Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Class Ix Sample Paper 01 For See 2021 1
Uploaded by
Alina SaraswatOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Class Ix Sample Paper 01 For See 2021 1
Uploaded by
Alina SaraswatCopyright:
Available Formats
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, GPRA CAMPUS, HYD–32
SAMPLE PAPER 01 FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM (2020-21)
SUBJECT: SCIENCE(086)
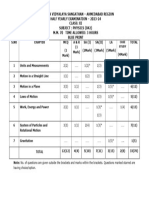
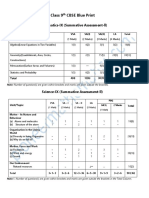
BLUE PRINT : CLASS IX
Case
VSA Study SA – I SA – II LA Unit
UNIT Chapter (1 mark) Question (2 marks) (3 marks) (5 marks)
Total
Total
s
Matter - Its Nature
Is Matter around us 1(1)*
-- -- -- 5(1) 8(4)
and Behaviour
pure 2(2)
Atoms and 1(1)* 27(14)
-- 2(1) 6(2) -- 11(6)
Molecules 2(2)
Structure of the 1(1)*
4(1)# 2(1) -- -- 8(4)
Atom 1(1)*
the Living World
The Fundamental
Organisation in
1(1) -- 2(1) 3(1) -- 6(3)
unit of life
1(1) 26(11)
Tissues 4(1)# 3(1) -- 10(5)
2(2)AR
Why Do we fall ill 1(1) 4(1)# -- -- 5(1)* 10(3)
Motion 1(1) 4(1)# 2(1)* -- -- 7(3)
Motion, Force and
Force and Laws of
1(1)AR -- 2(1)* 3(1) -- 6(3)
Work
motion
27(11)
Gravitation -- -- -- 3(1)* 5(1)* 8(2)
Work and Energy 1(1) -- 2(1) 3(1) -- 6(3)
Total 16(16) 16(4) 12(6) 21(7) 15(3) 80(36) 80(36)
Note: * - Internal Choice Questions and Yellow shaded with #- Case study questions
attempt 4 questions out of 5 questions
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, GPRA CAMPUS, HYD–32
SAMPLE PAPER 01 FOR CLASS IX SEE 2021
SUBJECT: SCIENCE MAX. MARKS : 80
CLASS :IX DURATION : 3 HRS
General Instructions:
(i) The question paper comprises four sections A, B, C and D. There are 36 questions in the
question paper. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Section–A - question no. 1 to 20 - all questions and parts thereof are of one mark each.
These questions contain multiple choice questions (MCQs), very short answer questions and
assertion - reason type questions. Answers to these should be given in one word or one
sentence.
(iii) Section–B - question no. 21 to 26 are short answer type questions, carrying 2 marks each.
Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
(iv) Section–C - question no. 27 to 33 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each.
Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words.
(v) Section–D – question no. - 34 to 36 are long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each.
Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
(vi) There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A
student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
(vii) Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
SECTION – A
1. Give one example of two miscible liquids where distillation can be used for separating them.
2. Define mixture.
OR
What is solute and solvent in brass?
3. The ion of an element has 3 positive charges. Mass number of the atom is 27 and the number of
neutrons is 14. What is the number of electrons in the ion ?
OR
2+
Write the Electronic configuration of Mg ion.
4. Define the law of constant proportion.
5. Helium atom has 2 electrons in its valence shell but its valency is not 2. Explain.
OR
According to Bohr and Bury scheme what is the maximum number of electrons present in M-
shell of an atom?
6. What is sedimentation?
7. Write the chemical formula of calcium oxide.
OR
In ammonia, nitrogen and hydrogen are always present in the ratio 14 : 3 by mass. State the law
which explains the above statement.
8. Name the organelle other than nucleus of a cell, which contains DNA.
9. Name the water conducting tissue present in gymnosperms.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2 -
10. Name the disease transmitted by animal bite.
11. A coolie is walking on a railway platform with a load of 30 kg on his head. How much work is
done by coolie?
12. How many Ag atoms are there in 0.0001 gram of Ag. Molar mass of Ag is 108 gram per mole.
13. If the time interval between lightning and thunder is 2 seconds, what is the distance of the point
of lightning. (Speed of sound in air is 346 ms-1)
OR
Name the quantity which is measured by the area occupied below the velocity - time graph.
For question numbers 14-16, two statements are given- one labelled Assertion (A) and the
other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b),
(c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
14. Assertion: Thigh muscles can get tired but not heart muscles.
Reason: Muscles of thigh are voluntary while muscles of heart are involuntary muscles.
15. Assertion: If a balanced force is applied on a wooden block it will move.
Reason: Unbalanced force changes the state of motion or rest while balanced force does not.
16. Assertion: Muscle fibers are contractile in nature.
Reason: Cells of muscle tissue can shorten forcefully and again return to the relaxed state.
OR
Assertion: Permanent tissue is composed of mature cells.
Reason: Meristematic tissue is a group of actively dividing cells.
Answer Q. No 17 - 20 contain five sub-parts each. You are expected to answer any four
subparts in these questions.
17. Read the following and answer any four questions from 17(i) to 17(v).
The graph shows the distance-time graph of three objects A, B and C. Study the graph and
answers the following questions:
(i) Which of the three is travelling the fastest?
(a) C (b) A (c) B (d) All are at equal speed
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3 -
(ii) One of the following is not a vector quantity. This one is :
(a) displacement (b) speed (c) acceleration (d) velocity
(iii) How far has B travelled in 1.4 hours?
(a) B travelled from 5 to 12 km in 1.4 hours. (b) B travelled from 1 to 12 km in 1.4 hours.
(c) B travelled from 4 to 12 km in 1.4 hours. (d) B travelled from 0 to 12 km in 1.4 hours.
(iv) How far has C travelled in 1.6 hours?
(a) C travelled from 8 to 12 km in 1.6 hours. (b) C travelled from 2 to 12 km in 1.6 hours.
(c) C travelled from 0 to 12 km in 1.6 hours. (d) C travelled from 1 to 12 km in 1.6 hours.
(v) State the formula used to find out speed from distance time graph.
(a) Speed = Time / Distance (b) Speed = Distance x Time
(c) Speed = Distance/Time (d) Time = Speed x Distance
18. Read the following and answer any four questions from 18(i) to 18(v).
In order to overcome the objections raised against Rutherford's model of the atom, Neil Bohr put
forward the following postulates about the model of an atom. Only certain special orbits known
as discrete orbits of electrons are allowed inside the atom. While revolving in discrete orbits the
electrons do not radiate energy.These orbits or shells are called energy levels.
(i) Atoms are made up of _________, __________ and __________ .
(a) electrons, protons, neutrons (b) cations, anions, charges
(c) positive charges, negative charges, bonds (d) ions, orbits, molecules
(ii) Who amended Rutherford's shortcomings?
(a) Dalton (b) Neil Bohr (c) J.J. Thomson (d) E. Goldstein
(iii) Name the number of electrons that K shell and L shell can accommodate.
(a) 8, 8 respectively. (b) 2, 8 respectively. (c) 1, 8 respectively. (d) 5, 10 respectively.
(iv) Rutherford’s alpha particle scattering experiment led to the discovery of :
(a) Nucleus (b) Electrons (c) Protons (d) Neutrons
(v) Where is the positive charge located inside the atom?
(a) Orbit (b) Ion (c) Nucleus (d) Neutron
19. Read the following and answer any four questions from 18(i) to 18(v).
Bacteria are unicellular organisms belonging to the prokaryotic group where the organisms lack
a few organelles and a true nucleus. Study the given diagram of bacterial cell and answer the
following questions.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4 -
(i) Label the parts marked 1, 2, and 3.
(a) 1- Nucleus, 2-Cell wall, 3- Plasma membrane.
(b) 1-Cell wall, 2- Nucleoid, 3- Plasma membrane.
(c) 1- Cytoplasm ,2- Nucleus, 3- Cell wall.
(d) 1- Nucleus, 2-Cytoplasm, 3- Cell wall.
(ii) Which structure present in the region 2 of a living cell bear genes?
(a) Chromosome (b) Plasma membrane (c) Cytoplasm (d) Cell wall
(iii) How nuclear region of a bacterial cell and nuclear region of an animal cell is different from
each other?
(a) Nuclear region of bacterial cell is well defined but lacks any covering while nuclear region of
an animal cell is poorly defined and membrane bound.
(b) Nuclear region of bacterial cell is poorly defined and has a covering while nuclear region of
an animal cell is poorly defined and membrane bound.
(c) Nuclear region of bacterial cell is poorly defined and lacks any covering while nuclear region
of an animal cell is well defined and membrane bound.
(d) Nuclear region of bacterial cell is poorly defined and lack any covering while nuclear region
of an animal cell is well defined and membrane bound.
(iv) A bacterial cell wall does all of the following except
(a) gives shape and rigidity to the cell (b) is the site of action for some antibiotics
(c) is associated with some symptoms of disease (d) protects the cell from phagocytosis
(v) Identify an example of single celled organism.
(a) Bird (b) Fish (c) Snake (d) Amoeba
20. Read the following and answer any four questions from 20(i) to 20(v).
Bone is a solid, hard porous tissue. It forms the natural skeleton and gives the body its basic
structure and also supports the body. Its matrix is impregnated with phosphates and carbonates of
calcium and magnesium which provides hardness to it. The matrix also contains ossein protein.
The matrix is arranged in concentric rings which are called lamellae. Bone cells lie between the
lamellae in fluid-filled spaces called lacunae. Bone cells are also called osteocytes.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 5 -
(i) What are bone cells also called ?
(a) Lacunae (b) Osteocytes (c) Neutrophils (d) Erythrocytes
(ii) The matrix inside the bone is arranged in concentric rings called __________
(a) Cytoplasm (b) Osteocyte (c) Lacunae (d) Lamellae
(iii) To form natural skeleton and to give support to the body is the main function of __________
(a) Cells (b) Muscles (c) Bones (d) Ligaments
(iv) The matrix of bone is impregnated with _____________
(a) Carbon dioxide and oxygen (b) Carbon dioxide and water
(c) Sulphates of sodium (d) phosphates and carbonates of calcium and magnesium
(v) Bone cells lie between the lamellae in fluid-filled spaces called ___________
(a) lamina (b) osteocytes (c) lacunae (d) ossein
SECTION – B
21. (a) Define polyatomic ion.
(b) Write the name of the compound (NH4)2SO4.
22. (a) Write two points of difference between nuclear region of a bacterial cell and nuclear region of
an animal cell.
(b) Which structure present in the nuclear region of a living cell bear genes?
23. A body covers one complete revolution around a circular park of circumference 176 m in 4
minutes. Find the displacement of the body after 6 minutes.
OR
A mechanic strikes a nail with hammer moving with a velocity of 20 m/s. The hammer comes to
rest in 0.02 s after striking the nail. Calculate the acceleration of the nail.
24. (a) When is the work done by a body said to be negative?
(b) An object of mass 5 kg is dropped from a height of 10 m. Find its kinetic energy, when it is
half way down.
25. An atom of an element has 7 electrons in its L shell.
(a) What is its atomic number?
(b) State its valency.
(c) Identify the element.
26. When two bodies X and Y collide with each other, X exerts a force of 5 N on Y towards east
direction. What is the force exerted by Y on X ? Justify your answer stating the law.
OR
A circular groove is provided in a saucer for placing the tea cup in it. Give reasons.
SECTION – C
27. Define atomicity. Give an example of each of monoatomic, diatomic, tetra-atomic and
polyatomic molecules.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 6 -
28. (a) Identify the given figures.
(b) State in brief their structure.
(c) Describe the role performed by the two.
29. (i) A ball is allowed to roll down from an inclined plane. It reaches the foot of the plane and
continues to roll on the ground. It stops after travelling some distance. Is this the violation of law
of inertia?
(ii) Give reasons for following. Glass wares are wrapped in straw during their transportation.
30. A ball is dropped from the top of a tower 100 m high and at the same time another ball is
projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m/sec. Calculate where and
when the two stones will meet. (Take g = 9.8 ms-2)
OR
What happens to the magnitude of the force of gravitation between two objects if: (i) mass of one
of the objects is tripled ? (ii) distance between the objects is doubled ? (iii) mass of both objects
is doubled ?
31. Draw a neat and well labelled diagram of a typical prokaryotic cell.
32. (a) Define atomic mass unit.
(b) Distinguish between molecular mass and molar mass.
(c) Give an example of
(i) diatomic, and
(ii) triatomic molecule of compounds.
33. A body of mass 5 kg is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 10 m/s. What is its kinetic
energy when it is thrown? Find its potential energy when it reaches at the highest point. Also find
the maximum height attained by the body. (g = 10 m/s2)\
SECTION – D
34. Study the picture given below and answer the following questions.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 7 -
(a) What can you conclude about spread of the disease with respect to the distance from an
infected person?
(b) What change will be observed in the above situation if the infected person is present in a
closed room?
(c) Name two diseases that can be spread through the above means.
(d) How can the spread of such diseases be controlled?
OR
Justify the following statements:
(a) "Availability of proper and sufficient food would prevent from infectious diseases".
(b) "The general ways of preventing infection mostly relate to preventing exposure". List three
points of prevention of exposure.
35. (a) Earth revolves around sun due to the gravity of sun. Why does the earth not move towards
sun?
(b) State and derive the formula for gravitational force of attraction between sun and earth.
(a) A metallic bar has a mass 200 g at poles. Does it change when taken to equator?
OR
(b) Does its weight change when brought to equator? If yes, how?
(c) Where on earth will the weight be zero?
(d) What would happen if there was no acceleration due to gravity?
36. (a) List any four properties of a colloid and mention any two properties in which colloids differ
from suspension.
(b) State what is Tyndall effect? Which of the following solutions will show Tyndall effect?
Starch solution, sodium chloride solution, Tincture iodine, air.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 8 -
You might also like
- Science Class Ix Sample Paper 02 For See 2021 1Document8 pagesScience Class Ix Sample Paper 02 For See 2021 1Alina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01rajman1990No ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02darshan8422No ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Document5 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Trust In godNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Document6 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Gowtham LNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Document6 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020CharuNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument8 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03Document6 pagesScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03darshan8422No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- 1095549296science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Document5 pages1095549296science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Abhishek JhaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Anonymous TvppppNo ratings yet
- Papers - LK: Answer All The Questions. Underline The Correct or Most Suitable AnswerDocument12 pagesPapers - LK: Answer All The Questions. Underline The Correct or Most Suitable AnswerShahif MNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01 2020 21Document8 pagesMaths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01 2020 21Psy KoTeaYenNo ratings yet
- Science Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02sparsh bagalNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xi Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01 For 2020 21Document6 pagesMaths Class Xi Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01 For 2020 21Srijita SahaNo ratings yet
- Science Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- VMC - SOSE IX HRT - 3 (Question Paper)Document12 pagesVMC - SOSE IX HRT - 3 (Question Paper)anshmaurya454No ratings yet
- VMC - SOSE IX HRT - 3 (Question Paper)Document10 pagesVMC - SOSE IX HRT - 3 (Question Paper)MD hamzaNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01garNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Viii Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesMaths Class Viii Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- JEE Main - Growth - Sample Paper-1 - StudentDocument16 pagesJEE Main - Growth - Sample Paper-1 - Studentanurag jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01hweta173No ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry by Team Neet SecretDocument152 pagesInorganic Chemistry by Team Neet Secret09 Krishna TrivediNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- 1333912206maths Class X Sample Paper 10 For Board Exam 2019Document5 pages1333912206maths Class X Sample Paper 10 For Board Exam 2019CYBER DUDE PLAYSNo ratings yet
- CBSE Term Test - T-02C - IX - Science (08 Sep 2019)Document5 pagesCBSE Term Test - T-02C - IX - Science (08 Sep 2019)Brunda bongaleNo ratings yet
- Blue Print For Common Physics Exams PDFDocument2 pagesBlue Print For Common Physics Exams PDF2007.satyamjaiswalNo ratings yet
- Ntse II 2016 Sat PaperDocument19 pagesNtse II 2016 Sat PaperMintu KhanNo ratings yet
- 1279188485maths Class X Sample Paper 02 For Board Exam 2019Document5 pages1279188485maths Class X Sample Paper 02 For Board Exam 2019Kamal govadaNo ratings yet
- Xi PhysicsDocument1 pageXi PhysicsjollygalileoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument51 pagesChemistry ProjectSiddhanth AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2018Document6 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2018jay danenjeyanNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 03 2020 21Document8 pagesMaths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 03 2020 21Psy KoTeaYenNo ratings yet
- Section-A: Physics Marks: 12: Science (Class-X) Major Test # 02Document2 pagesSection-A: Physics Marks: 12: Science (Class-X) Major Test # 02YASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02 2020 21Document9 pagesMaths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02 2020 21Psy KoTeaYenNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2018 3Document5 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2018 3Írfäñ MøhdNo ratings yet
- ISC Class 11 Bio Specimen PaperDocument6 pagesISC Class 11 Bio Specimen PaperparamNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- Class 9th CBSE Blue PrintDocument2 pagesClass 9th CBSE Blue PrintYash BawiskarNo ratings yet
- ANTHE 2012 Sample PaperDocument14 pagesANTHE 2012 Sample PaperRashmi Khare57% (7)
- Science Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2019Document5 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2019Kamal0% (1)
- BP Xi Physics See23-24Document2 pagesBP Xi Physics See23-24ashishkrsingh4565No ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2019Document5 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2019KamalNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 03 For Board Exam 2018 4Document5 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper 03 For Board Exam 2018 4Írfäñ MøhdNo ratings yet
- Blue Print CHEMISTRY SEE 2023-24 AGRA REGIONDocument2 pagesBlue Print CHEMISTRY SEE 2023-24 AGRA REGIONVanshNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2018 2Document5 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2018 2Írfäñ MøhdNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 20 Years Pyq's SheetDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure 20 Years Pyq's Sheetsakshimodi2004No ratings yet
- Gujarat NTS 2013 Provisional Key English Medium PDFDocument16 pagesGujarat NTS 2013 Provisional Key English Medium PDFSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Term I Reference Study Material 166 169Document4 pagesScience Class X Term I Reference Study Material 166 169Alina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Section ADocument1 pageSection AAlina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Examples of Lines and AnglesDocument5 pagesExamples of Lines and AnglesAlina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Cells Class 9Document68 pagesCells Class 9Alina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument13 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsAlina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Lines and AnglesDocument3 pagesLines and AnglesAlina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Sample ProblemsDocument8 pagesSample ProblemsKenn Earl Bringino VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Dash B Shear and Moment 1Document13 pagesDash B Shear and Moment 1Rosmari Aquino PascualNo ratings yet
- Turbine Start UpDocument15 pagesTurbine Start UprobiansahNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ADocument10 pagesModule 3 AProdyot SinhaNo ratings yet
- KATALOG RSI JULI 2020 Update 25 Juli 2020 PDFDocument35 pagesKATALOG RSI JULI 2020 Update 25 Juli 2020 PDFYulia HermansyahNo ratings yet
- Entropy and Entransy in Convective PDFDocument30 pagesEntropy and Entransy in Convective PDFMohammadreza NaghaviNo ratings yet
- DC Motor ModelingDocument13 pagesDC Motor ModelingMuhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Ut III Xii 2012 Chemistry Answer Key VSPDocument4 pagesUt III Xii 2012 Chemistry Answer Key VSPavclpubNo ratings yet
- Pier - RP1 PDFDocument88 pagesPier - RP1 PDFPraveen CyssanNo ratings yet
- KD800-2500 G6154Document10 pagesKD800-2500 G6154Leo Van Ezel ArcayNo ratings yet
- Open Hole FishingDocument89 pagesOpen Hole FishingShiela O100% (1)
- EEP3701 2023 Major Test 1 S2Document3 pagesEEP3701 2023 Major Test 1 S2MasoNo ratings yet
- NS EquationDocument81 pagesNS EquationRitik ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- A Genomic Model For Predicting The Ultraviolet Susceptibility of VirusesDocument14 pagesA Genomic Model For Predicting The Ultraviolet Susceptibility of Viruseschirag vyasNo ratings yet
- SNER Owners Manual PDFDocument64 pagesSNER Owners Manual PDFJesseNo ratings yet
- Capacity of Cone-Shaped Hollow Flexible ReinforcedDocument14 pagesCapacity of Cone-Shaped Hollow Flexible ReinforcedG.RameshNo ratings yet
- Thermoelastic Analysis of A Thin Circular Plate With Radiation Type ConditionsDocument6 pagesThermoelastic Analysis of A Thin Circular Plate With Radiation Type ConditionssijyvinodNo ratings yet
- Forced & Damped Oscillations (INSP)Document50 pagesForced & Damped Oscillations (INSP)devansh dewan100% (1)
- (копия)Document2 pages(копия)DaLLaSNo ratings yet
- Iso 22262-1-2012Document80 pagesIso 22262-1-2012Kunal ShingalaNo ratings yet
- 15572854118361575jy NARI MUX 2M InterfaceDocument2 pages15572854118361575jy NARI MUX 2M InterfaceKelly chatNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document5 pagesQuiz 1Mr. Bean BajrangiNo ratings yet
- CH Lab 3Document8 pagesCH Lab 3Mohammad Fahim NurNo ratings yet
- ARANER - Turbine Inlet Air Cooling Reference EbookDocument29 pagesARANER - Turbine Inlet Air Cooling Reference EbookSergio PereiraNo ratings yet
- GRP Flameproof Combination Signal - 110 DB (A) / 5 Joule: Series YL6SDocument6 pagesGRP Flameproof Combination Signal - 110 DB (A) / 5 Joule: Series YL6Sjuan palominoNo ratings yet
- Formal Meaning of ShapeDocument3 pagesFormal Meaning of ShapeChubs RiegoNo ratings yet
- Pages From 4355-AI-DX-00000017 - DSDocument2 pagesPages From 4355-AI-DX-00000017 - DSamitNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Microstrip CoupledDocument76 pagesDesign and Simulation of Microstrip CoupledyyryNo ratings yet
- Perancangan Mengajar: Dynamics & MechanismDocument5 pagesPerancangan Mengajar: Dynamics & MechanismHui ShanNo ratings yet
- 3 12 15 Tis L200RS A Ce 2015Document1 page3 12 15 Tis L200RS A Ce 2015MAZENNo ratings yet