Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03
Uploaded by
Kajal GuptaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03
Uploaded by
Kajal GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
SAMPLE PAPER 03 FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM (2017-18)
SUBJECT: SCIENCE
BLUE PRINT FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM: CLASS VIII
VSA
SA-I SA-II LA Total
CHAPTERS (1 mark)
(2 marks) (3 marks) (5 marks) Marks
FITB MCQ
Force and pressure 1(1) 1(1) 1(2) 1(3) -- 4(7)
Friction 1(1) 1(1) 1(2) 1(3) -- 4(7)
Sound 1(1) 1(1) 1(2) 1(3) -- 4(7)
Chemical effects of electric
1(1) 1(1) -- -- 1(5) 3(7)
current
Some natural Phenomena 1(1) 1(1) 1(2) -- 1(5) 4(9)
Light 1(1) -- 1(2) -- 1(5) 3(8)
Stars and solar system 1(1) 1(1) 1(2) -- -- 3(4)
Pollution of air and water -- 1(1) -- 2(6) -- 3(7)
Cell structure and function 1(1) 1(1) -- -- 1(5) 3(7)
Micro organisms 1(1) 1(1) 1(2) 1(3) -- 4(7)
Metals and non metals 1(1) 1(1) 1(2) 2(6) -- 5(10)
Total 10(10) 10(10) 8(16) 8(24) 4(20) 40(80)
FITB – Fill in the Blank, MCQ – Multiple Choice Questions,
VSA – Very Short Answer Type Questions, SA –Short Answer Type Questions
LA – Long Answer Type Questions
Note: Cell structure and function, Micro-organisms and Metals & Non-metals (30% i.e. 24 marks)
of 1st term syllabus covering significant topics/chapters have taken as per CBSE guidelines.
MARKING SCHEME FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM
NO. OF
SECTION MARKS TOTAL
QUESTIONS
VSA 1 24 24
SA – I 2 11 22
SA – II 3 8 24
LA 5 2 10
GRAND TOTAL 80
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
SAMPLE PAPER 03 FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM (2017-18)
SUBJECT: SCIENCE MAX. MARKS : 80
CLASS : VIII DURATION : 2½ HRS
General Instructions:
(i). All questions are compulsory.
(ii). This question paper contains 30 questions divided into four Sections A, B, C and D.
(iii). Section A comprises 10 Fill in the Blanks Questions and 10 Multiple Choice Questions, each of 1
mark. Section B comprises of 8 questions of 2 marks each. Section C comprises of 8 questions of
3 marks each and Section D comprises of 4 questions of 5 marks each.
SECTION – A (1 mark each)
FILL IN THE BLANKS: (10 MARKS)
1. ___________ discoverd penicillium.
2. Sodium and ___________ are soft enough to be cut with a knife.
3. _____________ is the cell organelle which produces energy by the oxidation of food.
4. 1 kilogram force is equal to _________________ newtons.
5. Friction is more on a ______________ surface than on a ______________surface.
6. __________ is the unit to measure the loudness of sound.
7. When electricity is passed through a liquid, it causes a _____________ change. This effect is
called the _____________ effect of current.
8. ____________ was the first person to prove that clouds build up charge during __________.
9. Kaleidoscope is based on the principle of ________________ .
10. The Milky Way galaxy is _______________ in shape.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: (10 marks)
11. Which bacteria is responsible for fixation of nitrogen?
(a) Vibrio cholerae (b) Rhizobium
(c) Escherichia coli (d) Bacillus typhosus
12. A liquid metal is —
(a) Nitrogen (b) Bromine (c) Mercury (d) Iodine
13. Chlorophyll is found in —
(a) Leucoplast (b) Chloroplast (c) Chromoplast (d) Centrosome
14. Weight of a body is measured in
(a) Kelvin (b) Newton/Kilogram force
(c) Force of gravity (d) None of these
15. Ball rolling on the floor stops due to —
(a) Gravitational force (b) Magnetic force (c) Muscular force. (d) Frictional force.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2 -
16. Sound waves travel fastest in —
(a) Air (b) Metals (c) Vacuum (d) Liquids
17. An electrolytic cell converts
(a) electrical energy to light energy. (b) chemical energy to electrical energy.
(c) chemical energy to light energy. (d) electrical energy to chemical energy.
18. Static electricity charges
(a) insulators (b) conductors (c) electrolytes (d) all the above
19. The distance travelled by light in one year is
(a) 780 million km (b) 1420 million km (c) 9.46×1012 km (d) 1.58 million km
20. Which air pollutant combines with haemoglobin present in the blood to form carboxy
haemoglobin?
(a) CO (b) CO2 (c) HCl (d) H2S
SECTION – B (2 marks each))
21. What makes the dough rise while preparing idli, dosa, bhaturas and dhoklas?
22. Why is it advised not to store pickels and curd in metallic utensils?
23. How does atmospheric pressure vary with altitude?
24. What is noise pollution? State three ways by which noise is produced in homes.
25. What is a natural satellite?
26. Why does an inflated balloon stick to the wall.
27. Why aeroplane's and ship's body is steamlined ?
28. Define dispersion.
SECTION – C (3 marks each)
29. What are metalloids ? Give example.
30. What are alloys ?
31. Why is it difficult to walk on a muddy road ?
32. Why do painter use sand papers in white washing the walls and in polishing doors ?
33. As a student and a responsible citizen of the country, list some ways by which you can help to
reduce water pollution.
34. Describe the harmful effects of :
(i) Burning of fossil fuels
(ii) Depletion of ozone layers
(iii) Water pollution.
35. Write note on AIDS.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3 -
36. Why do we need a medium to make sound travel? Name such mediums and compare their ability
to propagate sound.
SECTION – D (5 marks each)
37. What is lightning conductor? How does lightning conductor prevent damage to building during
lightning?
38. Write a note on chemical effects of electric current.
39. Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform?. Why are nerve
cells long?
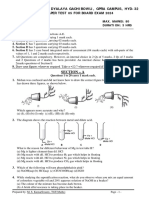
40. Distinguish between myopia and hypermetropia. Show with the help of suitable diagrams, how
these defects can be corrected ?
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4 -
You might also like
- Top 50 Most Delicious Taco Reci - Julie HatfieldDocument267 pagesTop 50 Most Delicious Taco Reci - Julie HatfieldMazhar Aslam100% (2)
- Mitsubishi Galant 4g63 Engine Repair ManualDocument29 pagesMitsubishi Galant 4g63 Engine Repair ManualMoaed Kanbar100% (1)
- Girl Scouts ActivitiesDocument5 pagesGirl Scouts ActivitiessluttybitchNo ratings yet
- Conveying Water Distribution SEODocument90 pagesConveying Water Distribution SEOmichelghanemNo ratings yet
- Old Fashioned Southern Tea CakesDocument2 pagesOld Fashioned Southern Tea CakesDB ScottNo ratings yet
- The Role of Technology in AgricultureDocument35 pagesThe Role of Technology in AgricultureDivyesh ThumarNo ratings yet
- Project Execution ProcedureDocument4 pagesProject Execution Procedurecyno2167% (3)
- Appointment Letter Staff Nurse Job DescriptionDocument3 pagesAppointment Letter Staff Nurse Job DescriptionRenita ChrisNo ratings yet
- Perineal Care Procedure GuideDocument2 pagesPerineal Care Procedure GuideAlhadzra AlihNo ratings yet
- API 578 Mock QuestionDocument4 pagesAPI 578 Mock QuestionsheikmoinNo ratings yet
- Science Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02sparsh bagalNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER 01 FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAM SCIENCE CLASS XDocument5 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER 01 FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAM SCIENCE CLASS Xhweta173No ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAMDocument4 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAMhweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class VII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01Document4 pagesScience Class VII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01soni.satindraNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01garNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- SQP Science Vii Kvs Ro LkoDocument25 pagesSQP Science Vii Kvs Ro Lkotharishr@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- GSA Mock 2022Document9 pagesGSA Mock 2022OMEGANo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper 01 For 2019 20 1Document6 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper 01 For 2019 20 1dick kumarNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Papers - LK: Answer All The Questions. Underline The Correct or Most Suitable AnswerDocument12 pagesPapers - LK: Answer All The Questions. Underline The Correct or Most Suitable AnswerShahif MNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- X Science SQP Term 2 (2021 22)Document20 pagesX Science SQP Term 2 (2021 22)Rohan VayaNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Anonymous TvppppNo ratings yet
- Periodic Test 2 Paper 1Document4 pagesPeriodic Test 2 Paper 1Bhavya JangidNo ratings yet
- Section-A: Physics Marks: 12: Science (Class-X) Major Test # 02Document2 pagesSection-A: Physics Marks: 12: Science (Class-X) Major Test # 02YASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- Iit Science 2Document4 pagesIit Science 2Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sample Paper 01 for See 2021 1Document8 pagesScience Class Ix Sample Paper 01 for See 2021 1Alina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Document5 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Trust In godNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024 1Document8 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024 1rmgokul78No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument8 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment - Class - 7 and 8Document4 pagesSummative Assessment - Class - 7 and 8Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sample Paper 02 for See 2021 1Document8 pagesScience Class Ix Sample Paper 02 for See 2021 1Alina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Document6 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Gowtham LNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper 04 For 2019 20 1Document7 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper 04 For 2019 20 1jay danenjeyanNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Document6 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020CharuNo ratings yet
- ALL QB's PDFDocument36 pagesALL QB's PDFanimesh0gargNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM (2017-18Document4 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR SESSION ENDING EXAM (2017-18Suman DesarkerNo ratings yet
- DNYANBHARATI SEMI ENGLISH SCHOOL SCIENCE EXAMDocument4 pagesDNYANBHARATI SEMI ENGLISH SCHOOL SCIENCE EXAMnilesh sableNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesMaths Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02PauraviNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesMaths Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Viii Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 01 1Document6 pagesMaths Class Viii Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 01 1Volety Sai SudheerNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SCIENCE SAMPLE PAPERDocument5 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SCIENCE SAMPLE PAPERrajman1990No ratings yet
- Sample QP - PHD MS CETDocument120 pagesSample QP - PHD MS CETSumsil ArafinNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- GR - 9 SCIENCE PREboard 23-24Document4 pagesGR - 9 SCIENCE PREboard 23-24ameenamuhamed2022No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03 1Document5 pagesMaths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03 1ahmedmansurr98No ratings yet
- Spring Practice 1 GCIFall 2020 FinalDocument15 pagesSpring Practice 1 GCIFall 2020 FinalJada SmithNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02darshan8422No ratings yet
- Annual Annual Annual Annual Examination, 2017 Examination, 2017 Examination, 2017 EXAMINATION, 2017 - 18 18 18 18Document3 pagesAnnual Annual Annual Annual Examination, 2017 Examination, 2017 Examination, 2017 EXAMINATION, 2017 - 18 18 18 18gungunNo ratings yet
- ANTHE 2012 Sample PaperDocument14 pagesANTHE 2012 Sample PaperRashmi Khare57% (7)
- 220224050635Document6 pages220224050635A KhanNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Chem Term Ii SQPDocument32 pagesClass Xii Chem Term Ii SQPAmaan KhanNo ratings yet
- EV20001 - Environmental Science - (Mid Sem Exam Autumn 2016Document5 pagesEV20001 - Environmental Science - (Mid Sem Exam Autumn 2016Abhinaba SahaNo ratings yet
- Std X Unit Test Science Physics Chemistry BiologyDocument1 pageStd X Unit Test Science Physics Chemistry BiologyLekshmy BNo ratings yet
- Final Class 8Document5 pagesFinal Class 8skygamerzz07No ratings yet
- Maths Class VII Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesMaths Class VII Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Shib Shankar PalNo ratings yet
- VMC - SOSE X HRT - 6 (Question Paper)Document18 pagesVMC - SOSE X HRT - 6 (Question Paper)h4warrioNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper 02 For Session Ending Exam (2019-20)Document5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper 02 For Session Ending Exam (2019-20)FRESH BOWLNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Hour Review Test - 5 Key PointsDocument17 pages3.0 Hour Review Test - 5 Key PointsArjun100% (1)
- Nanotechnology Commercialization: Manufacturing Processes and ProductsFrom EverandNanotechnology Commercialization: Manufacturing Processes and ProductsNo ratings yet
- Tarzan Page 1Document1 pageTarzan Page 1Macko MalilongNo ratings yet
- Appendix HDocument1 pageAppendix HKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- MAT T Er in Our SurroundingDocument8 pagesMAT T Er in Our SurroundingBharathNo ratings yet
- Surrogacy Bill - Google SearchDocument4 pagesSurrogacy Bill - Google SearchKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tarzan Page 1Document1 pageTarzan Page 1Macko MalilongNo ratings yet
- 5 6247031473925260217Document1 page5 6247031473925260217Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Surrogacy (Regulation) Bill, 2019Document3 pagesThe Surrogacy (Regulation) Bill, 2019Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tarzan Page 1Document1 pageTarzan Page 1Macko MalilongNo ratings yet
- 5 6247031473925260215Document1 page5 6247031473925260215Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chem 115 PLTL Activity Sheet 4Document8 pagesChem 115 PLTL Activity Sheet 4Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 5 6244779674111575332Document1 page5 6244779674111575332Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- This Is Just An Order Copy This Is Not An Invoice: Discounts Will Be Given On Actual MRP This Is Only A IndicativeDocument2 pagesThis Is Just An Order Copy This Is Not An Invoice: Discounts Will Be Given On Actual MRP This Is Only A IndicativeKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 5 6249055777911211400Document1 page5 6249055777911211400Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Activity Booklet Science 10th 2023Document41 pagesActivity Booklet Science 10th 2023Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cancellation Notice NR16121 11112021Document1 pageCancellation Notice NR16121 11112021Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- SSC Delhi Police SI Exam Tentative Answer Key ReleasedDocument1 pageSSC Delhi Police SI Exam Tentative Answer Key ReleasedKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- SSC issues mock test for CAPF, NIA, SSF and Assam Rifles 2021 examDocument1 pageSSC issues mock test for CAPF, NIA, SSF and Assam Rifles 2021 examKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- SN - AOD (17 Nov)Document2 pagesSN - AOD (17 Nov)Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Write Up Tentative Answer Key Steno 2020 25112021Document1 pageWrite Up Tentative Answer Key Steno 2020 25112021Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Final Option Form of JE-2019 25112021Document1 pageFinal Option Form of JE-2019 25112021Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Good and Best Analogy EditingDocument46 pagesGood and Best Analogy EditingKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- SSC Mts 20 August 2019 EditedDocument21 pagesSSC Mts 20 August 2019 EditedKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Staff Selection Commission: Category Cut-Off Marks (Paper 1 + Paper 2) Candidates AvailableDocument2 pagesStaff Selection Commission: Category Cut-Off Marks (Paper 1 + Paper 2) Candidates AvailableKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Final Option Form of JE-2019 25112021Document1 pageFinal Option Form of JE-2019 25112021Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument1 pageNotesKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Untitled HJFHGFHDocument1 pageUntitled HJFHGFHKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Daily Vocab 3 91Document4 pagesDaily Vocab 3 91Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ibps Po 2018 Books PDFDocument2 pagesIbps Po 2018 Books PDFKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Untitled HJFHGFHDocument1 pageUntitled HJFHGFHKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Good EditingDocument17 pagesGood EditingKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chery Amulet 1,6 Engine Service ManualDocument76 pagesChery Amulet 1,6 Engine Service ManualG x HxhNo ratings yet
- Project 3 - Gas Turbine Tutorial - ChemCad Draft - 01 15 2020Document58 pagesProject 3 - Gas Turbine Tutorial - ChemCad Draft - 01 15 2020Daniel Andres Canro CalderónNo ratings yet
- Galati penitentiary historyDocument2 pagesGalati penitentiary historyLupu IonutNo ratings yet
- Rotation: Medical Intensive Care Unit (South Campus) For Interns and ResidentsDocument6 pagesRotation: Medical Intensive Care Unit (South Campus) For Interns and ResidentsHashimIdreesNo ratings yet
- D 1123 - 99 Rdexmjmtotk - PDFDocument5 pagesD 1123 - 99 Rdexmjmtotk - PDFFrancisco GuerraNo ratings yet
- Solving Proportions Problems with Learning Activity SheetsDocument21 pagesSolving Proportions Problems with Learning Activity Sheetsceline fernandezNo ratings yet
- Text StructureDocument25 pagesText Structureapi-245317957No ratings yet
- Yoga & Diet To Prevent DepressionDocument5 pagesYoga & Diet To Prevent DepressionDietician Mrunmayee DixitNo ratings yet
- Edwards Auto 306 CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesEdwards Auto 306 CharacteristicsJuan Antonio Rubio-LaraNo ratings yet
- Type 3730-1 Electropneumatic PositionerDocument112 pagesType 3730-1 Electropneumatic PositionerDaniel ReyNo ratings yet
- Holy Names vs. Franklin SwimmingDocument3 pagesHoly Names vs. Franklin SwimmingstprepsNo ratings yet
- General Conditions of Contracts For NLNG 2018Document28 pagesGeneral Conditions of Contracts For NLNG 2018AF Dowell MirinNo ratings yet
- PMBOK - Chapter 9: Project Human Resource ManagementDocument16 pagesPMBOK - Chapter 9: Project Human Resource Management7565006No ratings yet
- 2020 End Year 6 PenulisanDocument8 pages2020 End Year 6 PenulisanZulhillmi ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- UNSG Report On Safety Security Humanitarian PersonnelDocument25 pagesUNSG Report On Safety Security Humanitarian PersonnelInterAction100% (1)
- Effectiveness of Breathing Exercise On Reducing Pain Perception and State Anxiety Among Primi ParturientsDocument8 pagesEffectiveness of Breathing Exercise On Reducing Pain Perception and State Anxiety Among Primi ParturientsPutra SpNo ratings yet
- SEN Code of Practice 2001Document148 pagesSEN Code of Practice 2001Matt GrantNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument5 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogFlordeliza Manaois RamosNo ratings yet
- Corticosteroid: Saut Samuel Simamora Department Ophthalmology Diponegoro University-Kariadi HospitalDocument21 pagesCorticosteroid: Saut Samuel Simamora Department Ophthalmology Diponegoro University-Kariadi HospitalSania NadianisaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Starch Nanoparticles in A New Ionic Liquid-in-Oil MicroemulsionDocument12 pagesPreparation of Starch Nanoparticles in A New Ionic Liquid-in-Oil MicroemulsionPaula NancyNo ratings yet