Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
G01-ARADA Claire P.Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
G01-ARADA Claire P.Copyright:
Available Formats
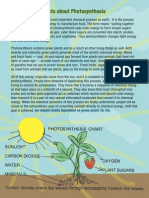
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon
dioxide, and water into glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen. It is a vital process that occurs in the
chloroplasts of plant cells.
During photosynthesis, plants use chlorophyll, a pigment found in chloroplasts, to capture sunlight
energy. This energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil into
glucose. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of this process.
The glucose produced through photosynthesis serves as a source of energy for the plant. It can be used
immediately or stored as starch for later use. In addition to providing energy, photosynthesis also plays a
crucial role in maintaining the oxygen levels in the atmosphere, which is essential for supporting life on
Earth.
Overall, photosynthesis is a fundamental process that not only enables plants to produce their own food
but also contributes to the balance of gases in the atmosphere. It is a key process in the Earth's
ecosystem and has a significant impact on the overall health and well-being of our planet.
You might also like
- PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesisSeema Rahul100% (1)
- Photosynthesis ProcessDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis ProcessAgus Dian PratamaNo ratings yet
- How Photosynthesis Occurs (Explanation Text)Document3 pagesHow Photosynthesis Occurs (Explanation Text)M Rifky Fauzan100% (2)
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisunknown999008No ratings yet
- Essay On PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageEssay On PhotosynthesisRameesha MalikNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisGiovanna CCNo ratings yet
- Written Report Topic: Introduction of Photosynthesis Sub. To: Prof. Ruthela Payawal Sub. By: Platero, Emily SDocument4 pagesWritten Report Topic: Introduction of Photosynthesis Sub. To: Prof. Ruthela Payawal Sub. By: Platero, Emily Sgtalite100% (1)
- The Marvels of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Marvels of PhotosynthesisDwight KintanarNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisAlexie AlmohallasNo ratings yet
- Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesProcess of PhotosynthesisJennifer Dizon100% (1)
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisdellavajames192000No ratings yet
- The Wonders of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Wonders of Photosynthesisarvinraghubar9No ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS (Explanation Text)Document4 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS (Explanation Text)khairun nisa'No ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS (Explanation Text)Document4 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS (Explanation Text)khairun nisa'No ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument1 pagePHOTOSYNTHESISofir keziahNo ratings yet
- Untitled (Draft) 2Document1 pageUntitled (Draft) 2silanpatlak28No ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS2024Document1 pagePHOTOSYNTHESIS2024jvilarma9No ratings yet
- Nutrient CycleDocument5 pagesNutrient CycleKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- What Is PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesWhat Is PhotosynthesisBarbara HenriquezNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis?Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis?PrageethNo ratings yet
- What Is The Photosynthesis Process and How Does ItDocument1 pageWhat Is The Photosynthesis Process and How Does ItlucyNo ratings yet
- The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Process of PhotosynthesisIndra WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 5Document1 pagePhotosynthesis 5Sami SandhuNo ratings yet
- CBSE - Class9 - Science - Capter 9 - PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesCBSE - Class9 - Science - Capter 9 - PhotosynthesismukeshNo ratings yet
- PhotsynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotsynthesisLady RedNo ratings yet
- Process of PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageProcess of PhotosynthesisGray Lee QueezerNo ratings yet
- Nabila Tisa Lathifah - Week 2Document11 pagesNabila Tisa Lathifah - Week 2Nabila LathifahNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument10 pagesAssignmentTeamireab DestaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 KSSM Chapter 2Document3 pagesScience Form 1 KSSM Chapter 2Nisa MuhdNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Are Complement To Each OtherDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Are Complement To Each OtherNisa Muhd100% (1)
- Biology Project KBDocument35 pagesBiology Project KBHarshita ThakkarNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesisapi-3729258No ratings yet
- Letter For RenewalDocument5 pagesLetter For RenewalBobby Arguilles PaboresNo ratings yet
- PhotosyntesisDocument1 pagePhotosyntesisSteven AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: (Gas) (Gas)Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis: (Gas) (Gas)Joshua WilsonNo ratings yet
- Effect of Photosynthesis On Earth S Life: Project Made By: Mostafa Hany Grade:8EDocument3 pagesEffect of Photosynthesis On Earth S Life: Project Made By: Mostafa Hany Grade:8EMezo7272No ratings yet
- Chemistry Note Assignment Photosynthesis: Submitted By: Fatima Javaid Submitted To: Sir Hamza RaisDocument4 pagesChemistry Note Assignment Photosynthesis: Submitted By: Fatima Javaid Submitted To: Sir Hamza RaisFatima JavaidNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesisHans ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesQuiz 2 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respirationangelica valenzonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Earth SystemsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Earth SystemsTwix ChweNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8.3 The Metabolic Processes in PlantsDocument13 pagesLesson 8.3 The Metabolic Processes in PlantsJohn Cesar CastilloNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Cycling ReportDocument12 pagesNutrient Cycling ReportGerry Jr LaynesaNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument3 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesAndre Miguel LlanesNo ratings yet
- The Importance of PhotosynthesisDocument11 pagesThe Importance of PhotosynthesisMateoNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Life EnergyDocument34 pagesEcosystem Life EnergyKeith C CabbabNo ratings yet
- Types of Biogeochemical CyclesDocument9 pagesTypes of Biogeochemical Cyclesstefanie.rios.2010No ratings yet
- Week 7-8 Science 9Document42 pagesWeek 7-8 Science 9Eden Rey ParoanNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Photosynthesis: Created By:reynaldo ThomasDocument7 pagesIntegrated Science Photosynthesis: Created By:reynaldo ThomasThompson Ta Ta JevonNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisGeorgia BuenavidesNo ratings yet
- Biology EssayDocument1 pageBiology EssayBooster HidroNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis #1Document1 pagePhotosynthesis #1Wally WestNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Science Presentation in Green Beige Illustrative Style - 20230920 - 192536 - 0000Document11 pagesPhotosynthesis Science Presentation in Green Beige Illustrative Style - 20230920 - 192536 - 0000Rei B.XNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument23 pagesPhotosynthesisBLESSING UHUONo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology Photosynthesis: Created By:r. ThomasDocument7 pagesHuman and Social Biology Photosynthesis: Created By:r. ThomasScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument3 pagesBiogeochemical Cyclesrhiannacallista.panganiban.pharmaNo ratings yet
- The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Process of Photosynthesisnelia mae laroyaNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISIDocument1 pagePHOTOSYNTHESISIUna Taib100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Assignment 5 PagesDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis Assignment 5 Pagesnirmala bhatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. Crop ScienceDocument57 pagesLesson 3. Crop ScienceKa Hilie Escote MiguelNo ratings yet