Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2020
Uploaded by
SubhaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2020
Uploaded by
SubhaCopyright:
Available Formats
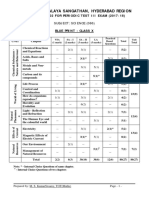
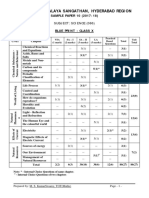
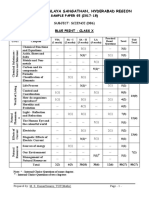
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, GPRA CAMPUS, HYD–32
SAMPLE PAPER 05 (2019-20)
SUBJECT: SCIENCE (086)
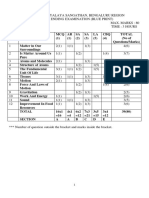
BLUE PRINT : CLASS X
MCQ VSA SA LA Unit
UNIT Chapter (1 mark) (1 mark) (3 marks) (5 marks)
Total
Total
Chemical Reactions and
1(1) -- 3(1) -- 4(2)
Chemical Substances -
Nature and Behaviour
Equations
Acids, Bases and Salts 1(1) -- 3(1)* -- 4(2)
Metals and Non-metals -- -- -- 5(1)* 5(1) 25(11)
1(1)
Carbon and its compounds -- -- 5(1) 7(3)
1(1)AR
Periodic Classification of
1(1)* 1(1) 3(1) -- 5(3)
Elements
Life Process -- -- 3(1) 5(1) 8(2)
World of Living
Control and Coordination 2(2) 2(2) 3(1) -- 7(5)
23(9)
How do organisms
-- -- -- 5(1)* 5(1)
reproduce?
Heredity and Evolution -- -- 3(1) -- 3(1)
Light - Reflection and
Phenomena
-- -- 3(1) 5(1)* 8(2)
Natural
Refraction
12(4)
The Human Eye and the
1(1)* -- 3(1)* -- 4(2)
colourful world
Effects of
Electricity 2(2) -- -- 5(1) 7(3)
Current
13(7)
Magnetic Effects of Electric 2(2)
-- 3(1) -- 6(4)
Current 1(1)AR
Sources of energy 1(1) 2(2) -- -- 3(3)
Resources
Natural
Our Environment -- -- 3(1)* -- 3(1) 7(5)
Management of Natural
1(1)* -- -- -- 1(1)
Resources
Total 10(10) 10(10) 30(10) 30(6) 80(36) 80(36)
Note: * - Internal Choice Questions of same chapter.
AR
– Assertion, Reason based question
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, GPRA CAMPUS, HYD–32
SAMPLE PAPER 05 (2019-20)
SUBJECT: SCIENCE MAX. MARKS : 80
CLASS : X DURATION : 3 HRS
General Instructions:
1. The question paper comprises three sections – A, B and C. Attempt all the sections.
2. All questions are compulsory.
3. Internal choice is given in each section.
4. All questions in Section A are one-mark questions comprising MCQ, VSA type and assertion-reason
type questions. They are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
5. All questions in Section B are three-marks, short-answer type questions. These are to be answered in
about 50 - 60 words each.
6. All questions in Section C are five-marks, long-answer type questions. These are to be answered in about
80 – 90 words each.
7. This question paper consists of a total of 30 questions.
SECTION – A
1. When we enter a dark room coming from outside, immediately the things inside the room do not
appear clear to our eyes. This is because
(a) pupils do not open at all in the dark. (b) pupils take time to adjust.
(c) light travels slower in a dark room. (d) pupils open very quickly in the dark.
OR
The phenomena of light responsible for the working of the human eye is
(a) reflection (b) refraction
(c) power of accommodation (d) persistence of vision
2. When a 4V battery is connected across an unknown resistor there is a current of 100 mA in the
circuit. The value of the resistance of the resister is:
(a) 4 Ω (b) 40 Ω (c) 400 Ω (d) 0.4 Ω
3. Unit of electric power may also be expressed as:
(a) volt-ampere (b) kilowatt-hour (c) watt-second (d) joule-second
4. It was found that water from a river was contaminated with Coliform bacteria. Which one of the
following pollutant might have got mixed with the water?
(a) Fertilizer run off (b) Industrial waste
(c) Pesticides (d) Human faecal matter
OR
Which one of the following stakeholders of forests causes the maximum damage to forest?
(a) People who live in or around the forest (b) The forest department of the government
(c) The wildlife and native enthusiasts (d) The industrialists
5. Which one of the following green house gases is a contributor due to incomplete combustion of
coal and petroleum?
(a) Oxides of nitrogen (b) Methane (c) Carbon monoxide (d) Carbon dioxide
6. Which of the following reactions is an endothermic reaction?
(a) Burning of coal.
(b) Decomposition of vegetable matter into compost.
(c) Process of respiration.
(d) Decomposition of calcium carbonate to form quick lime and carbon dioxide.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2 -
7. Identify the basic salt from the following salts:
(a) Na2CO3 (b) NH4Cl (c) NaNO3 (d) KCl
8. Answer question numbers 8(i) - 8(iv) on the basis of your understanding of the following
paragraph and the related studied concepts.
Renewable energy sources such as wind energy are vital for the Indian economy, not only from
the point of view of supply, but also from the perspective of environmental and social benefits.
India is the world’s fifth largest wind-power producer and the largest windmill facilities in India
are installed in Tamil Nadu. Muppandal is a small village of Tamil Nadu and one of the most
important sites of wind-farm in the state. It uses wind from the Arabian Sea to produce
renewable energy. The suitability of Muppandal as a site for wind farms stems from its
geographical location as it has access to the seasonal monsoon winds.
The electrical generators used on wind turbines in sites like Muppandal, produce an output AC of
240 V and a frequency of 50 Hz even when the wind speed is fluctuating. A transformer may be
required to increase or decrease the voltage so it is compatible with the end usage, distribution or
transmission voltage, depending on the type of interconnection.
8(i) State the principle behind electric generator.
8(ii) The output frequency of wind turbine is 50 Hz. What is meant by this statement?
8(iii) Why do you think Muppandal is at an advantageous position for this project?
8(iv) Based on the data represented in the graph below, which of the two cities A or B would be
an ideal location for establishing a wind-farm and why?
9. The positions of four elements A, B, C and D in the modern periodic table are shown below.
Which element is most likely to form an acidic oxide?
A
B
C
D
(a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3 -
OR
Elements P, Q, R and S have atomic numbers 11, 15, 17 and 18 respectively. Which of
them are reactive non-metals?
(a) P and Q (b) P and R (c) Q and R (d) R and S
10. Question numbers 10(i) - 10(iv) are based on the two tables given below. Study these tables
related to blood sugar levels and answer the questions that follow.
Table A (Blood glucose chart)
Remark Mean Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL)
380
350
Doctor’s 315
advice needed 280
250
215
180
Good
150
115
Excellent 80
50
Table B (Blood Report of Patient X and Y)
Blood Glucose ranges (mg/dL)
Time of check
Patient X Patient Y
Before breakfast (Fasting) < 100 70 – 130
Before lunch, supper and snack < 110 70 – 130
Two hours after meals < 140 < 180
Bedtime < 120 90- 15
10(i) Refer to Table B showing the blood report of the levels of glucose of patients X and Y.
Infer the disease which can be diagnosed from the given data.
10(ii) Identify the hormone whose level in the blood is responsible for the above disease.
10(iii) Which one of the following diets would you recommended to the affected patient?
(a) High sugar and low fat diet. (b) Low sugar and high protein diet.
(c) High Fat and low fiber diet. (d) Low sugar and high fiber diet.
10(iv) Refer to the Table A and suggest the value of the mean blood glucose level beyond which
doctor’s advice is necessary:
(a) 180 mg/dL (b) 115 mg/dL (c) 50 mg/dL (d) 80 mg/dL
11. Define catenation.
12. How does valency of an element vary across a period?
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4 -
For question numbers 13 and 14, two statements are given- one labeled Assertion (A) and
the other labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) as given below
i) Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
iii) A is true but R is false.
iv) A is false but R is true.
13. Assertion (A): Following are the structural isomers of butane.
Reason (R): Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in their
structures.
14. Assertion (A): A fuse wire is always connected in parallel with the mainline.
Reason (R): If a current larger than the specified value flows through the circuit, fuse wire
melts.
SECTION – B
15. Differentiate between the arrangement of elements in Mendeleev’s periodic table and Modern
periodic table.
16. Give one example each of the following decomposition reactions. Write one balanced chemical
equation in each case:
(a) The reaction which occurs on passing electric current.
(b) The reaction which occurs in the presence of sunlight.
(c) The reaction which occurs on heating of a substance.
17. A compound ‘X’ is a constituent of baking powder. It is used as an antacid. When ‘X’ is heated
it gives out a gas ‘Y’ which, when passed through lime water turns it milky and salt ‘Z’ is
formed which is the main constituent of washing powder. Identify X, Y and Z. Write the
balanced chemical equations for the reactions involved.
OR
(a) A solution turns red litmus paper to blue. What can be pH of this solution?
(b) 10mL of sodium hydroxide solution is completely neutralized by 8 mL of solution of
hydrochloride acid. If we take 20 mL of the same solution hydroxide, what will be the amount of
hydrochloride acid solution required to neutralized it?
(c) What type of medicine is used for the treatment of indigestion?
18. Draw a neat diagram of human brain and label on it the following parts: (i) Midbrain (ii)
Pituitary gland (iii) Cerebellum (iv) Cerebrum
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 5 -
19. Draw a diagram of human respiratory system and label on it: (a) Diaphragm (b) Larynx
20. (a) Name the defects of vision when a person cannot see clearly: (i) the nearby objects (ii) the
distant objects
(b) A person suffering from a defect of vision uses a corrective lens of power – 2D. Find the
nature and focal length of the corrective lens.
(c) Why does power of eye to see clearly nearby as well as far off object diminishing with age?
Name the defects that are likely to arise in eye in such a condition.
OR
What is a spectrum? How can we recombine the components of white light after a glass prism
has separated them? Illustrate it by drawing a diagram.
21. (a) A positively charged particle (alpha) projected towards west is deflected towards north by a
magnetic field. State the direction of magnetic field. State the rule used by you to find the
direction.
(b) Mention the factors on which the strength of forces experienced by a current carrying
conductor placed in a magnetic field depend.
22. (a) What are monohybrid and dihybrid cross ?
(b) How Mendel proved that tallness is the dominant trait and dwarfness is recessive in a pea
plant ?
23. “Damage to the ozone layer is a cause for concern.” Justify this statement. Suggest any two steps
to limit this damage.
OR
Why are bacteria and fungi called decomposers? List any two advantages of decomposers to the
environment.
24. Rohit wants to have an erect image of an object, using a converging mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(a) Specify the range of distance where the object can be placed in front of the mirror. Give
reason for your answer.
(b) Will the image be bigger or smaller than the object ?
(c) Draw a ray-diagram to show the image formation in this case.
SECTION – C
25. (a) How the metals at the top of the reactivity series can be extracted from their ores ? Explain
with an example.
(b) Name any one alloy made from
(i) a metal and a non-metal, and (ii) two metals.
OR
(a) Differentiate between roasting and calcination. Explain the two with the help of suitable
chemical equations. How is zinc extracted from its ore ?
(b) Name two metals that can be used to reduce metal oxides to metals.
26. (a) Draw a diagram to show the nutrition in Amoeba and label the parts used for this purpose.
Mention any other purpose served by this part other than nutrition.
(b) Name the glands associated with digestion of starch in human digestive tract and mention
their role.
(c) How is required pH maintained in the stomach and small intestine?
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 6 -
27. At what distance from a concave lens of focal length 20 cm, a 6 cm tall object be placed so as to
obtain its image at 15 cm from the lens? Also calculate the size of the image formed. Draw a ray
diagram to justify your answer for the above situation and label it.
OR
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using
a lens.
(a) Which type of lens should he use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length ‘f ’ of the lens should he place the candle flame so
as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case.
28. (a) Write the functions of the following parts in human female reproductive system:
(i) Ovary (ii) Oviduct (iii) Uterus
(b) Describe the structure and function of placenta.
OR
(a) Give one example each of a unisexual and a bisexual flower.
(b) How is the number of chromosomes of the parent cells maintained in the cells of the
offsprings of sexually reproducing organisms?
(c) Mention the changes the flower undergoes after fertilization.
29. Two wires A and B are of equal length and have equal resistance. If the resistivity of A is more
than that of B which wire is thicker and why?
For the electric circuit given below calculate:
(i) Current in each resistor,
(ii) Total current drawn from the battery, and
(iii) Equivalent resistance of the circuit.
30. Give reasons for the following:
(i) Element carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonding.
(ii) Diamond has a high melting point.
(iii) Graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
(iv) Acetylene burns with a sooty flame.
(v) Kerosene does not decolourise bromine water while cooking oils do.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 7 -
You might also like
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Document6 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Gowtham LNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Document6 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020CharuNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument8 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 08: Science Class XDocument5 pagesSample Paper 08: Science Class XKamal0% (1)
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03Document6 pagesScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03darshan8422No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2019Document5 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2019KamalNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER FOR PERIODIC TEST IIIDocument5 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER FOR PERIODIC TEST IIIhweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173100% (1)
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 09 (2017-18Document5 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 09 (2017-18hweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SCIENCE SAMPLE PAPERDocument5 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SCIENCE SAMPLE PAPERrajman1990No ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 02 (2017-18Document5 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 02 (2017-18hweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02darshan8422No ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Document5 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Trust In godNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 08 (2017-18Document5 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 08 (2017-18BHARAT kommanaNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2018Document5 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2018Maruti AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 1095549296science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Document5 pages1095549296science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Abhishek JhaNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sample Paper 02 for See 2021 1Document8 pagesScience Class Ix Sample Paper 02 for See 2021 1Alina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sample Paper 01 for See 2021 1Document8 pagesScience Class Ix Sample Paper 01 for See 2021 1Alina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Biology Blue PrintDocument1 pageBiology Blue Printaniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- Science BP PB1Document1 pageScience BP PB1ashly BTS (sushi)No ratings yet
- 8 ScienceDocument1 page8 ScienceMegha TalukdarNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01garNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class Xii Blue Prints For Board Exam 2023Document1 pageChemistry Class Xii Blue Prints For Board Exam 2023aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Anonymous TvppppNo ratings yet
- Class XII Sample PapersDocument111 pagesClass XII Sample PapersDhruv VigNo ratings yet
- Phy Chem EngDocument3 pagesPhy Chem Engnrupesh.kumar.mohanty28031No ratings yet
- SCIDocument2 pagesSCIDeepika KarraNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- Merge 01Document7 pagesMerge 01nrupesh.kumar.mohanty28031No ratings yet
- Xi PhysicsDocument1 pageXi PhysicsjollygalileoNo ratings yet
- Science Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- BP Maths Ix See 2022 23Document1 pageBP Maths Ix See 2022 23Chirag PadhiyarNo ratings yet
- Blue Print CHEMISTRY SEE 2023-24 AGRA REGIONDocument2 pagesBlue Print CHEMISTRY SEE 2023-24 AGRA REGIONVanshNo ratings yet
- Blueprint, See, XiDocument1 pageBlueprint, See, XikavisanjurohillaNo ratings yet
- Class 9th CBSE Blue PrintDocument2 pagesClass 9th CBSE Blue PrintYash BawiskarNo ratings yet
- Science Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02sparsh bagalNo ratings yet
- Science Class VII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01Document4 pagesScience Class VII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01soni.satindraNo ratings yet
- Physics 11Document2 pagesPhysics 11RishabhNo ratings yet
- Something From My FilesDocument1 pageSomething From My Filesankitajamatia06No ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGTHAN JAMMU REGION PRE BOARD -1( 2022-23) CLASS – XII CHEMISTRY (043) SET-1 BLUE PRINTDocument1 pageKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGTHAN JAMMU REGION PRE BOARD -1( 2022-23) CLASS – XII CHEMISTRY (043) SET-1 BLUE PRINTshivanandNo ratings yet
- Blue Print Final Paper Class 11TH ChemistryDocument1 pageBlue Print Final Paper Class 11TH ChemistryDevansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER 01 FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAM SCIENCE CLASS XDocument5 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER 01 FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAM SCIENCE CLASS Xhweta173No ratings yet
- null-3Document1 pagenull-3class6supertech6No ratings yet
- Class 7 science exam blueprintDocument1 pageClass 7 science exam blueprintArvind KumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 SA1 Science Model Question PaperDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 6 SA1 Science Model Question PaperDhrutiNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicschhetrinikita301No ratings yet
- Maths Basic Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Document6 pagesMaths Basic Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Dharmendra SankhlaNo ratings yet
- 5973 Fast Electronics Upgrade 2 PDFDocument2 pages5973 Fast Electronics Upgrade 2 PDFMarine JolieNo ratings yet
- 2.tutorial - D V SDocument2 pages2.tutorial - D V SVivek MenonNo ratings yet
- Family Law Discovery GuideDocument32 pagesFamily Law Discovery GuideDaya Baran100% (3)
- HDFC Life Click 2 Invest ULIP illustrationDocument3 pagesHDFC Life Click 2 Invest ULIP illustrationanon_315406837No ratings yet
- CCHIM - Terminology Standards Info - FAQDocument2 pagesCCHIM - Terminology Standards Info - FAQZubeen ShahNo ratings yet
- Windows Server 2019 Administration CourseDocument590 pagesWindows Server 2019 Administration CourseTrần Trọng Nhân100% (2)
- Credit/Debit Card Auto Debit AgreementDocument1 pageCredit/Debit Card Auto Debit AgreementMandy ChanNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Information Gathering For Through Listening For Everyday Life UsageDocument22 pagesEnglish: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Information Gathering For Through Listening For Everyday Life UsageGrayson RicardoNo ratings yet
- Customer Copy: H004 Estimated Bill of MaterialDocument8 pagesCustomer Copy: H004 Estimated Bill of MaterialjessicaNo ratings yet
- Ruta 57CDocument1 pageRuta 57CUzielColorsXDNo ratings yet
- Want To Be A Trader?: TradersworldDocument189 pagesWant To Be A Trader?: TradersworldLuis MásNo ratings yet
- Emissionbooklet 2019 PDFDocument210 pagesEmissionbooklet 2019 PDFSmriti SinghNo ratings yet
- Franchise AccountingDocument20 pagesFranchise AccountingJerichoPedragosa60% (5)
- A History of Sanskrit Literature (Arthur Berriedale Keith)Document3 pagesA History of Sanskrit Literature (Arthur Berriedale Keith)ahikar1No ratings yet
- First World War: University of Buea Faculty of Education Department of Educational Foundation and AdministrationDocument11 pagesFirst World War: University of Buea Faculty of Education Department of Educational Foundation and AdministrationGATTE EMILENo ratings yet
- Sir Thomas WyattDocument4 pagesSir Thomas WyattNoraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER II - Roots of The Filipino CharacterDocument6 pagesCHAPTER II - Roots of The Filipino CharacterErica Marie BagonNo ratings yet
- Clinicas de Derecho Ambiental Solicitan Negar Permiso de Construccion GasoductoDocument52 pagesClinicas de Derecho Ambiental Solicitan Negar Permiso de Construccion GasoductoDiálogoNo ratings yet
- PISIPIS NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL MUSIC SCORES AND LEARNING TASKSDocument13 pagesPISIPIS NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL MUSIC SCORES AND LEARNING TASKSLyrah SantuyoNo ratings yet
- Collapse of The Soviet Union-TimelineDocument27 pagesCollapse of The Soviet Union-Timelineapi-278724058100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Problem 5 To 7Document2 pagesChapter 1 Problem 5 To 7XienaNo ratings yet
- Brave BhagadattaDocument1 pageBrave BhagadattaabcdeflesNo ratings yet
- Guardian Ad Litem ReplyDocument39 pagesGuardian Ad Litem ReplyScottie ThomastonNo ratings yet
- GenAI For LawyersDocument22 pagesGenAI For LawyersRoberto Lemaitre PicadoNo ratings yet
- Imagineering Culture of Creative Collectivity - A Case Study of Disney Pixar Animation StudioDocument5 pagesImagineering Culture of Creative Collectivity - A Case Study of Disney Pixar Animation StudioArch Faith Lejarso-SerisolaNo ratings yet
- Rosemarys Comment Letter On Gas and Oil in HobackDocument3 pagesRosemarys Comment Letter On Gas and Oil in Hobackapi-23780829No ratings yet
- Philippine Constitution Association vs Salvador Enriquez ruling on veto power, pork barrelDocument1 pagePhilippine Constitution Association vs Salvador Enriquez ruling on veto power, pork barrellckdscl100% (1)
- Taj Luxury Hotels and Palaces Business Strategy CanvasDocument21 pagesTaj Luxury Hotels and Palaces Business Strategy CanvasAbhishek HandaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering 4-Year PlanDocument4 pagesCivil Engineering 4-Year PlanLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Post Modern ProtraitsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Post Modern Protraitsapi-373758397No ratings yet