Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Weather
Uploaded by
AMANDEEP SINGHOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Weather
Uploaded by
AMANDEEP SINGHCopyright:
Available Formats
World Weather Overview
Weather patterns across the globe vary widely due to factors such as geography,
climate zones, and atmospheric conditions. Here's an overview of weather
phenomena in different regions:
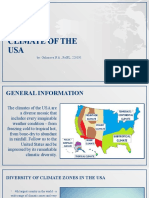
1. North America:
● United States: Varied climates ranging from arid deserts in the southwest to
temperate forests in the northeast. Regions like Tornado Alley experience
frequent tornadoes, while coastal areas are prone to hurricanes.
● Canada: Diverse climates from polar in the north to temperate in the south.
Winters can be harsh, especially in northern regions, with heavy snowfall and
sub-zero temperatures.
2. Europe:
● Western Europe: Mild maritime climate influenced by the Gulf Stream, with
moderate temperatures and frequent rainfall. The UK, France, and Ireland
experience relatively stable weather patterns.
● Eastern Europe: Continental climate with hot summers and cold winters.
Countries like Russia and Ukraine endure extreme temperatures, with Siberia
being one of the coldest inhabited regions on Earth.
3. Asia:
● East Asia: Monsoon climate prevails in countries like China, Japan, and Korea,
characterized by wet summers and dry winters. Typhoons are common in
coastal regions during the summer months.
● South Asia: Tropical climate with heavy rainfall during the monsoon season.
Countries like India and Bangladesh experience high temperatures and
humidity, with periodic cyclones affecting coastal areas.
4. Africa:
● North Africa: Desert climate dominates much of the region, with countries like
Egypt and Morocco experiencing hot, dry weather year-round. The Sahara
Desert is one of the hottest places on Earth.
● Sub-Saharan Africa: Diverse climates ranging from tropical rainforests in
Central Africa to savannas and deserts in the south. Seasonal rainfall patterns
influence agriculture and wildlife migration.
5. Australia and Oceania:
● Australia: Varied climates from tropical in the north to temperate in the south.
The country experiences extreme weather events like bushfires, droughts, and
cyclones, particularly in regions like Queensland.
● Oceania: Islands in the Pacific Ocean are vulnerable to rising sea levels and
tropical storms. Countries like Fiji and Vanuatu face climate-related
challenges such as coral bleaching and coastal erosion.
6. Antarctica:
● Antarctic Peninsula: Colder temperatures and strong winds prevail, with
icebergs calving from glaciers and floating in the surrounding Southern
Ocean.
● Interior: Extreme cold and dry conditions characterize the interior of
Antarctica, where temperatures can plummet below -80°C (-112°F) during the
winter months.
Conclusion:
World weather is influenced by a myriad of factors, including geographic location,
ocean currents, and atmospheric circulation. Understanding these patterns is crucial
for predicting and adapting to the impacts of climate change, which continue to
shape weather phenomena around the globe.
You might also like
- Underwater Campaigns - Daniel Chivers & Marco Bertini (v1.1)Document166 pagesUnderwater Campaigns - Daniel Chivers & Marco Bertini (v1.1)Paul Waler100% (7)
- The Climate in The UK and USADocument1 pageThe Climate in The UK and USAIasminAkhtarNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Climate: Enviropedia Climate Change Global Warming Ozone Air Pollution Weather & Climate Sustainability KidsDocument5 pagesPatterns of Climate: Enviropedia Climate Change Global Warming Ozone Air Pollution Weather & Climate Sustainability KidsVimal NairNo ratings yet
- Geography: Major Climate Types of The WorldDocument16 pagesGeography: Major Climate Types of The Worldkill hunterNo ratings yet
- NoneDocument23 pagesNoneDina GoolimovaNo ratings yet
- Major Climatic Regions of The WorldDocument3 pagesMajor Climatic Regions of The Worldsotonye georgeNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Climate: Enviropedia Climate Change Global Warming Ozone Air Pollution Weather & Climate Sustainability KidsDocument5 pagesPatterns of Climate: Enviropedia Climate Change Global Warming Ozone Air Pollution Weather & Climate Sustainability KidsVimal NairNo ratings yet
- What Is ClimateDocument12 pagesWhat Is ClimateDannielyn BuayaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesClimate ChangeAnyela BaezNo ratings yet
- Engleza USADocument9 pagesEngleza USARAUL moldovanNo ratings yet
- Climate of Anglo-AmericaDocument13 pagesClimate of Anglo-AmericaChemutai EzekielNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentmhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- World Climate and Climate Change Chapter 11 - Class 11 Geography NCERT - Class Notes - Samagra Book Series Batch (Hinglish)Document33 pagesWorld Climate and Climate Change Chapter 11 - Class 11 Geography NCERT - Class Notes - Samagra Book Series Batch (Hinglish)AVINASH ARYA 8TH SPARK 1No ratings yet
- Kian Ass # 2Document1 pageKian Ass # 2GilbertNo ratings yet
- Climate Vs WeatherDocument7 pagesClimate Vs WeatherRossvell HiloNo ratings yet
- IO Global Learning ClimatesDocument5 pagesIO Global Learning ClimatesharrisonNo ratings yet
- Gulf Stream Alaska Current British Columbia Great Lakes Ontario Quebec Labrador Current Newfoundland and Labrador Country ScandinaviaDocument3 pagesGulf Stream Alaska Current British Columbia Great Lakes Ontario Quebec Labrador Current Newfoundland and Labrador Country Scandinaviayonasmussie407No ratings yet
- Climate Types On EarthDocument19 pagesClimate Types On Earthpol ascuetaNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument13 pagesClimateShafic RuckyNo ratings yet
- A. Tropical Climate 1. Tropical Rain ForestDocument2 pagesA. Tropical Climate 1. Tropical Rain ForestLeah Marie AngelaNo ratings yet
- The United Kingdom Straddles The Geographic Mid-Latitudes Between 49 and 61 N. ItDocument2 pagesThe United Kingdom Straddles The Geographic Mid-Latitudes Between 49 and 61 N. ItAdela CîrligNo ratings yet
- Tropical Design - Atropicd - Arc201 - Ar. PaualDocument12 pagesTropical Design - Atropicd - Arc201 - Ar. PaualRossvell HiloNo ratings yet
- Koppen's ClassificationDocument3 pagesKoppen's ClassificationNeetu SinghNo ratings yet
- Climatic Zones of The WorldDocument1 pageClimatic Zones of The WorldMina JavedNo ratings yet
- Portfolio-TROPICAL DESIGN AR 170Document4 pagesPortfolio-TROPICAL DESIGN AR 170April Rose SantosNo ratings yet
- Clima Mundial Fatores: Clima Tropical, Clima Árido, Clima Temperado, Clima Continental e Clima GlacialDocument3 pagesClima Mundial Fatores: Clima Tropical, Clima Árido, Clima Temperado, Clima Continental e Clima GlacialsabrucanutoNo ratings yet
- Climate Group 1Document31 pagesClimate Group 1Cristina AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Geography Session 3 MCQsDocument17 pagesGeography Session 3 MCQskalmeen583No ratings yet
- Tropival Lesson 1Document70 pagesTropival Lesson 1Krichelle RamirezNo ratings yet
- Tropical DesignDocument201 pagesTropical DesignFrancis Grant ReladoNo ratings yet
- Geography 40 - Daily Class Notes - UPSC Sankalp HinglishDocument6 pagesGeography 40 - Daily Class Notes - UPSC Sankalp Hinglishanuraghavsingh01No ratings yet
- How Does Climate Vary Around The World?Document4 pagesHow Does Climate Vary Around The World?Mufaddal KaderbhaiNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument3 pagesClimateHazel CordanoNo ratings yet
- Ayesha Wasiq Class IV Topic: ClimateDocument12 pagesAyesha Wasiq Class IV Topic: ClimateAyesha Wasiq - 81482/TCHR/BNKMNo ratings yet
- Day 11 PDFDocument16 pagesDay 11 PDFჯონ ფრაატეეკNo ratings yet
- Climatic Factors:: Variation of Solar ActivityDocument12 pagesClimatic Factors:: Variation of Solar ActivityRODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLA100% (1)
- 1.1 Understanding Climate & Weather and Its Effects in The Tropical Zone PDFDocument29 pages1.1 Understanding Climate & Weather and Its Effects in The Tropical Zone PDFsalesjaninneNo ratings yet
- Weather 18Document56 pagesWeather 18Van Cole ClarinNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument38 pagesClimateCristine CaguiatNo ratings yet
- Types of Climates and Corresponding CharacteristecsDocument13 pagesTypes of Climates and Corresponding CharacteristecsRenhel EdradanNo ratings yet
- A Humid Subtropical ClimateDocument9 pagesA Humid Subtropical ClimateHachiman HikigayaNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument43 pagesClimateGabby VNo ratings yet
- Class:-9th Geography, Ch.18 A. Answer The Following QuestionsDocument6 pagesClass:-9th Geography, Ch.18 A. Answer The Following QuestionsVindhya SriNo ratings yet
- Weather and ClimateDocument1 pageWeather and Climateioana_iulia_7No ratings yet
- Q3 W5 Asynchronous TasksDocument3 pagesQ3 W5 Asynchronous Taskssy.valNo ratings yet
- El Niño: Normal ConditionsDocument3 pagesEl Niño: Normal ConditionsMaria AbregoNo ratings yet
- Climate and Climatic VariblesDocument6 pagesClimate and Climatic VariblesRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Isl Minggu 2 Sce 3103Document7 pagesIsl Minggu 2 Sce 3103Aleva KongNo ratings yet
- Climate Edit 2Document17 pagesClimate Edit 2Malemeko GriffinNo ratings yet
- Class 5 Subject Social Studies Chapter 6 Weather and ClimateDocument4 pagesClass 5 Subject Social Studies Chapter 6 Weather and Climatemeera2k10No ratings yet
- 406 Version 2Document14 pages406 Version 2X TimeNo ratings yet
- Climate and Weather Patterns (Lessons) 1Document5 pagesClimate and Weather Patterns (Lessons) 1patcris moncadaNo ratings yet
- Four Types of Climate in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesFour Types of Climate in The PhilippinesAnonymous P1iMibNo ratings yet
- Group I: Low-Latitude ClimatesDocument7 pagesGroup I: Low-Latitude ClimatestyobertsNo ratings yet
- New Curr 2019 GeoDocument166 pagesNew Curr 2019 GeoDealNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Climate: - Engr. Dielene F. de GuzmanDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Climate: - Engr. Dielene F. de GuzmanHeiro KeystrifeNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Soc. Stud 4Document14 pagesWeek 3 Soc. Stud 4Asther Jane B. VillacastinNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 3-Coastal Stabilization StructuresDocument2 pagesQUIZ 3-Coastal Stabilization StructuresAli DemirezenNo ratings yet
- 6e Lang2 Web 0610Document19 pages6e Lang2 Web 0610jian tongNo ratings yet
- Seasons of The Year: Caroll Esquivia Santos - Inglés IiDocument1 pageSeasons of The Year: Caroll Esquivia Santos - Inglés Iicaroll esquiviaNo ratings yet
- Para Jumble - 21949699 - 2023 - 11 - 10 - 00 - 37Document7 pagesPara Jumble - 21949699 - 2023 - 11 - 10 - 00 - 37RkNo ratings yet
- A Review of Combined Wave and Offshore Wind EnergyDocument13 pagesA Review of Combined Wave and Offshore Wind Energyaospino8No ratings yet
- Descriptive Text ExerciseDocument2 pagesDescriptive Text Exercisegusti annisaNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVEDocument4 pagesSUMMATIVEHoneylen BalogbogNo ratings yet
- Essay 2 FinalyDocument4 pagesEssay 2 FinalyJOSE MARTINEZ-GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesMultiple ChoiceMaryjoy PaladanNo ratings yet
- Capas de La TierraDocument3 pagesCapas de La TierraElvira Reyes RNo ratings yet
- Abarrane Issabeau Robinson B InggrisDocument7 pagesAbarrane Issabeau Robinson B Inggrisraven leandroNo ratings yet
- Physical OceanographyDocument2 pagesPhysical OceanographyHtoo WaiNo ratings yet
- Project AWARE - Hackathon PresentationDocument11 pagesProject AWARE - Hackathon PresentationERUA HACKATHON100% (1)
- 20 Amazing Water FactsDocument1 page20 Amazing Water FactsOWAIS AZIZ WANINo ratings yet
- Ocean CurrentDocument8 pagesOcean CurrentKarl GustavNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes: 1. Geo MeansDocument4 pagesGuided Notes: 1. Geo MeansAlicia ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Classification + PracticesDocument4 pagesWeek 6 Classification + PracticesPramudyaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 5 The Contributions of Engineering Field in The EcosystemDocument24 pagesGROUP 5 The Contributions of Engineering Field in The EcosystemKIENT GUIMBARDANo ratings yet
- Diel Vertical MigrationDocument9 pagesDiel Vertical MigrationT NgNo ratings yet
- Prediksi UN Bahasa Inggris 1Document6 pagesPrediksi UN Bahasa Inggris 1taufik nurrochmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Regional GeologyDocument11 pagesLecture 2 Regional Geologyabdo. sowanNo ratings yet
- Ocean Game PackDocument14 pagesOcean Game PackLim LimNo ratings yet
- Microplastic Pollution, A Threat To Marine Ecosystem and Human Health: A Short ReviewDocument21 pagesMicroplastic Pollution, A Threat To Marine Ecosystem and Human Health: A Short ReviewALFINA DAMAYANTINo ratings yet
- Final White PaperDocument8 pagesFinal White Paperapi-610470569No ratings yet
- FisheryDocument2 pagesFisheryKyle GalangueNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Ecosystem: There Are Two Types of Aquatic EcosystemsDocument1 pageAquatic Ecosystem: There Are Two Types of Aquatic EcosystemsYENNY MOSCOSONo ratings yet
- Coastal Area: Recommended ResourcesDocument5 pagesCoastal Area: Recommended ResourcesAzrul AnwarNo ratings yet
- The Deep Sea Angler Fish PresentationDocument11 pagesThe Deep Sea Angler Fish PresentationConnor GuyNo ratings yet
- Importance of MangrovesDocument22 pagesImportance of MangrovesDivya ChawhanNo ratings yet