Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CONCEPT OF ILLNESS. - PPT Download
CONCEPT OF ILLNESS. - PPT Download
Uploaded by
adeoyeoluwatofunmi16Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CONCEPT OF ILLNESS. - PPT Download
CONCEPT OF ILLNESS. - PPT Download
Uploaded by
adeoyeoluwatofunmi16Copyright:
Available Formats
Log in
Search... Search
1 / 30
CONCEPT OF ILLNESS.
Published by Erin Lang
Embed
Download presentation
Similar presentations
More
Presentation on theme: "CONCEPT OF
ILLNESS."— Presentation transcript:
1 CONCEPT OF ILLNESS
2 Sickness -is a state of social dysfunction
Sickness -is a state of social dysfunction. Likes to
remain away from social activities. Disease - is
maladjustment (Physiological/ Psychological) of the
human being to its environment -pathological change
in the structure or function of the body or mind
3 Illness
is a subjective state of person who feels aware of not
being well with evident sign and symptoms.
-abnormal process in which the persons level of
functioning is changed when compared to the previous
level
Illness is of two types
-acute
-chronic
4 Acute illness -generally has a rapid onset of
symptoms and last only a relatively short time -some
acute illness are life threatening, many don’t require
medical attention Stages of acute illness Stage 1-
experiencing symptoms -first indication of an illness
usually is recognizing one or more symptoms that are
incompatible with ones personal definition of health.
Eg.pain,fever
5 - the symptoms usually relieved by self care, if
not entered into next stage Stage 2- assuming the sick
role -the person now defines himself as being sick,
seeks validation of experience from others, give up
normal activities and assume a sick role -the person
may choose to do nothing, may seek out health care
provider for diagnosis and treatment -when help from
the health care provider is sought, the person become
a patient and enters the next stage
6 Stage 3-assuming a dependent role This stage is
characterized by the patients decisions to accept the
diagnosis and follow the prescribed treatment plan.
The person conforms to the opinion of others, often
requires assistance in carrying out activities of daily
living and need emotional support through acceptance,
approval and protection
7 Stage 4- achieving recovery and rehabilitation It
might begin in the hospital and conclude at home. In
this stage the person gives up the dependent role and
resumes normal activities and responsibilities. If health
education given, the individual may return to health at
a higher level of functioning than before the illness
8 Chronic illness -it is a permanent change -it
causes, or is caused by irreversible alteration in normal
anatomy and physiology -it require special patient
education for rehabilitation -it require a long period of
care and support
9 -Chronic illness usually have a slow onset and
many have periods of remission ( even though disease
is present, patient doesn’t experience symptoms) and
exacerbation ( the symptom of the disease reappear)
Eg. Heart problem, diabetes etc
10 Illness behaviour -people who are ill generally
adopt illness behaviour . These behaviour a!ect how
people monitor their bodies, define and interpret their
symptoms, take remedial actions and use the health
care systems ( mechanic, 1982) -if people perceive
themselves to be ill, illness behaviour act as coping
mechanism
11 Variables influencing illness bahaviour -external
-internal External variables -it include visibility of
symptoms, social group, cultural background,
economic variables, accessibility of health care and
social support
12 Internal variables -it include patients
perception of symptoms and the nature of illness -if
they perceive symptoms as descriptive, they seek
medical care -patient with acute illness, seek medical
care and adhere readily with therapy -patient with
chronic illness, not motivated to adhere with therapy
13 Impact of illness on patient and family -an
illness of a family member a!ect the function of the
entire family 1.Behavioral and emotional change -
individual’s behavioral and emotional reactions depend
on the nature of illness, the patients attitude towards
it, the reaction of others to it and the variables of
illness behaviour
14 -short term , non life threatening illnesses
evolve few behavioural changes in the functioning of
the patient and family Eg. A husband and father who
has a cold, lack the energy and patience to spend time
in the family activities and is irritable and prefers not to
interact with the family ( its a behavioural change, but
doesn’t last long) -severe illness have more emotional
and behavioural change
15 2. Impact on body image -body image is the
subjective concept of physical appearance. Some
illnesses result in the change in physical appearance.
The reaction is depend up on the type of change ( eg.
Loss of a limb), adaptive capacity of the person, rate at
which change take place, and the support services
available
16 -initially the change shocks the patient
-initially the change shocks the patient. As the patient
and family recognize the reality, they become anxious.
As the patient acknowledge the change, they accept
the loss. During rehabilitation, they learn how to adapt
the change
17 3. Impact on self concept -self concept is your
mental self image of all aspect of your personality -a
patient whose self concept changes, because of illness
is sometimes no longer able to meet family
expectations, leading to tension or conflict. As a result,
family member change their interaction with the
patient
18 4. Impact on family roles and family dynamics -
people may have many roles in life such as wage
earner, decision maker etc. when the illness occur, the
role change. Such a change is either short term or long
term -patient adjust more easily to short term change,
but guidance and counseling is required for long term
change
19 -family dynamics is the process by which the
family functions, make decisions, give support etc. -
because of the illness, family dynamics often change.
Another family member some times need to assume
the patients usual role and responsibilities. This often
create tension and anxiety . It may lead to conflicting
responsibilities
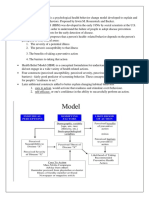
20 Health illness continuum -it is one way to
measure a persons level of health -this model views
health as a constantly changing state with high level
wellness and death being on opposite end of a
graduated scale or continuum -this continuum
illustrate the dynamic state of health, as a person
adapts to change in the internal and external
environment to maintain a state of well being
21 - A patient with a chronic illness may view
himself at di!erent points on the continuum at any
given time, depending on how well the patient believes
he or she is functioning with the illness
23 Causes and risk factor for developing diseases
DEFINITION OF RISK FACTOR -An attribute or exposure
that is significantly associated with the development of
disease -a determinant that can be modified by
intervention, thereby reducing the possibility of
occurrence of disease or other specified outcome
24 -Risk factors are often suggestive, ie, presence
of a risk factor does not imply that the disease will
occur, and in its absence diseases will not occur. -Risk
factors may be causative (eg, smoking for CA lung),
contributory (lack of physical exercise for CHD) or
predictive (eg, illiteracy for prenatal mortality).
25 Prominent risk factors Heart disease- smoking,
high BP, high cholesterol , diabetes, obesity Cancer-
smoking, alcohol, radiation, pollution, dietary factors
Stroke- smoking, high BP, high cholesterol Motor
vehicle accidents-alcohol, speed, non use of seat belt
Cirrhosis of liver-alcohol
26 Risk group / target group 1. Biological
situation -age group eg
Risk group / target group 1. Biological situation -age
group eg. Toddler more prone to accidents -sex eg.
Male more prone to Ca lung -physiological state eg.
Anemia is common in pregnant mother -genetic factors
eg. Family history of genetic disorder like mental
retardation, down syndrome, diabetes
27 -other health conditions eg. high blood
pressure lead to stroke 2
-other health conditions eg.high blood pressure lead to
stroke 2. Physical situations -rural (malnutrition), urban
(CAD) -living conditions, over crowding (asthma,
nutritional deficiency) -environment (cholera due to
impure water)
28 3.Socio cultural factors -social class (high class
more prone to CAD) -ethnic and cultural group -family
disruption (stress), education (infant mortality rate),
housing ( asthma) -customs ,habit, behaviour (
smoking, lack of exercise, over eating, drug addiction) -
access to health service (rural people) -lifestyle and
attitude(lack of exercise)
Download ppt "CONCEPT OF ILLNESS."
Similar presentations
About project Do Not Sell Feedback
SlidePlayer My Personal Privacy Policy
Terms of Service Information Feedback
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc.
All rights reserved.
Search... Search
You might also like
- Vedda Blood Sugar Remedy Web v2Document110 pagesVedda Blood Sugar Remedy Web v2thilanga100% (2)
- Concept of IllneesDocument30 pagesConcept of IllneesDiki DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Health & DiseaseDocument32 pagesConcepts of Health & DiseaseEggy PascualNo ratings yet
- Four ComponentsDocument8 pagesFour ComponentsRoselyn RioferioNo ratings yet
- Sc2211 EssaysDocument22 pagesSc2211 Essaysji ji euniNo ratings yet
- Activity WorksheetDocument3 pagesActivity WorksheetJasper CanitaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Health and IllnessDocument28 pagesConcept of Health and IllnessCeline Eliz Ang86% (7)
- HA LECTURE Transes 1Document10 pagesHA LECTURE Transes 1Erised DatuinNo ratings yet
- Theories and Concepts of Aging: Reynaldo S. Alipio, RN, MD, Mha, ManDocument82 pagesTheories and Concepts of Aging: Reynaldo S. Alipio, RN, MD, Mha, ManTuTitNo ratings yet
- Health and IllnessDocument7 pagesHealth and IllnessMary Ann SacramentoNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Health and IllnessDocument5 pagesConcepts of Health and Illnessjulesubayubay5428100% (1)
- Assingement of Psychology and SociologyDocument7 pagesAssingement of Psychology and SociologySurkhali BipanaNo ratings yet
- Noteshealth PsychDocument4 pagesNoteshealth PsychMaria Angelica CastilloteNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Notes Year One General Nursing in PakistanDocument62 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Notes Year One General Nursing in PakistanBheru Lal100% (2)
- Primary Health Care ADocument39 pagesPrimary Health Care AAmiel Francisco Reyes67% (3)
- 1 HEALTH AND ILLNESS HandoutsDocument5 pages1 HEALTH AND ILLNESS HandoutsVanessa Mae IlaganNo ratings yet
- Models of Health Promotion and Illness Prevention 1Document7 pagesModels of Health Promotion and Illness Prevention 1Krishnaveni MurugeshNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Health and IllnessDocument5 pagesConcepts of Health and IllnessDonna Flor NabuaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Illness, Persons and Their FamiliesDocument45 pagesChronic Illness, Persons and Their FamiliespheonixmtbtNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Professional NursingDocument41 pagesFoundations of Professional Nursingnb6pd5rvnxNo ratings yet
- TFN 2F Concepts of HealthDocument11 pagesTFN 2F Concepts of HealthLowell Jay Narciso LimosneroNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Health Beliefs and PracticesDocument14 pagesUnit Iii Health Beliefs and PracticesSteph YapNo ratings yet
- Health and Illness: Ronarica B. Diones, RN, RM, ManDocument78 pagesHealth and Illness: Ronarica B. Diones, RN, RM, ManRuffa Mae CalimagNo ratings yet
- Causes and Risk Factors For Developing IllnessDocument19 pagesCauses and Risk Factors For Developing IllnessSumit YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Stress, Health & Illness-1Document189 pagesUnit 4 Stress, Health & Illness-1noo.wannNo ratings yet
- Health and WellnessDocument2 pagesHealth and WellnessGalvan VinNo ratings yet
- CHRONICITYDocument5 pagesCHRONICITYvavafo7699No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Health and IllnessDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Health and IllnessMaria VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of NursingDocument58 pagesBasic Concept of NursingRajesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Health Psychology - More On Health Behaviour and TheoriesDocument24 pagesUnit 1 - Health Psychology - More On Health Behaviour and TheoriesSheeba ShamsudeenNo ratings yet
- Models of Health IllnessDocument3 pagesModels of Health Illnessjerikacorpuzmiranda100% (1)
- Publication 12 30892 233Document3 pagesPublication 12 30892 233W DNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 FUNDA LEC Concept of Health and IllnessDocument29 pagesNCM 103 FUNDA LEC Concept of Health and IllnessRosalinda LacuestaNo ratings yet
- Final Review - Medical SociologyDocument15 pagesFinal Review - Medical SociologyEmilyNo ratings yet
- Health Illness (2022)Document39 pagesHealth Illness (2022)AUDEH AHMADNo ratings yet
- DSC-3 (Assingment-1)Document6 pagesDSC-3 (Assingment-1)Preeti SinghNo ratings yet
- LEVELDocument7 pagesLEVELJhasmin SalipotNo ratings yet
- Social Work Within The Healthcare SystemDocument33 pagesSocial Work Within The Healthcare Systemcarolinemalungana04No ratings yet
- Social Determinants of Health NotesDocument18 pagesSocial Determinants of Health Noteschelsea pasiahNo ratings yet
- Presentation Group 1Document19 pagesPresentation Group 1coweyoloNo ratings yet
- Dimension of Health PDFDocument7 pagesDimension of Health PDFFersan AngelesNo ratings yet
- Health PsychologyDocument51 pagesHealth PsychologyShakeel Ahmed100% (3)
- 12 PsychiatricDocument28 pages12 PsychiatricamalNo ratings yet
- Evolução Dso Modelos de Assistência MédicaDocument9 pagesEvolução Dso Modelos de Assistência MédicaDaniel SousaNo ratings yet
- SHD Lecture Slides 2023 Themes 7 8Document62 pagesSHD Lecture Slides 2023 Themes 7 8pinehas nguluNo ratings yet
- Basic of Human Behavior in Health and Illness P 1Document20 pagesBasic of Human Behavior in Health and Illness P 1shenoudaharby1997No ratings yet
- Health Belief ModelDocument3 pagesHealth Belief ModelGiyo RamosNo ratings yet
- Health & IllnessDocument9 pagesHealth & Illnesskayanmohamd506No ratings yet
- Patient - Concepts of HealthDocument8 pagesPatient - Concepts of HealthMary CinconiegueNo ratings yet
- PY1101 Lecture 7 NotesDocument11 pagesPY1101 Lecture 7 NotesSeah Fu MeiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Context and TheoriesDocument33 pagesUnit 1 Context and TheoriesNimna KeminiNo ratings yet
- Impact of Illness Lecture - HandoutDocument5 pagesImpact of Illness Lecture - HandoutRyan PanNo ratings yet
- Health, Illness & Behaviour 2Document27 pagesHealth, Illness & Behaviour 2eresdNo ratings yet
- Health Belief ModelDocument3 pagesHealth Belief ModelPutri LenggogeniNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Models of HealthDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Models of HealthLalita A/P AnbarasenNo ratings yet
- Health Belief ModelDocument4 pagesHealth Belief ModelAshwini KatareNo ratings yet
- How to Live Longer: The Code to Your Amazing Life, Living Longer, Safer, and HealthierFrom EverandHow to Live Longer: The Code to Your Amazing Life, Living Longer, Safer, and HealthierNo ratings yet
- Integrative Medicine for Vulnerable Populations: A Clinical Guide to Working with Chronic and Comorbid Medical Disease, Mental Illness, and AddictionFrom EverandIntegrative Medicine for Vulnerable Populations: A Clinical Guide to Working with Chronic and Comorbid Medical Disease, Mental Illness, and AddictionNo ratings yet
- Brain Drain: How Highly Processed Food Depletes Your Brain of Neurotransmitters, the Key Chemicals It Needs to Properly FunctionFrom EverandBrain Drain: How Highly Processed Food Depletes Your Brain of Neurotransmitters, the Key Chemicals It Needs to Properly FunctionNo ratings yet
- NeurologiaDocument216 pagesNeurologiaPietro BracagliaNo ratings yet
- Healey, J. 2013 PDFDocument65 pagesHealey, J. 2013 PDFrobby mustofaNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument18 pagesObesityShakil KhanNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Non-Exercise Movement For Longevity: by Dr. MercolaDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Non-Exercise Movement For Longevity: by Dr. MercolaSellappan MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- English UasDocument15 pagesEnglish UasNurul NurhasanahNo ratings yet
- STS Malunggay Sugar CookiesDocument5 pagesSTS Malunggay Sugar CookiesCeline ValerieNo ratings yet
- HF ArticleDocument14 pagesHF ArticleDR. Shobhit RajNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Clinical Practice Recommendations, ADA2008 PDFDocument104 pagesDiabetes Clinical Practice Recommendations, ADA2008 PDFUchy CutejhyNo ratings yet
- Nihms Framinghan Study HeartDocument22 pagesNihms Framinghan Study Heartabraham landaetaNo ratings yet
- Ritalin Ritalin SRDocument15 pagesRitalin Ritalin SRMuhammad JamalNo ratings yet
- Pioneered Products of Sabinsa - Sep 16, 2011Document95 pagesPioneered Products of Sabinsa - Sep 16, 2011ameers333No ratings yet
- Paleolithic-Nutrition-Twenty-Five Years-Later-Eaton PDFDocument9 pagesPaleolithic-Nutrition-Twenty-Five Years-Later-Eaton PDFFran HrzicNo ratings yet
- Pad Screening Draft Evidence ReviewDocument92 pagesPad Screening Draft Evidence ReviewHaryadi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 7 Incredible Cashew Nut Benefits: From Heart Health To Gorgeous HairDocument4 pages7 Incredible Cashew Nut Benefits: From Heart Health To Gorgeous HairSadiq SayaniNo ratings yet
- The Belly Fat Diet John ChathamDocument92 pagesThe Belly Fat Diet John ChathamGurpreet Kaur100% (3)
- Molecules, Transport and HealthDocument29 pagesMolecules, Transport and Healthkamrunnisa100% (1)
- Heart Disease: Project Base Learning (PBL)Document26 pagesHeart Disease: Project Base Learning (PBL)syisyirararoroNo ratings yet
- Yoga Therapy TechniquesDocument222 pagesYoga Therapy TechniquesRam Prasad100% (2)
- Management of Hypertension in Heart Failure: Matthew R. Jonovich and John D. BisognanoDocument15 pagesManagement of Hypertension in Heart Failure: Matthew R. Jonovich and John D. BisognanojagodicamiliNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Tabitha Satkamp 2Document4 pagesLiterature Review Tabitha Satkamp 2api-608392349No ratings yet
- Adolescent Physical Activity Systematic ReviewDocument12 pagesAdolescent Physical Activity Systematic ReviewAleyzaNo ratings yet
- Sabbath Health Reading TopicsDocument27 pagesSabbath Health Reading TopicsIan Ng'andu ChinyamaNo ratings yet
- Form 1 EnglishDocument24 pagesForm 1 EnglishJack5688No ratings yet
- Preoperative Management of Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF) For HemodialysisDocument14 pagesPreoperative Management of Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF) For HemodialysisRafael CellestineNo ratings yet
- The Health and Social Benefits of RecreationDocument48 pagesThe Health and Social Benefits of RecreationDan RollorataNo ratings yet
- Chromium For Type 2 DiabetesDocument6 pagesChromium For Type 2 DiabetesSathishKumarNo ratings yet
- Healthy Foods Fact Versus Fiction-ManteshDocument320 pagesHealthy Foods Fact Versus Fiction-ManteshRodrigo Durán Cuiñas100% (7)
- Why Animals Don't Get Heart Attacks - But - Rath, Matthias, M.D PDF (Pauling-Rath Therapy Protocol)Document292 pagesWhy Animals Don't Get Heart Attacks - But - Rath, Matthias, M.D PDF (Pauling-Rath Therapy Protocol)Anonymous Jap77xvqPKNo ratings yet
- Exercise Is Medicine at Any Dose?Document2 pagesExercise Is Medicine at Any Dose?Carlos VieiraNo ratings yet