Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Robbins Eob15 PPT 06
Uploaded by
thienmanvt1230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views28 pagesThis chapter discusses perception and individual decision making. It covers factors that influence perception like the perceiver, target, and context. Attribution theory is explained, which looks at how we judge others based on internal vs. external causes of behaviors. Biases in perception like the fundamental attribution error and heuristics people use are also reviewed. Models of decision making like rational, bounded rationality, and intuition are contrasted. Biases and influences on decision making like individual differences and organizational constraints are examined. The chapter also explores ethics in decision making using utilitarianism, rights, and justice approaches. It concludes by looking at creativity and a three-stage model of the creative process in organizations.
Original Description:
Original Title
robbins_eob15_ppt_06
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis chapter discusses perception and individual decision making. It covers factors that influence perception like the perceiver, target, and context. Attribution theory is explained, which looks at how we judge others based on internal vs. external causes of behaviors. Biases in perception like the fundamental attribution error and heuristics people use are also reviewed. Models of decision making like rational, bounded rationality, and intuition are contrasted. Biases and influences on decision making like individual differences and organizational constraints are examined. The chapter also explores ethics in decision making using utilitarianism, rights, and justice approaches. It concludes by looking at creativity and a three-stage model of the creative process in organizations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views28 pagesRobbins Eob15 PPT 06
Uploaded by
thienmanvt123This chapter discusses perception and individual decision making. It covers factors that influence perception like the perceiver, target, and context. Attribution theory is explained, which looks at how we judge others based on internal vs. external causes of behaviors. Biases in perception like the fundamental attribution error and heuristics people use are also reviewed. Models of decision making like rational, bounded rationality, and intuition are contrasted. Biases and influences on decision making like individual differences and organizational constraints are examined. The chapter also explores ethics in decision making using utilitarianism, rights, and justice approaches. It concludes by looking at creativity and a three-stage model of the creative process in organizations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 28
Essentials of Organizational Behavior
Fifteenth Edition, Global Edition
Chapter 6
Perception and Individual
Decision Making
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Learning Objectives
6.1 Explain the factors that influence perception.
6.2 Describe attribution theory.
6.3 Explain the link between perception and
decision making.
6.4 Contrast the rational model of decision making
with bounded rationality and intuition.
6.5 Explain how individual differences and
organizational constraints affect decision making.
6.6 Contrast the three ethical decision criteria.
6.7 Describe the three-stage model of creativity.
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
What is Perception?
Learning Objective 6.1
• Perception: a process by which individuals
organize and interpret their sensory impressions
in order to give meaning to their environment
• The world as it is perceived is the world that is
behaviorally important
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Factors that Influence Perception
• Factors the influence perception include
– The perceiver: your personal characteristics attitudes
– The target: characteristics of the target
– The context: situational factors
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Person Perception: Making Judgments
About Others
Learning Objective 6.2
• Person perceptions: perceptions we form about
each other
• Attribution Theory: an attempt to explain the
ways we judge people differently, depending on
the meaning we attribute to a behavior
• Internal and External Causation
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Distinctiveness, Consensus, and
Consistency
• Distinctiveness – whether an individual displays
different behaviors in different situations
• Consensus – does everyone who faces a similar
situation respond in the same way as the
individual did?
• Consistency – does the person respond the same
way over time?
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Attribution Theory (Exhibit 6-1)
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Errors and Biases
• Fundamental attribution error:
– Tendency to underestimate the influence of external
factors and overestimate the influence of internal
factors
• Self-serving bias: occurs when individuals
overestimate their own (internal) influence on
successes and overestimate the external
influences on their failures
• Cultural differences exist
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Common Shortcuts in Judging Others
(1 of 2)
• Selective Perception: selectively interpret based
on interests, background, and attitude
• Halo and Horns Effects: drawing a general
impression based on a single characteristic
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Common Shortcuts in Judging Others
(2 of 2)
• Contrast Effects: our reaction is influenced by
others we have recently encountered (the context
of the observation)
• Stereotyping: judging someone on the basis of
the perception of the group to which they belong
• Threat of technological unemployment: AI taking
over jobs
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
The Link Between Perception and
Decision Making
Learning Objective 6.3
• Decision making occurs as a reaction to a
perceived problem
• Discrepancy between the current state and a desired
state
• Decisions: choices from among two or more
alternatives
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Decision Making in Organizations
Learning Objective 6.4
• Approaches to decision making
– Rational decision making
– Bounded rationality
– Intuition
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
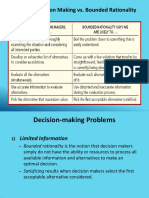
Rational Decision-Making Model
• Rational decision-making model
1. Define the problem
2. Identify the decision criteria
3. Allocate weights to the criteria
4. Develop the alternatives
5. Evaluate the alternatives
6. Select the best alternative
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Bounded Rationality
• The limited information-processing capability of
human beings makes it impossible to assimilate
and understand all the information necessary to
optimize
– People seek solutions that are satisfactory and
sufficient, rather than optimal (they “satisfice”)
• Bounded rationality is constructing simplified
models that extract the essential features from
problems without capturing all their complexity
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Intuition
• Intuitive decision making: a non-conscious
process created out of distilled experience
– Least rational decision-making model
– Affectively charged
– Can be a powerful complement to rational analysis in
decision making
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Common Biases and Errors in Decision
Making (1 of 2)
• Overconfidence Bias: a tendency to be
overconfident about our own abilities or the abilities of
others
• Anchoring Bias: a tendency to fixate on initial
information and fail to adequately adjust for
subsequent information
• Confirmation Bias: seeking out information that
reaffirms our past choices and discounting information
that contradicts past judgments
• Availability Bias: basing judgments on readily
available information
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Common Biases and Errors in Decision
Making (2 of 2)
• Escalation of Commitment: staying with a
decision even when there is clear evidence that it
is wrong
• Randomness Error: our tendency to believe we
can predict the outcome of random events
• Risk Aversion: preferring a sure gain of a
moderate amount over a riskier outcome
• Hindsight Bias: believing falsely that we could
have predicted the outcome of an event after that
outcome is already known
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Influences on Decision Making: Individual
Differences & Organizational Constraints
Learning Objective 6.5
• Individual differences
• Personality
• Gender
• General mental ability
• Cultural differences
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Organizational Constraints on Decision
Making
• Performance evaluation systems
• Reward systems
• Formal regulations
• System-imposed time constraints
• Historical precedents
• Decision making in times of crisis
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Ethics in Decision Making (1 of 2)
Learning Objective 6.6
• Three Ethical Decision Criteria
• Utilitarianism
– Provide the greatest good for the greatest number
• Rights
– Make decisions consistent with fundamental liberties and
privileges
• Justice
– Impose and enforce rules fairly and impartially so that there is
equal distribution of benefits and costs
Choosing between approaches !!!
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Ethics in Decision Making (2 of 2)
• Choosing between criteria
• Behavioral ethics
– Analyzing how people actually behave when
confronted with ethical dilemmas
• Lying
– Deadly to decision making
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Creativity and Innovation in Organizations
Learning Objective 6.7
• Creativity: the ability to produce novel and useful
ideas
• Helps people:
– See problems others can’t see
– Better fully understand problems
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Three-Stage Model of Creativity in
Organizations (Exhibit 6-4)
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Creative Behavior
Steps:
1. Problem formulation: identify a problem or
opportunity that requires a solution as yet
unknown
2. Information gathering: possible solutions
incubate in an individual’s mind
3. Idea generation: develop possible solutions
from relevant information and knowledge
4. Idea evaluation: evaluate potential solutions
and identify the best one
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Causes of Creative Behavior
• Creative potential:
• Intelligence and creativity
• Personality and creativity
• Expertise and creativity
• Ethics and creativity
• Creative environment
– Motivation
– Rewards and recognition
– Jobs with clear innovative expectations
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Creative Outcomes (Innovation)
• Creative outcomes: ideas or solutions judged to
be novel and useful by relevant stakeholders
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Implications for Managers
• Behavior follows perception, so to influence behavior at
work, assess how people perceive their work.
• Make better decisions by recognizing perceptual biases
and decision-making errors we tend to commit.
• Adjust your decision-making approach to the national
culture you’re operating in and to the criteria your
organization values.
• Combine rational analysis with intuition.
• Try to enhance your creativity.
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Discussion Questions
• The characteristics of the target can affect what
we perceive. While some of these assumptions
we make about surface characteristics are
harmful, some can be beneficial to the target.
Discuss the role of artificial intelligence in this
process.
• Individuals are not skilled at detecting lying. And
since lying can be deadly to decision making, how
can organizations create environments that are
not conducive to lying?
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education, Ltd.
You might also like
- Critical Thinking Secrets: Discover the Practical Fundamental Skills and Tools That are Essential to Improve Your Critical Thinking, Problem Solving and Decision Making SkillsFrom EverandCritical Thinking Secrets: Discover the Practical Fundamental Skills and Tools That are Essential to Improve Your Critical Thinking, Problem Solving and Decision Making SkillsNo ratings yet
- 04 PPT To Student Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument29 pages04 PPT To Student Perception and Individual Decision MakingTouleen AkoumNo ratings yet
- 05 Flex HboDocument26 pages05 Flex HboAbegail Mercado PamplonaNo ratings yet
- MGMT90018 Sem 2 Week 7 2023 Decision MakingDocument37 pagesMGMT90018 Sem 2 Week 7 2023 Decision MakingNooriNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument22 pagesPerception and Individual Decision MakingSabiha MirNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Part I.StrategyDocument48 pagesUnit 3. Part I.StrategysabynefaredNo ratings yet
- Perceptual ProcessesDocument26 pagesPerceptual ProcessesPratyum PradhanNo ratings yet
- Perception: Individual Decision MakingDocument31 pagesPerception: Individual Decision MakingsczameeNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision Making - FinalDocument36 pagesPerception and Individual Decision Making - Finaltracxx100% (4)
- Chapter 6Document25 pagesChapter 6Md. Saadman SakibNo ratings yet
- Decision Making by Individuals & GroupsDocument44 pagesDecision Making by Individuals & Groupsneera SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Perception and Decision MakingDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Perception and Decision MakingDaniyal WarsiNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument36 pagesPerception and Individual Decision MakingTayyab NaqviNo ratings yet
- Perception: DR Sireesha MamidennaDocument24 pagesPerception: DR Sireesha MamidennaAnu GupteNo ratings yet
- Robbins Eob13ge Ppt06Document28 pagesRobbins Eob13ge Ppt06Mingxiang WuNo ratings yet
- Decision Makers & LeadershipDocument34 pagesDecision Makers & LeadershipShelvy SilviaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Perception and Individual Decision Making in Organizational BehaviorDocument25 pages5 - Perception and Individual Decision Making in Organizational BehaviorJanaVrsalovićNo ratings yet
- IBO - Session 5 and 6 - Individual Decision MakingDocument15 pagesIBO - Session 5 and 6 - Individual Decision MakingAshwani RathourNo ratings yet
- Decision Making by Individuals & GroupsDocument35 pagesDecision Making by Individuals & Groupssgt_invictusNo ratings yet
- 6 Perceptions and Decison MakingDocument26 pages6 Perceptions and Decison MakingAgatNo ratings yet
- Session 12 13Document26 pagesSession 12 13KANIKA GORAYANo ratings yet
- 7 - Perceptions and AttributionsDocument29 pages7 - Perceptions and Attributionskajal chauhanNo ratings yet
- Perception & DMDocument25 pagesPerception & DMchinmayakumarbisoyi159No ratings yet
- 5 - Perception & Decision MakingDocument24 pages5 - Perception & Decision MakingAditya MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document50 pagesUnit 4systems kmfNo ratings yet
- Summary The Chapter 4 of Organizational BehaviorDocument3 pagesSummary The Chapter 4 of Organizational BehaviorĐặng Trần Thu UyênNo ratings yet
- 4 PerceptionDocument22 pages4 PerceptionkirsurkulkarniNo ratings yet
- 5.perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument22 pages5.perception and Individual Decision MakingAnas WahidNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument23 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Perception and Individual Decision Makingsrinivas pNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY Perilaku Keorganisasian Chapter 6 PDFDocument9 pagesSUMMARY Perilaku Keorganisasian Chapter 6 PDFLeman SingleNo ratings yet
- HBO Decision MakingDocument28 pagesHBO Decision MakingKha RenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document30 pagesChapter 9digibap102No ratings yet
- Problem Solving and Decision MakingDocument27 pagesProblem Solving and Decision MakingMehreen Sheyk100% (1)
- PerceptionDocument36 pagesPerceptionAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument20 pagesPerception and Individual Decision MakingM Soban Murad JoyiaNo ratings yet
- Robbins Eob15 PPT 07Document29 pagesRobbins Eob15 PPT 07thienmanvt123No ratings yet
- CH 04Document24 pagesCH 04sheetal gangradeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (M)Document23 pagesChapter 6 (M)samiyaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making by Individuals and GroupsDocument42 pagesDecision Making by Individuals and GroupsLaszlo Foldvari100% (1)
- Lec 03 - Ethics in Decision MakingDocument22 pagesLec 03 - Ethics in Decision MakingmonkeNo ratings yet
- Perceptions and Individual Decision Making C H - 6: Hajra AsadDocument11 pagesPerceptions and Individual Decision Making C H - 6: Hajra AsadAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Hartman 5e Accessible PPT Ch02Document15 pagesHartman 5e Accessible PPT Ch02khairulNo ratings yet
- Rational Decision Making vs. Bounded RationalityDocument9 pagesRational Decision Making vs. Bounded RationalityMike PartricksonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Managing Dynamic ProcessesDocument42 pagesChapter 2-Managing Dynamic ProcessesShewegen WaltengusNo ratings yet
- Hartman 5e Accessible PPT Ch02-1Document15 pagesHartman 5e Accessible PPT Ch02-1Chan Yi QiNo ratings yet
- 6 Chap PerceptionDocument26 pages6 Chap PerceptionJahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Life Skill EducationDocument10 pagesLife Skill EducationchonhaobamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 OBDocument24 pagesChapter 5 OBamnaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior MBA-542 Instructor: Erlan Bakiev, PH.DDocument27 pagesOrganizational Behavior MBA-542 Instructor: Erlan Bakiev, PH.DAqib ArshadNo ratings yet
- Ethical Decision MakingDocument39 pagesEthical Decision MakingAimanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Relationship, Fairness, Trust and EthicsDocument36 pagesLecture 3 Relationship, Fairness, Trust and EthicsHarishvardhanNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ProcessDocument24 pagesDecision Making ProcessWAQAS MURTAZANo ratings yet
- 6 Decision MakingDocument28 pages6 Decision MakingMajd MustafaNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document44 pagesChap 5Mai ĐặngNo ratings yet
- 05 Perception and Decision MakingDocument20 pages05 Perception and Decision MakingRonyNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument36 pagesPerception and Individual Decision MakingAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Art and Science of Consultancy - 3slide HandoutDocument8 pagesArt and Science of Consultancy - 3slide HandoutIsaac FullartonNo ratings yet
- 4robbins Mgmt15 PPT 02-Updated3Document46 pages4robbins Mgmt15 PPT 02-Updated3SanaaAbdelganyNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument48 pagesPerception and Individual Decision MakingSyed Ali XaidiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Week 4Document13 pagesLesson 3 - Week 4Jason CamaNo ratings yet
- DLL G9.Health Week 2Document5 pagesDLL G9.Health Week 2Alea Diaz EncaboNo ratings yet
- ESP - School BasedDocument42 pagesESP - School BasedGrace A. VidalNo ratings yet
- КМЖ 6 сыныпDocument3 pagesКМЖ 6 сыныпbekbayaida2004No ratings yet
- Spiral CuriDocument2 pagesSpiral CuriPrairie Dawn TilanoNo ratings yet
- UTS PEMBELAJARAN BERDIFERENSIASI - Fitra Pratama Dewi - 230211105793Document10 pagesUTS PEMBELAJARAN BERDIFERENSIASI - Fitra Pratama Dewi - 230211105793Fuad PratamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Kerby SabbalucaNo ratings yet
- My Elt ExercisesDocument23 pagesMy Elt ExercisesJosé Antonio Chero Ruiz100% (1)
- Feelings and EmotionsDocument8 pagesFeelings and EmotionsОльга КожевниковаNo ratings yet
- Career TheoriesDocument8 pagesCareer TheoriesMaria Nita BoloNo ratings yet
- LAS222 - Social PsychologyDocument4 pagesLAS222 - Social PsychologyKarla Angela ParasNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Inventory - 220808 - 100604Document14 pagesMental Health Inventory - 220808 - 100604Sunil Rathod100% (2)
- ICOBI 2019 A Study On Investigating The Writing Errors of ESL Sinhalese LearnersDocument6 pagesICOBI 2019 A Study On Investigating The Writing Errors of ESL Sinhalese Learnersrizla rumiNo ratings yet
- Lave Wenger 1991 Legitimate Peripheral ParticipationDocument11 pagesLave Wenger 1991 Legitimate Peripheral ParticipationGissela Naber SitzmannNo ratings yet
- Learning DifficultiesDocument11 pagesLearning DifficultiesTrisha RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Teaching by PrinciplesDocument18 pagesChapter - 4 Teaching by PrinciplesSilvana SilvaNo ratings yet
- Addressing The Reading Difficulties of Grade 3 Pupils in Kayok Elementary SchoolDocument60 pagesAddressing The Reading Difficulties of Grade 3 Pupils in Kayok Elementary SchoolPretpret Arcamo BanlutaNo ratings yet
- Visual Literacy Worksheet 2Document3 pagesVisual Literacy Worksheet 2api-552559988No ratings yet
- Lesson Personal Development - Lesson 2Document12 pagesLesson Personal Development - Lesson 2Elio SanchezNo ratings yet
- 1 ELLN Digital Course Proposal of San Isidro ES PDFDocument19 pages1 ELLN Digital Course Proposal of San Isidro ES PDFangelica sungaNo ratings yet
- M7L2 - LDR Group 2 & 4Document4 pagesM7L2 - LDR Group 2 & 4ByelRayaNo ratings yet
- Further Training On Disciplinary Knowledge of Foreign LanguagesDocument20 pagesFurther Training On Disciplinary Knowledge of Foreign LanguagesIsa RuizNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Learning Experience Dle TemplateDocument6 pagesDynamic Learning Experience Dle Templateapi-529114827No ratings yet
- Experiential Learning and Reflection in Construction of KnowledgeDocument7 pagesExperiential Learning and Reflection in Construction of KnowledgeNitish Soni0% (1)
- The Courage To Be Disliked: NotesDocument4 pagesThe Courage To Be Disliked: NotesMateusNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Nursing Students Knowledge of and Attitudes About Problem Based LearningDocument4 pagesInvestigation of Nursing Students Knowledge of and Attitudes About Problem Based LearningasdasdasdasNo ratings yet
- Trends 1ST Q Exam 2023-2024Document3 pagesTrends 1ST Q Exam 2023-2024Sittiehaya Angnie BAltNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Psychological Science 6th Edition Gazzaniga Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Psychological Science 6th Edition Gazzaniga Test Bank PDFchardskyishqb88100% (8)
- DLL Filipino 9 1st Week Q1Document3 pagesDLL Filipino 9 1st Week Q1Jazzle EnriquezNo ratings yet
- 4 Evaluation Sheet For Learning Area Books and Information in Digital FormatDocument4 pages4 Evaluation Sheet For Learning Area Books and Information in Digital FormatJaypee CandelariaNo ratings yet
- 871 1928 1 PBDocument15 pages871 1928 1 PBAjeng Nuranti SyafitriNo ratings yet