Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer in Physics 2
Uploaded by
kim natividadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reviewer in Physics 2
Uploaded by
kim natividadCopyright:
Available Formats
REVIEWER IN PHYSICS 2
CAPACITORS- device that stores electric potential energy and electric charge.
CIRCUIT GEOMETRY
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT-a path for transmitting electric current.
SERIES CIRCUIT- an electrical circuit in which the components are connected end-to-end, forming a
single path for the flow of electric current.
PARALLEL CIRCUIT- an electrical circuit where the components are connected in multiple paths, allowing
current to flow through each component independently.
CAPACITORS IN SERIES-PARALLEL COMBINATION
Step 1: Identify the smallest combination of capacitors that are either only in series or only in parallel.
Step 2: Use the appropriate formula (depending on whether the combination is in series or in parallel) to
determine the equivalent capacitance of the combination identified in Step 1.
Step 3: Replace all the component capacitors with a capacitor of capacitance calculated in step 2. Then
repeat Steps 1 to 3 to get the total capacitance.
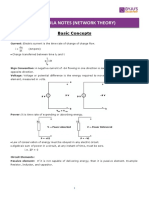
RESISTOR (R) (Ohms/Ω)- are used to reduce current flow. The main function of resistors in a circuit is
to control the flow of the current to other components
ELECTRIC CURRENT (I) (Amps/A) -The flow of electricity in an electronic circuit, and to the amount of
electricity flowing through a circuit.
VOLTAGE (V) (Volts/V)- The pressure from an electrical circuit's power source pushes charged
electrons (current) through a conducting loop, enabling them to do work such as illuminating a light.
OHM’S LAW- It is a formula used to calculate the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in
an electric circuit.
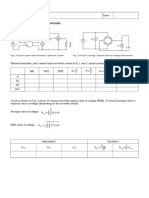
SERIES PARALLEL
CURRENT I T = I 1= I 2= I 3 I T + I 1+ ¿ I 2+ ¿ I 3
VOLTAGE V T =V 1 +¿ V 2 +V 3 V T =V 1=¿ V 2=V 3
RESISTOR RT = R1 +¿ R2 + R3 1 1
Formulas RT =¿ + + )-1
R2 R3
CAPACITOR 1 1 C T =¿ C 1+C 2 +C3
C T =¿ + + )-1
C2 C3
CHARGES QT =¿ Q1 = Q2 = Q3 QT =¿ Q1 + Q2 +
Q3
You might also like
- Expt 5.1Document6 pagesExpt 5.1Joel Catapang0% (1)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Impedance of RC Circuits: Series RC Circuits: Experiment No. 3Document17 pagesImpedance of RC Circuits: Series RC Circuits: Experiment No. 3NicoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Lab EE 213Document7 pagesElectrical Circuits Lab EE 213Ahmed QanahNo ratings yet
- Energy and PowerDocument15 pagesEnergy and PowerRaghavNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocument15 pagesElectrical Engineering Formulasajayyadav19100% (4)
- Kirchoff 00002Document25 pagesKirchoff 00002Ellen Kay CacatianNo ratings yet
- Verification of Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDocument4 pagesVerification of Maximum Power Transfer TheoremsivaiahjettiNo ratings yet
- Lab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Document11 pagesLab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Ece KayaNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument14 pagesDC CircuitsRaeniel SoritaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Lecture Notes Unit 1: Transient AnalysisDocument36 pagesUNIT-1: Lecture Notes Unit 1: Transient AnalysisRamalingeswar JNo ratings yet
- Engineering Circuit Analysis-CH3Document24 pagesEngineering Circuit Analysis-CH3Brenda Michelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- ES-1 Natural and Forced ResponseDocument39 pagesES-1 Natural and Forced ResponseGanesh DharmireddyNo ratings yet
- TOPIC-2 3 4 ModuleDocument67 pagesTOPIC-2 3 4 ModuleGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning of Current Transformers For Protection ApplicationsDocument9 pagesDimensioning of Current Transformers For Protection Applicationsprabhu_natarajan_n100% (1)
- Transient Response of LCRDocument3 pagesTransient Response of LCRAnkitMishraNo ratings yet
- Presentati w05d1Document23 pagesPresentati w05d1akirank1No ratings yet
- Hw2ans 2013 PDFDocument5 pagesHw2ans 2013 PDFAnthony AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Final Review PDFDocument19 pagesFinal Review PDFurfriend_jjn05No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC Analysis AllDocument32 pagesChapter 2 DC Analysis Allyibelta abebeNo ratings yet
- Free OscillationsDocument8 pagesFree OscillationsAnonymous 70j56EwNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryDocument6 pagesRC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document15 pagesChapter 3Gemechis AsfawNo ratings yet
- Ujt OscillatorDocument4 pagesUjt OscillatorSANTI MVEDJI Jean PaulNo ratings yet
- Expt 5.4Document6 pagesExpt 5.4Joel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Regulation of Dual-Output LCLC Resonant ConvertersDocument6 pagesModelling and Regulation of Dual-Output LCLC Resonant Convertersbacuoc.nguyen356No ratings yet
- Report Source FreeDocument43 pagesReport Source FreeCliford AlbiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Line or Naturally Commutated ConvertersDocument32 pagesChapter Two: Line or Naturally Commutated ConvertersMichael Adu-boahenNo ratings yet
- Numerical Overcurrent Relay and Relay CoordinationDocument7 pagesNumerical Overcurrent Relay and Relay Coordinationvoyimat216No ratings yet
- Mini Project 2Document8 pagesMini Project 2mohamadkhairudin3No ratings yet
- Astable MultivibratorDocument4 pagesAstable MultivibratorWaldo PulancoNo ratings yet
- The RC CircuitDocument2 pagesThe RC CircuitmailmadoNo ratings yet
- An-Najah University: Electrical Circuits LabDocument7 pagesAn-Najah University: Electrical Circuits LabAdel AtawiNo ratings yet
- Network Theory Formula Notesdoc 17Document24 pagesNetwork Theory Formula Notesdoc 17Manish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3. Single Tuned AmplifiersDocument14 pagesExperiment 3. Single Tuned AmplifiersSanjeev PandeyNo ratings yet
- The RC CircuitDocument2 pagesThe RC CircuitRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mohosin Ahmed Shisir - 233016010 - LR2 - EEE 1204 - Electric Circuit II LabDocument9 pagesMohosin Ahmed Shisir - 233016010 - LR2 - EEE 1204 - Electric Circuit II Labmohosin1ahmedNo ratings yet
- Alzahrani2019 PDFDocument22 pagesAlzahrani2019 PDFعزيزهtdar محبت دارNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy Generation Electrical Energy GenerationDocument10 pagesElectrical Energy Generation Electrical Energy GenerationKadhane NavnathNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Transil Apparent Dynamic ResistanceDocument5 pagesCalculation of Transil Apparent Dynamic ResistancebriceNo ratings yet
- Cs Lab Manual in PDFDocument56 pagesCs Lab Manual in PDFvasukonetiNo ratings yet
- First Order Differentiate PDFDocument21 pagesFirst Order Differentiate PDFDharamNo ratings yet
- 12-Presentation CTs & VTsDocument57 pages12-Presentation CTs & VTsmithun46No ratings yet
- RC Circuits and The Oscilloscope: ObjectiveDocument13 pagesRC Circuits and The Oscilloscope: Objectiveআব্দুল্লাহ আল ইমরানNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Temperature Compensated Logarithmic Amplifier: T TC R R R TCDocument2 pages1.1 Temperature Compensated Logarithmic Amplifier: T TC R R R TCnapoleon_velasc3617No ratings yet
- I DT DT DT DT: Class Notes On Electrical Measurements & InstrumentationDocument71 pagesI DT DT DT DT: Class Notes On Electrical Measurements & InstrumentationTia Nur AmaliahNo ratings yet
- May 6 Compressible-Flow-Homework Solutions: U U C T T H H C T T S S C T T RLN P PDocument6 pagesMay 6 Compressible-Flow-Homework Solutions: U U C T T H H C T T S S C T T RLN P PlmjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 - Direct-Current and CircuitsDocument11 pagesChapter 26 - Direct-Current and CircuitsClaire GacayanNo ratings yet
- Me 312Document20 pagesMe 312John Angelo MarzanNo ratings yet
- Lab #10: Sensor Signal ConditioningDocument10 pagesLab #10: Sensor Signal ConditioningNioNo ratings yet
- 2.-Electrotecnia Unit2 PDFDocument12 pages2.-Electrotecnia Unit2 PDFJayaraj LathaNo ratings yet
- UNIT II - PE - Control - 1PFWRectifiers PDFDocument24 pagesUNIT II - PE - Control - 1PFWRectifiers PDFramaNo ratings yet
- Lca Lab 4Document7 pagesLca Lab 4Usama MughalNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1: V IR Idt CDocument4 pagesAssignment # 1: V IR Idt Ctariqicp056No ratings yet
- Fully Integrated Universal Biquads Using Operational Transresistance Amplifiers With MOS-C RealizationDocument10 pagesFully Integrated Universal Biquads Using Operational Transresistance Amplifiers With MOS-C Realizationmohit kumar saxenaNo ratings yet
- Step Response LABDocument6 pagesStep Response LABGanesh ThapaNo ratings yet
- EE2 - Measurements Ac-CircuitDocument2 pagesEE2 - Measurements Ac-CircuitMaciej SergielNo ratings yet
- Op Amp Applications2Document26 pagesOp Amp Applications2Debashish PalNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet