Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Master Data
Uploaded by
tosik337210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesMaster Data
Uploaded by
tosik33721Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
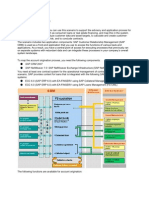
Master Data
In SAP SD, master data plays a crucial role in various business processes,
including sales and distribution. Here's an overview of the key aspects of
master data in SAP SD and how they are created and maintained:
Customer Master Data:
Customer master data contains information about your customers, including
their name, address, contact details, payment terms, shipping preferences, etc.
Creating and maintaining customer master data is essential for processing
sales orders, invoicing, and managing customer relationships.
Here are the steps to create and maintain customer master data:
Navigate to the SAP IMG menu path: SPRO > Cross-Application Components
> SAP Business Partner > Customers > Customer Accounts > Master Data >
Prepare Screen Layout of Customer Master Data.
Define customer account groups to specify the attributes and fields relevant
to different types of customers.
Create customer master records using transaction code XD01 (for creating
individual customer) or XD02 (for changing existing customer master records).
Enter relevant details such as customer name, address, contact information,
payment terms, etc.
Save the customer master record.
Material Master Data:
Material master data contains information about the products or materials
that your company sells or distributes.
It includes details such as material description, unit of measure, pricing
information, inventory levels, etc.
Maintaining accurate material master data is crucial for inventory
management, pricing, and order processing.
Here are the steps to create and maintain material master data:
Navigate to the SAP IMG menu path: SPRO > Logistics - General > Material
Master > Material > Create, Change, Display.
Define material types and material groups to classify materials based on
characteristics such as product category, industry sector, etc.
Create material master records using transaction code MM01 (for creating
materials) or MM02 (for changing existing material master records).
Enter relevant details such as material description, base unit of measure,
pricing information, etc.
Save the material master record.
Pricing Conditions and Condition Records:
Pricing conditions in SAP SD determine the prices and discounts applied to
sales transactions.
Condition records are used to maintain pricing conditions, including prices,
discounts, surcharges, etc., for different combinations of materials, customers,
and sales organizations.
Here are the steps to maintain pricing conditions and condition records:
Navigate to the SAP IMG menu path: SPRO > Sales and Distribution > Basic
Functions > Pricing > Pricing Control > Define Condition Types.
Define condition types to represent different pricing elements such as net
price, discounts, taxes, etc.
Configure pricing procedures to determine how pricing conditions are
calculated and applied in sales documents.
Maintain condition records using transaction code VK11 (for creating
condition records) or VK12 (for changing existing condition records).
Enter relevant details such as condition type, material/customer/sales
organization combination, pricing details, validity period, etc.
Save the condition record.
By creating and maintaining accurate customer master data, material master
data, and pricing conditions in SAP SD, you ensure smooth execution of sales
and distribution processes, accurate pricing, and effective customer
management.
You might also like
- Most Important Determinations in Sap SDDocument10 pagesMost Important Determinations in Sap SDkarthikbjNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Interview Questions & Answers With ExplanationsDocument116 pagesSAP SD Interview Questions & Answers With ExplanationsMiguel Alberto Maldonado Gonzalez100% (1)
- Account DeterminationDocument14 pagesAccount DeterminationManiJyotiNo ratings yet
- Master Data in SAPDocument79 pagesMaster Data in SAPSatyendra Gupta75% (4)
- SAP SD Training DocumentDocument24 pagesSAP SD Training DocumentgeekorbitNo ratings yet
- SD GuideDocument116 pagesSD GuidevenkatNo ratings yet
- Pre Reqisites To SD FI IntegrationDocument5 pagesPre Reqisites To SD FI IntegrationraghuNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Interview Questions & Answers With ExplanationsDocument116 pagesSAP SD Interview Questions & Answers With ExplanationsGiri DharNo ratings yet
- SAP Key PointsDocument74 pagesSAP Key Pointsimmanial yamarthi100% (2)
- Sap Fi - SDDocument30 pagesSap Fi - SDRahul singhNo ratings yet
- SAP SD TutorialDocument282 pagesSAP SD Tutorialalbertoca990100% (1)
- SAP Material Master For Beginners: Learn MM in 1 DayDocument20 pagesSAP Material Master For Beginners: Learn MM in 1 DayAshutosh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Maintain Credit Limit For Customers in SAPDocument6 pagesMaintain Credit Limit For Customers in SAPAyan PahariNo ratings yet
- Master Data in SDDocument40 pagesMaster Data in SDSoumabha Chatterjee100% (1)
- Ultimate Electronics - Book - CircuitLabDocument3 pagesUltimate Electronics - Book - CircuitLabEldon50% (2)
- SAP SD Questions & AnswersDocument220 pagesSAP SD Questions & Answersshuku03No ratings yet
- Sap MMDocument54 pagesSap MMmkumarshahi80% (5)
- Fuses f150Document7 pagesFuses f150ORLANDONo ratings yet
- RevAcctDet - SAP SDDocument66 pagesRevAcctDet - SAP SDHarik CNo ratings yet
- Sap SD MateriallDocument131 pagesSap SD MateriallArbind Padhy100% (1)
- (Ebook) Reliability and Risk Issues in Large Scale Safety-Critical Digital Control Systems, Springer 2009Document314 pages(Ebook) Reliability and Risk Issues in Large Scale Safety-Critical Digital Control Systems, Springer 2009Lake HouseNo ratings yet
- Fico and SD NotesDocument29 pagesFico and SD NotesViswanadha Sai MounikaNo ratings yet
- Materialmasterdatanew 160615124527Document36 pagesMaterialmasterdatanew 160615124527anwardwh5895No ratings yet
- Sap SD Interview QustionsDocument227 pagesSap SD Interview QustionsNaveen Kumar100% (2)
- Business PartnerDocument2 pagesBusiness PartnerAnand PatwariNo ratings yet
- How Does FI Integrate With SD and What Is Their Account DeterminationDocument11 pagesHow Does FI Integrate With SD and What Is Their Account DeterminationBiranchi MishraNo ratings yet
- SD MM Fi IntegrationDocument6 pagesSD MM Fi IntegrationSidhish KumarNo ratings yet
- Sap SD Faq PDFDocument116 pagesSap SD Faq PDFUmesh SambareNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumeSaharsh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Account OriginationDocument23 pagesAccount Originationsans1234No ratings yet
- SD QuestionsDocument227 pagesSD QuestionschaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Sap SD All DocumentsDocument6 pagesSap SD All Documentsrohit12345a0% (1)
- Sap SDDocument3 pagesSap SDZrNo ratings yet
- KT Review PresentationDocument23 pagesKT Review PresentationfonakNo ratings yet
- Sap CustomerDocument1 pageSap CustomerSriramaChandra MurthyNo ratings yet
- Sap SD Sap ErpDocument2 pagesSap SD Sap ErpAnjan KumarNo ratings yet
- SAP SD - SyllabusDocument2 pagesSAP SD - Syllabustosik33721No ratings yet
- Customer MasterDocument15 pagesCustomer Masterttraining225No ratings yet
- CMD & Cmir V1Document45 pagesCMD & Cmir V1tmaha87No ratings yet
- BP Role in CVDocument8 pagesBP Role in CVJancy SunishNo ratings yet
- Faq SDDocument2 pagesFaq SDRonnie SNo ratings yet
- Sales: SAP - Customizing GuideDocument5 pagesSales: SAP - Customizing GuideJosé FaiaNo ratings yet
- How To Define Pricing Procedure Determination in SAP SDDocument5 pagesHow To Define Pricing Procedure Determination in SAP SDYasmine ArabNo ratings yet
- Define Sales Order Reasons in Sap PDFDocument4 pagesDefine Sales Order Reasons in Sap PDFmarcosNo ratings yet
- Master DataDocument9 pagesMaster DataasifmubbuNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Interview Qns and AnsDocument10 pagesSAP SD Interview Qns and Ansgvrao233No ratings yet
- Sap Subject Project MaterialDocument233 pagesSap Subject Project MaterialpavanNo ratings yet
- Master Data in Materials Management: Vendor Master Material Master Service MasterDocument2 pagesMaster Data in Materials Management: Vendor Master Material Master Service MasterHafiz Muhammad AzamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.sap SDDocument29 pagesChapter 1.sap SDNabanita DasNo ratings yet
- Group Members: Nakul Agarwal 10FN-065 Pranshu Todaria 10DM-101 Mayank Kapur 10FN-059 Rahul Mahajan 10DM-195 Nachiappan PL 10FN-063Document68 pagesGroup Members: Nakul Agarwal 10FN-065 Pranshu Todaria 10DM-101 Mayank Kapur 10FN-059 Rahul Mahajan 10DM-195 Nachiappan PL 10FN-063Pranshu TodariaNo ratings yet
- Account Assignment CategoryDocument8 pagesAccount Assignment Categoryafmojdevn100% (1)
- Business Partner Master Data - Its Objective Is To Record and Retrieve BusinessDocument2 pagesBusiness Partner Master Data - Its Objective Is To Record and Retrieve BusinessAnjelainePinedaNo ratings yet
- SAP UnderstandingDocument5 pagesSAP UnderstandingSanchit BagaiNo ratings yet
- 7NAW To Be - Customer MasterDocument15 pages7NAW To Be - Customer MastersivasivasapNo ratings yet
- Devaraj SapDocument4 pagesDevaraj SapsekharsapindiaNo ratings yet
- Din cr100Document27 pagesDin cr100ThinkerNo ratings yet
- Archiving Object MMDocument4 pagesArchiving Object MMmail_girish20029690No ratings yet
- SAP SD - Define Access Sequences in SAPDocument5 pagesSAP SD - Define Access Sequences in SAPmboll14No ratings yet
- Ask Entre Pis 10 11 NewDocument12 pagesAsk Entre Pis 10 11 NewSuhaditya GuhaNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument6 pagesIntroSimi SanyaNo ratings yet
- ToC For SAP-SDDocument2 pagesToC For SAP-SDSrinivasa ReddyNo ratings yet
- Define Sales Area in SapDocument4 pagesDefine Sales Area in SapapparaoNo ratings yet
- Billing Process in SAP SDDocument2 pagesBilling Process in SAP SDtosik33721No ratings yet
- Sales ProcessDocument2 pagesSales Processtosik33721No ratings yet
- Enterprise StructureDocument2 pagesEnterprise Structuretosik33721No ratings yet
- SAP SD - SyllabusDocument2 pagesSAP SD - Syllabustosik33721No ratings yet
- Research 123452Document1 pageResearch 123452tosik33721No ratings yet
- Evolution of Media INDUSTRIAL ERADocument16 pagesEvolution of Media INDUSTRIAL ERAAlec Ruht MasulaNo ratings yet
- 3-Storeyed 31-3-2015-Schedule PDFDocument1 page3-Storeyed 31-3-2015-Schedule PDFSi Thu AungNo ratings yet
- Wakit, Nico P.Document5 pagesWakit, Nico P.yeng botzNo ratings yet
- Differential Settlement at Bridge ApproaDocument5 pagesDifferential Settlement at Bridge ApproaVictor De los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Reflector 2000W Led Lluminacion de Campos de Futbol Estadios Goled Philips Osram Opalux LedDocument5 pagesFicha Tecnica Reflector 2000W Led Lluminacion de Campos de Futbol Estadios Goled Philips Osram Opalux Ledluis perdigonNo ratings yet
- Sap Retail Two Step PricingDocument4 pagesSap Retail Two Step PricingShams TabrezNo ratings yet
- John Hopkins Evidence Table - Systematic ReviewDocument2 pagesJohn Hopkins Evidence Table - Systematic Reviewsandy ThylsNo ratings yet
- Rivers and Their Origin (Top MCQ)Document24 pagesRivers and Their Origin (Top MCQ)Anil Yadav100% (1)
- Revised Research ZoomDocument51 pagesRevised Research ZoomAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Formal Report Expt 5Document6 pagesFormal Report Expt 5AnonymouscatNo ratings yet
- Enterpreneurship Assignment 2Document8 pagesEnterpreneurship Assignment 2Khusbu JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Cable Systems For High and Extra-High Voltage: Development, Manufacture, Testing, Installation and Operation of Cables and Their AccessoriesDocument1 pageCable Systems For High and Extra-High Voltage: Development, Manufacture, Testing, Installation and Operation of Cables and Their AccessorieseddisonfhNo ratings yet
- History of Computer ReviewerDocument10 pagesHistory of Computer ReviewerNeil Andrew Aliazas78% (9)
- Chess AI: Competing Paradigms For Machine Intelligence: Shiva Maharaj Nick Polson Alex TurkDocument15 pagesChess AI: Competing Paradigms For Machine Intelligence: Shiva Maharaj Nick Polson Alex TurkDomingo IslasNo ratings yet
- The Magical Number 5: Towards A Theory of Everything?Document27 pagesThe Magical Number 5: Towards A Theory of Everything?cesarfrancaNo ratings yet
- Miracle Mills 300 Series Hammer MillsDocument2 pagesMiracle Mills 300 Series Hammer MillsSNo ratings yet
- FINAL ReportDocument48 pagesFINAL ReportMythri RangaswamyNo ratings yet
- pm2 5 Sensor 201605Document6 pagespm2 5 Sensor 201605Vennela NandikondaNo ratings yet
- PP in Ii 001Document15 pagesPP in Ii 001Dav EipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Fundamental and Derived QuantitiesDocument7 pagesChapter 01 Fundamental and Derived QuantitiesAlicia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Presented By: Marlon N. Tabanao JR., LPTDocument14 pagesEntrepreneurship: Presented By: Marlon N. Tabanao JR., LPTRoj LaguinanNo ratings yet
- Research 9: Activity 4: Background of The StudyDocument7 pagesResearch 9: Activity 4: Background of The StudyPhilip AmelingNo ratings yet
- BFISDocument1 pageBFISEverestNo ratings yet
- Critique of Violence - Walter BenjaminDocument14 pagesCritique of Violence - Walter BenjaminKazım AteşNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH TOEFL Structure (3rd Exercise)Document5 pagesENGLISH TOEFL Structure (3rd Exercise)susannnnnnNo ratings yet
- Pearson Letter To ParentsDocument2 pagesPearson Letter To ParentsPatricia WillensNo ratings yet