0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views4 pagesPower System Load Flow Analysis Lab
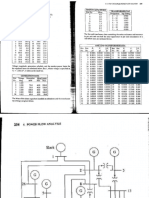
This document provides instructions for an electrical engineering laboratory assignment on power system analysis. Students are asked to use load flow methods like Gauss-Seidel, Newton-Raphson, and fast decoupled to solve 3-bus and 26-bus network examples. Tables of load data, shunt capacitors, transformer taps, and line/transformer parameters are provided for the 26-bus network. Students must demonstrate the distinctions between the load flow methods and submit a full laboratory report.
Uploaded by
Melissa MmatliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views4 pagesPower System Load Flow Analysis Lab
This document provides instructions for an electrical engineering laboratory assignment on power system analysis. Students are asked to use load flow methods like Gauss-Seidel, Newton-Raphson, and fast decoupled to solve 3-bus and 26-bus network examples. Tables of load data, shunt capacitors, transformer taps, and line/transformer parameters are provided for the 26-bus network. Students must demonstrate the distinctions between the load flow methods and submit a full laboratory report.
Uploaded by
Melissa MmatliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd