Professional Documents
Culture Documents
117A-PRELIM-ELEARNING-2nd Sem
Uploaded by
Jovielyn KowetOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
117A-PRELIM-ELEARNING-2nd Sem
Uploaded by
Jovielyn KowetCopyright:
Available Formats
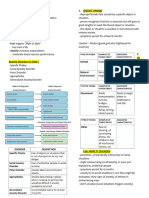
LESSON 1 - Learning theory
- Positive reinforcement
INTRODUCTION
- Individuals w/ clinical disorders
- therapist
- learning more structured ways of behaving
- Denver test COMMUNITY MENTAL HEALTH
- Primary, secondary, & tertiary prevention
- Interdisciplinary approach
MEDICAL & PSYCHOANALYTICAL
- Primary prevention
- Uncovering of childhood trauma & repressed feelings
- memories and thoughts that do not enter awareness
- uncover unconscious memories CRISIS INTERVENTION
- normative
- marriage
INFANCY & EARLY & LATE CHILDHOOD
- crisis intervention
- infancy
- eric erikson
- autonomy vs shame & doubt GROUP THERAPY
- individually focus on each group turn
- 7 – 10 individuals interacting together w/ a shared
ADOLESCENCE, YOUNG ADULTHOOD, ADULTHOOD & OLD-AGE
purpose
- intimacy vs isolation - participants
- 25 – 65 yrs old & giving back is important
- Young adulthood
FAMILY THERAPY
- the family
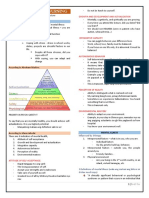
HIERARCHY OF NEEDS
- scapegoat
- Basic psychological needs (bottom) - undefined roles
- Self-actualization
- Abraham Maslow
MILLIEU & ADJUNCTIVE THERAPIES
- dance & art therapy
BEHAVIORIST
- environmental therapy
- client’s inner world WORKING PHASE – COMMUNICATION TOOLS
- using specific, targeted questions
- deflecting statements back to the client
MENTAL ILLNESS & MENTAL HEALTH
- asking why questions
- successfully mask the problems & crises
- different
- respond to them appropriately WORKING PHASE – BLOCKS TO COMMUNICATION
- false reassurance
- belittling
SUBLIMATION, ISOLATION, REACTION FORMATION, ETC.
- agreeing & can block communication
- sport activities
- projection
- reaction formation (contradict inner feeling) TERMINATION PHASE
- evaluation phase
- acceptance
SUPPRESSION, REPRESSION, DENIAL, ETC.
- orientation phase
- denial (ignoring)
- fixation (being stuck)
- denial (no prob. drinking) LESSON 2
OVERVIEW
CHARACTERISTICS - tension in response to a perceived physical or
psychological threat resulting in feelings of helplessness
- truth
and uncertainty
- All encompassing
- nervous system
- social
- anorexia
PREINTERACTION & ORIENTATION LEVELS
- assessment - monitor client closely
- assessment of nurse - moderate
- preinteraction & orientation - difficulty concentrating
PANIC - exaggerated preoccupation with physical health, not
based on real organic disorders
- sudden onset of intense apprehension, fear or terror
- going on and on
- fear that is out of proportion to external events
- redirect the client on other activities
- immobily
STRESS RELATED DISORDERS
- psychosocial factors
PHOBIC
- Hypotension
- agoraphobia - Set limits on rumination
- lifestyle changes
- gradual desensitization
DISSOCIATIVE DISORDERS
- splitting off an idea or emotion from one's consciousness
OBSESSIVE-COMPULSIVE
- rule out organic pathology
- recurring, irresistible impulse to perform an act - Schizophrenia
- anxiety reduction
- anxiety
ANTIANXIETY AGENTS
- oxazepam
POST TRAUMATIC STRESS
- seizures
- redirect away from manifestations - signs of drug dependence
- Significant, recognizable stressor or trauma outside the
usual range of experience
- distraction LESSON 3
SCHIZOPHRENIA
HYSTERIA - illusion (scarf snake)
- hallucination (covered with ants)
- physical manifestations and complaints without organic
- delusion (I am God)
impairment
- neurotic disorder
- decrease the time spent
TYPES
- provide a safe & restrictive environment
HYPOCHONDRIASIS - confront the client
- paranoid
PARANOID PERSONALITY
- serve food in open containers
- withdrawal
- binging
AUTISM & ADHD
- lack of interest in human contact
- attempt regression therapy
- children
MEDICATIONS
- antipsychotics
- increasing dopamine at the receptor site
- disorganization
EXTRAPYRAMIDAL EFFECTS
- hand tremors
- inability to sit still
- overly sedative
ANTICHOLINERGIC EFFECTS
- frequent urination
- increased likelihood of sunburn
- treat for hypotension
You might also like
- Self Help CBT Cognitive Behavior Therapy Training Course & Toolbox: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Book for Anger Management, Depression, Social Anxiety, OCD, Sleep Disorders, Addictions, Fears & moreFrom EverandSelf Help CBT Cognitive Behavior Therapy Training Course & Toolbox: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Book for Anger Management, Depression, Social Anxiety, OCD, Sleep Disorders, Addictions, Fears & moreRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Psychiatric Nursing NotesDocument13 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Notesapi-384275892% (26)
- Contextual Behavior Therapy For Sexual and Gender Minority Clients - NodrmDocument148 pagesContextual Behavior Therapy For Sexual and Gender Minority Clients - NodrmDAY100% (1)
- Sensory Processing BrochureDocument3 pagesSensory Processing Brochureapi-383884645No ratings yet
- EDST5134 - Assignment 1: Annotated BibliographyDocument8 pagesEDST5134 - Assignment 1: Annotated Bibliographyvu_minh1995_60171068No ratings yet
- Michael Jacobs v. Eric Leon, Et Al.Document22 pagesMichael Jacobs v. Eric Leon, Et Al.Michael_Roberts2019No ratings yet
- Trauma Sequelae (Libro)Document537 pagesTrauma Sequelae (Libro)Andrea BautistaNo ratings yet
- 117a MidtermDocument2 pages117a MidtermJonathan MangawiliNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Psychiatric NursingDocument4 pagesConcepts in Psychiatric NursingkurtsalvadorbsnNo ratings yet
- Psych - ArcDocument4 pagesPsych - ArcMae PenaredondoNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing 2.2 SSCTDocument16 pagesPsychiatric Nursing 2.2 SSCTEnna EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorder A: Cluster Types Description Approach A. ParanoidDocument4 pagesPersonality Disorder A: Cluster Types Description Approach A. ParanoidEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Psychiatric NursingDocument4 pagesConcepts in Psychiatric NursingkurtsalvadorbsnNo ratings yet
- Group2 B Concepts and Patterns of Human BehaviorDocument3 pagesGroup2 B Concepts and Patterns of Human Behaviorjackclaudefajardo15No ratings yet
- Crisis and Crisis InterventionDocument7 pagesCrisis and Crisis InterventionAud SyneNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior VictimologyDocument61 pagesHuman Behavior VictimologyRey Mark GedaroNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Lecture1Document6 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Lecture1Kazlle Sheen MinianoNo ratings yet
- This Person Is Not Manifesting To Reality Perception (Ego)Document4 pagesThis Person Is Not Manifesting To Reality Perception (Ego)Nica VictoriaNo ratings yet
- NCP Generalized Anxiety DisorderDocument4 pagesNCP Generalized Anxiety DisorderMikkel BigtingNo ratings yet
- PSYCHEDocument16 pagesPSYCHEblueprincess93No ratings yet
- Mental Health and Psychiatric NursingDocument56 pagesMental Health and Psychiatric NursingShienna Rose Ann ManaloNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument5 pagesPsychiatric NursingcelestineNo ratings yet
- Mental Health NursingDocument4 pagesMental Health NursingRegie EstamioNo ratings yet
- Personal DevelopmentDocument4 pagesPersonal Developmentanika janaeNo ratings yet
- Albert Ellis Rational Emotive Behavior TherapyDocument3 pagesAlbert Ellis Rational Emotive Behavior TherapyAthena DavidNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric and MentalDocument16 pagesPsychiatric and MentalJanine Garcia100% (2)
- PSYCHIATRYDocument21 pagesPSYCHIATRYdarrelNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Week 4Document6 pagesNCM 117 Week 4Ljae NatinoNo ratings yet
- 05b Neurobiologija UčenjaDocument17 pages05b Neurobiologija Učenjabotoks uwuNo ratings yet
- Ina PhsychDocument11 pagesIna PhsychEyanah Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Abpsy Lecture Chapter 1.1 - 2Document4 pagesAbpsy Lecture Chapter 1.1 - 2Tracey GoldNo ratings yet
- Disorder: Anorexia & Bulimia Nervosa: Factors: PREDISPOSINGDocument10 pagesDisorder: Anorexia & Bulimia Nervosa: Factors: PREDISPOSINGAldrin PaulinoNo ratings yet
- PERDEV REVIEWER 2nd QuarterDocument1 pagePERDEV REVIEWER 2nd QuarterDell OleahNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewerDocument7 pagesPsychiatric Nursing ReviewerJay Soriano0% (1)
- Psychiatric and Mental Health NursingDocument36 pagesPsychiatric and Mental Health NursingKaye V. VerroyaNo ratings yet
- NCM117 Lec TopicsDocument14 pagesNCM117 Lec TopicsEzra AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- Recreational NCD Grade 12Document30 pagesRecreational NCD Grade 12Rafael AnianoNo ratings yet
- AB PSYCH Chapter 2Document33 pagesAB PSYCH Chapter 2ALEXANDRA SAN PEDRONo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology (Last Discussion)Document18 pagesAbnormal Psychology (Last Discussion)FLORLYN VERALNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Summary (Chapter 1 - 2)Document29 pagesAbnormal Psychology Summary (Chapter 1 - 2)Louise Alenah LabragueNo ratings yet
- Anxiety: - Protects Us From Something BadDocument11 pagesAnxiety: - Protects Us From Something BadCram RaiboNo ratings yet
- ABPSY Finals ReviewerDocument48 pagesABPSY Finals ReviewerMary Grace AngelesNo ratings yet
- Reactive Attachment DisorderDocument28 pagesReactive Attachment DisorderkadingermftNo ratings yet
- Psychology Gestalt PsychologyDocument15 pagesPsychology Gestalt PsychologyYAGI, Miyuki F.No ratings yet
- Local Media2246351459788256841Document4 pagesLocal Media2246351459788256841Reyster AfricaNo ratings yet
- Module 7-Mental-Health-and-Well-BeingDocument17 pagesModule 7-Mental-Health-and-Well-BeingDaniela AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisorderfebieNo ratings yet
- Stressors and Responses: PhysicalDocument14 pagesStressors and Responses: PhysicalWinona BartolomeNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1a Dimension 2024Document9 pages3.1.1a Dimension 2024lachykoumisNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOLOGYDocument7 pagesPSYCHOLOGYLiela SagunNo ratings yet
- Stress, Health, & CopingDocument6 pagesStress, Health, & CopingThe Sage CarrotNo ratings yet
- Bullets in PsycheDocument115 pagesBullets in PsycheFEVIE ANNE BANATAONo ratings yet
- Abnormal PsychDocument15 pagesAbnormal PsychkilluhmaylucianoNo ratings yet
- Disorder: General Anxiety Disorder: Factors: PREDISPOSINGDocument7 pagesDisorder: General Anxiety Disorder: Factors: PREDISPOSINGAldrin PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Examination Psychiatric Nursing Assessment SpeechDocument2 pagesMental Status Examination Psychiatric Nursing Assessment SpeechElaine Louise O. Foronda100% (1)
- Pshiatric Nursing Final Coaching Nle Board ExamDocument16 pagesPshiatric Nursing Final Coaching Nle Board ExammariaalmiramsaritaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Well-Being in Middle and Late AdolescenceDocument6 pagesMental Health and Well-Being in Middle and Late AdolescenceLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Personality DisordersDocument18 pagesChapter 10 - Personality DisordersJan Kezeah AbingNo ratings yet
- AFFECTIVE DisordersDocument3 pagesAFFECTIVE DisordersJanine GarciaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing DemystifiedFrom EverandPsychiatric and Mental Health Nursing DemystifiedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Product List Clinics - IndustriesDocument7 pagesProduct List Clinics - IndustriesKhymberly Whey MercadoNo ratings yet
- The Impacton Techiesdueto Layofffromtheir EmployersDocument45 pagesThe Impacton Techiesdueto Layofffromtheir EmployersShravani ShreyaNo ratings yet
- Psychology and The Legal System Ninth Edition Edith Greene All ChapterDocument67 pagesPsychology and The Legal System Ninth Edition Edith Greene All Chapterjames.dorman550100% (5)
- Psychiatry EORDocument16 pagesPsychiatry EORAndrew BowmanNo ratings yet
- Journal of Anxiety DisordersDocument10 pagesJournal of Anxiety DisordersEstefania NavarroNo ratings yet
- 2013 - Complicated GriefDocument353 pages2013 - Complicated GriefSofía ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bhatia, S., & Priya, K. R. (2018) - Decolonizing Culture Euro-American Psychology and The Shaping of Neoliberal Selves in IndiaDocument24 pagesBhatia, S., & Priya, K. R. (2018) - Decolonizing Culture Euro-American Psychology and The Shaping of Neoliberal Selves in IndiaVijay JhaNo ratings yet
- A Practitioner's Guide To BreathworkDocument18 pagesA Practitioner's Guide To BreathworkOctavio Uriel Garrido Lopez100% (1)
- Discursive Essays ExamplesDocument5 pagesDiscursive Essays Examplesolylmqaeg100% (2)
- Hackmann 2011 Imagery Rescripting in PTSDDocument9 pagesHackmann 2011 Imagery Rescripting in PTSDAna FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Solution Focused Therapy For Trauma SurvivorsDocument11 pagesSolution Focused Therapy For Trauma SurvivorsJason SnapeNo ratings yet
- Causes of Stress and Its Impact On HealthDocument5 pagesCauses of Stress and Its Impact On HealthHana MohamedNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0165178114006428 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0165178114006428 MainMariaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DSM and ICDDocument21 pagesDifferences Between DSM and ICDPRITI PUNWANI 20224337No ratings yet
- EMDR TherapyDocument11 pagesEMDR TherapyHassanNo ratings yet
- Lit - Gregoria de JesusDocument8 pagesLit - Gregoria de JesusWinter BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Reading Report Ads ItDocument5 pagesReading Report Ads ItcourtneyNo ratings yet
- Effects of Childhood Trauma On Adolescent Mental HDocument9 pagesEffects of Childhood Trauma On Adolescent Mental Hlonjezoaustin357No ratings yet
- Local Media9217284258618033814Document2 pagesLocal Media9217284258618033814Rocelgie JimenezNo ratings yet
- Non FictionDocument5 pagesNon FictionSlick IncubatorsNo ratings yet
- P.E 11 AerobicsDocument31 pagesP.E 11 AerobicsLance AustriaNo ratings yet
- English Term PaperDocument19 pagesEnglish Term PaperThe • Best • KamatisNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography - Effect of War On ChildrenDocument10 pagesAnnotated Bibliography - Effect of War On ChildrenaiizNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument10 pagesAnxiety DisorderAsmaa Ateef2912No ratings yet
- Research Essay Adoption 2Document13 pagesResearch Essay Adoption 2api-542872339No ratings yet
- Toliongco vs. CADocument17 pagesToliongco vs. CAAnonymous KaNu0py71No ratings yet