Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Angry Bird
Uploaded by
billjohn.bueno.crsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Angry Bird
Uploaded by
billjohn.bueno.crsCopyright:
Available Formats
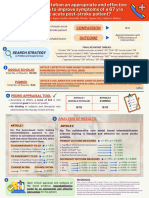
Will telerehabilitation be effective in improving
symptoms of a 67-year-old female acute stroke patient?
Esmile, Garces, Gregorio, Hirata, Katigbak, King, Licos, Lim, Ong
Population 67 year-old female acute stroke patient Analyses
Intervention Telerehabilitation Article 1
the effectiveness on the improvement of There is a significant group-effect using home-based motor training
Outcome Alternative
symptoms rehabilitation (TR) compared with conventional rehabilitation (CR) on
Hypothesis patients with subcortical stroke by combining motor function assessments
and multimodality MRI analysis methods.
Search Strategy Noninferiority 1-tailed test Superiority 1-tailed test
(“stroke” OR “Cerebrovascular Accident” OR Alpha 0.025 0.025
“CVA” OR “strokes” OR “Cerebrovascular
Accidents” OR “CVAs” OR “Brain Vascular Computed p- Change in FMA: 0.003 Change in FMA: 0.011
Accident” OR “Brain Vascular Accidents”) Change in MBI: 0.019 Change in MBI: 0.097
value
AND (“Telerehabilitation” OR “Remote
Final Rehabilitation” OR “Online Rehabilitation” OR
Change in FMA: 0.82 Change in FMA: 0.82
Keywords “Tele-rehab” OR “Telerehab” OR “Remote Effect Size
Change in MBI: 0.65 Change in MBI: 0.65
Rehab” OR “Online Rehab” ) AND
(“effectiveness” OR “Appropriateness” OR
95% CI* Change in FMA: 0.560, 6.972 Change in FMA: 0.076, 7.456
“Success” OR “Benefit” OR “Advantage” OR
97.5% CI* Change in MBI: 0.504, 10.349 Change in MBI: -0.0856, 11.098
“Advantages” OR “Benefits” OR “Efficacy” OR
“usefulness” OR “potency”)
Article 2
Database Bielefeld Academic Search Engine (BASE)
There is a significant group-effect using home-based motor training
Filters 2012 & above, English Alternative rehabilitation (TR) compared with conventional rehabilitation (CR) on patients
Hypothesis with subcortical stroke by combining motor function assessments and
Results 194 multimodality MRI analysis methods.
Alpha 0.05
Chen, J., Sun, D., Zhang, S., Shi, Y., Qiao, F.,
Zhou, Y., Liu, J., & Ren, C. (2020). FES: 0.126
Computed
Effects of home-based telerehabilitation in SSPSC — hospital: 0.029
Article 1 p-value
patients with stroke. Neurology, 95(17). SSPSC — home: 0.077
https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.000000000001082
1 Baseline 3 months 6 months
Chumbler, N. R., Li, X., Quigley, P., Morey, M. FES: 0.25 FES: 0.43 FES: 0.28
C., Rose, D., Griffiths, P., ... & Hoenig, H. Effect Size SSPSC - hospital: -0.53 SSPSC - hospital: 0.05 SSPSC - hospital: 0.28
(2015). A randomized controlled trial on SSPSC - home: -0.35 SSPSC - home: -0.17 SSPSC - home: 0.19
Stroke telerehabilitation: The effects on falls
Article 2 FES: -12.64, 3.04 FES: -18.86, -0.14 FES: -12.54, 2.74
self-efficacy and satisfaction with care.
Journal of telemedicine and telecare, 21(3), SSPSC - hospital: SSPSC - hospital: -4.72, SSPSC - hospital:
139-143. 95% CI -1.89, 6.49 3.72 -7.55, 1.55
https://doi.org/10.1177/1357633X15571995 SSPSC - home: -0.20, SSPSC - home: -1.09, SSPSC - home: -2.64,
2.80 2.49 1.04
Appraisal
Effects of home-based telerehabilitation in patients
Clinical Decision
with stroke: We will use the intervention secondary to the articles mentioned, indicating that
The paper was appraised using the PEDro scale, it received a
telerehabilitation is effective in improving the symptoms of an acute stroke patient;
score of 8/11. The paper was not able to blind all the
participants, and all the therapists who administered the
telerehabilitation (TR) is effective in the first 12 weeks of treatment. Specifically, on
therapy. Furthermore, the paper was not able to obtain from improved motor function and ADL performance; it is also more convenient and
more than 85% of the subjects initially allocated to groups for accessible therefore increasing patient compliance. TR may be a good approach in
the measures of at least one key outcome. aiming for the convenience of lessening the travel burden since physical therapy
sessions may be conducted via any messaging and video calling platforms as long
A randomized controlled trial on Stroke as the patient has an available gadget and internet connection. The two articles
telerehabilitation: The effects on falls self-efficacy proved that telerehabilitation is effective in motor functions and ADL performance
and satisfaction with care improvement and helped patients better translate and apply the exercises learned
The paper was appraised using the PEDro scale, it received a
during their in-hospital rehabilitation. As such, TR is still considered a viable
score of 9/11. The paper was not able to blind all the
alternative to traditional rehabilitation care for stroke survivors since it is effective,
participants, and all the therapists who administered the
therapy. efficient, and feasible.
You might also like
- Angry BirdDocument1 pageAngry Birdbilljohn.bueno.crsNo ratings yet
- Refining Angiographic Biomarkers of Revascularization: Improving Outcome Prediction After Intra-Arterial TherapyDocument5 pagesRefining Angiographic Biomarkers of Revascularization: Improving Outcome Prediction After Intra-Arterial TherapyDra. Carol Angélica Artigas GómezNo ratings yet
- Raj 2014Document16 pagesRaj 2014Ricardo VillagranaNo ratings yet
- Menon 2015Document11 pagesMenon 2015diasspriNo ratings yet
- !!!AMachineLearning basedSurfaceElectromyographyTopographyEvaluationforPrognosticPredictionofFunctionalRestorationRehabilitationinChronicLowBackPainDocument9 pages!!!AMachineLearning basedSurfaceElectromyographyTopographyEvaluationforPrognosticPredictionofFunctionalRestorationRehabilitationinChronicLowBackPainAhmet ÖztürkNo ratings yet
- How To Build Stroke Unit or Stroke CornerDocument36 pagesHow To Build Stroke Unit or Stroke CornerDimas PambudiNo ratings yet
- Magnesium AbstractDocument1 pageMagnesium Abstracthkw8g5snyxNo ratings yet
- Alberts Et Al. - 2015 - Using Accelerometer and Gyroscopic Measures To QuaDocument11 pagesAlberts Et Al. - 2015 - Using Accelerometer and Gyroscopic Measures To QuaYouriDuchêneNo ratings yet
- Delivering Effective Predictive Solutions in Healthcare: Michael Draugelis, Chief Data Scientist Penn MedicineDocument30 pagesDelivering Effective Predictive Solutions in Healthcare: Michael Draugelis, Chief Data Scientist Penn MedicineMichaelNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Health Status - PROVE-HF Trial - Pina Et AlDocument10 pagesImprovement of Health Status - PROVE-HF Trial - Pina Et AlAdel SALLAMNo ratings yet
- Lembar Jawaban Skillab Evidence Based Medicine (Ebm) Nama: Annisa Khaira Ningrum NIM: 04011181320058Document8 pagesLembar Jawaban Skillab Evidence Based Medicine (Ebm) Nama: Annisa Khaira Ningrum NIM: 04011181320058Yuni AnjarNo ratings yet
- Radiology 101 The Basics & Fundamentals of Imaging - 4E (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Document17 pagesRadiology 101 The Basics & Fundamentals of Imaging - 4E (PDF) (UnitedVRG)claudedNo ratings yet
- Outpatient Stroke RehabilitationDocument28 pagesOutpatient Stroke RehabilitationMochammad Syarief HidayatNo ratings yet
- Online Appendix B2 (Pleural Disease) - Pleural Effusion Image Guided or Non Image GuidedDocument7 pagesOnline Appendix B2 (Pleural Disease) - Pleural Effusion Image Guided or Non Image Guided4wntsgj69pNo ratings yet
- Tenecteplase in AisDocument2 pagesTenecteplase in Aisapi-550597190No ratings yet
- Determination of Minimum Clinically Important Difference in Pain, Disability, and Quality of Life After Extension of Fusion For Adjacent-Segment DiseaseDocument7 pagesDetermination of Minimum Clinically Important Difference in Pain, Disability, and Quality of Life After Extension of Fusion For Adjacent-Segment DiseasewilsonwqaNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Prostate Gland Motion and Deformation During CK SBRTDocument11 pagesReal-Time Prostate Gland Motion and Deformation During CK SBRTRicardo MejíasNo ratings yet
- SmallestdetectablechangeDocument4 pagesSmallestdetectablechangeBimo AnggoroNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2021Document6 pagesZhang 2021KOBE BRIAN PETEROSNo ratings yet
- Abe 2022 Oi 220481 1654263485.26457Document11 pagesAbe 2022 Oi 220481 1654263485.26457b4b758h7jhNo ratings yet
- Jung2020 Article PredictionOfAmyloidΒPETPositivDocument10 pagesJung2020 Article PredictionOfAmyloidΒPETPositivDuy UngdungNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & ResearchDocument8 pagesOrthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & ResearchVõ Văn Phúc ToànNo ratings yet
- Current Problems in Diagnostic RadiologyDocument6 pagesCurrent Problems in Diagnostic RadiologyAshish MehtaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Scientific AbstractsDocument1 page2018 Scientific AbstractsRurgenciasNo ratings yet
- Automated Diagnosis of Congenital Dislocation of The: Index TeamsDocument6 pagesAutomated Diagnosis of Congenital Dislocation of The: Index Teamsdiablo3 3No ratings yet
- ASL Perfusion Differentiating Neoplastic From Neoplastic Intraaxial Brain LesionsDocument10 pagesASL Perfusion Differentiating Neoplastic From Neoplastic Intraaxial Brain LesionspoppyNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Operator Volume and Long-Term Outcomes After Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocument15 pagesRelationship Between Operator Volume and Long-Term Outcomes After Percutaneous Coronary InterventionsarahNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Manual Therapy Techniques Compared To Conventional Physical Therapy in Tension-Type HeadacheDocument7 pagesEffectiveness of Manual Therapy Techniques Compared To Conventional Physical Therapy in Tension-Type HeadacheFamilia Bravo MunarrizNo ratings yet
- Biomarker Progressions Explain Higher Variability in Stage S - 2014 - AlzheimerDocument14 pagesBiomarker Progressions Explain Higher Variability in Stage S - 2014 - AlzheimerPriscilla ChantalNo ratings yet
- Gray 2011Document4 pagesGray 2011Naufal IlmiNo ratings yet
- Physics-Informed Neural Networks For Brain Hemodynamic Predictions Using Medical ImagingDocument19 pagesPhysics-Informed Neural Networks For Brain Hemodynamic Predictions Using Medical ImagingSebastián Nicolás Jara CifuentesNo ratings yet
- J Amjcard 2012 02 043Document5 pagesJ Amjcard 2012 02 043Efe Ge KaNo ratings yet
- RMN en Pacientes Con SintomasDocument9 pagesRMN en Pacientes Con SintomasMeryNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Elevated Intracranial Pressure in Critically Ill AdultsDocument10 pagesDiagnosis of Elevated Intracranial Pressure in Critically Ill AdultsGiancarlo Maruri MunarettoNo ratings yet
- Yan 2017Document13 pagesYan 2017Ktherine Sandoval AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Equine-Assisted Activities and Therapies On Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled TrialDocument9 pagesEffect of Equine-Assisted Activities and Therapies On Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled TrialRobsonBorgesNo ratings yet
- 1.predictive Model For Early Functional Outcomes Following Acute Care After Traumatic Brain InjuriesDocument8 pages1.predictive Model For Early Functional Outcomes Following Acute Care After Traumatic Brain Injuriesธนพร ฉัตรศรีพงษ์No ratings yet
- BeatProfiler Multimodal in Vitro Analysis of Cardiac Function Enables Machine Learning Classification of Diseases and DrugsDocument12 pagesBeatProfiler Multimodal in Vitro Analysis of Cardiac Function Enables Machine Learning Classification of Diseases and DrugsBharath RNo ratings yet
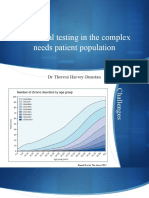
- Functional Testing in The Complex Needs Patient Population: DR Theresa Harvey-DunstanDocument62 pagesFunctional Testing in The Complex Needs Patient Population: DR Theresa Harvey-DunstanJohn Agana AyamgaNo ratings yet
- Franca 2020 AtaxiaDocument6 pagesFranca 2020 AtaxiainervavsNo ratings yet
- Brain Injury GuidelinesDocument6 pagesBrain Injury Guidelinesmukesh pokharelNo ratings yet
- Data Set Assignment DoneDocument10 pagesData Set Assignment Donemastertutors6No ratings yet
- The Value of Preoperative Exercise and Education For Patients Undergoing Total Hip and Knee ArthroplastyDocument15 pagesThe Value of Preoperative Exercise and Education For Patients Undergoing Total Hip and Knee ArthroplastyemilNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Chronic Fatigue SyndromeDocument46 pagesThe Biology of Chronic Fatigue SyndromeAgustinus Benediktus Danang PutroNo ratings yet
- Personalization and Pragmatism - Pediatric Intracranial Pressure and Cerebral Perfusion Pressure Treatment ThresholdsDocument4 pagesPersonalization and Pragmatism - Pediatric Intracranial Pressure and Cerebral Perfusion Pressure Treatment ThresholdsdrdivyapukNo ratings yet
- Deriving The Effective Atomic Number With A Dual-Energy Image Set Acquired by The Big Bore CT SimulatorDocument12 pagesDeriving The Effective Atomic Number With A Dual-Energy Image Set Acquired by The Big Bore CT SimulatorFadli SaputroNo ratings yet
- CE (Ra1) F (SH) PF1 (SC SS) PFA (SC KM) PN (KM)Document4 pagesCE (Ra1) F (SH) PF1 (SC SS) PFA (SC KM) PN (KM)Ofkom UnhasNo ratings yet
- JHLT Abstract 2019-1Document1 pageJHLT Abstract 2019-1G WNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonar - FormulasDocument9 pagesCardiopulmonar - FormulasJoão SouzaNo ratings yet
- Ecop 09 00286Document11 pagesEcop 09 00286GabrielNo ratings yet
- Qims 12 01 766Document15 pagesQims 12 01 766Hamza ArjahNo ratings yet
- Mri 2017 PDFDocument6 pagesMri 2017 PDFAshish AwasthiNo ratings yet
- 7210 Diametro Thorax y Columna LumnoSacraDocument9 pages7210 Diametro Thorax y Columna LumnoSacraOscar Javier GarciaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Approach: Evidence SummaryDocument6 pagesAnterior Approach: Evidence SummaryAhmed DRIDINo ratings yet
- 2017 Article 141 Part4Document5 pages2017 Article 141 Part4Karina MonasaNo ratings yet
- CT 2Document6 pagesCT 2samaneh shirkouhiNo ratings yet
- Impairment Recovery: Predictor RehabilitationDocument9 pagesImpairment Recovery: Predictor RehabilitationCristian HanganNo ratings yet
- Point-Of-Care Ultrasound Use in Patients With Cardiac Arrest Is Associated Prolonged Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Pauses: A Prospective Cohort StudyDocument4 pagesPoint-Of-Care Ultrasound Use in Patients With Cardiac Arrest Is Associated Prolonged Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Pauses: A Prospective Cohort StudyPacoNo ratings yet
- JBJS - Do Oblique Views Add Value in The Diagnosis of Spondylolysis in AdolescentsDocument7 pagesJBJS - Do Oblique Views Add Value in The Diagnosis of Spondylolysis in AdolescentsjauNo ratings yet
- Tele Rehab OA 2Document11 pagesTele Rehab OA 2Kavya MittalNo ratings yet
- Tele MedicineDocument16 pagesTele MedicineManas AroraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 - Rehabilitation Systems in Ambient Assisted Living EnvironmentsDocument19 pagesChapter 04 - Rehabilitation Systems in Ambient Assisted Living EnvironmentsFernanda CamposNo ratings yet
- Telepractica y Fonoaudiologia - Referencias (Retamal-Walter) PDFDocument2 pagesTelepractica y Fonoaudiologia - Referencias (Retamal-Walter) PDFAlejandro QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Late Breaking Research Papers Þ Posters E13Document2 pagesLate Breaking Research Papers Þ Posters E13Ida Ayu Trisna DewiNo ratings yet
- Telehealth Stroke Dysphagia Evaluation Safe and Effective: Original PaperDocument11 pagesTelehealth Stroke Dysphagia Evaluation Safe and Effective: Original PaperAfganNo ratings yet
- Provision of Speech-Language Pathology Services During COVIDDocument5 pagesProvision of Speech-Language Pathology Services During COVIDShamil CrescasNo ratings yet
- Handoll Et Al-2022-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsDocument373 pagesHandoll Et Al-2022-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewstrongndNo ratings yet
- Effects and Costs of Real-Time Cardiac Telerehabilitation - Randomised Controlled Non - Inferiority TrialDocument8 pagesEffects and Costs of Real-Time Cardiac Telerehabilitation - Randomised Controlled Non - Inferiority TrialarwitarahayuNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Physical Therapy Services Through Telemedicine During The Covid-19 Pandemic: Systematic ReviewDocument10 pagesEffectiveness of Physical Therapy Services Through Telemedicine During The Covid-19 Pandemic: Systematic ReviewViorentina YofianiNo ratings yet
- Laver Et Al-2020-Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews PDFDocument80 pagesLaver Et Al-2020-Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews PDFPamela DíazNo ratings yet
- 21 - Telemedicine InrehabilitationDocument11 pages21 - Telemedicine InrehabilitationMariaNo ratings yet
- NCP Respiratory Guidance On Setting Up Virtual Pulmonary Rehabilitation For Asthma and CopdDocument24 pagesNCP Respiratory Guidance On Setting Up Virtual Pulmonary Rehabilitation For Asthma and CopdeimearNo ratings yet
- Health InformaticsDocument29 pagesHealth Informaticswatson191No ratings yet
- Home Base TechnologyDocument12 pagesHome Base TechnologyScientec cseNo ratings yet
- Telehealth in Occupational Therapy: AOTA Position PaperDocument18 pagesTelehealth in Occupational Therapy: AOTA Position PaperdanielNo ratings yet
- 4 Family-Centered Early Intervention For Children With Disabilities Provided Through TelepracticeDocument24 pages4 Family-Centered Early Intervention For Children With Disabilities Provided Through TelepracticeJanice Cheuk Yin LoNo ratings yet
- Acceptance of Tele-Rehabilitation by Stroke Patients: Perceived Barriers and FacilitatorsDocument8 pagesAcceptance of Tele-Rehabilitation by Stroke Patients: Perceived Barriers and Facilitatorsana irianiNo ratings yet
- Blueprint For Telerehab GuidelinesDocument4 pagesBlueprint For Telerehab GuidelinesBill WongNo ratings yet
- Voice Therapy Telepractice, Voice Care For The 21st Century, Towey, 2017Document8 pagesVoice Therapy Telepractice, Voice Care For The 21st Century, Towey, 2017marcela riqueroNo ratings yet
- Telehealth System (e-CUIDATE) To Improve Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: Rationale and Study Protocol For A Randomized Clinical TrialDocument10 pagesTelehealth System (e-CUIDATE) To Improve Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: Rationale and Study Protocol For A Randomized Clinical TrialCaroPlachotNo ratings yet
- JCM 11 00011Document11 pagesJCM 11 00011Lal NandaniNo ratings yet
- Tele Rehabilitation Service Delivery Journey From Prototype To Robust in Home Use D and R OnlineDocument10 pagesTele Rehabilitation Service Delivery Journey From Prototype To Robust in Home Use D and R OnlineFelipe Palma UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of AAC: A Case-Based Approach To Enhancing CommunicationDocument585 pagesFoundations of AAC: A Case-Based Approach To Enhancing CommunicationOlivia Cain100% (2)
- Rehabilitation and ProstheticsDocument2 pagesRehabilitation and ProstheticsAmit BhattNo ratings yet
- El Gran Libro de HTML5 CSS3 y JavascriptDocument303 pagesEl Gran Libro de HTML5 CSS3 y JavascriptHeriberto Aguirre MenesesNo ratings yet
- Luisa2021 PDFDocument33 pagesLuisa2021 PDFangela espinozaNo ratings yet
- Psychology WebDocument27 pagesPsychology WebしまののえだにNo ratings yet
- Computer Based Treatment of Poststroke Language Disorders A Non Inferiority Study of Telerehabilitation Compared To in Person Service DeliveryDocument23 pagesComputer Based Treatment of Poststroke Language Disorders A Non Inferiority Study of Telerehabilitation Compared To in Person Service DeliveryALENo ratings yet
- INCOG 2 0 Guidelines For Cognitive Rehabilitation.1Document6 pagesINCOG 2 0 Guidelines For Cognitive Rehabilitation.1ragarate1982No ratings yet