Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cloud Service Models
Cloud Service Models
Uploaded by
temp413040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views16 pagesThere are three main cloud service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides computing infrastructure resources, PaaS provides development platforms, and SaaS provides access to applications. Each service model provides different levels of control, with IaaS providing the most control over infrastructure and SaaS providing the least control. Future cloud service models may include additional "as a service" offerings like storage, databases, and security delivered through the cloud.
Original Description:
Original Title
cloud service models
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are three main cloud service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides computing infrastructure resources, PaaS provides development platforms, and SaaS provides access to applications. Each service model provides different levels of control, with IaaS providing the most control over infrastructure and SaaS providing the least control. Future cloud service models may include additional "as a service" offerings like storage, databases, and security delivered through the cloud.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views16 pagesCloud Service Models
Cloud Service Models
Uploaded by
temp41304There are three main cloud service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides computing infrastructure resources, PaaS provides development platforms, and SaaS provides access to applications. Each service model provides different levels of control, with IaaS providing the most control over infrastructure and SaaS providing the least control. Future cloud service models may include additional "as a service" offerings like storage, databases, and security delivered through the cloud.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Cloud Service Models
Dr. Amit Praseed
Dr. Amit Praseed
Can you name some cloud services
which you use?
Dr. Amit Praseed
Cloud Services
• There are three types of services offered by
cloud service providers
– Software as a Service (SaaS)
– Platform as a Service (PaaS)
– Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Dr. Amit Praseed
Software as a Service
• Provides access to applications running on a
cloud infrastructure, including network,
servers, OS, storage or individual applications
• Accessible from client devices via a browser
or program interface
• Customer does not manage or control
underlying infrastructure or applications –
limited customization
• Eg: Google Documents, Sharepoint etc.
Dr. Amit Praseed
SaaS Features
• One to Many
• Web Access
• Centralized Management
• Multi-device support
• Scalability
• Availability
• API integration
Dr. Amit Praseed
When to use SaaS?
• You should use SaaS for:
– On demand software
– Software for startups
– Software compatibility
– Varying loads
• SaaS might not be a good option if:
– Unreliable network connection
– Confidential data
Dr. Amit Praseed
SaaS - Pros and Cons
Pros Cons
• No installation • Security
• Cost savings • Connectivity
• Less maintenance • Loss of Control
• Ease of Access
• Dynamic scalability
• Disaster Recovery
• Multitenancy
Dr. Amit Praseed
Platform as a Service
• Provides ability to create and/or deploy
applications on cloud infrastructure
– Languages, libraries, services and tools are
provided by the vendor
• Customer does not manage or control
underlying infrastructure but can customize
the applications
• Eg: Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure etc.
Dr. Amit Praseed
Features of PaaS
• All-in-one (dev+test+deploy+host+maintain)
• Web Access
• Offline access
• Built in Scalability
• Collaborative
• Diverse tools available
Dr. Amit Praseed
When to use PaaS?
• PaaS is a good option if:
– Collaborative development
– Automated testing and deployment
– Less time to market
• PaaS might not be a good option if:
– Frequent migration / Vendor Lock-In
– Infrastructure customization
– Platform flexibility
– On-prem integration
Dr. Amit Praseed
PaaS – Pros and Cons
Pros Cons
• Quick development and • Vendor Lock-In
deployment • Security
• Reduces ownership cost • Less flexibility
• Agile software development • Depends on network
• Collaboration connection
• Ease of use
• Less maintenance
• Scalability
Dr. Amit Praseed
Infrastructure as a Service
• Provides ability to provision processing,
storage, networks, and other resources
– Deploy and run arbitrary software, OS and
applications
• Customer does not manage or control
underlying infrastructure but can control the
OS, storage and deployed applications
• Eg: Amazon Web Services etc.
Dr. Amit Praseed
Features of IaaS
• Web Access to resources
• Centralized management
• Elasticity and dynamic scaling
• Shared infrastructure
• Preconfigured VMs
• Metered Services
Dr. Amit Praseed
IaaS – Pros and Cons
Pros Cons
• Pay as you use • Security
• Reduced operational cost • Interoperability / Vendor
• Elastic resources Lock-In
• Better resource utilization • Network performance
• Green IT
Dr. Amit Praseed
Comparison of Cloud Services
Traditional Setup Infrastructure as a Platform as a Software as a
Service (IaaS) Service (PaaS) Service (SaaS)
Data Data Data Data
Applications Applications Applications Applications
Runtime Runtime Runtime Runtime
Environment Environment Environment Environment
Virtualization Virtualization Virtualization Virtualization
Servers Servers Servers Servers
Storage Storage Storage Storage
Network Network Network Network
Under user’s control Under common control Under provider’s control
Dr. Amit Praseed
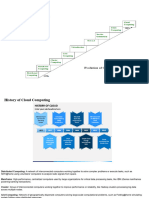
Future of Cloud - XaaS
• Network as a Service (NaaS)
• Desktop as a Service (DEaaS)
• Storage as a Service (STaaS)
• DB as a Service (DBaaS)
• Data as a Service (DaaS)
• Security as a Service (SECaaS)
• Identity as a Service (IDaaS)
Dr. Amit Praseed
You might also like
- AZ-900T00 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals-01Document21 pagesAZ-900T00 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals-01MgminLukaLayNo ratings yet
- Regedit by Niicoo - Cr20.RegDocument6 pagesRegedit by Niicoo - Cr20.RegUn Capaxxx100% (1)
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Exam Cram: Second EditionFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Fundamentals Exam Cram: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AZ-900 Exam Prep Downloadable Slide DeckDocument453 pagesAZ-900 Exam Prep Downloadable Slide Decksushainkapoor photo100% (3)
- Social Media Content Calendar PDFDocument3 pagesSocial Media Content Calendar PDFMonika GahlotNo ratings yet
- La Presse BDocument7 pagesLa Presse BSitara QadirNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - The New Era: - by Mohd Tareque Khan TY I.T. (705069) CoepDocument43 pagesCloud Computing - The New Era: - by Mohd Tareque Khan TY I.T. (705069) CoepVikas JainNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: When It's Smarter To Rent Then To BuyDocument28 pagesCloud Computing: When It's Smarter To Rent Then To BuyAbhishek RepswalNo ratings yet
- 3 Cloud ServicesDocument85 pages3 Cloud ServicesMahima PatelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Cloud Computinganam kazi100% (4)
- Device To Saas Cloud Security Access Brokers Part-1: Himani Singh Sept 2016Document39 pagesDevice To Saas Cloud Security Access Brokers Part-1: Himani Singh Sept 2016manishNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing ServicesDocument25 pagesCloud Computing ServicesSakshi KakadeNo ratings yet
- CC Week 05Document49 pagesCC Week 05Muhammad ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Azure Fundamentals EnglishDocument144 pagesAzure Fundamentals EnglishLuisa Garcia100% (1)
- Sit1503 Unit2Document63 pagesSit1503 Unit2nitheshsundararajan78No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesCloud ComputingYashvi KankarwalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument22 pagesAn Introduction To Cloud ComputingKunwar AdityaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Services IAAS, PAAS, SAAS and VirtualizationDocument49 pagesCloud Computing Services IAAS, PAAS, SAAS and VirtualizationBhuvaneshwari BNo ratings yet
- Short Introduction To Cloud Computing Saas Paas and Iaas549Document22 pagesShort Introduction To Cloud Computing Saas Paas and Iaas549VladeK231No ratings yet
- Presentation On Cloud Service Models: Prentation By-Group: - 6Document21 pagesPresentation On Cloud Service Models: Prentation By-Group: - 6mbhushitaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Saas and Cloud ComputingDocument22 pagesAn Introduction To Saas and Cloud ComputingstacayNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure As A Service (Iaas) : Presented byDocument8 pagesInfrastructure As A Service (Iaas) : Presented bySwapan DasNo ratings yet
- Cloud: ComputingDocument26 pagesCloud: ComputingEdu On PointsNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing PresentationDocument34 pagesCloud Computing PresentationWaleed EducationalNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides 5 - Cloud Architecture and Type of CloudsDocument33 pagesLecture Slides 5 - Cloud Architecture and Type of CloudsPanshul SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Cloud Computing Lecture 5aDocument22 pagesWeek 3 Cloud Computing Lecture 5asanwalNo ratings yet
- Saas and Cloud ComputingDocument22 pagesSaas and Cloud Computingqureshi_zakirNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument42 pagesCloud ComputingSHANKAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- Platform As A Service: Presented By: N Kalyan Gupta 1602-17-733-314 B Madhukumar 1602-17-733-323Document22 pagesPlatform As A Service: Presented By: N Kalyan Gupta 1602-17-733-314 B Madhukumar 1602-17-733-323Kalyan NarlaNo ratings yet
- The Strategy of IT Interprise in The Cloud Computing Era: Presented By: Nguyen Dieu LinhDocument41 pagesThe Strategy of IT Interprise in The Cloud Computing Era: Presented By: Nguyen Dieu Linhdieulinh_k28No ratings yet
- Introduction To Platform-as-a-Service and Cloud Foundry!Document34 pagesIntroduction To Platform-as-a-Service and Cloud Foundry!Narasimhaiah NarahariNo ratings yet
- Cloud Security ChapterDocument95 pagesCloud Security ChapterKajalNo ratings yet
- Total Cloud Control With Em12cDocument11 pagesTotal Cloud Control With Em12cgamezzzzNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Saas and Cloud Computing: Ross CooneyDocument39 pagesAn Introduction To Saas and Cloud Computing: Ross CooneyReetu KellurNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument22 pagesCloud ComputingRaghavendra GudiNo ratings yet
- Virtual Training Day - SlidesDocument121 pagesVirtual Training Day - Slidesjulee.lp220No ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1Document44 pagesChapter 3.1ishasingh2116No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument72 pagesIntroduction To Cloud ComputingLipsa Rani JenaNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Cloud Computing PDFDocument42 pagesUnit3 Cloud Computing PDFonlyfor collegeuseNo ratings yet
- U3 Introduction CCDocument66 pagesU3 Introduction CCsakshi bhegadeNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 NotesDocument11 pagesUNIT 2 Notes2022aspire37No ratings yet
- AWS CP 2022 Day1Document98 pagesAWS CP 2022 Day1Piyush palNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Paradigm: A.Vamshidhar ReddyDocument8 pagesCloud Computing Paradigm: A.Vamshidhar ReddySudhamsha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Azure Sales TrainingDocument27 pagesMicrosoft Azure Sales TrainingBinie KadamNo ratings yet
- MIS CloudDocument14 pagesMIS Cloudabhiseknanda82495No ratings yet
- Azure FundamentalDocument117 pagesAzure Fundamentalivanjanitra10aNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing 1Document50 pagesCloud Computing 1aryansaxena2137No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud Computing: Mohamed Rahal ENIT 2018Document99 pagesIntroduction To Cloud Computing: Mohamed Rahal ENIT 2018Nouradin Hassan DararNo ratings yet
- Platform As A Service (PaaS) 1Document24 pagesPlatform As A Service (PaaS) 1purushothaman.rojeNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: "The Web Is Replacing The Desktop"Document13 pagesCloud Computing: "The Web Is Replacing The Desktop"Manoj BagdeNo ratings yet
- Cloud Architecture SummaryDocument12 pagesCloud Architecture SummaryKranti KambleNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument13 pagesCloud Computingsandip enzNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing ProjectsDocument20 pagesCloud Computing ProjectsAbdul SubhanNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesCloud ComputingPriti chavanNo ratings yet
- Assignment (IaaS, PaaS)Document5 pagesAssignment (IaaS, PaaS)Ahmad AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Module - Cloud ComputingDocument21 pagesModule - Cloud ComputingAlisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Service Models: Amity School of Engineering & TechnologyDocument37 pagesService Models: Amity School of Engineering & TechnologyNiharika SinghNo ratings yet
- ICC Lecture 03b Cloud Service Models and Deployment Models 12102022 101309amDocument57 pagesICC Lecture 03b Cloud Service Models and Deployment Models 12102022 101309amMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Service Models Module - 4Document29 pagesCloud Computing Service Models Module - 4Aditya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesCloud ComputingSUPRIYO BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument27 pagesCloud ComputingAnuja UpadhyeNo ratings yet
- CloudComputing 2Document16 pagesCloudComputing 2Revanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Workspace One Editions ComparisonDocument12 pagesWorkspace One Editions ComparisonNan Win AungNo ratings yet
- Clash of Clans Free Gems GeneratorDocument2 pagesClash of Clans Free Gems GeneratorfortnitehackNo ratings yet
- Ict Best Brain Omega Mock QuestionsDocument12 pagesIct Best Brain Omega Mock QuestionsEugy OfoeNo ratings yet
- Manula RES2DMODDocument23 pagesManula RES2DMODSergio Jr S FachinNo ratings yet
- Imp, BLTDocument3 pagesImp, BLTNARENDRANo ratings yet
- XGPS160 OM Rev 1.3Document20 pagesXGPS160 OM Rev 1.3ivanNo ratings yet
- Naukri Jyothi (5y 0m)Document4 pagesNaukri Jyothi (5y 0m)Rohit BhasinNo ratings yet
- Et200sp Ai Energymeter 400vac ST Manual en-US en-USDocument109 pagesEt200sp Ai Energymeter 400vac ST Manual en-US en-USLuca ForniNo ratings yet
- What Pet Should I Get Worksheets.Document22 pagesWhat Pet Should I Get Worksheets.Brenda Segovia GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Oracle Server Manager For Windows Installation Guide: Release 2.1Document22 pagesOracle Server Manager For Windows Installation Guide: Release 2.1sadicosadicoNo ratings yet
- Working With Files: Loop Xpath Query (XML Files) Loop Json Query (Json Files)Document3 pagesWorking With Files: Loop Xpath Query (XML Files) Loop Json Query (Json Files)Arbi GharbiNo ratings yet
- Study Guide: Object Oriented Programming (OOP)Document9 pagesStudy Guide: Object Oriented Programming (OOP)AjNo ratings yet
- Тренажеры Body Sculpture 2018Document26 pagesТренажеры Body Sculpture 2018SonjuNo ratings yet
- WilliamStallings Chp3 PDFDocument60 pagesWilliamStallings Chp3 PDFAlfonsus devinNo ratings yet
- Secure Access 6.4 Study Guide-Online-DesbloqueadoDocument446 pagesSecure Access 6.4 Study Guide-Online-DesbloqueadoDiegoNo ratings yet
- Govpub C13Document52 pagesGovpub C13MHD SHAERNo ratings yet
- Indonesia: The Scoop of The Day The Latest UpdatesDocument6 pagesIndonesia: The Scoop of The Day The Latest UpdatesGuntur SekarNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 NetworkingDocument3 pagesUnit 6 Networking2I2075 Farhan AmrullahNo ratings yet
- Extreme Programming and Scrum - Getting Started With Agile Software DevelopmentDocument56 pagesExtreme Programming and Scrum - Getting Started With Agile Software Developmenttitli123No ratings yet
- MLNX - EN Documentation Rev 4.9-5.1.0.0 LTS - 10!23!2022Document206 pagesMLNX - EN Documentation Rev 4.9-5.1.0.0 LTS - 10!23!2022BJNo ratings yet
- Gfa 148Document2 pagesGfa 148Sidney Chaves de LimaNo ratings yet
- Qa Intervi̇ew FragenDocument453 pagesQa Intervi̇ew FragenHANo ratings yet
- Resume AJITSWAMIDocument3 pagesResume AJITSWAMISharon JNo ratings yet
- 1629-15 Philip Stark Arlo Audit IssuesDocument91 pages1629-15 Philip Stark Arlo Audit IssuesPaul WallNo ratings yet
- QM - CW - SO - G2 - 10 - Eglobe G2 - Export Diagnostic Data V4Document7 pagesQM - CW - SO - G2 - 10 - Eglobe G2 - Export Diagnostic Data V4Никита ВеликоцкийNo ratings yet
- Flowchartandalgorithmbasics PDFDocument195 pagesFlowchartandalgorithmbasics PDFDurgrim44No ratings yet
- An Empirical Study of Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact On Human Resource FunctionsDocument6 pagesAn Empirical Study of Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact On Human Resource FunctionsSonale Taneja TandoanNo ratings yet