Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asia (: / Eɪʒə/ / Eɪʃə/ Continent
Asia (: / Eɪʒə/ / Eɪʃə/ Continent
Uploaded by
Stratan AdelinaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Asia (: / Eɪʒə/ / Eɪʃə/ Continent
Asia (: / Eɪʒə/ / Eɪʃə/ Continent
Uploaded by
Stratan AdelinaCopyright:
Available Formats
Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ ⓘ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent[note 1][10][11] in the
world by both land area and population. [11] It covers an area of more than 44 million
square kilometers,[note 2] about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total
surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human
population,[12] was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion
people[13] constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. [14]
Asia
Area 44,579,000 km2(17,212,000 sq mi)
(1st)[1]
Population 4,694,576,167 (2021; 1st)[2][3]
Population 100/km2 (260/sq mi)
density
GDP (PPP) $72.7 trillion (2022 est; 1st)[4]
GDP $39 trillion (2022 est; 1st)[5]
(nominal)
GDP per $8,890 (2022 est; 4th)[6]
capita
Islam (28.0%)
Religions Hinduism (22.8%)
No religion (13.9%)
Buddhism (11.1%)
Chinese folk
religion(9.7%)
Christianity (8.4%)
Ethnic religions (3.5%)
New religions (1.3%)
Other (1.3%)[7]
Demonym Asian
Countries 49 UN members
1 UN observer
5 other states
Dependencies List
Akrotiri and Dhekelia
British Indian Ocean
Territory
Christmas Island
Cocos (Keeling)
Islands
Hong Kong
Macau
Non-UN List
states Abkhazia
Northern Cyprus
Palestine
South Ossetia
Taiwan
Languages List of languages
Time zones UTC+02:00 to UTC+12:00
Internet TLD .asia
Largest cities List of metropolitan areas
Lists of cities
UN M49 code 142 – Asia
001 – World
Map of the most populous part of Asia showing
physical, political, and population characteristics, as per 2018
Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both
Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean,
on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border
of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical
and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved
since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two
continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of
which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly
accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa;
and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the
south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from
Europe.[15]
You might also like
- Brief History of Korea: Isolation, War, Despotism and Revival: The Fascinating Story of a Resilient But Divided PeopleFrom EverandBrief History of Korea: Isolation, War, Despotism and Revival: The Fascinating Story of a Resilient But Divided PeopleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- AustraliaDocument38 pagesAustraliaRumburak100% (1)
- AsiaDocument34 pagesAsiaKarl GustavNo ratings yet
- Day 2B ECDIS PRESENTATIONDocument83 pagesDay 2B ECDIS PRESENTATIONjames100% (3)
- Master's Own Standing OrdersDocument4 pagesMaster's Own Standing OrdersCelal Bozdogan100% (1)
- Facts About Korea 2009 (English)Document258 pagesFacts About Korea 2009 (English)Republic of Korea (Korea.net)100% (3)
- 2nd Mate Past Question Papers Till Nov18 1Document143 pages2nd Mate Past Question Papers Till Nov18 1arbaazNo ratings yet
- Interesting Facts On The 7 Continents of The WorldDocument13 pagesInteresting Facts On The 7 Continents of The WorldExcel Joy MarticioNo ratings yet
- Facts About Korea (English)Document258 pagesFacts About Korea (English)Republic of Korea (Korea.net)100% (7)
- Module in Ss4-2 Year Bsed - Social StudiesDocument10 pagesModule in Ss4-2 Year Bsed - Social StudiesEduardo Quidta100% (1)
- Jump To Navigation Jump To Search: This Article Is About The Continent. For Other Uses, SeeDocument17 pagesJump To Navigation Jump To Search: This Article Is About The Continent. For Other Uses, SeeJeje NutNo ratings yet
- Australia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument5 pagesAustralia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchNicolas Ferney BARRETO MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- AsiaDocument32 pagesAsiamaxdsNo ratings yet
- Eurasia - WikipediaDocument4 pagesEurasia - WikipediatrianaNo ratings yet
- Indonesia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument52 pagesIndonesia: Jump To Navigation Jump To Searchiorga10No ratings yet
- List of Countries and Capitals With Currency and LanguageDocument36 pagesList of Countries and Capitals With Currency and LanguagescykeiNo ratings yet
- List of Countries and Capitals With Currency and LanguageDocument78 pagesList of Countries and Capitals With Currency and LanguageAnne DeeNo ratings yet
- Indian Ocean: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument3 pagesIndian Ocean: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchNatia SaginashviliNo ratings yet
- AsiaDocument24 pagesAsiaRumburakNo ratings yet
- Natural TourismDocument16 pagesNatural TourismArjie GabrielNo ratings yet
- Pakistan InfoDocument20 pagesPakistan InfoJatinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Geography: Northern AsiaDocument3 pagesGeography: Northern AsiahiNo ratings yet
- Data G20 V2Document11 pagesData G20 V2Derry Berni CahyadyNo ratings yet
- List of CountriesDocument21 pagesList of CountriesabhiNo ratings yet
- IndonesiaDocument59 pagesIndonesiaYullian RachmatNo ratings yet
- Hawaii: Hawaiki Kawaii Hawai (Disambiguation) Hawaii (Island) Hawaii (Disambiguation)Document7 pagesHawaii: Hawaiki Kawaii Hawai (Disambiguation) Hawaii (Island) Hawaii (Disambiguation)Nicolas Ferney BARRETO MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- The Area of South Korea - Google SearchDocument1 pageThe Area of South Korea - Google SearchHasan HayitovNo ratings yet
- India: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument78 pagesIndia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchZKAND LoganNo ratings yet
- Commonwealth of AustraliaDocument4 pagesCommonwealth of AustraliaLali HajzeriNo ratings yet
- Azerbaijan: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument39 pagesAzerbaijan: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchMariana ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Asian CountriesDocument3 pagesAsian Countrieslechumanan26No ratings yet
- DSFSDGFSGDocument6 pagesDSFSDGFSGabhiroop kNo ratings yet
- Australia, Officially The Commonwealth of Australia, Is A: o o o o o o o o o o o o o oDocument2 pagesAustralia, Officially The Commonwealth of Australia, Is A: o o o o o o o o o o o o o oAnik GuinNo ratings yet
- AustraliaDocument14 pagesAustraliaRaviteja VegiNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Capiz State University PontevedracampusDocument12 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Capiz State University PontevedracampusLorence Albert EstilloroNo ratings yet
- East AsiaDocument1 pageEast AsiaSauransh GuptaNo ratings yet
- ПрезентацияDocument6 pagesПрезентацияБалауса КадыргазыкызыNo ratings yet
- OceaniaDocument3 pagesOceaniahtsjekrbwkejtrhNo ratings yet
- Malaysia: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument4 pagesMalaysia: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchJianhengMokNo ratings yet
- Transcultural ReportingDocument5 pagesTranscultural ReportingKarl OngNo ratings yet
- The Continents of TH WorldDocument2 pagesThe Continents of TH WorldluisNo ratings yet
- Profile - AustraliaDocument12 pagesProfile - Australiaanthonyh80No ratings yet
- Great BritainDocument3 pagesGreat BritainAndreea BajureanuNo ratings yet
- List of Countries and Capitals With Currency and LanguageDocument36 pagesList of Countries and Capitals With Currency and LanguageGaby López MoguelNo ratings yet
- Ecuador: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument32 pagesEcuador: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchА. ЕлдинNo ratings yet
- Pakistan: 37 Visitors From Here!Document7 pagesPakistan: 37 Visitors From Here!Shanz KhanNo ratings yet
- BAR1Document2 pagesBAR1jafasoh293No ratings yet
- India: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument39 pagesIndia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchА. ЕлдинNo ratings yet
- India - A CountryDocument68 pagesIndia - A CountryJason BluthNo ratings yet
- Republic of India: Bhārat Ga ArājyaDocument5 pagesRepublic of India: Bhārat Ga ArājyaKrish PranavNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesMultiple ChoiceAung Htet LingNo ratings yet
- Jamhuri Ya KenyaDocument4 pagesJamhuri Ya KenyarosarosieNo ratings yet
- Nigeria: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument51 pagesNigeria: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchMerlyn LakasaNo ratings yet
- 2 WDDocument3 pages2 WDMuhammed MinhajNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Lesson2 - Act 3Document2 pagesModule 3 Lesson2 - Act 3Heyhey LahlahNo ratings yet
- Vietnam: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument87 pagesVietnam: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchYongkyNo ratings yet
- Continent: CSS, PMS, NTS, Fia, Ib, PPSC, BPSC, KPSC, SPSCDocument6 pagesContinent: CSS, PMS, NTS, Fia, Ib, PPSC, BPSC, KPSC, SPSCAftab SaqiNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About The Republic of IndiaDocument6 pagesThis Article Is About The Republic of IndiaAjithNo ratings yet
- Social Science Major 5 - Japan (Comprehensive)Document32 pagesSocial Science Major 5 - Japan (Comprehensive)Fredrich RamaNo ratings yet
- Hawaii - WikipediaDocument7 pagesHawaii - WikipediaLaurentiu NicaNo ratings yet
- England - WikipediaDocument6 pagesEngland - WikipediatrianaNo ratings yet
- Thailand: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument36 pagesThailand: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchSadiq KerkerooNo ratings yet
- Model For The Basic VavachiDocument216 pagesModel For The Basic VavachiArunNo ratings yet
- Lesson 18Document10 pagesLesson 18Kha LaiNo ratings yet
- Bearing, Azimuth Dan Angle RightDocument14 pagesBearing, Azimuth Dan Angle RightBriyan Ibnu HusnaNo ratings yet
- Nilgiri SDocument7 pagesNilgiri SNaveen LCC0% (1)
- Geographic PictionaryDocument45 pagesGeographic Pictionarytrangnguyen86No ratings yet
- Appalachian and Cordillera Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAppalachian and Cordillera Lesson Planapi-273897319No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence 2541Document188 pagesLecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence 2541Angel TrianoNo ratings yet
- L1.3 - GeographyDocument34 pagesL1.3 - GeographyRicia GaelNo ratings yet
- Hiking and Cycling: Around CantabriaDocument64 pagesHiking and Cycling: Around Cantabriakeve66No ratings yet
- TACHEOMETRYDocument35 pagesTACHEOMETRYAzzam Idris100% (1)
- Directional Drilling and Surveying 2Document18 pagesDirectional Drilling and Surveying 2Dibawah Pengaruh KafeinNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On Electoral GeographyDocument11 pagesTerm Paper On Electoral GeographyPrakash SinghNo ratings yet
- As Mo (Ju) Ke As Ra Ve Mo (Ju) : Vimsottari Dasa : Rah Jup Sat Merc Ket Ven Sun Moon MarsDocument2 pagesAs Mo (Ju) Ke As Ra Ve Mo (Ju) : Vimsottari Dasa : Rah Jup Sat Merc Ket Ven Sun Moon Marstoll_meNo ratings yet
- B A-B Sc-SyllabusDocument26 pagesB A-B Sc-SyllabusAkshat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sid Vicious ChartDocument2 pagesSid Vicious ChartCosmin A. TomescuNo ratings yet
- Igu2014 ProgrammeDocument243 pagesIgu2014 ProgrammeJulian Ren Renfo100% (1)
- Ilorin MetropolisDocument1 pageIlorin MetropolisabdulNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Georeferencing Topo Sheets Topo Maps Satellite Image or Scanned Maps in QGISDocument7 pagesTutorial Georeferencing Topo Sheets Topo Maps Satellite Image or Scanned Maps in QGISNapy IseultNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 - DrainageDocument4 pagesCBSE Notes Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 - DrainageHarish Lunge100% (1)
- Udl Unit Planning Chart-2Document14 pagesUdl Unit Planning Chart-2api-203221125No ratings yet
- Hydrology Report FinalDocument63 pagesHydrology Report FinaltobinareNo ratings yet
- 01 July 2020 - Introduction To Global Positioning System by Dr. AshutoshDocument88 pages01 July 2020 - Introduction To Global Positioning System by Dr. AshutoshMALUZ MOSENo ratings yet
- SUG559 Advanced Cadastral SurveyingDocument37 pagesSUG559 Advanced Cadastral SurveyingFarisa ZulkifliNo ratings yet
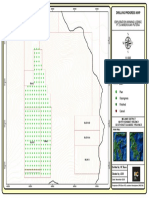
- Drilling Progress Map Week - 48Document1 pageDrilling Progress Map Week - 48Muhaimin ParsapalayNo ratings yet
- Conceptos de FronteraDocument9 pagesConceptos de Fronterajohnfcg1980No ratings yet
- Admission, Department of Geography, CUH - 2020-21Document1 pageAdmission, Department of Geography, CUH - 2020-21Rishi KantNo ratings yet