Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marketing Analytics
Uploaded by
andresbu92Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marketing Analytics
Uploaded by
andresbu92Copyright:
Available Formats
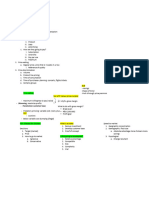
Session 4
lunes, 29 de enero de 2024 2:05 p. m.
Forecasting Techniques
• analogy( historical data)
• Judgement- based (insights
• Modelingg (
○ awarenesss= Funtction (exposure)
Ype of prices
○ Availability= funtion of (reach)
1. (Value base) Max- price = surplus }
• Services
2. Break even= Price- variable= unit margin = to cover fixed costs
3. Price for profit= extra resource
4. Based on benchmarking= competition- for mature markets- Quality signal
Pricing:
Thermometer
Price discriimnation
Max revenue
Pricing rules
WTP
Abiility 1. Cost plus princing
• Geography (ability) Price set based on variable and overhead costs by adding a markup percentage ( or
• By effort other financial objective)
• Demographic
• Time of consumption
2. Value pricing
Value framing
More factors to consider when setting prices
• Stage of the PLC
• Marketing objectives
• Psycological aspects
• Decisiion maker
• Industry conditions
Why do we care?
Producto profitaibility Customer profitability
Current sales >>>> Customer lifetime value
Brand wquity >>>>> Customer equity
Market share >>>>>> Customer equitty share
Customer lifetime Value
T=0 moment of acquisition, the moment when the customer buys for first time
Prospecting cost: customer acquisition cost
1. Prospecting Acquisition
2. Acquisition 1 order
a. Acquisition rate or response rate X
i. KPI 1: order size $$ Avg order size
ii. KPI2: Margin % X
3. Retention Avf margin: retailers want to maximize it
1. KPI1. order size =total contribution
2. KP2. gros margin
3. KPI3. frequency: purchase cycle: period of time
4. Atrition- churn- why¡? Acquired X 1 order x Order Size= revenues
1. Brand switching Revenues - COGS= total contribution (or gross profit)
No more need lifestage
2. KP2. gros margin
3. KPI3. frequency: purchase cycle: period of time
4. Atrition- churn- why¡? Acquired X 1 order x Order Size= revenues
1. Brand switching Revenues - COGS= total contribution (or gross profit)
2. No more need- lifestage Total contribution - marketing finxed cost= Net marketing costribution
3. Satisfaction
4. satiation
aRE ALL CUSTOMERS PROFITABLE?
FRM method (recency, frequency, monetary value)
Recency- how recently did the customer purchase?
Frequency- how often do the purchase?
Monethary value- how much do they spend?
Profitability through customer journey Response rate : is atractive enough (1st MOT P&G) this measure interest
- Prospecting Retention rate: loyalty (2nd MOT P&G) this measures satisfaction
- Acquisition 1st moment of true- 1st purchase- or TRIAL
- Retention
Customer relationship management
- RFM.
You might also like
- Cost: Drivers of Supply ChainDocument3 pagesCost: Drivers of Supply ChainPooja ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Marketin 1Document1 pageMarketin 1andresbu92No ratings yet
- Session 12Document28 pagesSession 12Hamza BennisNo ratings yet
- MKT221 Ch19 PPTDocument47 pagesMKT221 Ch19 PPTMarcyNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - Session 1 - MMUI 2023Document53 pagesManagerial Economics - Session 1 - MMUI 2023Ayu PoernomoNo ratings yet
- YMANECON P - Chapter 14 Fundamentals of Managerial Economics Supply and DemandDocument6 pagesYMANECON P - Chapter 14 Fundamentals of Managerial Economics Supply and DemandkatesmesinaNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Level 1 - Economics - SlideDocument42 pages2024 - Level 1 - Economics - Slidek60.2113340007No ratings yet
- Developing Price Strategies and Programs: Course: 460-741 Marketing ManagementDocument47 pagesDeveloping Price Strategies and Programs: Course: 460-741 Marketing ManagementIntira ItsarajirasetNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - Session 1 - MMUI 2023Document54 pagesManagerial Economics - Session 1 - MMUI 2023pusdiklatkm2No ratings yet
- DSA II Notes UptoRegressionDocument38 pagesDSA II Notes UptoRegressionShakil Reddy BhimavarapuNo ratings yet
- Revman ReviewerDocument10 pagesRevman ReviewerMaximo TibursyoNo ratings yet
- F5笔记总结分享Document43 pagesF5笔记总结分享su cheongNo ratings yet
- Revenue and Pricing ManagementDocument64 pagesRevenue and Pricing ManagementMmoh87No ratings yet
- TFC Supply Chain ManagementDocument37 pagesTFC Supply Chain ManagementSalahdineNo ratings yet
- Where To Play & How To Win Case Interview GuideDocument18 pagesWhere To Play & How To Win Case Interview GuideAnonymous GL6svDNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7-Strategy-Price: DiscriminationDocument38 pagesLecture 7-Strategy-Price: Discriminationh priovolosNo ratings yet
- ICON Profitability CasesDocument14 pagesICON Profitability Casesdarshita bhuwalkaNo ratings yet
- MKT 304 Chapter17Document35 pagesMKT 304 Chapter17duldulNo ratings yet
- Live Q&A Session With Mayank Kumar Co-Founder, MD, Upgrad: Introduction To The CompanyDocument15 pagesLive Q&A Session With Mayank Kumar Co-Founder, MD, Upgrad: Introduction To The Companytirtha gangulyNo ratings yet
- Prepare For The Rest of The Course: Chapter 2. Firms, Consumers and The Market: Learning ObjectivesDocument17 pagesPrepare For The Rest of The Course: Chapter 2. Firms, Consumers and The Market: Learning Objectivesmoha dahmaniNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Pricing StrategyDocument47 pagesModule 2 Pricing StrategyAmit YereshimiNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCheat SheetTAY SZE YEE, CHLOENo ratings yet
- 2305 InventoryDocument6 pages2305 InventoryDexterNo ratings yet
- 1-Working CapitalDocument13 pages1-Working CapitalAwaiZ zahidNo ratings yet
- 6290 Lec 2 Inventory ManagementDocument61 pages6290 Lec 2 Inventory ManagementPayman SalimiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our Presentation: GroupDocument38 pagesWelcome To Our Presentation: GroupMiskatul ArafatNo ratings yet
- Pricing 1Document2 pagesPricing 1Anne GonzalesNo ratings yet
- MM Unit 3Document60 pagesMM Unit 3Pragya YadavNo ratings yet
- Pricing: Marginal Cost Plus Total Variable Cost Special Order Sales PriceDocument7 pagesPricing: Marginal Cost Plus Total Variable Cost Special Order Sales Priceainsyasya 98No ratings yet
- Principles - Ch2 - Customer Value and Valuing CustomersDocument48 pagesPrinciples - Ch2 - Customer Value and Valuing CustomersdaNo ratings yet
- Deterministic-Inventory (Supply Chain Management)Document28 pagesDeterministic-Inventory (Supply Chain Management)rajat aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Lecture FiveDocument92 pagesLecture FiveGEORGENo ratings yet
- Auditing 2Document10 pagesAuditing 2antonette seradNo ratings yet
- Sesi01 Dasar Ekonomi ManajerialDocument26 pagesSesi01 Dasar Ekonomi ManajerialjuwelismailNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - 2024 - Process and Technology RevisedDocument71 pagesLecture 5 - 2024 - Process and Technology Revisedjs7350231No ratings yet
- Pricing Strategy ReviewerDocument1 pagePricing Strategy ReviewerRemyyNo ratings yet
- ECO SALE JD 06 - Ecocycle Solution ConsultantDocument5 pagesECO SALE JD 06 - Ecocycle Solution ConsultanttuanhoangmNo ratings yet
- Neo-Classical Theory of FirmsDocument14 pagesNeo-Classical Theory of FirmsAnuNo ratings yet
- Case CheatsheetDocument2 pagesCase Cheatsheethds200302No ratings yet
- CRM Unit 5 - Customer Analytics Part IDocument23 pagesCRM Unit 5 - Customer Analytics Part IHồng PhúcNo ratings yet
- Strategic FitDocument16 pagesStrategic FitMir Jahanzeb TalpurNo ratings yet
- Business ModelsDocument18 pagesBusiness ModelsJorge Humberto Chambi VillarroelNo ratings yet
- Capacity Planning and Analysis PDFDocument22 pagesCapacity Planning and Analysis PDFShimanta EasinNo ratings yet
- Elements of SCMDocument37 pagesElements of SCMAogo OlajideNo ratings yet
- BA2088 - Lecture 3 Corporate Credit II - Corporate Credit Analysis Using Financial Statements & RatiosDocument52 pagesBA2088 - Lecture 3 Corporate Credit II - Corporate Credit Analysis Using Financial Statements & RatioskeuqNo ratings yet
- 11 4.3 PricingDocument23 pages11 4.3 PricingDurga Prasad SmartNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document9 pagesChapter 6Sao Nguyễn ToànNo ratings yet
- Optimization of High-Frequency Trading Systems: David SweetDocument32 pagesOptimization of High-Frequency Trading Systems: David SweetangersjayNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Mid Term MBADocument6 pagesManagerial Accounting Mid Term MBASumon SahaNo ratings yet
- Idea in Practice: Focus On What The Majority of Your Buyers ValueDocument40 pagesIdea in Practice: Focus On What The Majority of Your Buyers ValueShreshtha MalhotraNo ratings yet
- PricingDocument35 pagesPricingSauban AhmedNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management, Supply Contracts and Risk PoolingDocument81 pagesInventory Management, Supply Contracts and Risk PoolingnaniagricoNo ratings yet
- Mix 4 Main Case Frameworks: Market Sizing ProfitabilityDocument2 pagesMix 4 Main Case Frameworks: Market Sizing ProfitabilityAna ChanifahNo ratings yet
- ECON 2a PrelimsDocument8 pagesECON 2a PrelimskestenpeytNo ratings yet
- Nota Topik 2Document14 pagesNota Topik 2Nurul Ain Kisz'tinaNo ratings yet
- Pricing DecisionDocument38 pagesPricing Decisionsamrulezzz100% (1)
- Lecture 3-Active Investment IIDocument35 pagesLecture 3-Active Investment IISimoniiNo ratings yet
- 50 Procurement Formulas!Document9 pages50 Procurement Formulas!ebnugroho123No ratings yet
- Pricing for Profitability: Activity-Based Pricing for Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandPricing for Profitability: Activity-Based Pricing for Competitive AdvantageNo ratings yet
- Solar Irrigation System Using Brush Less DC Motor: Renu Singh, Ahmed Sharique Anees, Devang TyagiDocument5 pagesSolar Irrigation System Using Brush Less DC Motor: Renu Singh, Ahmed Sharique Anees, Devang TyagiEdamEdamNo ratings yet
- Construction Material Management PDFDocument19 pagesConstruction Material Management PDFBala SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument9 pagesStrategic ManagementSree Raja Sekhar KatamNo ratings yet
- Airline Operating CostsDocument27 pagesAirline Operating Costsawahab100% (7)
- MagzDocument72 pagesMagzrandom personNo ratings yet
- 57-The Last-Hour Trading Technique PDFDocument4 pages57-The Last-Hour Trading Technique PDFNavin Chandar100% (1)
- Real Estate ProjectDocument63 pagesReal Estate Projectmeetabhishek_kgp90% (10)
- ECON Chapter 6Document12 pagesECON Chapter 6rorNo ratings yet
- Overstocking: Amount Available: Exceeds DemandDocument37 pagesOverstocking: Amount Available: Exceeds Demandmushtaque61No ratings yet
- Brand Marketing Project Manager in NYC Resume Colleen CollierDocument2 pagesBrand Marketing Project Manager in NYC Resume Colleen CollierColleenCollierNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - OligopolyDocument24 pagesManagerial Economics - Oligopolyranjitamodak2003No ratings yet
- Foreign Aid and Conflict in Pakistan An Empirical AnalysisDocument24 pagesForeign Aid and Conflict in Pakistan An Empirical AnalysisJournal of Development Policy, Research & PracticeNo ratings yet
- Louis PhilipDocument7 pagesLouis PhilipbrijkishoredubeyNo ratings yet
- Procurement Management Plan Rev.00Document17 pagesProcurement Management Plan Rev.00Rouzbeh HashemiNo ratings yet
- Comparing Cost Benefit and Multi-Criteria Analysis PDFDocument27 pagesComparing Cost Benefit and Multi-Criteria Analysis PDFMFNo ratings yet
- 1Q 2013 Data Book Investor RelationsDocument19 pages1Q 2013 Data Book Investor Relationsgiba269No ratings yet
- Conditional Deed of Sale 1Document3 pagesConditional Deed of Sale 1John Paul Pagala AbatNo ratings yet
- Cipm Principles StudysessionsDocument13 pagesCipm Principles StudysessionsGurDeepSiNghNo ratings yet
- 2010-09-10 013205 WinterschidDocument6 pages2010-09-10 013205 WinterschidJa Mi LahNo ratings yet
- FIN347 DraftDocument11 pagesFIN347 DraftMUHAMMAD AIMANNo ratings yet
- Ratio 2 by Shantanu SirDocument39 pagesRatio 2 by Shantanu SirTarun Garg100% (1)
- Platts 11 Janv 2013Document9 pagesPlatts 11 Janv 2013Wallace YankotyNo ratings yet
- Padhle 11th - 8 - Producer's Equilibrium - Microeconomics - EconomicsDocument5 pagesPadhle 11th - 8 - Producer's Equilibrium - Microeconomics - EconomicsRushil ThindNo ratings yet
- Business StrategyDocument13 pagesBusiness StrategyMAx100% (1)
- BM Assignment Brand Extensions Royal Enfield SectionC Group15Document12 pagesBM Assignment Brand Extensions Royal Enfield SectionC Group15Nitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Sample Financial ENT600Document10 pagesSample Financial ENT600Calvin Ohsey0% (1)
- Comparative Politics - p.57-64 - FriedmanDocument9 pagesComparative Politics - p.57-64 - FriedmanSteele SchoeberlNo ratings yet
- Tata JLRDocument34 pagesTata JLRgouravjain86No ratings yet
- Ch24 ShowDocument46 pagesCh24 ShowMahmoud AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Economic Impact of Retailing in Pakistan 1Document20 pagesEconomic Impact of Retailing in Pakistan 1atta_tahirNo ratings yet