-1sahuunnati977No ratings yet
- MathsBasic MS Class 10 2022 23Document9 pagesMathsBasic MS Class 10 2022 23methesmrtyNo ratings yet
- Unified Council: National Level Science Talent Search ExaminationDocument6 pagesUnified Council: National Level Science Talent Search ExaminationpriyaamirthaNo ratings yet
- Test Paper # 5: Ijso (Stage-I) Test SeriesDocument17 pagesTest Paper # 5: Ijso (Stage-I) Test SeriesUpma GandhiNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Applied Maths QP Set A 2023-24Document7 pagesClass Xii Applied Maths QP Set A 2023-24ramyababu21682No ratings yet
- X Maths QP Code 3 PDFDocument6 pagesX Maths QP Code 3 PDFAshlyn Crasta100% (1)
- 09 SamplequesDocument7 pages09 SamplequesNirvaan GargNo ratings yet
- Standard Sample Paper XyzDocument7 pagesStandard Sample Paper XyzMaurya Sachin100% (1)
- Sample Question Paper - 4 Class - X Session - 2021-22Document15 pagesSample Question Paper - 4 Class - X Session - 2021-22Harsimar KaurNo ratings yet
- Math Standard Sample Paper 4Document17 pagesMath Standard Sample Paper 4susrudhansNo ratings yet
- 15th PMO Qualifying Area StageDocument9 pages15th PMO Qualifying Area StageSuper ManNo ratings yet
- Packet 0 A - Are You Ready For CalculusDocument3 pagesPacket 0 A - Are You Ready For CalculusteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- MS Xii Maths KVS GuwahatiDocument10 pagesMS Xii Maths KVS GuwahatishreeyaNo ratings yet
- Cbjemass 07Document10 pagesCbjemass 07V.R.M SistlaNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Science SQP Term 1Document24 pagesScience SQP Term 1methesmrtyNo ratings yet
- MathsStandard SQPDocument10 pagesMathsStandard SQPAsad farukiNo ratings yet
- SocialScience SQPDocument14 pagesSocialScience SQPmethesmrtyNo ratings yet
- MathsBasic SQPDocument9 pagesMathsBasic SQPCharushree ChundawatNo ratings yet
- PM Shri KV Gachibowli Maths Class X Sample Papers - 240128 - 082834Document155 pagesPM Shri KV Gachibowli Maths Class X Sample Papers - 240128 - 082834rutrackeracc22No ratings yet
- Discrete StructuresDocument317 pagesDiscrete Structureskshitizjain07No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Basic Tools For WritingDocument58 pagesLesson 2 - Basic Tools For WritingNorhayati Hj BasriNo ratings yet
- Produce and Evaluate A Creative Text-Based Presentation (Statement T-Shirt) Using Design Principle and Elements (MIL11/12TIMDocument5 pagesProduce and Evaluate A Creative Text-Based Presentation (Statement T-Shirt) Using Design Principle and Elements (MIL11/12TIMestrina bailonNo ratings yet
- Soal Latihan (C.4) 010 Calender Days and MonthsDocument1 pageSoal Latihan (C.4) 010 Calender Days and MonthsRahmat RahmatNo ratings yet
- Python-RDM Documentation: Release 0.1Document36 pagesPython-RDM Documentation: Release 0.1IENSOUBO DidierNo ratings yet
- Classroom Expectations Sy19-20Document1 pageClassroom Expectations Sy19-20api-365451133No ratings yet
- Abhidharma - Class Notes (Intro)Document10 pagesAbhidharma - Class Notes (Intro)empty2418No ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Putri Arifa Nur'Aini - 464211052Document3 pagesAssignment 3 - Putri Arifa Nur'Aini - 464211052Putri Arifa N.No ratings yet
- Rhea - Samuel A. - Brief Grammar and Vocabulary of The Hakkari - 1869Document39 pagesRhea - Samuel A. - Brief Grammar and Vocabulary of The Hakkari - 1869Anonymous qkhwe0nUN1No ratings yet
- Leasing .NET Core - Xamarin Forms + Prism - Xamarin Classic + MVVM CrossDocument533 pagesLeasing .NET Core - Xamarin Forms + Prism - Xamarin Classic + MVVM CrossJoyner Daniel Garcia DuarteNo ratings yet
- Book of Dzyan - WikipediaDocument3 pagesBook of Dzyan - WikipediaAnonymous PqxjViUtDtNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAmelyn Goco MañosoNo ratings yet
- Fast FormulasDocument25 pagesFast FormulasSumit KNo ratings yet
- Written in Some Neutral Interface Definition Language (IDL) : 26. MiddlewareDocument6 pagesWritten in Some Neutral Interface Definition Language (IDL) : 26. MiddlewareSoundarya SvsNo ratings yet
- Lefl 102Document10 pagesLefl 102IshitaNo ratings yet
- Powers of 2 TableDocument3 pagesPowers of 2 Tablehackna0% (1)
- Identifying The True IP of I2P Service HostsDocument23 pagesIdentifying The True IP of I2P Service HostsHaddad SammirNo ratings yet
- Cambio SoftwareDocument31 pagesCambio SoftwareMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- The Past Simple Tense of The Verb TO BE1JJ-1 PDFDocument10 pagesThe Past Simple Tense of The Verb TO BE1JJ-1 PDFfrank rojasNo ratings yet
- Sach Bai Tap Trac Nghiem Tieng Anh 9Document240 pagesSach Bai Tap Trac Nghiem Tieng Anh 9Minh Chanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- E10 User Manual PDFDocument30 pagesE10 User Manual PDFRodrygo Bortotti100% (1)
- RTI Manual Case StudiesDocument78 pagesRTI Manual Case StudiesMlm Webpagelike Carelifes WebpagelikeNo ratings yet
- Basics of ProgrammingDocument30 pagesBasics of ProgrammingssssmailnatNo ratings yet
- Turabian Style Citations: Library Resource GuideDocument7 pagesTurabian Style Citations: Library Resource Guidejwtan2010No ratings yet
- 3 Eps 211 2024Document5 pages3 Eps 211 20248knpjk26b7No ratings yet
- Introducción Gramatica InglesaDocument25 pagesIntroducción Gramatica InglesaJavi TarNo ratings yet
- CakePHP BookDocument312 pagesCakePHP BookrizalihsanNo ratings yet
- Vagrant Up and Running (Presentation Slides)Document20 pagesVagrant Up and Running (Presentation Slides)erminio.antonioNo ratings yet
- English 9 q2 ExamDocument2 pagesEnglish 9 q2 ExamAlphaNo ratings yet
- Deductive DatabasesDocument23 pagesDeductive DatabasesMuhammed JishanNo ratings yet