Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Curve Sketching by Student
Curve Sketching by Student
Uploaded by
Laila Shawky0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThis document provides guidance on curve sketching by outlining key steps:
1) Define the domain and identify any x- or y-intercepts.
2) Determine if the function is even, odd, or neither based on its behavior around x = 0.
3) Check for vertical, horizontal, or oblique asymptotes by examining limits as x approaches infinite values.
4) Analyze the behavior of the first and second derivatives to find local extrema, points of inflection, and determine where the function is increasing/decreasing and concave up/down.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides guidance on curve sketching by outlining key steps:
1) Define the domain and identify any x- or y-intercepts.
2) Determine if the function is even, odd, or neither based on its behavior around x = 0.
3) Check for vertical, horizontal, or oblique asymptotes by examining limits as x approaches infinite values.
4) Analyze the behavior of the first and second derivatives to find local extrema, points of inflection, and determine where the function is increasing/decreasing and concave up/down.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCurve Sketching by Student
Curve Sketching by Student
Uploaded by
Laila ShawkyThis document provides guidance on curve sketching by outlining key steps:
1) Define the domain and identify any x- or y-intercepts.
2) Determine if the function is even, odd, or neither based on its behavior around x = 0.
3) Check for vertical, horizontal, or oblique asymptotes by examining limits as x approaches infinite values.
4) Analyze the behavior of the first and second derivatives to find local extrema, points of inflection, and determine where the function is increasing/decreasing and concave up/down.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
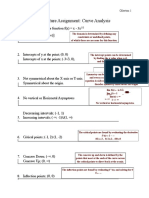
Curve sketching
1. Domain Df
Values of x where the function is defined
2. Y, X- axis intercepts
Y-intercepts, at X = 0
X-intercepts, at Y = 0
3. Symmetry “function is odd, even or neither nor”
The function is EVEN if f(X) = f(-X)
The function is ODD if f(X) = - f(-X)
If f(X) ≠ f(-X) or f(X) ≠ - f(-X) then the function is NEITHER EVEN NOR ODD
4. Asympotic lines
Asymptote lines: lines such that the distance between them and the curve approaches
ZERO as they move together to infinity.
1. Vertical asymptotes: there is a vertical asymptote at X = a
If limx→a+ f(x) = ∞ or limx→a- f(x) = ∞
OR limx→a+ f(x) = -∞ or limx→a- f(x) = -∞
2. Horizontal asymptotes: there is a horizontal asymptote at Y = L
If limx→∞ f(X) = L OR limx→ -∞ f(X) = L
3. Oblique asymptotes: the line Y = mX + c is a horizontal asymptote
If limx→∞ [ f(X) - ( mX + C )] = 0 OR limx→ -∞ [ f(X) - ( mX + C )] = 0
5. Behavior
a. Increasing, decreasing and local points
b. Concavity and infliction points
1. f`(X) = 0 and f`(X) undefined to get local points
2. Draw a number line and put the local points to find the intervals where the function is
increasing and decreasing
If f`(X) → -ve the function is decreasing
, f`(X) → +ve the function is increasing
3. f``(X) = 0 and f``(X) undefined to get infliction points
4. draw a number line and put the points to find the intervals where the function is
concave up and down
If f``(X) → -ve concave down
, f``(X) → +ve concave up
You might also like
- PDF Math 1210 Project 2Document4 pagesPDF Math 1210 Project 2api-259969905No ratings yet
- Limits Intuitive Definition To The Limit:: Calculus DifferentialDocument10 pagesLimits Intuitive Definition To The Limit:: Calculus DifferentialMarcela CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Math 150 Exam 1 Review SheetDocument3 pagesMath 150 Exam 1 Review SheetTuongVNguyenNo ratings yet
- 03 Rational FunctionsDocument37 pages03 Rational FunctionsJudy Ann ShengNo ratings yet
- X and Y-InterceptDocument21 pagesX and Y-InterceptjudeNo ratings yet
- Section 3.2 NotesDocument4 pagesSection 3.2 NotesJean GNo ratings yet
- Curve Sketching Is Another Practical Application of Differential CalculusDocument11 pagesCurve Sketching Is Another Practical Application of Differential CalculusAmmad ImamNo ratings yet
- Calculus I Formulas-Chapter-3-Dr. Wadii Hajji: 1 Steps To Graph A FunctionDocument1 pageCalculus I Formulas-Chapter-3-Dr. Wadii Hajji: 1 Steps To Graph A FunctionInesNo ratings yet
- 14 - Rational Function - MC - Guide and LabDocument13 pages14 - Rational Function - MC - Guide and LabElsa BrounsNo ratings yet
- Limits and Continuity 2.9Document3 pagesLimits and Continuity 2.9Johanna I. De Jesus MatosNo ratings yet
- EgricizimiDocument13 pagesEgricizimiBarış DuranNo ratings yet
- Continuity: X A X ADocument16 pagesContinuity: X A X Aluis calderonNo ratings yet
- Derivatives 1Document25 pagesDerivatives 1Krrje INo ratings yet
- Final Notes For AB and BCDocument16 pagesFinal Notes For AB and BCsapabapjava2012No ratings yet
- IvhanDocument59 pagesIvhanIvhani MaseleseleNo ratings yet
- Intercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Rational FunctionsDocument33 pagesIntercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Rational Functionsaiza100% (2)
- Graph Function DiffDocument6 pagesGraph Function DiffZain UlabideenNo ratings yet
- Calculus To First ExamDocument9 pagesCalculus To First ExamSteven WalkerNo ratings yet
- Limits and Continuity PDFDocument107 pagesLimits and Continuity PDFAnonymous 0MTQ0BNo ratings yet
- Appli CsDocument5 pagesAppli CshazrolNo ratings yet
- Graphing Rational FunctionsDocument21 pagesGraphing Rational FunctionsBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- Math Report - 041207Document13 pagesMath Report - 041207Gian AnireNo ratings yet
- UGCM1653 - Chapter 2 Calculus - 202001 PDFDocument30 pagesUGCM1653 - Chapter 2 Calculus - 202001 PDF木辛耳总No ratings yet
- Many FormulasDocument11 pagesMany FormulasDillep NandaNo ratings yet
- How To FP2 - Revision Notes: Rational FunctionsDocument5 pagesHow To FP2 - Revision Notes: Rational FunctionsTiara TatyanadewiNo ratings yet
- A) Graphs of Functions NotesDocument10 pagesA) Graphs of Functions NotesHaoyu WangNo ratings yet
- Introductory Calculus: Jacob LeeDocument14 pagesIntroductory Calculus: Jacob LeeMunmun BhadraNo ratings yet
- MATHS T STPM FUNCTIONSDocument41 pagesMATHS T STPM FUNCTIONSlimsiewthiang67% (3)
- Calculus: V V V V VDocument4 pagesCalculus: V V V V VYogesh NitNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 Topic 4Document9 pagesCalculus 1 Topic 4muradNo ratings yet
- PC Functions RationalDocument11 pagesPC Functions RationalHector R.No ratings yet
- RATIONAL LessonDocument31 pagesRATIONAL LessonChristian AcaylarNo ratings yet
- FAEN 101: Algebra: Dr. Joseph K. AnsongDocument20 pagesFAEN 101: Algebra: Dr. Joseph K. Ansongnimdie jacksonNo ratings yet
- 1385106121Document70 pages1385106121Abhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Infinite Limits: Right X Approaches 1 From The LeftDocument3 pages1.3 Infinite Limits: Right X Approaches 1 From The LeftFrancis Rey Bactol PilapilNo ratings yet
- Basic Cal - W4Document32 pagesBasic Cal - W4Norman LoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Quadratic Functions and ModelsDocument47 pages3.1 Quadratic Functions and ModelsLeonardo TorresNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 - Lecture 1Document32 pagesCalculus 1 - Lecture 1Trần Nhật DươngNo ratings yet
- Convex FunctionsDocument9 pagesConvex Functionseustachy2No ratings yet
- Theorems On Limits at InfinityDocument1 pageTheorems On Limits at Infinitysiyensiya at matematikaNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Functions Their GraphsDocument40 pagesPolynomial Functions Their GraphsMaria MagdalenaNo ratings yet
- Function PDFDocument3 pagesFunction PDFDany DwNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Grade 10 MathematicsDocument2 pagesLesson 6 Grade 10 MathematicsMarieanne SantosNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Polynomial Functions: Grade 10 MathematicsDocument2 pagesGraphs of Polynomial Functions: Grade 10 MathematicsMarieanne SantosNo ratings yet
- Local and Absolute Extremum: y FX FCDocument19 pagesLocal and Absolute Extremum: y FX FCcikguhafidzuddinNo ratings yet
- Vertical Horizontal PDFDocument8 pagesVertical Horizontal PDFRj LegoreNo ratings yet
- Inequalities and Functions 2 - AdanteDocument11 pagesInequalities and Functions 2 - AdanteKarenNo ratings yet
- TRIGODocument7 pagesTRIGOizzatisafeeNo ratings yet
- M113 (Calculus) FormulasDocument68 pagesM113 (Calculus) FormulasTESLA - Harison NartatesNo ratings yet
- Handout 4 - LimitsDocument5 pagesHandout 4 - LimitsMarvin Yebes ArceNo ratings yet
- Introduction: in Nearly Every Physical Phenomenon We Observe That One Quantity DependsDocument10 pagesIntroduction: in Nearly Every Physical Phenomenon We Observe That One Quantity DependsbushraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes by Dr. Abdul Rauf NizamiDocument14 pagesLecture Notes by Dr. Abdul Rauf NizamiHafiz HammadNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Analysis of Functions Increasing and Decreasing FunctionsDocument7 pages4.1 Analysis of Functions Increasing and Decreasing FunctionsAnemesh BaruaNo ratings yet
- 15 Exponential Growth DecayDocument17 pages15 Exponential Growth Decayapi-276566085No ratings yet
- Curve TracingDocument82 pagesCurve TracingDr-Preeti JainNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document59 pagesCH 5Wudneh Amare0% (1)
- Limit and Continuity PDFDocument46 pagesLimit and Continuity PDFrajesh laddhaNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)