Professional Documents
Culture Documents
All About Kenya
Uploaded by
helpertech830 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesAll About Kenya
Uploaded by
helpertech83Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
All About Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya (Swahili: Jamhuri ya
Kenya), is a country in East Africa. A member of the African Union
with a population of more than 47.6 million in the 2019 census, Kenya
is the 28th most populous country in the world and 7th most populous
in Africa. Kenya's capital and largest city is Nairobi, while its oldest
and second largest city, is the major port city
of Mombasa, situated on Mombasa Island in the Indian Ocean and
the surrounding mainland. Mombasa was the capital of the British
East Africa Protectorate, which included most of what is now Kenya
and southwestern Somalia, from 1889 to 1907. Other important cities
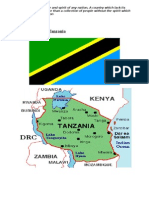
include Kisumu and Nakuru. Kenya is bordered by South Sudan to the
northwest, Ethiopia to the north, Somalia to the east, Uganda to the
west, Tanzania to the south, and the Indian Ocean to the southeast.
Kenya's geography, climate and population vary widely, ranging from
cold snow-capped mountaintops (Batian, Nelion and Point Lenana on
Mount Kenya) with vast surrounding forests, wildlife and fertile
agricultural reg]ions to temperate climates in western and rift valley
counties and further on to dry less fertile arid and semi-arid areas and
absolute deserts (Chalb
i Desert and Nyiri Desert).
Kenya's earliest inhabitants were hunter-gatherers, like the
present-day Hadza people. According to archaeological dating of
associated artefacts and skeletal material, Cushitic speakers first
settled in Kenya's lowlands between 3,200 and 1,300 BC , a phase
known as the Lowland Savanna Pastoral Neolithic. Nilotic-speaking
pastoralists (ancestral to Kenya's Nilotic speakers) began migrating
from present-day South Sudan into Kenya around 500 BC . Bantu
people settled at the coast and the interior between 250 BC and 500
AD.
European contact began in 1500 AD with the Portuguese Empire, and
effective colonisation of Kenya began in the 19th century during the
European exploration of the interior. Modern-day Kenya emerged
from a protectorate established by the British Empire in 1895 and the
subsequent Kenya Colony, which began in 1920. Numerous disputes
between the UK and the colony led to the Mau Mau revolution, which
began in 1952, and the declaration of independence in 1963. After
independence, Kenya remained a member of the Commonwealth of
Nations. The current constitution was adopted in 2010 and replaced
the 1963 independence constitution.
Kenya is a presidential representative democratic republic, in which
elected officials represent the people and the president is the head of
state and government. Kenya is a member of the United Nations, the
Commonwealth, World Bank, International Monetary Fund,
COMESA, International Criminal Court, as well as other
international organisations. With a GNI of 1,840, Kenya is a
lower-middle-income economy. Kenya's economy is the second largest
in eastern and central Africa, after Ethiopia, with Nairobi serving as a
major regional commercial hub. Agriculture is the largest sector; tea
and coffee are traditional cash crops, while fresh flowers are a
fast-growing export. The service industry is also a major economic
driver, particularly tourism. Kenya is a member of the East African
Community trade bloc, though some international trade organisations
categorise it as part of the Greater H orn of Africa. Africa is Kenya's
largest export market, followed by the European Union.
You might also like
- UFA Orange Book CompleteDocument212 pagesUFA Orange Book CompleteThe Estimator67% (3)
- Zambias Challenges at IndependenceDocument7 pagesZambias Challenges at Independencemuna moono100% (2)
- False Nationalism False InternationalismDocument211 pagesFalse Nationalism False InternationalismMofabioNo ratings yet
- Subject: Political Science Iii Course: Ba LLB Semester Iii Lecturer: Ms. Deepika Gahatraj Module: Module I, Origin of International Relation As A Discipline Nature and Scope Approaches To StudyDocument4 pagesSubject: Political Science Iii Course: Ba LLB Semester Iii Lecturer: Ms. Deepika Gahatraj Module: Module I, Origin of International Relation As A Discipline Nature and Scope Approaches To StudyÁř RehmanNo ratings yet
- KenyaDocument1 pageKenyaJOYCENo ratings yet
- KenyaDocument11 pagesKenyaMário LealNo ratings yet
- Kenya and South Africa: East and Southern African NationsDocument3 pagesKenya and South Africa: East and Southern African NationsJoshua NituralNo ratings yet
- Geography: East-Central Africa South of Sudan, North of Uganda and Kenya, West of EthiopiaDocument13 pagesGeography: East-Central Africa South of Sudan, North of Uganda and Kenya, West of Ethiopiayen yenNo ratings yet
- Kenia HistoryDocument26 pagesKenia HistoryAlejandro Carlos CaleroNo ratings yet
- Tanzania (Tanzania (Document2 pagesTanzania (Tanzania (Andrei Sergiu PleșcaNo ratings yet
- Kenya (: ListenDocument12 pagesKenya (: ListenLaura Maria GalanNo ratings yet
- Kenya: Historical BackgroundDocument7 pagesKenya: Historical BackgroundLunaNo ratings yet
- South Africa Final VersionDocument3 pagesSouth Africa Final VersionValentina ReynaNo ratings yet
- Tanzania's History, Geography, Wildlife and GovernmentDocument34 pagesTanzania's History, Geography, Wildlife and GovernmentJohnBenardNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Nigeria's History, People and EconomyDocument34 pagesIntroduction to Nigeria's History, People and Economykrishna yadavNo ratings yet
- Kenya ColonizationDocument6 pagesKenya ColonizationFarrah EssamNo ratings yet
- TanDocument7 pagesTanAnil KakdeNo ratings yet
- Acea TanzaniaDocument29 pagesAcea TanzaniaBabu Wambura100% (1)
- Philippines (Filipino: Republika NG Pilipinas) ,: ListenDocument1 pagePhilippines (Filipino: Republika NG Pilipinas) ,: ListenpogchampNo ratings yet
- Pestel KeniaDocument5 pagesPestel KeniaSiegel TomNo ratings yet
- Ben inDocument4 pagesBen inBen'Esson Isaac-laleNo ratings yet
- Philippines History, Geography, and Culture in 40 CharactersDocument1 pagePhilippines History, Geography, and Culture in 40 CharactersffNo ratings yet
- Kenya Brief Description: (CITATION BBC181 /L 1033)Document10 pagesKenya Brief Description: (CITATION BBC181 /L 1033)Melchor Sumaylo PragaNo ratings yet
- Indonesia (: - DƏ - ZHƏ - Doh - Zee-ƏDocument2 pagesIndonesia (: - DƏ - ZHƏ - Doh - Zee-ƏYoga Pranata SuharyaNo ratings yet
- The Catholic University of Eastern Africa Faculty of Law EAC Assignment: Presented By:Robin Muthomi Mutiga Registration Number:1033021Document19 pagesThe Catholic University of Eastern Africa Faculty of Law EAC Assignment: Presented By:Robin Muthomi Mutiga Registration Number:1033021robin muthomiNo ratings yet
- Oxford Business Group - Indonesia Report 2012Document5 pagesOxford Business Group - Indonesia Report 2012Oxford Business GroupNo ratings yet
- Tanzania: United Republic of TanzaniaDocument6 pagesTanzania: United Republic of TanzaniaSarah SullivanNo ratings yet
- KenyaDocument46 pagesKenyaPranav Deshmukh0% (1)
- IndonesiaDocument23 pagesIndonesiaEarl TrinidadNo ratings yet
- BotswanaDocument5 pagesBotswanaadrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- Nigeria NewsDocument3 pagesNigeria Newsnicolasdelafuente07No ratings yet
- CambodiaDocument8 pagesCambodiaAntonette Aglanang BusacayNo ratings yet
- Las Islas FilipinasDocument2 pagesLas Islas Filipinasewe female sheepNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Is An Archipelago Comprising Thousands of IslandsDocument1 pageIndonesia Is An Archipelago Comprising Thousands of IslandsMartin SianturiNo ratings yet
- ESSAYDocument19 pagesESSAYSANDRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Southeast Asia An Overview 2017Document48 pagesChapter 1 Southeast Asia An Overview 2017ibudanish79No ratings yet
- Section 1: Physical Geography: Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesSection 1: Physical Geography: Chapter SummaryKalorina0No ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHY OF BENINDocument5 pagesGEOGRAPHY OF BENINRit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- UgandaDocument1 pageUgandaMzee KodiaNo ratings yet
- NigeriaDocument44 pagesNigeriaiorga10No ratings yet
- The Impact of Colonialism To Zambia Clas PDFDocument15 pagesThe Impact of Colonialism To Zambia Clas PDFEdith ChishimbaNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia Kampala::: +256: 241.038 KM : Ugandan Shilling:: 37,58 Milioane (2013) : Limba Engleză, Limba SwahiliDocument1 pageWikipedia Kampala::: +256: 241.038 KM : Ugandan Shilling:: 37,58 Milioane (2013) : Limba Engleză, Limba SwahiliHilitanu TeoNo ratings yet
- About KenyaDocument24 pagesAbout KenyaMariana MouraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For A History of KenyaDocument10 pagesLecture Notes For A History of KenyaSaina KennethNo ratings yet
- PhilipinesDocument2 pagesPhilipinesAvaNo ratings yet
- Country Studies6Document2 pagesCountry Studies6DokhnadzesesiliaNo ratings yet
- Kenya 2Document4 pagesKenya 2api-315976838No ratings yet
- History of Nigerian PeopleDocument31 pagesHistory of Nigerian PeopleDavid OkoyeNo ratings yet
- COASTAL States of West AfricaDocument10 pagesCOASTAL States of West AfricaZak StoophNo ratings yet
- History of KenyaDocument31 pagesHistory of KenyaCintia Delfina NelsonNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia: A Brief History and Overview (39 charactersDocument1 pageEthiopia: A Brief History and Overview (39 characterslukas_doniNo ratings yet
- Landlocked Country Addis Ababa: Homo SapiensDocument1 pageLandlocked Country Addis Ababa: Homo Sapienslukas_doniNo ratings yet
- Internation Marketing AssDocument25 pagesInternation Marketing AssBeki SafayiNo ratings yet
- Information of PhilippinesDocument6 pagesInformation of PhilippinesHamza SheerazNo ratings yet
- Philippines (Filipino: Republika NG Pilipinas) ,: "Philippine" Redirects Here. For The Town in The Netherlands, SeeDocument1 pagePhilippines (Filipino: Republika NG Pilipinas) ,: "Philippine" Redirects Here. For The Town in The Netherlands, SeeJullia Marie RosalinasNo ratings yet
- Philippines (Filipino: Republika NG Pilipinas) ,: "Philippine" Redirects Here. For The Town in The Netherlands, SeeDocument1 pagePhilippines (Filipino: Republika NG Pilipinas) ,: "Philippine" Redirects Here. For The Town in The Netherlands, SeeJullia Marie RosalinasNo ratings yet
- Angola and TaiwanDocument4 pagesAngola and TaiwanBanggayNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument265 pagesChapter IIbrianpdNo ratings yet
- GST 103-1Document9 pagesGST 103-1j9927091No ratings yet
- Tanzania (Tanzania (: Homo Homo Erectus Homo SapiensDocument4 pagesTanzania (Tanzania (: Homo Homo Erectus Homo SapiensrNo ratings yet
- Exotic Locations: Pavel Adrian & Bucica ConstantinDocument9 pagesExotic Locations: Pavel Adrian & Bucica ConstantinPavelF.AdrianNo ratings yet
- Animal Farm Essay - Structure and Sample EssayDocument3 pagesAnimal Farm Essay - Structure and Sample Essayruthmahase12No ratings yet
- Vật Lí Đại Cương-Tập 1-Trần Ngọc Hợi, Nguyễn Văn Thiều-Cơ-nhiệtDocument515 pagesVật Lí Đại Cương-Tập 1-Trần Ngọc Hợi, Nguyễn Văn Thiều-Cơ-nhiệtTân NhậtNo ratings yet
- Desi Indian Call Girls in Dubai 0564419067 Call NowDocument2 pagesDesi Indian Call Girls in Dubai 0564419067 Call NowIndian Call Girls In DubaiNo ratings yet
- Uganda Election Trends Since 1958Document8 pagesUganda Election Trends Since 1958Waidembe YusufuNo ratings yet
- Rizal's Contradictory Stance on the Philippine RevolutionDocument14 pagesRizal's Contradictory Stance on the Philippine RevolutionShishie Bodiongan100% (1)
- Polk County BallotDocument2 pagesPolk County BallotinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Jaap Bakema and The Open Society: April 2018Document13 pagesJaap Bakema and The Open Society: April 2018jose0% (1)
- The Kashmir Conflict: A Kashmiri Perspective: by Mehraj HajniDocument3 pagesThe Kashmir Conflict: A Kashmiri Perspective: by Mehraj HajniParul RajNo ratings yet
- Peace and War - A Theory of International Relations (PDFDrive)Document847 pagesPeace and War - A Theory of International Relations (PDFDrive)Vincit Omnia VeritasNo ratings yet
- Nagpur School Education Options FormDocument1 pageNagpur School Education Options FormPNo ratings yet
- Titles Included in PassportsDocument4 pagesTitles Included in PassportsGorka A.No ratings yet
- MPTC Pithapuram - MergedDocument7 pagesMPTC Pithapuram - MergedKamalakar BandiNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document11 pagesCH 1Enas LotfyNo ratings yet
- Women Empowerment PPT - SD - KounainDocument16 pagesWomen Empowerment PPT - SD - KounainTajuddin ShaikNo ratings yet
- Bombay High Court Judgment Impacts RBI EmployeesDocument32 pagesBombay High Court Judgment Impacts RBI EmployeesVilas_123No ratings yet
- 12345Document5 pages12345Kristine Kate Estrada SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Senate Committee 2011Document9 pagesSenate Committee 2011Etefia EtefiaNo ratings yet
- Test Term in Ale Bac Blan Southern Voices Bis Answer KeyDocument8 pagesTest Term in Ale Bac Blan Southern Voices Bis Answer KeyAngel Angeleri-priftis.No ratings yet
- Signatories Vs RCEPDocument2 pagesSignatories Vs RCEPRapplerNo ratings yet
- Britain's Queen Elizabeth Dies Aged 96Document1 pageBritain's Queen Elizabeth Dies Aged 96Eric HuangNo ratings yet
- English Advanced Test 1Document5 pagesEnglish Advanced Test 1Thành ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Notions Film Viewing Guide SP22Document2 pagesEthnic Notions Film Viewing Guide SP22elise martelNo ratings yet
- Đề 203Document6 pagesĐề 203Plaza StoneNo ratings yet
- 5) Political GlobalizationDocument73 pages5) Political GlobalizationBea Nicole EstradaNo ratings yet
- PPG-Test Question 1st QTR and Key AnswerDocument4 pagesPPG-Test Question 1st QTR and Key Answergelo100% (1)
- Political legitimacy types and formsDocument12 pagesPolitical legitimacy types and formsKrizzha Nicole PerezNo ratings yet
- List of Ethnic Slurs: Main MenuDocument104 pagesList of Ethnic Slurs: Main MenuJesse MNo ratings yet