Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oral Disorder
Oral Disorder
Uploaded by
202170022Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oral Disorder
Oral Disorder
Uploaded by
202170022Copyright:
Available Formats
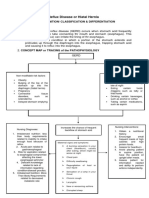
ORAL DISORDER 10.
What symptoms are associated with
diverticulitis?
DIVERTICULUM
- Abdominal pain (typically on the left side), fever,
1. What is a diverticulum? nausea, and changes in bowel habits.
- A diverticulum is a small, bulging pouch that can
develop in the lining of various organs, commonly
found in the digestive system. 11. How is diverticulum diagnosed?
- Through colonoscopy and CT scan.
2. What are the types of diverticulum?
- Esophageal Diverticulum and Colonic 12. What are the treatment options for
Diverticulum. diverticulosis?
- Dietary measures like a high-fiber diet and
sometimes medication to manage symptoms.
3. Where is an esophageal diverticulum located?
- In the esophagus, the tube that connects the
throat to the stomach. 13. What is the treatment for diverticulitis?
- Antibiotics and dietary changes, initially starting
with a clear liquid diet followed by a low-fiber diet.
4. What are the subtypes of esophageal
diverticulum?
- Zenker's diverticulum, Traction diverticulum, and 14. What are the potential complications of
Epiphrenic diverticulum. diverticulum?
- Abscess formation and perforation.
5. Where does a colonic diverticulum primarily
occur?
15. How can diverticulum be prevented?
- In the large intestine or colon.
- By dietary changes including a high-fiber diet
and adequate fluid intake to promote regular bowel
movements and support digestive health.
6. Who is more prone to colonic diverticulum?
HIATAL HERNIA
- Older adults.
1. What is a hiatal hernia?
7. What conditions are colonic diverticulum often
associated with? - : A hiatal hernia is a condition characterized by
the protrusion of a portion of the stomach through
- Diverticulosis and diverticulitis.
the diaphragm and into the chest cavity.
8. What are the causes of diverticulum?
2. What are the types of hiatal hernia?
- Diverticulosis and genetic factors.
- Sliding Hiatal Hernia
- Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia
9. What are the symptoms of diverticulosis?
- Often asymptomatic or may cause bloating,
3. Describe a sliding hiatal hernia.
constipation, or mild cramps.
- In a sliding hernia, the junction of the esophagus
and stomach, known as the gastroesophageal
junction, and a portion of the stomach slide into the 10. What lifestyle modifications are recommended
chest. for managing hiatal hernia?
- Dietary Changes
4. What is a paraesophageal hiatal hernia? - Weight Management
- In this less common type, the gastroesophageal - Posture and Sleeping Positions
junction remains in its normal location, but a portion
of the stomach herniates into the chest alongside
the esophagus. 11. What medications are commonly used to treat
hiatal hernia?
5. What are the causes of hiatal hernia? - Antacids
- Age - Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
- Obesity - H2 Blockers
- Trauma
- Genetics 12. What surgical interventions are available for
hiatal hernia?
- Fundoplication
6. What are the common symptoms of hiatal
hernia? - Laparoscopic Surgery
- Heartburn
- Regurgitation 13. What should be considered in postoperative
care for hiatal hernia?
- Chest Pain
- Dietary Restrictions
- Difficulty Swallowing
- Monitoring
7. How is hiatal hernia diagnosed?
14. What is the long-term outlook for individuals
- Barium Swallow with hiatal hernia?
- Endoscopy - The prognosis is generally positive with
appropriate management, including lifestyle
- Manometry modifications and, if necessary, surgical
interventions.
8. What are the treatment options for hiatal hernia?
- Lifestyle Changes 15. What preventive measures can be taken for
hiatal hernia?
- Medications
- Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
- Surgery
- Regular Check-ups
9. What complications can arise from hiatal hernia?
16. Why is patient education important for
- Esophagitis managing hiatal hernia?
- Strangulation - Understanding Triggers: Educating patients
about foods and activities that may trigger
symptoms.
- Importance of Follow-up: Stressing regular
follow-up appointments and communication with
healthcare providers. 8. How can lifestyle modifications help manage
GERD?
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) - Lifestyle changes such as adjusting eating
1. What is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease habits, dietary adjustments, maintaining proper
(GERD)? sleeping posture, quitting smoking, and limiting
alcohol and caffeine intake can help manage
- GERD is a chronic condition characterized by GERD symptoms.
the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus,
resulting in various symptoms.
9. Why are regular medical follow-ups important for
individuals with GERD?
2. What are the symptoms commonly associated
with GERD? - Regular medical follow-ups are essential for
monitoring and adjusting treatment as needed to
- Symptoms of GERD include heartburn, effectively manage GERD and prevent
regurgitation, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, complications.
chronic cough, and hoarseness or sore throat.
10. In conclusion, what should be understood about
3. What is the primary cause of GERD? GERD?
- The main cause of GERD is a weakened lower - GERD is a common and treatable condition that
esophageal sphincter (LES), which allows stomach requires a holistic approach to management,
acid to flow back into the esophagus. including lifestyle changes, medications, and
sometimes surgical intervention, to improve
symptoms and prevent complications.
4. What factors contribute to the development of
GERD?
- Contributing factors to GERD include obesity,
pregnancy, hiatal hernia, and certain lifestyle
factors.
5. How is GERD diagnosed?
- GERD can be diagnosed through clinical
assessment, endoscopy, pH monitoring, and X-
rays.
6. What are the available treatment options for
GERD?
- Treatment for GERD includes lifestyle
modifications, medications, and in severe cases,
surgical intervention.
7. What complications can arise from untreated
GERD?
- Complications of untreated GERD may include
esophagitis, Barrett's esophagus, and esophageal
cancer.
You might also like
- Case Study #1 ScenarioDocument12 pagesCase Study #1 ScenarioHMG TVNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafy (2020-2021)Document199 pagesGastroenterology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafy (2020-2021)Mohammed Risq100% (2)
- Managing Opioid-Induced ConstipationDocument9 pagesManaging Opioid-Induced ConstipationTom Rue100% (1)
- Antirheumatic and Antigout DrugsDocument66 pagesAntirheumatic and Antigout DrugsBadri KarkiNo ratings yet
- Frando-Detailed Learning Module 7.2.Document15 pagesFrando-Detailed Learning Module 7.2.Ranz Kenneth G. FrandoNo ratings yet
- End - Stage Renal DiseaseDocument59 pagesEnd - Stage Renal DiseaseJonathan Diaz93% (15)
- II. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument16 pagesII. Anatomy and PhysiologyLee Cel100% (1)
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument8 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseEunice Ericka FloresNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument8 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseEunice Ericka FloresNo ratings yet
- 2016 UPH Pathology Review TemploDocument203 pages2016 UPH Pathology Review TemploSherlock Holmes33% (3)
- Presentation On Hiatal HerniaDocument37 pagesPresentation On Hiatal HerniaRaju Shrestha100% (2)
- Should We Allow Animal ExperimentationDocument2 pagesShould We Allow Animal Experimentationturbo100% (1)
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ALFREDO MAGAT Vs INTER ORIENT MARITIME ENTERPRISES, Et. Al.Document2 pagesALFREDO MAGAT Vs INTER ORIENT MARITIME ENTERPRISES, Et. Al.Lara CacalNo ratings yet
- Function of G I System: The Primary Digestive Functions Are Break Down Food Particles "Document113 pagesFunction of G I System: The Primary Digestive Functions Are Break Down Food Particles "cherryann_12100% (1)
- Dyspepsia and Homeopathic TreatmentDocument62 pagesDyspepsia and Homeopathic Treatmentdrmsupriya100% (1)
- Baby BathDocument31 pagesBaby Bathshobharani durgam100% (2)
- Stages of LaborDocument15 pagesStages of LaborJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Gi Disorders Amd AchalasiaDocument4 pagesGi Disorders Amd Achalasia202170022No ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome in AdultsDocument10 pagesIrritable Bowel Syndrome in Adultssadiq517No ratings yet
- Inbound 7389658305523535294Document5 pagesInbound 7389658305523535294nene.marylouise22No ratings yet
- GI Tract DisordersDocument6 pagesGI Tract DisordersAbo AmgadNo ratings yet
- 2023 Gastro Intestinal System ProblemsDocument84 pages2023 Gastro Intestinal System Problemsmerga wekwayaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction Halel Khaled Al-WardDocument10 pagesIntestinal Obstruction Halel Khaled Al-Wardمنيب سالمNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea (AGE)Document2 pagesDiarrhea (AGE)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Gastric and Duodenal UlcerDocument19 pagesGastric and Duodenal UlcerEnerolisa ParedesNo ratings yet
- Constipation and Bowel Obstructions PP Rat 10.2020Document26 pagesConstipation and Bowel Obstructions PP Rat 10.2020Osman Bin SaifNo ratings yet
- Constipation: A Guide For WomenDocument4 pagesConstipation: A Guide For WomenfauziahandnNo ratings yet
- GastrointestinalDocument16 pagesGastrointestinalCelestial, Maybelle MarieNo ratings yet
- Constipation and Bowel Obstructions PP Rat 10.2020Document20 pagesConstipation and Bowel Obstructions PP Rat 10.2020Vaidya M.R. PoornimaNo ratings yet
- Case 034: ConstipationDocument7 pagesCase 034: ConstipationZauza100% (1)
- DIVERTICULOSISDocument21 pagesDIVERTICULOSISTiffany AdriasNo ratings yet
- GIT-III Module PDFDocument9 pagesGIT-III Module PDFFaiz MansoorNo ratings yet
- Constipation Diarrhea Fecal IncontinenceDocument40 pagesConstipation Diarrhea Fecal IncontinenceLiza Marie IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient With UIDocument35 pagesCare of Patient With UILimYiNo ratings yet
- NCP 3Document3 pagesNCP 3May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Health Issues Related To Digestive SystemDocument14 pagesHealth Issues Related To Digestive SystemJanani MurganNo ratings yet
- HND 203Document9 pagesHND 203ngolediopeNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 2 Management of Patients With Gastric, Intestinal and Colonic DisordersDocument19 pagesStudy Guide 2 Management of Patients With Gastric, Intestinal and Colonic DisordersKc Cabanilla LizardoNo ratings yet
- Pedi Chs 28 and 29 QuizDocument5 pagesPedi Chs 28 and 29 QuizMyra Cheriece MorrowNo ratings yet
- SGD Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesSGD Digestive SystemZH TVNo ratings yet
- Umbilical and Epigastric Hernia Information For PatientsDocument13 pagesUmbilical and Epigastric Hernia Information For PatientsSavulescu OvidiuNo ratings yet
- Zoo ProjectDocument38 pagesZoo Project121320053030No ratings yet
- ConstipationDocument22 pagesConstipationOsama ALGabriNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Abstract Intro Disch PLNDocument7 pagesCase Pres Abstract Intro Disch PLNMheaye JheaaNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease in Children: Dr. MaitaiDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease in Children: Dr. MaitaiAlvin OmondiNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Gastrointestinal SystemDocument73 pagesWeek 11 Gastrointestinal Systemashwaaq9999No ratings yet
- GIT Module Final Year MBBS: KMU (IHPER) - Central Curriculum CommitteeDocument9 pagesGIT Module Final Year MBBS: KMU (IHPER) - Central Curriculum Committeeshaifahamid12No ratings yet
- 5-Esophageal Diseases: Hugh K. Duckworth M.DDocument5 pages5-Esophageal Diseases: Hugh K. Duckworth M.DJames FlanneryNo ratings yet
- CA of The GI SystemDocument4 pagesCA of The GI System202170022No ratings yet
- Diarrhoea and ConstipationDocument13 pagesDiarrhoea and ConstipationShinta UnairNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)Document7 pagesIrritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)Hisyam DinGanuNo ratings yet
- Project HERNIADocument31 pagesProject HERNIADARSHIKA BHANWARNo ratings yet
- HirschsprungDocument60 pagesHirschsprungapi-399602400No ratings yet
- GIT Conditions in PaedsDocument36 pagesGIT Conditions in PaedsAmbrose Kibet KiruiNo ratings yet
- Course Topic Cu11 DigestionDocument14 pagesCourse Topic Cu11 DigestionMichelle MallareNo ratings yet
- Constipation Paliatif CareDocument17 pagesConstipation Paliatif Careshu mitunNo ratings yet
- Presentation Abdominal Pain, MassesDocument36 pagesPresentation Abdominal Pain, MassesNur Hamizah Md FuziNo ratings yet
- Patient Scenario, Chapter 45, Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Gastrointestinal DisorderDocument93 pagesPatient Scenario, Chapter 45, Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Gastrointestinal DisorderDay MedsNo ratings yet
- Open Cholecystectomy: By: Santoyo, Sarah Jane R. BSN 3-B Group 6-Operating RoomDocument6 pagesOpen Cholecystectomy: By: Santoyo, Sarah Jane R. BSN 3-B Group 6-Operating RoomJullie Anne SantoyoNo ratings yet
- Hiatal HerniaDocument8 pagesHiatal Hernianevelle4667No ratings yet
- JurnalDocument7 pagesJurnalAdy Adha NorsanieNo ratings yet
- ROJoson PEP Talk: ABDOMINAL OBSTRUCTION - OVERVIEWDocument68 pagesROJoson PEP Talk: ABDOMINAL OBSTRUCTION - OVERVIEWrojosonNo ratings yet
- GastroDocument6 pagesGastroKathleen PabalanNo ratings yet
- Keep It Simple SurgeonDocument2 pagesKeep It Simple SurgeonErlan SantosNo ratings yet
- Gastric Ulcers: Presented By: Dr. Jawaria Memon & Dr. Deep KumarDocument31 pagesGastric Ulcers: Presented By: Dr. Jawaria Memon & Dr. Deep KumarDeep KhemaniNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Hypothyroidism Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Parkinson's Disease Colon Cancer Tuberculosis DiverticulitisDocument3 pagesIrritable Bowel Syndrome Hypothyroidism Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Parkinson's Disease Colon Cancer Tuberculosis DiverticulitisIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- CONT03 Poor Bowel Control - A4 - April 2023-F - LRDocument2 pagesCONT03 Poor Bowel Control - A4 - April 2023-F - LRrares.baicuNo ratings yet
- DiverticulitisDocument23 pagesDiverticulitisSuhanda SaputraNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) National Recommendations OnDocument20 pagesAssessment of Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) National Recommendations Onmilica cucuzNo ratings yet
- Duttons Introductory Skills and Procedures For The Physical Therapist Assistant 1St Edition Mark Dutton Full ChapterDocument51 pagesDuttons Introductory Skills and Procedures For The Physical Therapist Assistant 1St Edition Mark Dutton Full Chaptersusie.blankenship630100% (6)
- Daily Test Chapter 1 Analytical Exposition XDocument5 pagesDaily Test Chapter 1 Analytical Exposition Xdepnie1995No ratings yet
- Counselling-GATHER ApproachDocument23 pagesCounselling-GATHER ApproachAnilkumar JaraliNo ratings yet
- Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes Recent StudiesDocument11 pagesSelf-Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes Recent StudiesSelaNo ratings yet
- Cauda Vs ConusDocument7 pagesCauda Vs ConusDaniel Alon100% (2)
- 2 - Asking PICOT Question - Part 1 - CorrectedDocument20 pages2 - Asking PICOT Question - Part 1 - Correctedاللعيب-Al-l3iebNo ratings yet
- RESPONDANT MEMORIAL KamalDocument39 pagesRESPONDANT MEMORIAL KamalArshmeet Singh PanesarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Micro 303-محولDocument12 pagesChapter Two Micro 303-محولshimaa dewedarNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 HEALTH Q3 - M1Document17 pagesGrade 8 HEALTH Q3 - M1Virginia IniegoNo ratings yet
- 6439-Article Text-59821-1-10-20231030Document12 pages6439-Article Text-59821-1-10-20231030Rakhmat RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- German Neurologist On Face Masks Oxygen Deprivation Causes Permanent Neurological Damage PDFDocument4 pagesGerman Neurologist On Face Masks Oxygen Deprivation Causes Permanent Neurological Damage PDFOpieNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Ultra Sonic Skin Care DevicesDocument3 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Ultra Sonic Skin Care DevicesMuqarrub Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Artikel Bahasa Inggris Depresi 2Document6 pagesArtikel Bahasa Inggris Depresi 2Serli SafitriNo ratings yet
- DGJKHVDocument7 pagesDGJKHVGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANo ratings yet
- GNUR 297 (Nutrition) Exam 2 Study GuideDocument17 pagesGNUR 297 (Nutrition) Exam 2 Study GuideMeghan Elizabeth100% (1)
- 100 Preboard General Education Sure LetDocument11 pages100 Preboard General Education Sure LetRoyana Joy FuentesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Abstract: Bañag, Daraga, Albay Contact Nos.: (Globe) 09271684061 (Smart) 09475160066Document1 pageClinical Abstract: Bañag, Daraga, Albay Contact Nos.: (Globe) 09271684061 (Smart) 09475160066kolintang1No ratings yet
- Brosur Wondfo Fia Meter PlusDocument2 pagesBrosur Wondfo Fia Meter PlusIsti RismaNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument4 pagesEnglishFajarNo ratings yet
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanNo ratings yet