Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hepatic Disorders
Uploaded by
neyralorannn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesCirrhosis of the liver is late stage liver disease where scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, blocking blood flow through the liver and slowing nutrient and drug processing. Cirrhosis has many causes like viruses, toxic metals, and autoimmune liver disease where the immune system attacks the liver. Symptoms include yellow skin, fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, itching, and easy bruising. Treatment aims to prevent further liver damage, treat complications, and detect liver cancer early. Hepatitis is liver inflammation sometimes caused by viruses, which can lead to cirrhosis. It may cause flu-like symptoms along with loss of appetite, dark urine, and yellow eyes and skin. Diagnosis involves blood tests, liver biopsy,
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCirrhosis of the liver is late stage liver disease where scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, blocking blood flow through the liver and slowing nutrient and drug processing. Cirrhosis has many causes like viruses, toxic metals, and autoimmune liver disease where the immune system attacks the liver. Symptoms include yellow skin, fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, itching, and easy bruising. Treatment aims to prevent further liver damage, treat complications, and detect liver cancer early. Hepatitis is liver inflammation sometimes caused by viruses, which can lead to cirrhosis. It may cause flu-like symptoms along with loss of appetite, dark urine, and yellow eyes and skin. Diagnosis involves blood tests, liver biopsy,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesHepatic Disorders
Uploaded by
neyralorannnCirrhosis of the liver is late stage liver disease where scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, blocking blood flow through the liver and slowing nutrient and drug processing. Cirrhosis has many causes like viruses, toxic metals, and autoimmune liver disease where the immune system attacks the liver. Symptoms include yellow skin, fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, itching, and easy bruising. Treatment aims to prevent further liver damage, treat complications, and detect liver cancer early. Hepatitis is liver inflammation sometimes caused by viruses, which can lead to cirrhosis. It may cause flu-like symptoms along with loss of appetite, dark urine, and yellow eyes and skin. Diagnosis involves blood tests, liver biopsy,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
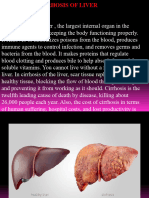
Cirrhosis of the liver is late stage liver disease
in which scar tissue appears in place of healthy
liver tissue.
The scar tissue blocks the flow of blood through
the liver and slows the processing of nutrients,
hormones and drugs.
There are many causes of cirrhosis, including
viruses, toxic metals and autoimmune
(оутоимьюн) liver disease in which the body's
immune system attacks the liver.
Patients with cirrhosis may have few or no
symptoms and signs of liver disease.
Some of the more common symptoms and
signs of cirrhosis include: yellowing of the skin;
fatigue (фетіг); weakness; loss of appetite;
itching; easy bruising from decreased production
of blood clotting factors by the diseased liver.
Treatment of cirrhosis is designed to prevent
further damage to the liver, treat complications
of cirrhosis, and preventing or detecting liver
cancer early.
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. It may
be caused by drugs, alcohol use, or certain
medical conditions. But in most cases, it's caused
by a virus.
Initial features are of nonspecific flu-like
symptoms, common to almost all acute viral
infections and may include malaise, muscle
and joint aches, fever, nausea or vomiting,
diarrhea, and headache.
More specific symptoms, which can be present
in acute hepatitis from any cause, are: loss of
appetite, aversion to smoking among smokers,
dark urine, yellowing of the eyes and skin and
abdominal discomfort.
Diagnosis is made by assessing an individual's
symptoms, physical exam, and medical history,
in conjunction with blood tests, liver biopsy, and
imaging. Blood testing includes blood chemistry,
liver enzymes, serology and nucleic acid testing.
You might also like
- 4 Stages of Cirrhosis of The Liver 18 Symptoms, CDocument9 pages4 Stages of Cirrhosis of The Liver 18 Symptoms, CRammy KhanNo ratings yet
- What Is Sclerosis of The LiverDocument2 pagesWhat Is Sclerosis of The LiverLuinel PlasenciaNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis FinalDocument16 pagesLiver Cirrhosis FinalAmanda ScarletNo ratings yet
- PH Le BotomyDocument15 pagesPH Le BotomyPatty MenéndezNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis: On This PageDocument23 pagesCirrhosis: On This PageHasna FauziyahNo ratings yet
- Chirosis HepaticDocument8 pagesChirosis HepaticCikalHrNo ratings yet
- Histopathology of Liver Cirrhosis and Pancreas in DiabetesDocument7 pagesHistopathology of Liver Cirrhosis and Pancreas in DiabetesJagadeesh K GaganNo ratings yet
- ColDocument40 pagesCol12F 24 Renu SinghNo ratings yet
- Primary Billiary CirrhosisDocument6 pagesPrimary Billiary CirrhosisElvantia MarilynNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis CaseDocument8 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Casemarlx5No ratings yet
- Nephritis by Triveni SidhaDocument23 pagesNephritis by Triveni SidhaTriveni SidhaNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Is A Late Stage of Scarring (Fibrosis) of The Liver Caused byDocument7 pagesCirrhosis Is A Late Stage of Scarring (Fibrosis) of The Liver Caused byAnne MaputiNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument7 pagesHepatitisPriyaNo ratings yet
- My Case Study of Liver CirrhosisDocument13 pagesMy Case Study of Liver Cirrhosisdysphile100% (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis TreatmentDocument5 pagesLiver Cirrhosis TreatmentPrajith NairNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of The LiverDocument4 pagesCirrhosis of The LiverDaphineNo ratings yet
- What Is Kidney MalfunctioningDocument7 pagesWhat Is Kidney MalfunctioningPooja SinghNo ratings yet
- Liver DiseasesDocument4 pagesLiver DiseasesApril Kate BanagodosNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument4 pagesLiver CirrhosisromyNo ratings yet
- Chole StasisDocument3 pagesChole StasisMichelle G. AVENANo ratings yet
- Drug Induced Liver DiseaseDocument15 pagesDrug Induced Liver DiseaseMUGHALNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesLiver CirrhosisAzette Agpi100% (3)
- Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesLiver CirrhosisTiffany AdriasNo ratings yet
- AlcoholDocument3 pagesAlcoholsionveuxonpeuxNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis: Classification and External ResourcesDocument7 pagesHepatitis: Classification and External ResourcesWisnu AdiputraNo ratings yet
- Preventive Health Screen - RecommendationsDocument17 pagesPreventive Health Screen - Recommendationspalavi_kharadeNo ratings yet
- ChatPDF-Hepatobiliary Diseases 3Document4 pagesChatPDF-Hepatobiliary Diseases 3AmirahNo ratings yet
- Chronic Glumerulonephritis HandoutsDocument8 pagesChronic Glumerulonephritis HandoutsLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- Lupusand GIbleedDocument2 pagesLupusand GIbleedAshley Noonan SteereNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis in ChildrenDocument4 pagesCirrhosis in ChildrenFakhri DesktopNo ratings yet
- UTIDocument3 pagesUTIEldrine Joy PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Hepatitis HandoutDocument2 pagesAutoimmune Hepatitis HandoutClarisse SantosNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis - Wikipedia, The ...Document11 pagesCirrhosis - Wikipedia, The ...PrakashNo ratings yet
- Non Viral HepatitisDocument8 pagesNon Viral HepatitisKeith Wesley YbutNo ratings yet
- Project in Mapeh (Health)Document8 pagesProject in Mapeh (Health)guache warrinNo ratings yet
- Case Study Liver CirrhosisDocument20 pagesCase Study Liver CirrhosisFate ZephyrNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument24 pagesHepatitisEric PeprahNo ratings yet
- Kidney DisorderDocument5 pagesKidney DisorderTWINKLE MAE EGAYNo ratings yet
- Nikhilesh Choudhury 2023Document18 pagesNikhilesh Choudhury 2023palashshome091No ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of Liver: Shemil Clinical Instructor DmwimsDocument25 pagesCirrhosis of Liver: Shemil Clinical Instructor DmwimsSrihari DivyaNo ratings yet
- Brief Background of The Disease: Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesBrief Background of The Disease: Liver CirrhosisLyra Lustre RNNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument5 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseFaye R. PelayoNo ratings yet
- Nephritis: Alport Syndrome, or Hereditary NephritisDocument3 pagesNephritis: Alport Syndrome, or Hereditary NephritisSuneel Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Liver FailureDocument4 pagesChronic Liver FailureJasmine Faith SilvaNo ratings yet
- Summary About Liver CirrhosisDocument1 pageSummary About Liver CirrhosisShaina MentangNo ratings yet
- Conditions and DiseasesDocument6 pagesConditions and Diseasesapi-3709951No ratings yet
- 10 Nursing Care Plan For Liver CirrhosisDocument1 page10 Nursing Care Plan For Liver CirrhosisAngie Mandeoya0% (1)
- Non Communicable Disease Grade 7Document4 pagesNon Communicable Disease Grade 7Joshua RamirezNo ratings yet
- Liver Disease: Overview of The LiverDocument6 pagesLiver Disease: Overview of The LiverMustafa AlmasoudiNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of The Liver: CausesDocument6 pagesCirrhosis of The Liver: CausespakdejackNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument4 pagesHepatitisAlambusha ShuklaNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument180 pagesUrinalysisLiza Hutahaean100% (1)
- Pregnancy: FatigueDocument5 pagesPregnancy: FatigueRizza IslaNo ratings yet
- Urine Test Strips and Microscopy: Compendium of UrinalysisDocument180 pagesUrine Test Strips and Microscopy: Compendium of UrinalysisLory LaneNo ratings yet
- Liver Disease - WikipediaDocument61 pagesLiver Disease - WikipediaJamesNo ratings yet
- Tic Biliary DisordersDocument11 pagesTic Biliary Disorderspipoy18No ratings yet
- Chronic-Glomerulonephriti 8743411Document13 pagesChronic-Glomerulonephriti 8743411Shravan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Group 13 Case Presentation Output Liver CirrhosisDocument36 pagesGroup 13 Case Presentation Output Liver CirrhosisEm ArellanoNo ratings yet
- GlomerulonephritisDocument2 pagesGlomerulonephritisHenry KaweesaNo ratings yet
- SurgeryDocument2 pagesSurgeryneyralorannnNo ratings yet
- Functions of HormonesDocument2 pagesFunctions of HormonesneyralorannnNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Physiology of Endocrine SystemneyralorannnNo ratings yet
- Brain. Spinal CordDocument1 pageBrain. Spinal CordneyralorannnNo ratings yet
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (39)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (83)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeFrom EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (267)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- I Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionFrom EverandI Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (256)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (61)