Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Int Qs Igcse
Uploaded by
zhye26Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Int Qs Igcse
Uploaded by
zhye26Copyright:
Available Formats
dy
1. A curve is such that = 2 x 2 − 5 . Given that the point (3, 8) lies on the curve, find the
dx
equation of the curve.
[4]
4
2. A curve has equation y = .
x
(i) The normal to the curve at the point (4, 2) meets the x-axis at P and the y-axis at Q. Find
the length of PQ, correct to 3 significant figures.
[6]
(ii) Find the area of the region enclosed by the curve, the x-axis and the lines x = 1 and x = 4.
[4]
dy 16
3. A curve is such that = , and (1, 4) is a point on the curve.
dx x 3
(i) Find the equation of the curve.
[4]
1
(ii) A line with gradient − is a normal to the curve. Find the equation of this normal,
2
giving your answer in the form ax + by = c.
[4]
(iii) Find the area of the region enclosed by the curve, the x-axis and the lines x = 1 and x = 2.
[4]
© Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Bangkok Patana School 1
dy 4
4. A curve is such that = , and P (1, 8) is a point on the curve.
dx (6 − 2 x )
(i) The normal to the curve at the point P meets the coordinate axes at Q and at R. Find the
coordinates of the mid-point of QR.
[5]
(ii) Find the equation of the curve.
[4]
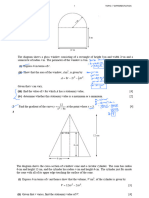
5.
y
y = x3 – 3x2 – 9x + k
x
O
The diagram shows the curve y = x3 − 3x2 − 9x + k, where k is a constant. The curve has a
minimum point on the x-axis.
(i) Find the value of k.
[4]
(ii) Find the coordinates of the maximum point of the curve.
[1]
(iii) State the set of values of x for which x3 – 3x2 – 9x + k is a decreasing function of x.
[1]
(iv) Find the area of the shaded region.
[4]
© Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Bangkok Patana School 2
6.
y
R1
O x
A B
R2
The diagram shows the curve y = x(x – 1)(x – 2), which crosses the x-axis at the points O (0, 0),
A (1, 0) and B (2, 0).
(i) The tangents to the curve at the points A and B meet at the point C. Find the x-coordinate
of C.
[5]
(ii) Show by integration that the area of the shaded region R1 is the same as the area of the
shaded region R2.
[4]
6
7. The equation of a curve is y = .
5 − 2x
(i) Calculate the gradient of the curve at the point where x = 1.
[3]
(ii) A point with coordinates (x, y) moves along the curve in such a way that the rate of
increase of y has a constant value of 0.02 units per second. Find the rate of increase of x
when x = 1.
[2]
(iii) The region between the curve, the x-axis and the lines x = 0 and x = 1 is rotated through
12
360° about the x-axis. Show that the volume obtained is π.
5
[5]
© Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Bangkok Patana School 3
8.
y
y = 3x
x
O 1 4
1
The diagram shows the curve y = 3 x 4 . The shaded region is bounded by the curve, the x-axis
and the lines x = 1 and x = 4. Find the volume of the solid obtained when this shaded region is
rotated completely about the x-axis, giving your answer in terms of π.
[4]
9. Find the area of the region enclosed by the curve y = 2√x, the x-axis and the lines x = 1
and x = 4.
[4]
dy
10. A curve is such that = 4 – x and the point P(2, 9) lies on the curve. The normal to the curve
dx
at P meets the curve again at Q. Find
(i) the equation of the curve,
[3]
(ii) the equation of the normal to the curve at P,
[3]
(iii) the coordinates of Q.
[3]
© Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Bangkok Patana School 4
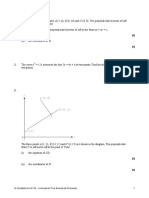
11.
y
(1, 18)
(4, 3)
x
O 1 1.6
dy k
The diagram shows a curve for which = − 3 , where k is a constant. The curve passes
dx x
through the points (1, 18) and (4, 3).
16
(i) Show, by integration, that the equation of the curve is y = + 2.
x2
[4]
The point P lies on the curve and has x-coordinate 1.6.
(ii) Find the area of the shaded region.
[4]
© Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Bangkok Patana School 5
12.
y
Q y = (3x + 1)
2
1 P
x
O 1
The diagram shows the curve y = √(3x + 1) and the points P (0, 1) and Q (1, 2) on the curve.
The shaded region is bounded by the curve, the y-axis and the line y = 2.
(i) Find the area of the shaded region.
[4]
(ii) Find the volume obtained when the shaded region is rotated through 360° about the
x-axis.
[4]
Tangents are drawn to the curve at the points P and Q.
(iii) Find the acute angle, in degrees correct to 1 decimal place, between the two tangents.
[4]
© Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Bangkok Patana School 6
13.
y
6
y=
3x – 2
x
O 1 2
6
The diagram shows part of the curve y = .
3x − 2
(i) Find the gradient of the curve at the point where x = 2.
[3]
(ii) Find the volume obtained when the shaded region is rotated through 360° about the
x-axis, giving your answer in terms of π.
[5]
© Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Bangkok Patana School 7
14.
y
C D
y = x3 – 6 x2 + 9 x
x
O B
The diagram shows the curve y = x3 – 6x2 + 9x for x ≥ 0. The curve has a maximum point at A
and a minimum point on the x-axis at B. The normal to the curve at C (2, 2) meets the normal to
the curve at B at the point D.
(i) Find the coordinates of A and B.
[3]
(ii) Find the equation of the normal to the curve at C.
[3]
(iii) Find the area of the shaded region.
[5]
© Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Bangkok Patana School 8
You might also like
- On the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)From EverandOn the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)No ratings yet
- Question's 5Document21 pagesQuestion's 5Irfan RanaNo ratings yet
- PM FM 5Document2 pagesPM FM 5biloma6323No ratings yet
- SMSO 2004 Paper 1Document4 pagesSMSO 2004 Paper 1api-25887606No ratings yet
- Gradients Tangents and Normals-Qp Cie-Ial-MathsDocument3 pagesGradients Tangents and Normals-Qp Cie-Ial-MathsExcella Maths & Science CenterNo ratings yet
- W 1Document1 pageW 1LOVE WITH MATHEMATICSNo ratings yet
- 9709 s15 QP 12Document2 pages9709 s15 QP 12Tanzim RahmanNo ratings yet
- CP2 - Paper 2Document3 pagesCP2 - Paper 2prashasti0410No ratings yet
- Solomon L QP - C1 OCRDocument3 pagesSolomon L QP - C1 OCRMuhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- D1 Diff With Normal & Tangents QPDocument19 pagesD1 Diff With Normal & Tangents QPvocalsfnNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Pastpaper Question'sDocument13 pagesDifferentiation Pastpaper Question'sUrnext bestalternw100% (1)
- 9 Basic Differentiation QP Cie Ial MathsDocument2 pages9 Basic Differentiation QP Cie Ial MathsLOVE WITH MATHEMATICSNo ratings yet
- 2007 IJC PrelimDocument23 pages2007 IJC PrelimWen LongNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument6 pagesDifferentiationAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- TKSSDocument22 pagesTKSSsignboonsgslNo ratings yet
- 05 Assignment 4A (Students)Document5 pages05 Assignment 4A (Students)Roopa kingkaraNo ratings yet
- Math 2003Document130 pagesMath 2003Tilak K CNo ratings yet
- 2022 Y6 TP Revision Paper 1 (QN)Document3 pages2022 Y6 TP Revision Paper 1 (QN)akdc 33No ratings yet
- Exam Questions HomeworkDocument3 pagesExam Questions HomeworkSam Hnatiuk0% (1)
- Question's MATHS QuadraticsDocument4 pagesQuestion's MATHS QuadraticsumaraNo ratings yet
- Solomon G QP - C1 OCRDocument3 pagesSolomon G QP - C1 OCRMuhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument7 pagesAdditional MathematicsAadiNo ratings yet
- TMJC 9758 2022 Promo ESUDocument5 pagesTMJC 9758 2022 Promo ESUSimrah Sultanah (Njc)No ratings yet
- MGSAM1Document3 pagesMGSAM1JASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations General Certi Cate of EducationDocument8 pagesCambridge International Examinations General Certi Cate of EducationHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- 2021 JC1 Promo Practice Paper BDocument4 pages2021 JC1 Promo Practice Paper Bvincesee85No ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics: Zimbabwe School Examinations CouncilDocument8 pagesPure Mathematics: Zimbabwe School Examinations CouncilLustreNo ratings yet
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math (Promotion Exam) Victoria Junior CollegeDocument8 pages2019 JC1 H2 Math (Promotion Exam) Victoria Junior CollegeanuNo ratings yet
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Advanced LevelDocument6 pagesZimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Advanced LevelNigel ShambokoNo ratings yet
- 2010 AJC H2 Math Promo With AnswersDocument8 pages2010 AJC H2 Math Promo With AnswersCindy KrisnadiNo ratings yet
- Y1 Assignment 9Document4 pagesY1 Assignment 9poppy nunnNo ratings yet
- 2020 - HCI - Promo - QN - No Ans PDFDocument6 pages2020 - HCI - Promo - QN - No Ans PDFJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- 9709 s13 QP 33Document2 pages9709 s13 QP 33Ananthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- DHS H2 2021 Prelim P1Document5 pagesDHS H2 2021 Prelim P1猪猪侠No ratings yet
- 2022 IP4 EoY Holiday Homework Set BDocument6 pages2022 IP4 EoY Holiday Homework Set BSoon Wei TingNo ratings yet
- 2018 JC2 H1 Maths SA2 Hwa Chong InstitutionDocument17 pages2018 JC2 H1 Maths SA2 Hwa Chong InstitutionjunaidahNo ratings yet
- 2010 Yjc H2ma Prelim p1Document4 pages2010 Yjc H2ma Prelim p1cjcsucksNo ratings yet
- A Level H2 Math Anderson Serangoon JC2 Prelim 2019Document55 pagesA Level H2 Math Anderson Serangoon JC2 Prelim 2019Dwayne JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (Mei) : Advanced Gce UnitDocument4 pagesMathematics (Mei) : Advanced Gce UnitThanh QuangNo ratings yet
- A-Levels Pure Mathematics ExemplarDocument16 pagesA-Levels Pure Mathematics ExemplarDarlingtonNo ratings yet
- Exam Pure MathsDocument4 pagesExam Pure MathsThabzgotkeyNo ratings yet
- Sec 4 Additional Mathematics Mock CADocument2 pagesSec 4 Additional Mathematics Mock CAapi-3728508No ratings yet
- 2016 STPM 954-P2 QSDocument1 page2016 STPM 954-P2 QSSIM KAH SENG KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Repaso Derivada - Integrales PDFDocument7 pagesRepaso Derivada - Integrales PDFFelipe AndradeNo ratings yet
- June 2011 QP - FP2 OCRDocument4 pagesJune 2011 QP - FP2 OCRahmed.ahsanm2005No ratings yet
- A Watermelon Is Assumed To Be Spherical in Shape While It Is Growing. Its MassDocument4 pagesA Watermelon Is Assumed To Be Spherical in Shape While It Is Growing. Its MassHANSNo ratings yet
- June 2011 QP - FP2 OCR (A)Document16 pagesJune 2011 QP - FP2 OCR (A)ahmed.ahsanm2005No ratings yet
- JC 1 H2 Maths Promo Practice Paper 1Document6 pagesJC 1 H2 Maths Promo Practice Paper 1brianfletcher182No ratings yet
- Revision p2 06Document3 pagesRevision p2 06api-3816473No ratings yet
- Work Sheet Class 9 PDFDocument12 pagesWork Sheet Class 9 PDFBurhan SyedNo ratings yet
- 2018 SAJC H2 Prelim P1 + SolutionDocument20 pages2018 SAJC H2 Prelim P1 + Solutiontoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Revision III AsDocument4 pagesRevision III AsTimaVNo ratings yet
- D2 Diff With Stationary Points in Nature - QPDocument8 pagesD2 Diff With Stationary Points in Nature - QPvocalsfnNo ratings yet
- 11 Derivative Paper2Document7 pages11 Derivative Paper2Selahattin GüntaşNo ratings yet
- Solomon I QP - C1 OCRDocument3 pagesSolomon I QP - C1 OCRMuhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelnoorlailyNo ratings yet
- ACSIAM1Document3 pagesACSIAM1JASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- Is Given by V 3 30 72 - + - Find The Distance Between The Particle's Two Positions of Instantaneous Rest.Document6 pagesIs Given by V 3 30 72 - + - Find The Distance Between The Particle's Two Positions of Instantaneous Rest.Tanzim RahmanNo ratings yet
- Test 1 MathematicsDocument3 pagesTest 1 MathematicsEvan NormanNo ratings yet
- Rebellion - Sagas of Iceland - The History of The Vikings Vol. 1Document28 pagesRebellion - Sagas of Iceland - The History of The Vikings Vol. 1Manuel Velasco100% (1)
- Tillotson HD & HR Service ManualDocument11 pagesTillotson HD & HR Service ManualBeckyNo ratings yet
- HSD Spindle Manual ES789 ES799 EnglishDocument62 pagesHSD Spindle Manual ES789 ES799 EnglishCamilo Andrés Lara castilloNo ratings yet
- Festivals of IndiaDocument51 pagesFestivals of IndiaDhatchayani RamkumarNo ratings yet
- QB Som He306 2015 2016Document23 pagesQB Som He306 2015 2016etayhailuNo ratings yet
- BR Safetymatrix enDocument12 pagesBR Safetymatrix enHamidreza MoaddeliNo ratings yet
- Figure Eight Island Homeowners' Association, Inc. Case StudyDocument16 pagesFigure Eight Island Homeowners' Association, Inc. Case StudyYoong YingNo ratings yet
- .Cancer DiseaseDocument10 pages.Cancer DiseasejanakrajchauhanNo ratings yet
- Allegheny Power Planning CriteriaDocument19 pagesAllegheny Power Planning Criteriaksdp1No ratings yet
- Score Fusion of Finger Vein and Face For Human Recognition Based On Convolutional Neural Network ModelDocument9 pagesScore Fusion of Finger Vein and Face For Human Recognition Based On Convolutional Neural Network ModelFressy NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Bock09 - Video Compression SystemsDocument300 pagesBock09 - Video Compression SystemsWong_Ngee_SengNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Laboratory: Open-Ended LabDocument7 pagesGeotechnical Laboratory: Open-Ended LabNoorshahira Md IsaNo ratings yet
- The Determinants of Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in Malaysian e Hailing ServicesDocument8 pagesThe Determinants of Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in Malaysian e Hailing ServicesYoannisa AtinaNo ratings yet
- 4mb/01r-Que-2023 Jun Edexcel PastpaperDocument24 pages4mb/01r-Que-2023 Jun Edexcel Pastpaperaugust.shwanNo ratings yet
- Neo Neurophone Patrick FlanaganDocument2 pagesNeo Neurophone Patrick FlanaganalexanderjfernandesNo ratings yet
- Auto Repair and Car Wash Business PlanDocument31 pagesAuto Repair and Car Wash Business PlanKiraYagamiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits 1 QPDocument7 pagesElectrical Circuits 1 QPKitty MinogueNo ratings yet
- Trane 5 Ton HP Cond submittat4TWB3060-SUB-106 - 05.05 - 11012009Document2 pagesTrane 5 Ton HP Cond submittat4TWB3060-SUB-106 - 05.05 - 11012009nobleairNo ratings yet
- Sandvik DD210Document4 pagesSandvik DD210Lener Elvin Lopez LavadoNo ratings yet
- Mass, Weigth and Density IGCSEDocument6 pagesMass, Weigth and Density IGCSEsapiniNo ratings yet
- Harmonization of HR Policies - RoughDocument119 pagesHarmonization of HR Policies - RoughFrancis SoiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes MCQsDocument2 pagesEnzymes MCQsNobody's PerfectNo ratings yet
- 24 Port - 48 Port CAT6A Patch PanelDocument2 pages24 Port - 48 Port CAT6A Patch PanelSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Tinnitus - Neil Bauman PHD - April '09Document2 pagesDrugs and Tinnitus - Neil Bauman PHD - April '09DownTheTheRabbitHole108No ratings yet
- Elements of HardscapingDocument57 pagesElements of HardscapingNathar ShaNo ratings yet
- Fuhs - Towards An Integral EpistemologyDocument39 pagesFuhs - Towards An Integral EpistemologyjmcmichaelNo ratings yet
- The Order of Melchizedek by Francis Myles (Myles, Francis)Document382 pagesThe Order of Melchizedek by Francis Myles (Myles, Francis)cap4090% (10)
- Maximizing Bass Reflex System Performance Through Optimization ofDocument32 pagesMaximizing Bass Reflex System Performance Through Optimization ofGilberto MontaniNo ratings yet
- REE0913ra LegazpiDocument6 pagesREE0913ra LegazpiScoopBoyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Rex A Kaiju Thriller (Matthew Dennion) (Z-Library)Document163 pagesAtomic Rex A Kaiju Thriller (Matthew Dennion) (Z-Library)Strictly Aviator Amritansh VermaNo ratings yet