Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prof. Ed. 108 SG5
Uploaded by
kai DMCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prof. Ed. 108 SG5
Uploaded by
kai DMCopyright:
Available Formats
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev.
0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
STUDY GUIDE FOR MODULE NO. 5
THEORIES AND PRINCIPLES IN THE USE AND
DESIGN OF TECHNOLOGY-DRIVEN LESSONS
MODULE OVERVIEW
How teachers integrate technology in the teaching and learning process depends very much on their
beliefs on how people learn. Specifically, they need to know who their learners are and how to approach
instruction. The educators’ role is to provide learning experiences that will help achieve the defined outcomes.
In this module, you will be acquainted with different theories and learning principles.
MODULE LEARNING OBJECTIVES
At the end of this Module, you should be able to:
1. Identify learning principles and theories that are applied in technology-driven teaching-learning
models; and
2. Use the learning principles and theories as basis in the development of the teaching plans and
selection of instructional materials.
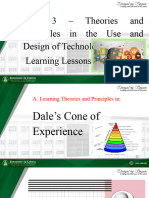
EDGAR DALE’S CONE OF EXPERIENCE
)
What is Dale’s Cone of Experience?
The cone of experience is a pictorial device used to explain the interrelationships of the various types
of audio-visual media, as well as their individual “position” in the learning process. The cone’s utility in
selecting instructional resources and activities is as practical today as when Dale created it.
Edgar Dale introduced the Cone of Experience that shows the progression of learning experiences
from the concrete to the abstract.
There are elements that should be taken into consideration. One way of putting it is the 8 M’s of
teaching and each element contributes to ensuring effective instruction.
The Eight M’s of Teaching
1. Milieu- the learning environment
- The classroom management and other school facilities are the most important because it helps the learners
to rest and relax while thinking. It must be comfortable for them.
2. Matter- the content of learning
- The subject content must be mastered by the class. Some says, "too much, too soon", it means if you try to
teach them too much just for a day, they will probably going home without absorbing all your discussions.
Instead, teach them with the right information just enough, for them to master it. "Little matter, but well
mastered"
3. Method- teaching and learning activities
-This consist of purposeful, planned activities and tasks done by the teachers and learners in the classroom.
Do it with such unique way of planning and organizing you must not forget to apply values and let them work
with it, for them to become a wise and good citizen someday.
4. Material- the resources of learning
-Materials are important. It must be picked wisely by the teacher because it will serve as an example to his/
her learners all visuals must be good and decent, it must be well prepared. Lastly, as a teacher you must be
responsible to make simple but meaningful materials for the learners
5. Media- communication system
-This pertains to the communication system in teaching- learning situation. The best example to this is how
the teacher approaches his/her students using verbal or non-verbal way of communication.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 1
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
6. Motivation- arousing and sustaining interest in learning
-We knew that the learners would learn only those he wants to learn. And if a student is not interested, he will
simply "go through the motion". To make them all cooperative to the lesson, you must think of a good and
"catchy" motivation that will catch their attention.
7. Mastery- internalization of learning
-This is the function of teacher direction and student self-activity with teacher supervision. A learner must not
be forced to master all the lesson in the book, but to learn and retain it in their minds.
8. Measurement- evidence that learning took place
-The final element of teaching- learning sequence. This is to measure the learning, retained in the mind of the
learners. And to measure it, they will undergo through tests which will yield the evidence in form of test score.
The cone of experience of experience is a visual model that shows a continuum of learning; a pictorial
device that presents bands of experience. It does not strictly define the bands to be mutually exclusive but
allows the fluid movement across the levels. In the fact, the sensory aids may overlap and even blend into one
another.
The version of Dale's Cone of experience with percentages as to which band will hone higher order
thinking skills and engage learners more may be confusing because it may not necessarily mean that learning
better takes place when materials or activities belong to the upper level of the cone or that the nature of
involvement is more active if it is in the bottom.
The Bands in Dale's Cone of Experience
Direct Purposeful Experiences — these refer to foundation of experiencing learning. Using the senses,
meaningful knowledge and understanding are established. This experiential learning where in learns by doing.
Contrived Experiences — it is category that representation such as models, miniatures, or mockups are
used. There are things or events that may be beyond the learner’s grasp and so contrived experiences can
provide a substitute.
Dramatized Experiences — these are commonly used as activities that allows students to actively participate
in a reconstructed experience through roleplaying or dramatization.
Demonstration — when one decides to show how things are done, a demonstration is the most appropriate
expert. It is an actual execution of a procedure or a process.
Study Strips — this are actual visits to certain locations to observe a situation or a case which may not be
available inside the classroom.
Exhibits — these are displays of models such as pictures, artifacts, posters, among others that provide the
message or information. These are basically viewed, however, there are exhibits that allow the viewers to
manipulate or interact with the display and as a result, the exhibit becomes more engaging and fun.
Television and Motion Pictures — this technology equipment provide a two-dimensional reconstruction of a
reality. These allow learners to experience the situation being communicated through the mediated tools.
They provide a feeling of realism as a viewer’s trying to understand the massage portrayed by actors in the
films.
Still Pictures, Recordings, Radio — still are pictures or images. Together in this category are the audio
recorded materials or information broadcast through the radio.
Visual Symbols — these are more abstract representations of the concept or the information.
Verbal Symbols — this category appears to be the most abstract because they may not exactly look like the
concept or object, they represent but are symbols, words, codes, or formulae.
They found that direct instruction, or lecture, is most used in the classroom and has “a significant effect on
retention”. Reading, although it appears to have little value based on Dale's Cone will influence the students'
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 2
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
ability to learn throughout their lives.
In addition, Bruner’s 3-tiered model of learning points out that every area of knowledge can be
presented and learned in three distinct steps.
1. Enactive- a series of actions.
2. Iconic - a series of illustrations or icons
3. Symbolic- a series of symbols.
With young learners it is highly recommended that a learner proceeds from the enactive to iconic and
lastly to the symbolic. A young learner would not be rushed to move to immediate obstruction at the highest
level without the benefit of a gradual scaffolding. However, when the learner is matured and capable to direct
his own learning it may move fluidly across the cone of experience.
LEARNING ACTIVITY 1
Individually, how would you relate the Cone of Experience to the teaching-learning process with the
levels identified by Bruner’s three-tiered model of learning? How would you apply it as a future
educator? Be ready to share your answers in class.
TPACK AS A FRAMEWORK FOR TECHNOLOGY-DRIVEN TEACHING AND LEARNING
As you prepare to be a teacher, how do you assess your content knowledge of your specialization in
terms of your teaching skills? What strategies or techniques do you know will work if you use it when
teaching? If you will consider using a technological tool when teaching what would it be?
Shulman’s Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK) is a framework which involves the teacher’s
competence in delivering the concepts being taught by simplifying complex ones if needed or leading the
students to study a concept more deeply and extensively. This is made possible due to the teachers
understanding of the amount and the content structure of knowledge.
Mishra and Koehler continued to build upon Schulman’s PCK and incorporated technology hence,
TPACK.
TPACK is a framework that combines the teacher’s three knowledge areas: technological knowledge, content
knowledge, and pedagogical knowledge. This framework shows the interconnectedness of content knowledge
with pedagogical knowledge and the integration of technology in making teaching more engaging, relevant,
and effective. It looks at how these knowledge areas intercept or work together to increase student’s
motivation and make the content more accessibly engaging to students.
The Technological, Pedagogical and Content Knowledge known as TPACK is a theoretical model describing
the capability of the 21st century teacher. To be relevant to the learners of today, the teachers should be able
to blend his knowledge and capability in the content of the discipline.
CK is content knowledge. It is the ‘what’ - understanding of the content such as language arts, math, science,
and history, among others. This is composed of facts, concepts, theories, or principles in a given discipline.
Pedagogical knowledge (PK) is the ‘How’. It is the expert’s knowledge in the science of teaching from
educational and learning theories to individual difference to strategies and techniques as well as assessment
of learning.
The intersection of the pedagogical and content areas of knowledge is the PCK. This how much
competencies the teachers have in making the students learn concepts and skills. This includes the
knowledge of how to use techniques that can meaningfully address different learning styles while supporting
content with deeper understanding.
This is the TK or the technological knowledge. This is the teachers’ knowledge on how to select, use and
integrate these tools in the teaching and learning context. This is not only about the tools but also about the
quality of content that students can access through appropriate applications and sites.
When technology is used in a specific subject area to enrich and deepen student’s understating of content this
is the intersection called TCK or Technological-Content Knowledge. For example, to deepen students’
understanding of a concept or area of study, students can gather information and collect data and evidence
using technology tools and present this information using an application.
Furthermore, TPK which is Technology-Pedagogical knowledge is knowing how to select, use or develop
technology to manage student learning. For example, who will use collaborative tools that will allow students
to work together and share information? How will you use an application that will allow students to creatively
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 3
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
share their well-researched project in class or to other outsides of the school? If they need to communicate
with an expert in the industry, what tools can they employ so that they may be able to interview the right
expert who can assist them in their capstone project? As a teacher, using the appropriate technology to
ensure effective instruction is TPK.
It allows student to learn content through digital tools. They can document and record evidence and plot out a
strategy using a collaborative tool where the group can discuss their action plan while in or out of school. The
drawn plan can be presented using a productivity tool (i.e. PowerPoint presentation or a digital story) to
pertinent persons for feedback.
The intersection of all knowledge areas is known as the TPACK. So, TPACK is about what teachers know,
how they teach and how technology is used in the delivery of the lesson to make it more engaging and
making learning more relevant in the 21st century.
TPACK will start with content and then pedagogy and layer in technology. Sometimes, you might get
excited about the technological tool and design a lesson around it. Remember, it is NOT about the technology
tool but it is the right blend of the three knowledge areas.
LEARNING ACTIVITY 2
Individually, evaluate your personal capability in relation to the TPACK Framework. Draw your TPACK
state and explain and exemplify the meaning of your model.
SAMR
Transforming technology into a blended learning experience has become a necessity for those
educators wanting to engage student centered learning in the 21st century classroom. While it is possible to
create a successful and highly interactive student-based learning experience without technology, it is
technology that can amplify the learning experience. It must be remembered that amplification will have an
effect on great educational pedagogy but will also do the same for instruction that may not meet the goal. As
teachers invite technology into the classroom it has become evident that as learners themselves, they go
through formative steps as they become proficient in the blended experience.
Through the work of Dr. Ruben Puentedura, Ph. D. the SAMR Model (Substitution Augmentation
Modification Redefinition) provides a wonderful lens to look at this progression. It must be understood that the
goal is to create lessons that allow for the ability to facilitate lessons that practice Redefinition. At the same
time, it must be remembered that all the stages allow for technology interaction and increased student
engagement. There are times where simple
Substitution is all that is needed and is most appropriate given the learning target. As educators
become familiar with the SAMR Model it allows them to reflect and evaluate their technology integration
practice while striving for powerful learning experiences. While learning activities can get blurred between the
steps of SAMR, it must be remembered that educators are working on a progression. The first two steps
involve technology as an enhancement tool and the last two involve technology as a transformation tool. Many
times, the steps between enhancement and transformation can take a bit of time as educators practice,
reflect, and learn.
In the space below you will find those important SAMR Steps.
Substitution - Tech acts as a direct tool substitute, with no functional change
This is the lowest level of technology integration. At this stage, technology replaces an activity that
may have been done before using an analog version. This is the very first stage of enhancement of a lesson
using technology. This might include word processing a student authored story rather than handwriting it.
While it is the lowest level it still might be a wonderful use of the technology. Another example might be the
teacher curating the curriculum for students using their LMS (Learning Management System). The teacher
has worked hard at finding articles, reading lists, research links, and even You Tube videos on a various topic.
The web is being used as a substitution for what may have been a prior resource list given to students. Once
again, it is a wonderful start with some great learning opportunities, but it still is a substitution. According to Dr.
Ruben R. Puentedura, the teacher is just using the technology to replace a resource list that could be used in
the library. Keep in mind that this can be still very useful. Does the substitution of technology serve the
learning target, or might it get in the way? Did the technology substitution assist in student engagement? The
teacher must reflect on what might have been gained because of the substitution.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 4
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
Augmentation – Tech acts as a direct substitute tool, with functional improvement
The next step includes the Augmentation Stage, going one level up the ladder from Substitution. It is
important to remember that this step is still at the enhancement level. At this stage, the technology has
improved the learning experience by adding functionality that would have not been as possible with the
technology. In a word processing document student are taught to use different tools such as the word count,
thesaurus, and grammar checks. Perhaps students are using calculators or spreadsheets to solve a problem.
It could be that students are researching, and the teacher directs students to current news events, blogs, or
interpretations of the research by various authors.
Students could compare and contrast viewpoints, view up-to-date information that may not be in the
library, or even have the opportunity to participate in the comment section of a blog. While the line could be
blurred between Substitution and Augmentation there really is a deeper learning because of the technology.
There should be a step up in both student engagement and rigor. A teacher must reflect and recognize that
the technology has added to the learning experience. They must determine if the overall learning has been
improved because of the technology integration.
Modification – Tech allows for significant task redesign
At this stage, the technology could change the look and feel of what students perform. There really is
a definite change in the lesson that may have started with an analog foundation. Transformation has begun!
This step demands more reflection and work from the facilitating teacher. At the same time, Modification
brings in the student opportunity to proceed up Bloom’s Taxonomy. This might include authoring a
collaborative story in a Google Doc so that peer editing, and collaboration can happen anytime and anyplace.
Perhaps even some pictures are added to the story or report to further engage the intended audience.
Students may use advanced searching skills to find articles on their own that contrast viewpoints from
different counties. Perhaps students compile their research collectively using a group inside of a bookmarking
tool such as Diigo. A word cloud might be employed to study the meaning of an article or author’s writing.
While students use traditional literary critique, a word cloud might provide a new analysis such as visual look
at word frequency in a reading. This brings about an entirely new layer to the learning environment. Students
might use a Google Form to collect and analyze data. In this method of data collection students may be able
to survey larger and more diverse populations, while having a layer of tools to represent the data to an
audience. Many times, modification allows more student voice and the outcome may not be as prescribed. At
the modification stage a teacher must reflect on whether the technology did allow for some project redesign
that enhanced the project while still accomplishing the learning objectives. It could be that multiple
modifications may allow a lesson to advance to the next level.
Redefinition - Tech allows for creation of new tasks that were previously inconceivable
At this stage, the technology allows students to jump outside the original design box. This is so much
more than a redesign. It focuses on the employment of new tasks. While the teacher may initiate some of
these, student voice and choice must also be employed. A story could change into a picture book, a slide
show, or even a movie. The audience could go beyond the school and include the community, state, county,
or world. Mentors could be virtual. Perhaps students are curating and creating their own content to be used by
other students. Imagine a research that allows students to create their own search engine using Google
Custom Search.
The original standards remain with addition of new skills that circle around 21st century skills. The
redesign was made possible because of the blending of the technology into the learning process eliminating
the constraints and barriers of the physical classroom. At the same time, the technology might appear
transparent to the learning process. Students become producers, creators, and innovators. They begin to own
their own learning process. At this stage, the teacher must reflect on whether the redesign still accomplished
original standards while also allowing for engaged student centered learning.
All educators must realize that the final goal of any classroom is redefinition. At the same time, there
will be times when even the most proficient educators with technology conduct a task at the substitution level.
It really comes down to the tool fitting the task and learning target. An understanding of the SAMR Model
allows educators to reflect on their own progress while investigating ways to use educational technology in a
useful and productive way. The SAMR Model allows all educators to view the steps they are taking down the
road of technology enhancement toward true transformation. It is a wonderful and exciting journey!
BLOOM’S DIGITAL TAXONOMY
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 5
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
The purpose of Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy is to inform instructors of how to use technology and digital
tools to facilitate student learning experiences and outcomes. It aims, “To expand upon the skills associated
with each level as technology becomes a more ingrained essential part of learning.” The use of this adapted
version and the examples of tools it provides focus “should not be on the tools themselves, but rather on how
the tools can act as vehicles for transforming student thinking at different levels.” Outlined below are the levels
featured within Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy. Each level is accompanied by a description of its relevance and
examples of digital tools that connect with this taxonomy framework.
Infographic Credit: Ron Carranza
Creating –To produce new or original work. Tools – Animating, blogging, filming, podcasting, publishing,
simulating, wiki building, video blogging, programming, directing
Evaluating – To justify a stand or decision; to make judgements based on criteria and standards through
checking and critiquing. Tools – Grading, networking, rating, testing, reflecting, reviewing, blog commenting,
posting, moderating
Analyzing – To draw connections among ideas, concepts, or determining how each part interrelate to an
overall structure or purpose. Tools – Mashing, mind mapping, surveying, linking, validating
Applying – To use information in new situations such as models, diagrams, or presentations.
Tools – Calculating, Charting, editing, hacking, presenting, uploading, operating, sharing with a group
Understanding – To explain ideas, concepts, or construct meaning from written material or graphics.
Tools – Advanced searching, annotating, blog journaling, tweeting, tagging, commenting, subscribing
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 6
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
Remembering – To recall facts, basic concepts, or retrieval of material. Tools – Bookmarking, copying,
googling, bullet-pointing, highlighting, group networking, searching
Bloom's Taxonomy and SAMR model
Dr. Ruben Puntedura developed the SAMR model as a structure for educators to clarify how they are
engaging technology into teaching and learning. Ruben built his approach in the form of a ladder and equates
it with a student climbing the cognitive scale associated with Bloom’s Taxonomy. (i.e. as a task moves from
lower to upper levels of Bloom’s taxonomy, so does a task move from lower to upper levels of SAMR).
Although always a popular tool Bloom's taxonomy has seen a recent resurgence in popularity as
educators have explored technology and its integration into teaching and learning. Dr. Ruben Puentedura's
SAMR model has become a way of thinking about technology integration and his theory has seen widespread
adoption within the education community. Puentedura's work has revolved around the idea that technology
can "redefine" the types of activities that students participate in with technology. He identified four levels of
ICT integration, Substitution, Augmentation, Modification and Redefinition (SAMR). Like Bloom's SAMR is not
a hierarchy, but does describe increasingcomplexity.
By linking Bloom's Taxonomy to SAMR we are able to create tasks with specific objectives linked to
curricula that deeply embed technology and are enhanced by its use rather than using technology for the sake
of it. In other words, we can design complex and authentic tasks that are made possible only through the use
of technology.
THE ASSURE MODEL
ASSURE model is a guide in crafting an instructional flow that can guide the teacher in integrating
appropriate technology and media into the instructional process. It also refers to a systematic approach that
the teacher can use when writing an instructional plan.
This model you need to be critical thinkers by using instructional materials or digital to discuss your
lesson of your learners.
This model is composed of six essential steps in planning instruction.
1. Analyze Learners
With the learner as the center of the instructional process, the initial consideration is to get a clear picture
of the learners learning styles, age level, interests or preferences, background, special needs, and cultural
diversity.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 7
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
2. State Objectives
This is the main instruction guide that will direct the flow to reach the target. Known as the learning
outcome expected of the lesson, this statement describes what the learner would be able to perform because
of the instruction.
3. Select Methods, Media, and Materials
Selecting the appropriate way of delivering the lesson and using the applicable media or technology can
effectively make learners acquire understanding of the lesson or gain the competence desired. The teacher
must decide which strategy, materials or technology would be best considering the learners and the desired
learning outcomes.
4. Utilize Methods, Media, and Materials
Having selected the strategy, media and materials is halfway of the task done. Planning how to
implement these entails a lot of consideration. Bearing in mind the learning outcome of the lesson, the teacher
decides which part of the instructional flow will a material or technology be employed and the manner on how
it will be more effective to achieve the learning outcome.
5. Require Learner Participation
Student engagement is an important element. The learners must be made to understand their role in
taking accountability of their own learning. Therefore, the teacher must design sections of the lesson where
the learners are guided to participate in and perform tasks with minimal or no supervision at all.
6. Evaluate Student Performance
Assessing learners’ performance can take place across phases of the lesson. However, it is emphasized
that the basic rule is that the evaluation should be congruent to the learning outcome provide in the lesson.
Some learning outcomes can be sufficiently evaluated using a pen and paper test but there are other learning
outcomes that can be assessed by using rubric or having an aggregated write-up using a portfolio
assessment. The teacher decides which is appropriate for the intention of the evaluative activity.
The ASSURE process is just a matter of common sense. However, it is good to flow a regimented
guide to improve your teaching technique. Any effective teacher knows that the perfection of their technique
does not come overnight, and there is always room for improvement.
It also refers to a systematic approach that the teacher can use when writing an instructional plan or
by following the ASSURE process, you will be sure to improve your teaching for many years to come.
Integrating technology into the curriculum is very important because it is the best way to make a positive
difference in education. While many specific strategies can be used to add technology, the following model is
one example of how to integrate technology into your future lessons. The ASSURE model can be also an
instructional model for planning a lesson and the technology that will enhance it. We can also discover who
the pioneers of this model are.
When creating a digital story, it is important that we have the content written. In this part of the
module, we will learn the steps in producing a digital story and we will talk about the five (5) Elements in
writing a story. Through ASSURE model, it will be our guide in creating appropriate designs and formats on
how to create a Digital Story.
The ASSURE model can be defined as a plan that aids teachers and presenters to design and develop
the most suitable learning environment for their students. It can be used as a strategy for writing lesson plans
and improve the teaching learning process. The assure model was developed by Heinrich and Smaldino in
1999 with the co-authors Molenda and Russel.
Steps in Producing a Digital Story
1. Brainstorming a story concept.
2. Create a story board that will contain the graphics, sounds, text, narration, and music needed.
3. Collect pictures, materials and store them in an organized fashion.
4. Using productivity tools put them together using iMovie, moviemaker, vimeo, PowerPoint presentation,
powtoon, power director, viva video, and the like.
5. Edit, revise, and share your story.
When creating a digital story, it is important that you have the content written. The substances are
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 8
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
important to be clear. What is the message is all about? Then organize the flow of events using the right
language. Tell a good story.
When you have all information stored out, you need to think of a perspective that you can take as you tell
the story. The point of view will be you “through line” it will connect all the elements of your story and end it
with a concluding statement that will create a cohesive presentation.
When writing the script, you need to consider important elements:
1. Point of View strong awareness of audience in the design. Students can clearly explain why they felt the
vocabulary, audio and graphics chosen to fit in the target audience.
2. Dramatic Question realization is dramatically different from expectation.
3. Voice Pacing the pace (rhythm and voice punctuation) fits the story line and helps the audience really “get
into” the story.
4. Soundtrack/Emotion music stirs a rich emotional response that matches the storyline well.
5. Economy the story is told with exactly the right amount off detail throughout. It does not seem to short nor
does it seem too long.
Therefore, the ASSURE model is just one strategy to effectively integrate technology into curriculum.
Some teachers create an ASSURE poster to help them remember the steps of the model. As you become a
more experienced teacher, you will probably find that steps in the assure model are second nature and that
will lead to better teaching. As you revise lessons from year to year, remember to keep in mind new and
emerging technologies that might be more effective to enhance your teaching skills.
LEARNING ACTIVITY 3
As a group, produce a two-minute digital story that tells your own understanding of the ASSURE
model. You can share the digital story produced by posting it in your portfolio.
MODELS OF TECHNOLOGY-ENHANCED INSTRUCTIONALL LESSONS
The conventional way of teaching in this century may outmode the preference of present learners. The
traditional way of teaching of teachers may not hold students’ attention from a longer time. The center stage is
not taken by the teachers now.
The role of learners in this millennium are no longer limited to being a receiver of information. They desire
to be actively involved in the retrieval of information, repackaging them, and using them to create something
unconceivable before.
The learning place can also evolve especially when you consider the varied roles that learners play. They
can learn and perform the task in any physical or virtual location.
Learners can become….
Contributors
Learners can upload materials such as video or an audio, post a message, submit an output in a drop box
or add documents and eBooks and add a picture or contribute to a digital world.
Creators
Students can also collate a digital portfolio or commonly known as ePortfolio or an interactive resource.
They can produce a digital story, edit the entries and share.
Communicators
Students can chat with peers, post a reply in a blog, and contribute a comment to the let thread flow.
Creating a wiki, editing, and adding to it gives the students the chance to communicate their thoughts.
Collaborators
Capstone projects can be outputs of collaboration. Participate in group works with the aim to accomplish a
task or commenting on blogs are few ways on performing the role of a collaborator in a new idea of a learning
place.
Technology Tools Teachers can use to Engage Students in Learning
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 9
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
There are many great ideas on how to integrate a technological tool or an application in teaching the
lesson. Identifying the possible role that students need to be can guide them to choose the appropriate way of
using the right tool. Integration of technology is important because learners become engaged and they learn
better, hence, a wheel integrated phase of technology is critical. Teachers need to be trained in new
technology purchases to use them effectively. They need to understand the benefits to learning and to
themselves. One common tool that is used by the teachers to integrate technology inside the learning place is
a mobile device which is a computing gadget such as a smart-phone or a tablet computer that can be
handled and carried along by the user.
Technology tools must be used as a fundamental component of a class as long as they are
appropriate and strategically integrated to facilitate learning for the integration of technology in a lesson is an
informed judgement of a qualified and innovative teacher.
A blog (shortening of “weblog”) is an online journal or informational website displaying information in the
reverse chronological order, with latest posts appearing first. It is a platform where a writer or even a group of
writers share their views on an individual subject. It is a webpage that you need to create and where you can
write and post your ideas. These are updated on a regular basis which can inspire or educate those who read
it.
8 Types of Blogs
1. Personal Blogs
For the personal blogger, there were no rules to follow or themes to adhere. Their blogs were the open pages
of their diaries, entered through a word processor and published on simple HTML pages. Personal bloggers
today tend to follow the same trajectory, although they no longer must fight the barrier to entry of setting up a
website.
2. Business Blogs
Business bloggers are those who blog for their business. That could be a business they own or the company
they work for. A business blogger will write about the topics that will attract their ideal customers.
3. Professional Blogs
Professional bloggers are those who blog to make money online. Professional bloggers tend to either focus
on one blog or many niche blogs to generate revenue. Each blog would need to have the potential for
attracting a large audience, producing lots of traffic, and being a good fit for advertisers and product sales.
4. Niche blogs
Niche blogs are very specific! Some of the niche blog ideas might be food blogging, training programs with
your own weight, poems writing, as well as French bulldog lovers. With a niche blog, you can focus more on a
topic thus making research rather easy.
5. Reverse blogs
Reverse or guest host blogs are a unique but modern type of blog. Instead of the owner creating content, the
content is supplied by the public. A reverse blog has a team who moderate posts, prevent unpleasant
interactions and promote slow topics for greater interactivity.
6. Affiliate Blogs
Affiliate bloggers are those that blog to generate affiliate marketing commissions. Instead of creating their own
products, they write blog posts that review products by others.
7. Media blogs
Media blogs are defined by the content they produce. This type of blog is popular among people in different
fields.
8. Freelance bloggers
Freelance bloggers are those who are paid for providing services, for example writing content for other
businesses. If you are looking for a way to get paid for writing as a service and have experience in blogging,
freelance blogging is the way to go.
Padlet
Is another tool that can be accessed online and suited for sharing information or content and can
allow engagement of studies. Is an online “bulletin” board, where students and teacher can collaborate,
reflect, share links and picture, in a secure location.
Blog
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 10
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
The main purpose of a blog is to connect you to the relevant audience. There are many reasons for
starting a personal blog and only a handful of strong ones for business blogging. These are the major types of
blogs but there are a lot more to discover. There are also community blogs, nonprofit blogs, live webcam
blogs, live game screencast blogs, device type blogs, podcast blogs, various video blogs, and mixes of all
types. Hopefully, you should be able to choose your type and start your own blog to begin your blogging
journey.
In designing a lesson, always remember that it is not about the technology tool upon which the lesson
revolves. Rather it must be the objective of the lesson and the knowledge and skills to be taught that will guide
you in selecting the appropriate tool or aid to achieve those objectives.
So, the following steps may be a good guide:
Step 1: identify learning objectives based on topic or content. Determine if the objectives are
observable or can be manifested by the learner consider the topic or subject matter that needs to be covered
in the lesson.
Step 2: determine knowledge and skills. Analyze student knowledge and skills determine how
students will be able to learn the knowledge and skills look for resources that can be useful in achieving the
objectives.
Step 3: select a tool or an instructional aide to use. Be familiar with the tool you have selected and
learn how to use it. Consider the content that needs to be placed in the tool or the information that goes with
the use of the two.
Step 4: determine the method of assessment. Use criteria to evaluate the technology tool in
instructional aid but always considering the content as the most important criterion. Consider the quality of
information that technological skills needed by the students or how you can present the technology tool that
will suit your objectives.
A Sample Plan Making Use of a Mobile Device
Performance Outcomes
Learners must be able to:
a. identify the plot of a given fiction.
b. write a summary of one section of the plot.
c. create a script to enact one section of the plot: and
d. use a mobile device to document the section of the plot and which must be uploaded for the class to
review.
Prepare Things Needed in Setting up the Classroom
a. A literary material from a book
b. Mobile device with a camera
c. internet access
d. Mobile devices must be charged
e. Teacher needs to ensure that a platform has been setup where learners can upload their material.
Plan and Push the Instructional Flow
a. After finishing a fiction literature such a short story or a particular text discuss with learners the
elements of a plot the beginning the middle and the end of the story.
b. Divide the class into smaller groups assigning each team to work on the plot of the story in any of the
beginning, middle, or end.
c. Each team will write a short script that summarizes the portion of the plot assigned to them.
d. Then they will act out a scene and make use of their mobile device to record their final play.
e. The recording will then be uploaded to the class site or class wiki for the rest of the big class to view
and comment.
Provide Plausible Possibilities
a. The written script of a scene can be acted out like in a radio plane using the audio recording feature of
their mobile device like in a podcast this can also be uploaded in the class site.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 11
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
b. As a team create a different ending or inject a different way in the story that tin can select the best
plausible twist.
LEARNING ACTIVITY 4
Individually, finish the fragments by providing your personal ideas to continue the thought.
1. I will use technology in my lesson plan only when…
2. In selecting a technology tool to be integrated in a lesson, I should…
3. I will implement technology tools to make my students connect with…
4. An example of technology integration in a lesson is…
5. A creative way of using a mobile tool in a lesson is…
LEARNING ACTIVITY 5
As a group, write a semi-detailed lesson plan in an assigned topic that will employ the use of a mobile device.
SUMMARY
Y
Here are some pointers to remember:
The cone of experience of experience is a visual model that shows a continuum of learning; a pictorial
device that presents bands of experience.
A young learner would not be rushed to move to immediate obstruction at the highest level without the
benefit of a gradual scaffolding.
TPACK is about what teachers know, how they teach and how technology is used in the delivery of
the lesson to make it more engaging and making learning more relevant in the 21st century.
SAMR Model it allows Teachers to reflect and evaluate their technology integration practice while
striving for powerful learning experiences.
ASSURE model is a guide in crafting an instructional flow that can guide the teacher in integrating
appropriate technology and media into the instructional process.
REFERENCES
Bilbao, et al. (2019). Technology for teaching and learning 1. Quezon City, PH: Lorimar Publishing, Inc.
Lucido, P. & Corpuz, B. (2012). Educational technology 1 2nd edition.Quezon City, PH: Lorimar Publishing,
Inc.
https://www.youtube.com/
watch?v=p-eSxgRetvkTPACK in Two Minutes
https://www.youtube.com/
watch?v=FagVSQIZELY
Introduction to the TPACK Model Video From https://www.youtube.com/
Watch?v=glkn9Veggxo
Shulman, L. (1986). Those who understand: Knowledge growth in teaching. Retrieved from
https://www.jstor.org/stable
/117586
How to apply the SAMR model with Ruben Puentedura (video file). Retrieved from htt
Smaldino ps://www.youtube.com/
Watch?v=ZQTx2UQQvbU
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 12
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in PROF ED 108 TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1 Module No.5
Egbert, J. (2009). Supporting learning with technology essentials of classroom practice. Pearson
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 13
You might also like
- The AVIVA model (E-Book): A competence-oriented approach to teaching and learningFrom EverandThe AVIVA model (E-Book): A competence-oriented approach to teaching and learningNo ratings yet
- Applying Learning Theories to Technology-Driven LessonsDocument13 pagesApplying Learning Theories to Technology-Driven LessonsMark Wendel SalvadorNo ratings yet
- TTL 1 MODULE 5 60 PointsDocument15 pagesTTL 1 MODULE 5 60 PointsMika Virtudazo100% (1)
- TTL 1 Module 5 60 PointsDocument16 pagesTTL 1 Module 5 60 PointsDesiree Matabang100% (3)
- Unit 5 Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technology Driven Lessons 2Document80 pagesUnit 5 Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technology Driven Lessons 2Kim Leysa100% (1)
- Course Pack Prof Ed. 10 Module 5Document11 pagesCourse Pack Prof Ed. 10 Module 5Ever Shekhaina-XavierNo ratings yet
- Hesson 2 Cone of ExperienceDocument4 pagesHesson 2 Cone of ExperienceJeff Beloso BasNo ratings yet
- Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technology-Driven LessonsDocument39 pagesTheories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technology-Driven LessonsNicole TacardonNo ratings yet
- Edck5-Chapter 3Document13 pagesEdck5-Chapter 3arln mndzNo ratings yet
- Ped105Ttle Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument13 pagesPed105Ttle Technology For Teaching and LearningangillyNo ratings yet
- Edgar Dales Cone of ExperienceDocument5 pagesEdgar Dales Cone of ExperienceJerry F. Abellera Jr.No ratings yet
- Final Term Lecture 1 8M's, Dale, BrunnerDocument34 pagesFinal Term Lecture 1 8M's, Dale, BrunnerAlfredo de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Benigay Answerm10Document6 pagesBenigay Answerm10juliet calingacion100% (5)
- Module 4 Lessons 3,4 ACTIVITY1Document4 pagesModule 4 Lessons 3,4 ACTIVITY1Vannessa LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- Ced 102-Lesson Week 7-8Document48 pagesCed 102-Lesson Week 7-8Rosemarie D. ObispoNo ratings yet
- Week 7 9 Ced 102 PDFDocument45 pagesWeek 7 9 Ced 102 PDFMARK JAYSON MATIRANo ratings yet
- Narrative Module 5Document14 pagesNarrative Module 5Jeane Klaire ObadoNo ratings yet
- TTL Lesson 1 and 2Document36 pagesTTL Lesson 1 and 2nathanielranudaNo ratings yet
- FINALE TTL Finalism PortfolioDocument38 pagesFINALE TTL Finalism PortfolioRadelyn Malbas SulasulaNo ratings yet
- A Chinese Tale SlidesManiaDocument22 pagesA Chinese Tale SlidesManiaMarie fe CompaneroNo ratings yet
- M3, L1Document10 pagesM3, L1Denosta Mercurio JonelNo ratings yet
- Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of TechnologyDocument14 pagesTheories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technologypenosajoy98No ratings yet
- Dale's Cone of Experience and Instructional ToolsDocument33 pagesDale's Cone of Experience and Instructional ToolsMhel Ryan FloresNo ratings yet
- TLE 1-Unit 3-4 Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods in TLEDocument41 pagesTLE 1-Unit 3-4 Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods in TLEMaisy Hope Vargas100% (1)
- Lesson 4 Approaches, Methods of Teachng EPPDocument6 pagesLesson 4 Approaches, Methods of Teachng EPPDivine Grace Galorio57% (7)
- 1st Sem 2021-2022 - Module 5 - Lesson 1 - Task 1Document3 pages1st Sem 2021-2022 - Module 5 - Lesson 1 - Task 1Bettymae AndayaNo ratings yet
- Cone of ExperienceDocument19 pagesCone of Experiencebelloac49No ratings yet
- Dales Cone of ExperienceDocument12 pagesDales Cone of ExperienceRexson Dela Cruz TagubaNo ratings yet
- TTL 1 Lessons 5Document15 pagesTTL 1 Lessons 5ere chanNo ratings yet
- 5 E Model and MethodsDocument4 pages5 E Model and MethodsHernandez, Glexie Myles M.No ratings yet
- Self-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)Document6 pagesSelf-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)loli popNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Capiz State University Burias Campus Burias, Mambusao, Capiz College of EducationDocument19 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Capiz State University Burias Campus Burias, Mambusao, Capiz College of EducationJeroven Nicolas MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technology-Driven Learning LessonsDocument22 pagesLesson 6 Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technology-Driven Learning LessonsAnn Michelle DiazNo ratings yet
- SLM - Ro - Mil-Q2 Module 9Document27 pagesSLM - Ro - Mil-Q2 Module 9Bill Villon100% (8)
- k4 TheoriesDocument4 pagesk4 TheoriesBobo YouNo ratings yet
- EPP Module 2Document11 pagesEPP Module 2Diana Alegrado89% (9)
- Oral Communication Module 3 Models of Communication FinalDocument21 pagesOral Communication Module 3 Models of Communication FinalLaolao Auring GaborNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Module 3 Models of Communication Final Copy COPDocument21 pagesOral Communication Module 3 Models of Communication Final Copy COPMary Mae Leecon100% (3)
- SLM - Ro - Mil-Q2 Module 2Document28 pagesSLM - Ro - Mil-Q2 Module 2Bill Villon88% (24)
- Edukasyon: SA PagpapakataoDocument13 pagesEdukasyon: SA PagpapakataoJurnelene Lei UGOSNo ratings yet
- Ced101 Module 3Document22 pagesCed101 Module 3Rheya Em DiNo ratings yet
- Effective Teaching Strategies for Student LearningDocument4 pagesEffective Teaching Strategies for Student LearningEver Shekhaina-XavierNo ratings yet
- mEDIA INFORMATION LITERACY 01 OF 05Document24 pagesmEDIA INFORMATION LITERACY 01 OF 05Rex MaxNo ratings yet
- Empowermen T Technologies: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document24 pagesEmpowermen T Technologies: Quarter 1 - Module 1Gladzangel Loricabv100% (4)
- Epp Report PresentationDocument19 pagesEpp Report PresentationAnne Dinio Pablo100% (2)
- Approaches, Methods and Techniques in Teaching EPPDocument8 pagesApproaches, Methods and Techniques in Teaching EPPApril Anacio KaweNo ratings yet
- BET 4108-Educational Technology - CAT 1 and 2Document6 pagesBET 4108-Educational Technology - CAT 1 and 2Elias BonkeNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Module 1 Nature and Process of Communication FinalDocument27 pagesOral Communication Module 1 Nature and Process of Communication FinalAngelrose AbrisNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Module 1 Nature and Process of Communication FinalDocument27 pagesOral Communication Module 1 Nature and Process of Communication FinalAngelrose Abris75% (4)
- Tle-Eim: Quarter 1-Module 3: Requesting Tools, Equipment, and MaterialsDocument18 pagesTle-Eim: Quarter 1-Module 3: Requesting Tools, Equipment, and Materialskakaibakaon100% (2)
- Module 3a: 5 Hours Topics:: 3. The SAMR ModelDocument6 pagesModule 3a: 5 Hours Topics:: 3. The SAMR ModelMay annNo ratings yet
- Educational TechnologyDocument7 pagesEducational TechnologyMarie Ann Toong QuicoNo ratings yet
- Ed Tecth Leson CompleteDocument19 pagesEd Tecth Leson CompleteEva Joy DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument24 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyBill Villon100% (5)
- Educational Technology 1: Brenda B. Corpuz, PH.D Paz B. Lucido, PH.D AuthorsDocument20 pagesEducational Technology 1: Brenda B. Corpuz, PH.D Paz B. Lucido, PH.D Authorsrapet_bisahan0% (1)
- Edgar DaleDocument3 pagesEdgar DaleRachelle BarawelNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 108 SG4Document11 pagesProf. Ed. 108 SG4Fate VargasNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 108 SG3Document10 pagesProf. Ed. 108 SG3Fate VargasNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 108 SG2Document7 pagesProf. Ed. 108 SG2Fate VargasNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 108 SG1-1Document6 pagesProf. Ed. 108 SG1-1Fate VargasNo ratings yet
- Environmental, Health and Safety Guidelines For Textiles ManufacturingDocument20 pagesEnvironmental, Health and Safety Guidelines For Textiles ManufacturingHitesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics. ASSIGNMENT 2Document5 pagesProbability and Statistics. ASSIGNMENT 2ByhiswillNo ratings yet
- Structural Stainless Steel Designing With Stainless Steel: Ing. Maarten FortanDocument153 pagesStructural Stainless Steel Designing With Stainless Steel: Ing. Maarten FortanJohn Philip Neri BesedillasNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document24 pagesSet 1TutorTutorNo ratings yet
- DesignMind Data WarehouseDocument31 pagesDesignMind Data WarehouseMark GinnebaughNo ratings yet
- RIZAL: INSPIRATION FOR A NEW GENERATIONDocument11 pagesRIZAL: INSPIRATION FOR A NEW GENERATIONErica B. DaclanNo ratings yet
- RAF Bomber Command March 1943Document4 pagesRAF Bomber Command March 1943catracho84No ratings yet
- Strategic Planning Assignment - TescoDocument16 pagesStrategic Planning Assignment - TescoKayode Trinity Omosebi100% (1)
- Brfo193 Radiotherapy Dose Fractionation Third-Edition PDFDocument137 pagesBrfo193 Radiotherapy Dose Fractionation Third-Edition PDFMed MedNo ratings yet
- 1z0 447 DemoDocument5 pages1z0 447 Demojosegitijose24No ratings yet
- Position Paper For The Art Controversy "Poleteismo" of Mideo CruzDocument2 pagesPosition Paper For The Art Controversy "Poleteismo" of Mideo CruzAalayah Gwendel Wayne CarumbaNo ratings yet
- Faktor OrganisasiDocument9 pagesFaktor OrganisasiNur Fatin NabilahNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument9 pages1 SMhasanuddinnst1No ratings yet
- Senior Power Apps Engineer JobDocument3 pagesSenior Power Apps Engineer JobMichałNo ratings yet
- Review of Dr. Mark Cheng's "Prehab-Rehab 101" SeriesDocument6 pagesReview of Dr. Mark Cheng's "Prehab-Rehab 101" SeriesWilliam TortorielloNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapKeith20% (5)
- Wma11 01 Que 20221011Document28 pagesWma11 01 Que 20221011Maks LubasNo ratings yet
- Timbering Week 5Document22 pagesTimbering Week 5FikaduKitessa0% (1)
- Balanced Scorecard ThesisDocument59 pagesBalanced Scorecard Thesisapi-3825626100% (5)
- Daniel J. Wood - Realm of The Vampire - History and The Undead-Galde Press (2013)Document156 pagesDaniel J. Wood - Realm of The Vampire - History and The Undead-Galde Press (2013)Jerry KanneNo ratings yet
- 286129Document23 pages286129Cristian WalkerNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Advanced Pattern Making - IDocument9 pages5.1 Advanced Pattern Making - IRisul Islam EmonNo ratings yet
- Lean Healthy Raw Food Winter RecipesDocument60 pagesLean Healthy Raw Food Winter RecipesKaio Sol100% (6)
- Romeo and Julliet - Close Read AnalysisDocument5 pagesRomeo and Julliet - Close Read Analysisapi-514407929No ratings yet
- Baxa Resumen PDFDocument12 pagesBaxa Resumen PDFChepe Camacho100% (3)
- Generic IOMMU APIsDocument2 pagesGeneric IOMMU APIsRajesh raviNo ratings yet
- Seagate WD Hard Drive Price List From Billion HoDocument4 pagesSeagate WD Hard Drive Price List From Billion HoALi RAzaNo ratings yet
- TECHNICALPAPER2Document8 pagesTECHNICALPAPER2spiderwebNo ratings yet
- SMS Security Android AppDocument8 pagesSMS Security Android AppSuman SouravNo ratings yet
- Holzma PR Hob and Ex Linger Enu 18533Document7 pagesHolzma PR Hob and Ex Linger Enu 18533esfandiar232477No ratings yet