Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cellular Aberration Module 1
Uploaded by
Karolien Faye DongaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cellular Aberration Module 1
Uploaded by
Karolien Faye DongaCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
Cellular Aberration Module 1
bs nursing (Southwestern University PHINMA)
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
as the functioning of the components of the
immune system, it prevent the cells form further
cellular damage or DNA mutation)
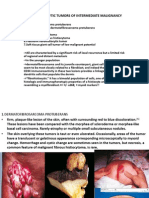
1. INTRODUCTION TO ONCOLOGY ● DYSPLASIA
2. LABORATORY TESTS, DIAGNOSTIC TESTS, ● EXTRAVASATION
AND SURGERY ● GRADING
3. ANTINEOPLASTIC THERAPY ● GRAFT-VERSUS-HOST DISEASE (GVHD)-
4. RADIATION THERAPY (undesirable, very bad effect, because the donor
5. NURSING INTERVENTIONS the graft or the donor is not giving good effect to
6. ONCOLOGIC DISORDERS the host, but rather it affects the recipient)
● GRAFT-VERSUS-TUMOR-EFFECT (GVTE)-
(desirable, good effect, because the graft or the
donor is giving good effect to the recipient)
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
● MALIGNANT
On completion of this chapter, the learner will be able to:
● METAPLASIA
1. Compare the structure and function of the
● MUCOSITIS- (inflammation of the mucosal
normal cell and the cancer cell.
lining, slightly similar to stomatitis but different in
2. Explain the origin of cancer.
terms of location (lips, gums, buccal area, throat,
3. Identify agents and risk factors that contribute to
stomach, intestine,anus)
carcinogenesis.
● MYELOSUPPRESSION
4. Discuss the importance of antioxidants from the
● NADIR- (aka NADIR COUNT, in which the blood
devastating effects of free radicals.
forming elements are unforgivably low, WBC in
5. Differentiate between the benign and malignant
particular that makes clients so immune
tumors.
suppressed, it jeopardize the existence of the
6. Explain the roles of the immune system.
client because they might die of septicemia, not
7. Describe the role of nurses in health education
just WBC but also platelet, RBC, and so on and
and prevention of oncologic disorders.
so forth)
8. Discuss the levels of prevention.
● NEOPLASIA
● NEUTROPENIA
● ONCOLOGY
● ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable)- ● PLEOMORPHISM
(you as a nurse, even if you have small dose of ● PRECISION MEDICINE
exposure to radiation or even if it does not affect ● RADIATION THERAPY
you, but as much as possible you have to avoid ● STOMATITIS- (inflammation of the mucosal
it) lining, oral cavity (lips, gums, buccal area)
● ALOPECIA- (ideally, we cannot say it’s ● STAGING
permanent or temporary, but rather usually ● TARGETED THERAPIES
temporary, it means to say that we have ● TUMOR-SPECIFIC ANTIGEN
different responses to chemotherapy it can be ● VESICANT
either permanent or temporary) ● WARBURG EFFECT-(other defense
● ANAPLASIA mechanism of cancer cells in which it converts
● ANGIOGENESIS- (is one of the defense glucose into lactic acid through glycolysis even
mechanism of cancer cells in which it triggers with the presence of oxygen)
the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) ● XEROSTOMIA
for the formation of new blood vessels, in order
for the cancer cells to maintain its nourishment
because cancer cells are parasitic in nature,
Cancer is not a single disease with a single cause;
very dependent of the glucose, protein, and
rather, it is a group of distinct diseases with different
growth hormone coming from the host, that’s
causes (multifactorial, unknown cause, genetics, familial,
why it has to be nourished with the expense of
physical, chemical, or even if you don’t have any history
new blood vessels, this explains why cancer
of cancer in the family but still you can be a victim of
cells and tumors are growing everyday)
random mutation), manifestations, treatments
● APOPTOSIS
(manifestations and treatments will vary depending on
● BIOLOGIC RESPONSE MODIFIER (BRM)
which organ it will affect), and prognoses (matters on
THERAPY
how early or how late the recognition). -Brunner and
● BIOPSY
Suddarth’s TMSN, 14th edition
● BRACHYTHERAPY
● CANCER
TOP 10 CAUSES OF MORTALITY (2017)
● CARCINOGENESIS
1. ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASES
● CHEMOTHERAPY
2. NEOPLASMS
● CONTROL
3. CEREBROVASCULAR
● CURE
4. PNEUMONIA
● CYTOKINES- (substance produced by the
5. DIABETES MELLITUS
immune system, it enhances production as well
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
6. HYPERTENSION ○ it is selectively permeable, WHY?
7. CHRONIC RESPIRATORY DISEASES because it only allows molecules or
8. RESPIRATORY TUBERCULOSIS small substances, larger molecules
9. OTHER HEART DISEASES cannot penetrate into the cell
10. GENITOURINARY ○ generally, the functions of the cell
membrane acts as barrier
TOP 10 CANCERS (2018) ○ controls the flow of substances
1. BREAST ○ helps identify the cell to other cells
2. LUNG ○ participates in cell signalling , in which
3. COLON cells are communicating at each other
4. LIVER from the scalp down to toes
5. PROSTATE
6. CERVIX ● WHAT IS GLYCOCALYX? The sugar coat on
7. THYROID the extracellular surface of the plasma
8. LEUKEMIA membrane. It is composed of carbohydrates of
9. RECTUM membranes that includes the glycolipids and
10. OVARY phospholipids.
● CELL MEMBRANE
● NUCLEUS
● CYTOPLASM
● ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
○ ROUGH
○ SMOOTH
● RIBOSOMES ● NUCLEUS- command center of the cell because
● GOLGI COMPLEX of the presence of the DNA
● LYSOSOMES ○ controls cellular functions
● PEROXISOMES ○ directs cellular activities
● MITOCHONDRIA ○ produces ribosomes in nucleoli
○ as you can observe, there are many
ribosomes surrounding the nucleus, it is
synthesize by the nucleus and
assembled in the cytoplasm
○ also you can observe the presence of
the endoplasmic reticulum, it makes a
trap, because the potent form of the
ribosomes are confined there
○ you can also observe the presence of
chromatin, these are complex of DNA,
proteins and some of the RNA
● CELL MEMBRANE- separates internal and
external environment of the cell
○ protects cell from fast cellular damage
and dehydration
○ we also notice the presence of pores in
which the nutrients or the chemical
● PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
substances will get into the cell through
○ TRANSCRIPTION- occurs within the
that channel
nucleus, in which the genetic
○ substances can be passive or active
information represented the sequence of
form
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
base triplets in DNA, will serve as ■ HOW DOES THE FOLLOWING
template for copying the information REACHES PLASMA
○ TRANSLATION- occurs outside the MEMBRANE? because they
nucleus, it is in the cytoplasm to be have the mechanism to
exact, WHY? because the mRNA are transport glycoproteins and
large molecules, the highlight of this one phospholipids in the manner of
is for the synthesis of proteins with EXOCYTOSIS, through the
ribosome and RNA vesicle transporting it towards
○ WHY ARE PROTEINS IMPORTANT IN the cell membrane, that explains
THE LIFE OF A CELL? Because it why the cell membrane contains
determines the physical and chemical the following
characteristics of the cells. ○ SMOOTH ER
■ absence of ribosomes, but
● CYTOPLASM- semi-fluid gelatinous material or despite that you cannot discard
nutrient matrix also know to be CYTOSOL the vitality of the smooth ER
○ the rest of the organelles were bathe ■ it is responsible in the synthesis
within the entity of the cytoplasm of the fatty acids and steroids
EXCEPT for the plasma membrane ■ it inactivates or detoxify drugs
○ where majority of chemical of metabolic and other potentially harmful
reactions occur substances (just like alcohol),
● ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM- divided into two because of that it gives you the
types: ROUGH and SMOOTH idea that it must be the liver
○ ROUGH ER because it is a known organ for
detoxification process, other
than the liver we also have
kidneys and intestines, or any
parts of the body that involves
detoxification process, your
SMOOTH ER is always behind
that
■ it removes phosphate groups
from glucose-6-phosphate, this
is in the process of
DEPHOSPHORYLATION, it
increases your free glucose,
WHY? because the body is in
■ WHY IS IT ROUGH? presence need of energy, the
of ribosomes mitochondria cannot extract
■ Ribosomes- produces proteins’ energy without having glucose
■ role of ROUGH ER: synthesizes ■ stores and releases calcium
GLYCOPROTEINS AND ions, that gives you the idea that
PHOSPHOLIPIDS the moment there is cell
■ through this we’ll now have the destruction aka cell lysis, once
idea how does cell membrane the cell is damage the calcium
possesses the glycoproteins thrown away from the cell, it will
and phospholipids leak out and incorporate with
your blood circulation, may
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
result to increase blood calcium ● these are the transfer RNA (tRNA)
level---HYPERCALCEMIA
(there is bad effect of high
calcium, it will be filtered in the
kidneys and causes renal failure
● RIBOSOMES- known for the site of protein
synthesis
○ ribosomes cannot function by itself ● the tRNA carries the three bases, aka
without merging with other subunits ANTICODON, the bases in the mRNA are called
○ once combined in can now be potent for CODON
protein synthesis
● the tRNA carries amino acids which are which
○ WHY ARE SUBUNITS OF RIBOSOMES are essential or non-essential amino acids, that
SYNTHESIZED AND ASSEMBLED? is heading towards the ribosomes to have
the ribosome is being synthesized in the PROTEIN CHAIN
nucleus (nucleolus), and then
assembled in the cytoplasm
● during the start of protein synthesis, it will
always start with the “AUG” anticodon
● the picture above shows the ribosome, the site
for protein synthesis, large and small subunits
are emerged together in order to become a
potent material in the synthesis of protein
● these are the growing protein chain, it is
important to remember that most of the proteins
synthesized by the ribosomes are not mature,
therefore it has to processed by another
organelle GOLGI APPARATUS which is known
● this is the messenger RNA, when comparing as the packaging plant (transform into
mRNA and transfer RNA, they are both in something important)
opposite direction ● WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO HAVE PROTEINS?
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF PROTEINS? the
role of proteins is not only one but there are
other functionalities of your proteins:
○ STRUCTURAL- (collagen, bone,
connective tissues, keratin, hairs,
fingernails)
○ REGULATORY- (hormones,
neurotransmitter)
○ CONTRACTILE- (movement of muscles
or contractility)
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
○ IMMUNOLOGICAL
○ TRANSPORT
○ CATALYTIC- (speeds up reaction)
● GOLGI COMPLEX- known to be as a packaging
plant, anything that is not mature will become a
mature form for various uses
○ FUNCTIONS:
■ modifies, sort, packages, and ● it will then be processed in the MEDIAL
transport proteins received from CISTERN, until it will become mature and ready
the rough ER (any substances for distribution
produced in ER specifically
rough ER are not mature yet, it
has to be repackaged by the
golgi apparatus to become a
potent material for better use)
■ forms secretory vesicles that
discharge processed proteins
via exocytosis into extracellular
fluid
■ forms membrane vesicles that ● it will now then be confined to in the TRANSFER
ferry new molecules to the VESICLE
plasma membrane
■ forms transport vesicles that
carry molecules to other
organelles, such as
LYSOSOMES
● then, it will EXIT or TRANS FACE
● for your proteins or any kind of hormones in
which that are not yet mature, it has to be
transported in the GOLGI APPARATUS,
proteins and hormones will be transported
through the TRANSPORT VESICLES
● then, it will be delivered throughout the body
through SECRETORY VESICLES in the manner
of EXOCYTOSIS, only the specific receptors or
cell will recognize that
● HOW DO ENTRY AND EXIT FACES DIFFER IN
FUNCTION? the ENTRY FACE receives and
modifies proteins from wrapped from the
endoplasmic reticulum, while the EXIT FACE
modifies, sort, and packages the molecules and
is now ready for transport to other destination
● the first part of golgi apparatus is named as the
ENTRY or CIS FACE
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
● lysosome membranes also includes transporters
that move final products of digestion such as
glucose, fatty acids and amino acids into the
CYTOSOL, it is more powerful compared to
cytosol
● it can perform engulfing of another organelle
once the organelle is dead or not anymore
useful, it will engulf or digest it, called as
AUTOPHAGY
● PEROXISOMES
● WHAT ARE THE THREE GENERAL
● there are two types of hydrogen peroxide, the
DESTINATIONS FOR PROTEINS THAT LEAVE
ENDOGENOUS in which the body is able to
GOLGI COMPLEX? some proteins are: secreted
synthesize it, and EXOGENOUS coming from
from the cell by exocytosis, incorporated into the
the external sources such as the Agua
plasma membrane (fats, glycolipids,
Oxygenada (2 H2O2- hydrogen peroxide)
phospholipids), occupy storage vesicles that
become lysosomes
● LYSOSOME- the prefix lyso- means dissolving
and -somes means body, it means to say that it
is a dissolving body, it aids in dissolving or
digesting something
○ FUNCTIONS:
■ digest substances that enter a ● CATALASE- present in the blood, once the
cell via ENDOCYTOSIS and catase is in contact with the hydrogen
transport final products of peroxide--it will oxidize, that’s why it will be
digestion into CYTOSOL broken down into two molecules----water (2
(ENDOCYTOSIS: engulfing; H2O) + oxygen (O2)
EXOCYTOSIS: transport going ● WHY IS IT THAT THERE ARE A LOT OF
outside the cell) BUBBLES WHEN WE APPLY HYDROGEN
■ carry out AUTOPHAGY, the PEROXIDE ON THE WOUNDS? the very
digestion of worn-out organelles reason why there are bubbles is that the blood
■ it implements AUTOLYSIS, the contains the catalase, because of that there are
digestion of an entire cell bubbles on it, it does not represent the
■ accomplishes extracellular abundance of microorganisms present on the
digestion wound, whether there are a lot of bubbles in it or
● WHAT IS THE NAME OF THE PROCESS IN not, still it does not mean the presence of
WHICH THE WORN-OUT ORGANELLES ARE microorganisms
DIGESTED BY LYSOSOMES? AUTOPHAGY ● the very reason why we apply hydrogen
peroxide for the purpose of hoping to kill the
microbes, but the disadvantage is it also
oxidizes the tissues
● OXIDATION- is the removal of charges, the cell
contains both cations and anions, the very
reason why it should posses the ions because it
provides electricity to the cell, without electrical
current or electricity the cell cannot function, it
cannot perform its tasks, as expected, that’s why
when the cell is oxidized there will be removal of
charges and it weakens the cell, and if there are
● these are the membranes enclosed vesicles that a lot of cells in your body that has been oxidized,
form from the GOLGI COMPLEX, they contain as expected they weaken tissues and they are
as many as 60 kinds of powerful DIGESTIVE prone to damage and CELLULAR MUTATION
ENZYMES and HYDROLYTIC ENZYMES that ● that’s why oxidation most especially from
can break down wide variety of molecules once external surface is very bad to our health, also
lysosome is fused with vesicles during that explains why we need to take
ENDOCYTOSIS ANTIOXIDANT to buffer the oxidizing agent that
● cause lysosome enzymes works best in the destroys the functionality of the cell
acidic pH, mostly they are found in the gastric ● example: the mouthwash, they are oxidizing
agents, we gargle that because we are hoping to
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
kill the microbes and then we have to spit it out contains the lipids, fats and cholesterol
that’s because it is not good once it is absorbed (fat-soluble) which is exactly opposite in terms of
longer in our body property of glucose
● that explains why it is not good to administer ● that explains why GLUCOSE cannot
large amounts of hydrogen peroxide to our immediately penetrate into the cell, that’s why it
wound because other than it oxidizes the requires INSULIN as a key for entry. when it
microbes and soon die, but the problem with that reaches into the cytoplasm, GLUCOSE will then
is it also oxidizes the tissues, instead of helping be converted into PYRUVIC ACID, once
the tissue to recuperate to heal faster but hen it became PYRUVIC ACID that’s the best time
destroys the cell, instead of promoting healing when the mitochondria will convert that to ATP
process, it delays the healing process. or ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE
● example: what will happen to your hair once you ● ATP is a form of energy and it is calorigenic, it
apply hydrogen peroxide? Your hair will oxidize gives HEAT
that’s why the color separates from the hair, ● DNA regulates body temperature, it dictates the
black hair will turn to blond desirable temperature, that is why it has to
● just apply small amount of hydrogen peroxide maintain 36.5-37.5 degree celsius. WHY IT HAS
instead of soaking it because it impairs or delays TO BE IN THAT BRACKET? because the
the healing process metabolic activity of our body cannot prosper
without having this physiologic bracket; if it fall
below we become HYPOMETABOLIC, if it goes
● MITOCHONDRIA- powerhouse of the cell above we become HYPERMETABOLIC
because it is where ATP is being extracted
● MITOSIS- a cellular division in which the main
cell splits into two identical cells
● PHASES OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY: PMAT
○ PROPHASE
■ EARLY PROPHASE-
membranes are intact,
chromosomes are not
● the mitochondria contains ribosomes well-defined
(RIBOSOMES: mitochondria, endoplasmic ■ LATE
reticulum, surfaces of the nucleus) PROPHASE-chromosomes are
● WHERE DOES RIBOSOME PRODUCED? well-defined, centrioles are
nucleolus in the nucleus, assembled in the migrating towards the opposite
cytoplasm pole
■ at the last part of the prophase
the membranes disappeared;
with the expense of SPINDLE
FIBER, chromosomes will be
held and directed towards the
middle
● enzymes confines in the mitochondria,
participates in ATP SYNTHESIS
● HOW DO MITOCHONDRIA CRISTAE
CONTRIBUTE IN ATP PRODUCTION?
○ MITOCHONDRIA CRISTAE increases
the surface are available for chemical
reactions, and contains some of the
enzymes needed for ATP production
○ METAPHASE- alignment of
chromosomes called METAPHASE
PLATE
■ IF YOU OBSERVED THAT A
CELL DID NOT HAVE
CENTROSOME, WHAT
COULD YOU PREDICT ABOUT
ITS CAPACITY FOR CELL
● GLUCOSE is a water soluble nutrient;
DIVISION? cell division won’t
meanwhile, the composition of cell membrane
prosper because the spindle
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
fiber and centrosome
participates in the cell division, it
cannot complete its process or
sequence
○ ANAPHASE
■ EARLY ANAPHASE-
chromosome is splitted in half/ ● G1 PHASE- cell is metabolically active, it
V-SHAPE, pulled towards the duplicates the organelles necessary for
opposite end metabolic activity, cytosolic components will be
■ LATE ANAPHASE- CLEAVAGE duplicated, same thing with the centrosome
FURROW responsible for replication
● S PHASE (SYNTHESIS)- DNA is being
replicated
● G2 PHASE- cell growth continuous to perform
and other proteins are being synthesized
because proteins are necessary for metabolic
activity, centrosome being replicated again
● MITOTIC (M) PHASE- main cell is splitted into
two identical cells
● G0- it is important because it is known to be the
RESTING PHASE of cell division
○ naay part sa atong body na kailangan
G0, naa sad part satong body na dili
○ TELOPHASE- splitted equally, the cell
kinahanglan og G0 (ex.1 during organ
make sure that before it is completely
development or formation: cycle begins
splitted it assures identical distribution of
in G1-S PHASE-G2-M PHASE
properties and components
paulit-ulit, once fully formed naa na
dayon ang G0, siya magsabi na tama na
kasi tapos na, kasi if hindi mag rest or
walang G0 that means the cell is always
dividing or duplicating and that is the
behaviour of CANCER CELLS--walang
G0) (ex.2 if may lacerated wound ka, in
the lacerated wound the body has a
behaviour of healing, while still in the
process of healing G1-S PHASE-G2-M
PHASE hanggang sa mag completely
healed na yung wound mo, kung totally
healed na mag rest na ang cell
duplication----G0, dahil if walang G0, it
keeps on duplicating and that’s a typical
behavior of CANCER CELLS)
○ examples of the parts in our body
● INTERPHASE- in the mitotic sequence
without G0 is BONE MARROW because
interphase is not anymore part of it because it is
it keeps on synthesizing the RBC,
also considered as PROPHASE
platelets, and any blood forming
● CYTOKINESIS- occurs during ANAPHASE and
elements, dahil if may G0 sa ating bone
completed next to TELOPHASE
marrow all synthesis of blood forming
elements will STOP; another example
are HAIR FOLLICLES, it keeps of
growing because other than the growth
hormone wala yung G0; another
example is our SKIN, the outermost
layer of our skin must be replaced;
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
another is the MUCOSAL LINING ○ Cellular photo-oncogenes (known for
especially anything that involves causing dermal problems such as
peristaltic activity; another is the GUMS PSORIASIS)
it is in contact with solid materials so it ■ Epidermal growth factor
needs to be shed receptor (EGFR)
● ANTINEOPLASTIC or ANTI-CANCER DRUGS- ■ c-Myc (found in chromosome 8)
the mode of action of this medication STOP ● Chromosome 8
rapidly dividing cells , since cancer cells are ● Promising target for
rapidly dividing thus ma inhibit ng gamot ito ang cancer drugs
proliferation of cancer cells, BUT other than ○ Cell-Signalling Protein:
cancer cells may part sa ating body na normal ■ Kirsten Ras (KRAS/ KRAS2)
cells ma affected because of this drug such as (these are tumor inhibitor, the
the bone marrow, hair follicles, THUS, this is problem is that once it is
why there is ALOPECIA in clients who undergo mutated, it will become a
this therapy, will also have STOMATITIS promoter or accelerator of tumor
because yung oral cavity affected because it is development------mas delikado)
rapidly dividing, another is a decreased
production of GAMETES (sperm and egg)
because these are also rapidly dividing cells,
● p53- a tumor suppressive gene
resulting to AZOOSPERMIA in men
● SOMATIC CELLS- aka body cells or tissue ● the virus is derived, then it begins to infect
normal cells, the DNA from the virus will go to
the nucleus, but then the cell has antidote the
p53 to be specific, the tumor suppressive genes
prevent the viral DNA from replicating and the
cell lives
● on the other hand, if the same virus infects a
cancer cell, the DNA of that virus will go to the
nucleus, and there is NO p53 around because it
is defective, therefore the viral DNA will continue
to multiply, will eventually burst the cell, release
lots of viruses to the surrounding environment
that could infect both normal and cancer cells,
but the normal cells are kind of immune to the
THREE PHASES virus due to the presence of p53, while the
● INITIATION: a person is exposed in cancer cells will continue to be killed
CARCINOGENS
○ CARCINOGENS
■ Chemical
■ Physical ● Performs cellular proliferation (division)
■ Biologic Agent (Vascular Endothelial Growth (VEGF)- in order
○ but since your immune system is intact to maintain its nourishment and it can divide
and well functioning dira ra siya taman, successfully for survival)
di na mag prosper into next stage sa ● Contact inhibition loss (contact inhibition- each
molecular process, iF hindi makaya sa organ of the body have respect to their
body it will prosper to the next level neighboring organs, so si liver there’s no reason
● PROMOTION: na naa liver sa kidney, ang kidney sab di pud
○ Repeated exposure to promoting agents pwede motubo sa lungs, so naay contact
○ Dose of promoter inhibition because they are respecting each
○ Innate characteristics and genetic other; but since ang gipag-usapan nato is
stability of the target cell CANCER--there is contact inhibition loss, wala
○ minsan sa iba, sa promotion lang taman na pake to each other)
kasi nakayanan pa ng immune system ● Cancer cell biology
na mag inhibit or deter ang mutation ng ○ Synthesize protein and glucose (means
cells, BUT if you have frequent or that cancer cells are parasitic in nature,
repeated exposure to carcinogens hindi ginagamit niya ang imo GLUCOSE,
na makaya (such as always eating GROWTH HORMONE, and PROTEINS,
instant noodles, canned goods, there is the moment you cannot provide these
a higher chance that cancer will three, cancer cells will synthesize
develop) THEIR own glucose and protein to
● PROGRESSION: there is now effect on our maintain their nourishment, pero ato
body or organs body padayon japon ga produce growth
○ Cellular oncogenes (genes that trigger hormone)
mutations and development of cancer) ○ Abnormally large nuclei
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
○ Strong attraction to growth factors to be stable----if hindi siya mag nakaw, always siya ma
(atong body ga produce everyday og unstable and highly reactive)
growth factors kaya nga maglaki ato
tiyan tungod sa ato ka takaw that sends
hormones na kailangan natin ipalaki ang
stomach para the next time you eat food
you can cater large amounts, SAME
THING during resting hours na there is
higher levels of GROWTH HORMONE
PRODUCTION in our body, instead of
the healthy cells are enjoying it
CANCER CELLS are competing with
utilization of GROWTH FACTOR, they
use it for them to grow)
● EPIDEMIOLOGY AND ETIOLOGY
○ HOW DO MALIGNANT CELLS
SURVIVE? (maraming paraan para sila
ay mag survive: such as angiogenesis, ● WHAT WILL HAPPEN TO HEALTHY ATOMS?
no G0, capable of producing protein and It will cause damage to the cells making it
glucose) vulnerable to CELLULAR MUTATION (ma weak
○ WHEN CAN MALIGNANT CELLS ang cell)
MAKE IMPLANTATION POSSIBLE? (it ● ANTIOXIDANT: (kusa binibigay ang electrons
happens when cancer cells were being nya kasi wala naman mangyayari or walang
trapped in minute blood vessels and can mawawala or hindi masisira if mawalan siya ng
continually grow there) electrons)(dahil dyan maiiwasan ang free
● CANCER CLASSIFICATION: radicals na mag-agaw ng
○ 1. SOLID TUMOR: (formation of mass elevtrons----importance of ingesting
○ 2. HEMATOLOGICAL CANCER (in supplements rich in antioxidants)
blood forming elements e.g., leukemia) ● SOURCES OF FREE RADICALS:
○ Exposures to UV radiation in sunlight
● COMMON SITES FOR METASTASIS ○ Exposure to x-rays
○ Brain ○ Some reaction that occur during normal
○ Liver metabolic processes
○ Lungs
○ Spinal cord
○ Bones
● PRIMARY
○ Diet
○ Obesity
● An atom or group of atoms with an unpaired ○ Insufficient physical activities (sedentary
electron in the outermost shell. lifestyle)
● DISADVANTAGES OF UNPAIRED ● SECONDARY
ELECTRONS: ○ Tobacco use as (major risk factors)
○ Makes a free radical unstable ○ Heavy alcohol consumption
○ Highly reactive ■ increases risk of cancers:
○ Bad domino effect to nearby cells MOUTH, PHARYNX, LARYNX,
● WHEN CAN FREE RADICAL BECOME ESOPHAGUS, LIVER, COLON,
STABLE? RECTUM, BREAST)
○ By either giving up their unpaired ○ Poor diet and obesity
electron ■ BREAST CANCER (in
○ Taking on an electron from another postmenopausal women),
molecule (BAD EFFECT: free radicals COLON, ENDOMETRIUM,
may break apart important body ESOPHAGUS, KIDNEY
molecules) ■ OBESITY: increased risk for
(atom or group of atoms nga walay pairs-----unpaired cancers: PANCREAS,
atoms)(unpaired electrons in the outermost shells)(the GALLBLADDER, THYROID,
disadvantage of having an unpaired electron kay ang OVARY, CERVIX
himuon sa free radicals maghanap siya ng pair or ○ Sedentary lifestyles
magnanakaw siya ng electrons sa healthy cells for them ○ Other risk factors:
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
■ Long-term ingestion of ■ Radioactive materials (this
carcinogens or co-carcinogens initiates formation of free
■ Absence of protective radicals in the
substances in the diet body-----CANCER DEVELOPS)
○ EXCESSIVE/ OVER exposure to
sunlight
■ Fair-skinned (because of low
● Bacteria melanin content---protecting our
○ Helicobacter pylori skin from skin or DNA mutation)
■ notable microbe that can cause ■ Clothing styles
PEPTIC ULCER or GASTRIC ● Sleeveless shirts
ULCER, once left untreated it
● Shorts
may develop to GASTRIC ● Sunbathing
CANCER) ● CHEMICAL AGENTS
(base on research, the bacteria account very small ○ Dye (colored hair)
percentage in causing cancer) ○ Asbestos (substance present in items
such as faucet, flooring, roofing, sink,
● Protozoans wheeles------ for now it is band because
○ Trypanosoma cruzi of mutagenic effect)
■ Chagas disease
○ Pesticides and formaldehydes
● Helminths ○ Arsenic , soot, and tars (soot: black
○ Schistosomiasis powder present in spider webs,
○ Opisthorchiasis
tambucho)(tars: abundant in barbeques,
○ Clonorchiasis maitim/sunod na part ng meat----cannot
● Fungi be digested but very absorbable----high
○ Malassezia fungi (in skin and scalp) in carcinogenic substances)
■ Skin cancer ○ Benzene
■ Colorectal cancer ○ Cadmium
○ Aflatoxin-producing fungi ○ Tobacco/ cigar use (smoking cigarette is
■ Aspergillus flavus WRONG bec of grammatical errors)
■ Aspergillus parasiticus
■ Known to cause cancer of
■ (foods rich in aflatoxin: PEANUT ● Lungs
BUTTER in acceptable range ● Head and neck
BUT if you keep on consuming ● Esophagus
the product there will be ● Stoma
accumulation of aflatoxin in your ● Pancreas
circulation)(kanang daot na ● Cervix
peanuts----HIGHLY ● Kidney
CARCINOGENIC (RICH IN ● Bladder and with acute
AFLATOXIN) myeloblastic leukemia
● Viruses ■ Passive or seconhnad smoking:
○ Epstein-Barr virus (causative agent for
● Lung cancer
MONONUCLEOSIS)(common in people ● Childhood leukemia
na nagka HIV-AIDS because they are ● Cancer of:
very immunosuppressed) ○ Larynx
■ Burkitt lymphoma ○ Pharynx
■ Nasopharyngeal cancer ○ Brain
○ Hepatitis B virus (HBV) ○ Bladder
■ Liver cancer ○ Rectum
○ Human papillomavirus (HPV)(HPV
○ Stomach
vaccine) ○ Breast
■ Cervical Cancer ■ Other combustible forms of
■ Head and neck cancers tobacco
● Cigars
● Pipes
● Roll-your-own products
● PHYSICAL AGENTS ● Water pipes (or hookah)
○ CHRONIC irritation or inflammation
(LONG-TERM inflammation or irritation)
○ Exposure to ionizing radiation
■ Repeated X-ray procedures
■ Radiation therapy
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
● Shared environments
● Cultural/ lifestyle factors
● By chance alone (maybe victim of random
mutation)
DIETARY FACTORS (LONG-TERM)
● Fats and oils from animal sources
● Alcoholic beverages or heavy alcohol use
● Salted-cured (nakagarapon na maalat)
● Smoked meats (barbeque)
● Nitrate- and nitrite- containing foods (sausages
or hotdogs)
● Red and processed meats
HORMONAL AGENTS
● PROLONGED or CHRONIC estrogen
replacement therapy (ERT): (estrogen
accelerates development of
cancer)(postmenopausal women----long term
use of estrogen----develop
GENETIC PREDISPOSITION
CANCER)(postmenopausal women---have low
● Hereditary cancer syndrome (passing on of
estrogen levels---low estrogen levels could
cancer genes from one generation to another)
result to OSTEOPOROSIS and other hormonal
○ Two or more first degree or
manifestations such as vaginal dryness, mood
second-degree relatives (chances of
acquiring cancer is HIGH especially in instability)(low estrogen---decreased
calcium----teeth to bones)
first and second degree relatives)
● Diethylstilbestrol (DES)
○ Early onset of cancer in family members
● Oral contraceptives
younger than 50 years
○ HOW CAN WOMEN ACQUIRE
○ Same type of cancer in several family
CANCER? DES or oral contraceptives
members
are composed of estrogen
○ Evidence of an autosomal dominant
inheritance pattern of cancers affecting
several generations of a family HORMONAL IMBALANCES
● Early onset of menses before age 12
○ BRCA1 (chromosome 17)
● Delayed onset of menopause after age 55
○ BRCA2 (chromosome 11)
■ BOTH are tumors in person’s ● Null parity (never giving birth)
● Delayed childbirth after age 30 are all
genes, once mutated, increases
associated with an increased risk of BREAST
women’s risk of BREAST
CANCER
CANCER (MASTECTOMY: a
prophylactic (preventive)
IDIOPATHIC (unknown cause)
surgery for breast cancer)
● Breast
○ Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome
● Colon
(MEN1 and MEN2)----(possible to have:
ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer, ● Rectal
● Lymphatic
stomach, thyroid, renal, prostate cancer,
● Bone marrow
lung cancer
● Pancreas
FAMILIAL FACTORS (cancer existed within members
or circle of family)
● Owing to genetics
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
FACTS ABOUT METASTATIC TUMORS
● Tumors are difficult to treat EVEN with early
intervention
● Metastatic tumors are mostly resistant to
chemotherapy
● Some metastatic tumors are resistant to
radiation
● Surgical resection is best when tumors are small
CLASSIFICATION OF MALIGNANT TUMORS BASED
ON CELLULAR ORIGIN
● CARCINOMA
○ Originates in epithelial tissue
■ Example:
● Skin
● Lining of the body tissue
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
● ADENOCARCINOMA
○ Originates in glandular tissue
■ Example:
● Breast
● Prostate
● Thyroid
● SARCOMA
○ Originates in:
■ Fat
■ Muscle
■ Blood vessels
■ Deep skin tissues
■ Nerves
■ Bones
■ Cartilage
● EMBRYONAL
○ Originates in embryonic tissue
● LYMPHOMAS
○ Originates in lymphatic system
● LEUKEMIAS
○ Originates in blood-forming organs
● MYELOMA
○ Plasma
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
● NORMAL IMMUNE RESPONSES
○ T-lymphocytes (once abnormal cell is
detected it can immediately proliferate
CYTOTOXIC cells or direct destruction
of cancer cells)(directs cancer cells to
undergo APOPTOSIS- program cell
death)(capable of inviting additional
immune system response such as
B-lymphocytes)
○ B-lymphocytes (are the one that
develops ANTIBODIES for a specific
cancer
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
● IMMUNE SYSTEM EVASION (paraan na hindi
mamatay ang cancer cells sa ating body----their TERTIARY (rehabilitation, restoration)
means of surviving---defense mechanism nila) ● Intent is to halt the disease or injury process and
○ (a.k.a. Tumor cell antigen) (if a cancer assist the person in obtaining an optimal health
does not have a TAA, it can be status
immediately detected by the body’s ● Maximize use of remaining capacities
immune system----mamatay ito)(since ● Restoration and rehabilitation
ang cancer cells may TAA, thus it will ● Monitor for and preventing recurrence of the
NEVER be labeled as foreign by our primary cancer
body---our immune system will be
deceived)
○ Tumor antigen-antibody complexes
(slightly similar to TAA, but its PRIMARY PREVENTION
mechanism is pinipigilan niya ay ● Reduce risk of disease
pinipigilan niya ang immune system na ○ Health promotion
magdevelop ny antibodies para hindi ○ Risk reduction strategies
siya masisira) ○ Example:
● GENETIC DISORDERS ■ Use of immunization
○ Hypogammaglobulinemia (very low ● Human papilloma (HPV)
vaccine
immunoglobulins produced by the body)
(a genetic disorder in which the immune ○ Cervical cancer
system, particularly the DNA, CANNOT ○ Head and neck
cancer
dictate the synthesis of more or
appropriate number of ● Hepatitis B virus(HBV)
immunoglobulins-----low vaccine
immunoglobulins ○ Recommended
produced----IMMUNOSUPPRESSED) by the CDC
(hypogammaglobulinemia: genetic ○ Reduce risk of:
disorder; AIDS: acquired) ■ Hepatiti
○ Agammaglobulinemia (no s
■ Liver
immunoglobulin produced by the
body)(very immunosuppressed) cancer
(the role of the immune system is not just protecting our GUIDELINES OF CANCER PREVENTION
body from viral, bacterial, fungal, or any forms of Individual Choices
infection BUT it plays a vital role in stopping chances of ● Be lean without being underweight
cancer development) (identifies changes or ● Avoid excessive weight gain
abnormalities)(abnormal cells or transformed cells will be ● Engage in regular physical activity
recognized by the immune system-----called as ● Limit consumption of high-calorie foods and
SURVEILLANCE CELLS)(transformed cells will be beverages
destroyed immediately by the immune system-----if it ○ Engage in:
fails to identify abnormal cells---TUMORS can develop ■ At least 150 minutes of
moderate intensity, or
and progress)
■ 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity
physical activity each week
● Limit sedentary behavior such as:
○ Sitting
PRIMARY (wala sakit)(prevention, education, advocacy) ○ Lying down
● Health promotion ○ Watching television
● Health education ● Intentional physical activity above usual
● Genetic screening activities can have many health benefits
● Marriage counseling
● Use of specific immunization Consume a Health Diet, With an Emphasis on Plant
● Attention to personal hygiene Sources
● Use of environmental sanitation ● Limit consumption of processed meat and red
● Avoidance of allergens meats (tumor promoters)
● Protections from carcinogens ● Eat at least 2½ cups of vegetables and fruits
each day
SECONDARY (naa sakit)(early detection) ● Choose whole grains in preference to processed
● Early diagnosis and prompt treatment (refined) grains
● Case finding measures ● Limit consumption of alcoholic beverages
● Individual and mass screening survey ○ Women: no more than 1 week per day
● Prevent complication and sequel ○ Men: two per day
● Shorten period of disability ● Foods that reduces risk of cancer
● Disability limitations ○ High fiber
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
○ Cruciferous vegetables ● Unusual bleeding or discharge
■ Broccoli (steamed) ● Unexplained anemia
■ Cauliflower ● Thickening or lump in breast or elsewhere
■ Spinach (if hindi alam asan na ● Indigestion
culture ang kangkong, its best to ● Obvious change in wart (precancerous) or mole
avoid it because it absorbs ● Nagging cough or hoarseness
toxins---can be absorbed by the ● Sudden weight loss
body once ingested)
○ Carotenoids CANCER SCREENING GUIDELINE FOR
■ Apricots (may be with chicken) ASYMPTOMATIC CLIENTS
■ Peaches ● COLORECTAL CANCER (MALES AND
FEMALES)
Community Action ○ Digital rectal examination ANNUALLY
● Increase access to: beginning at the AGE OF 50 (use of
○ Affordable, fingers to palpate prostate)
○ Healthy foods in communities,
○ Worksites and
○ Schools
● Decrease access to:
○ Food and beverages of low nutritional
value
○ Particularly to youth
● Provide safe, enjoyable, and accessible
environments for physical activity
○ Schools ○ Fecal occult blood test ANNUALLY
○ Worksites beginning at AGE 50
○ Transportation ○ Sigmoidoscopy EVERY 5 YEARS
○ Recreation in communities beginning at AGE 50
SECONDARY LEVEL OF PREVENTION
● Involves
○ Screening
○ Early detection activities
● Seek to identify
○ Precautionary lesions
○ Early-stage cancer
● Detection of cancer at an early stage may
reduce; ○ Colonoscopy EVERY 10 YEARS or
○ Costs double contrast barium enema EVERY
○ Use of resources, and 5 TO 10 YEARS
○ Morbidity ● BREAST CANCER (FEMALES)
Nurses continue to develop community-based screening ○ MONTHLY breast self-examination
and detection programs that address barriers to health beginning at the AGE 20
care or reflect the socioeconomic and cultural beliefs of ○ Clinical breast examination
the target population. ■ EVERY 3 YEARS from AGE
● Understanding the role of genetics in cancer cell 20s to 30s
development. ■ ANNUALLY beginning at AGE
● Cancer risk evaluation programs 40
○ Interdisciplinary in-depth assessment ○ Mammogram ANNUALLY at AGE 40
○ Screening and over
○ Education
○ Counseling
○ Follow-up monitoring
THE NINE WARNING SIGNS OF CANCER
(CAU2TIONS/ CAUTION US)
● Change in bowel or bladder habits
● Any sore that does not heal
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
● CERVICAL AND UTERINE CANCER
○ Papanicolao (Pap) Smear
■ ANNUALLY for all who have
been sexually active ● Position:
○ Inspect breast visually
○ Palpate in front of the mirror with arms
at various positions
○ Perform the examination
■ Lying down, first with a pillow
under one shoulder,
■ Then with a pillow under the
other shoulder, and
■ Finally lying flat
● Perimeter:
○ Examine the following:
■ Who have reached AGE 18 ■ Entire breast
(after woman has had three (3) ■ Nipples
or more consecutive satisfactory ■ Axillary tail that extends into the
normal annual examination) armpits, and
○ Pelvic examination ■ Nearby lymph nodes
● Palpation:
■ EVERY 1 TO 3 YEARS with
pap test beginning at AGE 18 to ○ Palpate with the pads of the fingers,
40 without lifting the fingers as they move
○ Endometrial tissue sample across the breast
■ At menopause ● Pressure:
■ If high risk ○ Light pressure
■ Thereafter at the discretion of ○ Moderate pressure
the physician ○ Firm pressure
● Pattern:
○ The vertical strip pattern (up and down)
○ The pie-wedge pattern (center to
outwards)
○ The circular pattern (circular motion from
nipples to outwards)
○ NOTE!! Don’t forget palpating the axilla
● Practice:
○ Practice breast self examination\
○ Become familiar with the feel of the
breast tissue
○ NOTE!!! Practitioner can provide
● PROSTATE CANCER
feedback on your method
○ Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and
● Plan
digital rectal examination
○ Know what to do if you suspect a
■ ANNUALLY beginning at AGE
change in your breast tissue
50 for MEN
○ Know your family history of breast
■ Who had at least a 10-year life
cancer
expectancy
○ NOTE!!! Have mammography done as
■ For younger men who are at
often as your healthcare provider
high risk
recommends (immediate detection)
SEVEN P’s METHOD OF BREAST
SELF-EXAMINATION
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|21438798
CELLULAR ABERRATION
TERTIARY PREVENTION
● Focus:
○ Monitoring for recurrence
○ Preventing recurrence
● Screening for the development of second
malignancies
● For survivors:
○ Assess for the development of second
malignancies
■ Lymphoma
■ Leukemia
○ Associated with:
■ Antineoplastic agents
■ Radiation therapy
○ May also develop secondary
malignancies not related to treatment
but GENETIC MUTATIONS
(environmental exposures, lifestyle
factors)
Downloaded by Karolien Faye A. Donga (karolienfayedonga07@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Bites by Crotalinae Snakes (Rattlesnakes, Water Moccasins (Cottonmouths), or Copperheads) in The United States - Management - UpToDateDocument19 pagesBites by Crotalinae Snakes (Rattlesnakes, Water Moccasins (Cottonmouths), or Copperheads) in The United States - Management - UpToDateAlin VázquezNo ratings yet
- Toxicity Testing: (Micronucleus Assay and Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay)Document20 pagesToxicity Testing: (Micronucleus Assay and Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay)hoythereNo ratings yet
- Trial Watch: Radioimmunotherapy For Oncological IndicationsDocument13 pagesTrial Watch: Radioimmunotherapy For Oncological IndicationsTrabelsiNo ratings yet
- Delantar 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomaDocument26 pagesDelantar 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomasharedNo ratings yet
- PLGG Therapeutic Training April2022Document17 pagesPLGG Therapeutic Training April2022susy juliaoNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Parotid MassDocument50 pagesBilateral Parotid MassKassim OboghenaNo ratings yet
- BARRIER and Cannot Reach The CNSDocument4 pagesBARRIER and Cannot Reach The CNSJan Federick BantayNo ratings yet
- The Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation GuidelineDocument8 pagesThe Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation GuidelinekityamuwesiNo ratings yet
- A Central Giant Cell Granuloma in Anterior Mandible-A Case ReportDocument4 pagesA Central Giant Cell Granuloma in Anterior Mandible-A Case Reportsenja raharjaNo ratings yet
- Aula 08 - Terapia AntineoplásicaDocument58 pagesAula 08 - Terapia AntineoplásicaSara PollastreliNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing TransesDocument4 pagesOncology Nursing Transesmblanco.dchNo ratings yet
- Bandal 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomaDocument25 pagesBandal 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomasharedNo ratings yet
- Anti-Infective Therapy "Antibiotics": Definitions Chemotherapeutic Agent Anti-Microbial AgentDocument8 pagesAnti-Infective Therapy "Antibiotics": Definitions Chemotherapeutic Agent Anti-Microbial AgentMohamed EbrahimNo ratings yet
- JR Bangsal 2 Ke IDocument6 pagesJR Bangsal 2 Ke IFitri Kasmita SariNo ratings yet
- Anti-VEGF Agents and Their Clinical Applications: Dr. Sriniwas Atal MD. Resident OphthalmologyDocument67 pagesAnti-VEGF Agents and Their Clinical Applications: Dr. Sriniwas Atal MD. Resident OphthalmologySriniwasNo ratings yet
- Diclofenaco IntraarticularDocument6 pagesDiclofenaco IntraarticularGustavo CaladoNo ratings yet
- Streptomycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesStreptomycin Drug Studym B100% (1)
- Injectableagentsversus Surgeryforrecurrent Temporomandibularjoint DislocationDocument7 pagesInjectableagentsversus Surgeryforrecurrent Temporomandibularjoint Dislocationmehak malhotraNo ratings yet
- Guarda Nardin 2008Document10 pagesGuarda Nardin 20086mqpjqh2vqNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Challenges in The Diagnosis and Treatment of Myasthenia GravisDocument13 pagesOvercoming Challenges in The Diagnosis and Treatment of Myasthenia GravisAndres MardonesNo ratings yet
- 8 Drug Study NCM 112Document15 pages8 Drug Study NCM 112Marie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management of Ameloblastoma ConservativeDocument6 pagesSurgical Management of Ameloblastoma ConservativeZachary DuongNo ratings yet
- Oncology Skills ChecklistDocument7 pagesOncology Skills Checklistnorthweststaffing100% (2)
- L38 Anticancer ChemotherapyDocument30 pagesL38 Anticancer ChemotherapyVenniilaaSaravananNo ratings yet
- Granuloma Inguinale: Basic Information DiagnosisDocument2 pagesGranuloma Inguinale: Basic Information Diagnosiseibar camarenaNo ratings yet
- Fneur 11 00743Document12 pagesFneur 11 00743pacomeNo ratings yet
- Basic MST OS GCT - QMDocument192 pagesBasic MST OS GCT - QMvicky174No ratings yet
- Oncology 3rd NotesDocument10 pagesOncology 3rd Notesmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- 2015-Hornbeak Et Al-Immunosuppressive Therapy and UveitisDocument8 pages2015-Hornbeak Et Al-Immunosuppressive Therapy and UveitisRichard GabrielNo ratings yet
- Nanoscale: Accepted ManuscriptDocument14 pagesNanoscale: Accepted ManuscriptSkycancer DukeNo ratings yet
- Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders10Document40 pagesNeuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders10Barbara LomeNo ratings yet
- The Roles of in Ammation in Keloid and Hypertrophic ScarsDocument10 pagesThe Roles of in Ammation in Keloid and Hypertrophic ScarsireneardianiNo ratings yet
- Peer Langer Nano 2007Document10 pagesPeer Langer Nano 2007Camilo Ernesto Moreno CristanchoNo ratings yet
- Pharma Part 1 and 2Document10 pagesPharma Part 1 and 2BRYCE WILLIAM GONo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Advantages: Rapid Absorption, Convenience, LowDocument53 pagesPharmacology: Advantages: Rapid Absorption, Convenience, LowkrstnkyslNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Implant 1Document26 pagesJurnal Internasional Implant 1Abdi Gerhan Bandaso PaliNo ratings yet
- 8 Ortho Oncology - 210217 - 194331Document11 pages8 Ortho Oncology - 210217 - 194331Nabil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy in Ent PDFDocument30 pagesChemotherapy in Ent PDFPushkar Raaj PatidarNo ratings yet
- S 001 LBLDocument22 pagesS 001 LBLBhl ZarroukNo ratings yet
- Conchem q4 Module 4Document10 pagesConchem q4 Module 4Tiffany Moore100% (1)
- The Rationale of Surgical Treatment in Pediatric Spine TuberculosisDocument6 pagesThe Rationale of Surgical Treatment in Pediatric Spine TuberculosisSpica KentNo ratings yet
- 42 - Principles of Cancer TherapyDocument54 pages42 - Principles of Cancer TherapyLucero BautistaNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Surgical Strategy For Insular GliomaDocument13 pagesHHS Public Access: Surgical Strategy For Insular GliomaPreethi SridharanNo ratings yet
- Bio 139 Oct 25 - Nov 20 2018Document18 pagesBio 139 Oct 25 - Nov 20 2018Yana CatherineNo ratings yet
- Management of Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors A ReviewDocument22 pagesManagement of Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors A ReviewROSARIO PAZ MILLÁNNo ratings yet
- Brach y TherapyDocument6 pagesBrach y TherapyRetchel LosariaNo ratings yet
- S1-05a Pediatrics II Viral Infections PDFDocument5 pagesS1-05a Pediatrics II Viral Infections PDFAl Giorgio SyNo ratings yet
- Occlusal Splints and Temporomandibular Disorders: Why, When, How?Document5 pagesOcclusal Splints and Temporomandibular Disorders: Why, When, How?blogger bloggerNo ratings yet
- 2.2. Surgical OncologyDocument21 pages2.2. Surgical OncologyMiguel C. DolotNo ratings yet
- 1.54 PHARMA Chemotherapy of NeoplasmsDocument11 pages1.54 PHARMA Chemotherapy of NeoplasmsAbigail PaasaNo ratings yet
- Radiation Therapy PDFDocument1 pageRadiation Therapy PDFJames Joel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Analgesia in Intensive Care - Part 2Document7 pagesAnalgesia in Intensive Care - Part 2Yashoda PereraNo ratings yet
- A Small Study of The Relationship BetweeDocument3 pagesA Small Study of The Relationship BetweeDr. Hilder HernandezNo ratings yet
- Impact On Handling and Stress On MAbDocument22 pagesImpact On Handling and Stress On MAbvikram kaithwasNo ratings yet
- FINAL Neuroendocrine TumoursDocument35 pagesFINAL Neuroendocrine Tumoursabhinav_choudhary03No ratings yet
- Linee Guida ESMODocument2 pagesLinee Guida ESMODPNo ratings yet
- L01 Histopath Mtap2Document22 pagesL01 Histopath Mtap2sini gangNo ratings yet
- Kyle LiDocument12 pagesKyle Liapi-407846283No ratings yet
- Trauma Suturing Techniques: Key PointsDocument10 pagesTrauma Suturing Techniques: Key PointsAstidya MirantiNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Immunity: Reviewing the Potential of ProbioticsFrom EverandAnticancer Immunity: Reviewing the Potential of ProbioticsNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency VirusDocument7 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency VirusKarolien Faye DongaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Rotation Drug StudyDocument10 pages2nd Rotation Drug StudyKarolien Faye DongaNo ratings yet
- The Child With Gastrointestinal DysfunctionDocument197 pagesThe Child With Gastrointestinal DysfunctionKarolien Faye DongaNo ratings yet
- The Nano WorldDocument9 pagesThe Nano WorldKarolien Faye DongaNo ratings yet
- Arts in The Cordillera Region - DongaDocument22 pagesArts in The Cordillera Region - DongaKarolien Faye DongaNo ratings yet
- June 2009 Nle HirapDocument35 pagesJune 2009 Nle HirapDavid BrilloNo ratings yet
- MRI of Cervical Cancer - Springer 2019Document15 pagesMRI of Cervical Cancer - Springer 2019jansen siahaanNo ratings yet
- SketchyPath ChecklistDocument1 pageSketchyPath ChecklistFajar Raza100% (1)
- 10 MRCP 2 Oncology NOTES Passmedicine PDFDocument54 pages10 MRCP 2 Oncology NOTES Passmedicine PDFHussein GhannamNo ratings yet
- Agenda - Biblioteka de Biomarkeri - FINALDocument1 pageAgenda - Biblioteka de Biomarkeri - FINALOlteanu Gheorghe-EmilianNo ratings yet
- Kep KritisDocument193 pagesKep Kritisari cahyaNo ratings yet
- Issue Overview Animal TestingDocument7 pagesIssue Overview Animal Testingapi-509547764No ratings yet
- Carcinocin MateriaDocument6 pagesCarcinocin MateriassNo ratings yet
- Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of The BreastDocument8 pagesAtypical Ductal Hyperplasia of The BreastleartaNo ratings yet
- LAw & Ethics AssignmentDocument12 pagesLAw & Ethics AssignmentThilinaAbhayarathneNo ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma DR: Gehan MohamedDocument19 pagesOsteosarcoma DR: Gehan MohamedNico DougaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients With Cancer: Maintaining Tissue IntegrityDocument5 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Cancer: Maintaining Tissue Integrityela garciaNo ratings yet
- Budwig Cancer GuideDocument108 pagesBudwig Cancer GuideasoboohbahNo ratings yet
- Classification of Bone Tumors NewDocument38 pagesClassification of Bone Tumors NewSyed WahajNo ratings yet
- Tumori Fibrohistiocitare IntermediareDocument39 pagesTumori Fibrohistiocitare IntermediareOana BarbuNo ratings yet
- 200 Points in Special PathologyDocument15 pages200 Points in Special Pathologyjihadeqitaal100% (1)
- Skills Lab ObstetriDocument44 pagesSkills Lab Obstetricharlesy TNo ratings yet
- Multidisciplinary Patient Care Navigator To Help Patients at Brinton Lake - Crozer-Keystone Health System - PADocument2 pagesMultidisciplinary Patient Care Navigator To Help Patients at Brinton Lake - Crozer-Keystone Health System - PAnbmyersNo ratings yet
- Cancer - 2011 - Hajdu - A Note From History Landmarks in History of Cancer Part 2Document10 pagesCancer - 2011 - Hajdu - A Note From History Landmarks in History of Cancer Part 2Pilar AufrastoNo ratings yet
- History of Herbal TritmentDocument10 pagesHistory of Herbal TritmentTorentSpyNo ratings yet
- Marine Corps Institute: Semper Fit Advanced Fitness CourseDocument222 pagesMarine Corps Institute: Semper Fit Advanced Fitness CoursesrollinsNo ratings yet
- ReishiMax Clinical StudyDocument7 pagesReishiMax Clinical StudynsagelocspaNo ratings yet
- IMRT & Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Christopher GolbyDocument41 pagesIMRT & Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Christopher GolbyAmr MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Healthiest FruitDocument15 pagesTop 10 Healthiest FruitFauzia IkaNo ratings yet
- Associations USMLEDocument99 pagesAssociations USMLEnu.bombinaNo ratings yet
- Cancerimmunotherapies: Philip J. BergmanDocument22 pagesCancerimmunotherapies: Philip J. BergmanRiefkyansyah PutraNo ratings yet
- DR Eric and Sabrina Zielinski Non Toxic Body Care Diy RecipeDocument141 pagesDR Eric and Sabrina Zielinski Non Toxic Body Care Diy Recipefizz100% (1)
- Chronic Illness in Canada: Impact and InterventionDocument592 pagesChronic Illness in Canada: Impact and InterventionShalini BaggaNo ratings yet
- Canon Technology Highlights 2013 eDocument0 pagesCanon Technology Highlights 2013 eAyşenur EnçNo ratings yet
- Osu1053355296 PDFDocument279 pagesOsu1053355296 PDFandres guerreroNo ratings yet