Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Akeup
Uploaded by
talaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Akeup
Uploaded by
talaCopyright:
Available Formats
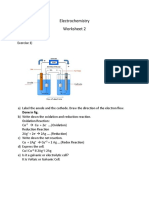
Circle the best correct answer for all the following multiple choice questions:
Q1. The correlation coefficient of calibration curve is an indication of:
A) linearity B) selectivity C) sensitivity D) precision.
Q2. Recovery results of analyte A from serum was closer to 100 % than analyte B, then:
A) Sensitivity of analyte A is larger than B B) Sensitivity of analyte B is larger than A.
C) Effect of serum on A is larger than B. D) Effect of serum on B is larger than A.
Q3. In a spectrometric method for determination of iron in sea water a blank sample reads
an average of -0.002 absorption unit and a standard deviation of 0.003 absorption unit.
The LOD signal must read ------ absorption unit.
A) 0.03 B) 0.032 C) 0.028 D) 0.007
Q4. Which statement is correct about the LOD:
A) It is calculated at S/N = 10 B) It is related to LOQ
C) It is an indication of recovery D) All previous statements are correct.
Q5. When silver electrode is employed in measuring chloride ion in aqueous solution it is
classified as:
A) reference electrode B) ion-selective electrode C) indicator electrode of first
kind D) indicator electrode of second kind
Q6-7: Consider the following half reactions:
I3- + 2e 3 I- E0= 0.636 V, Cl2 + 2e 2 Cl- E0= 1.36 V
S4O6 2- + 2e 2 S2O3 2- E0= 0.10 V, H2-ascorbic acid + 2H+ + 2e ascorbic acid E0=
0.39V
Q6. A solution of I3 – is standardized by:
A) Direct titration with I-.
B) Direct titration with standardized S4O6 2-.
C) Direct titration with standardized S2O3 2-.
D) Addition of excess I- and titration of produced I3 – with standardized S2O3 2-.
Q7. A quantitative method for Cl2 is based on:
A) Direct titration with I-.
B) Direct titration with standardized I3 -.
C) Direct titration with standardized S2O3 2-.
D) Addition of excess I- and titration of produced I3 – with standardized S2O3 2-.
Q8. The half reaction for silver/silver chloride electrode is:
A) ½ HgCl2 (s) + e Hg (l) + Cl- (aq) B) Hg+ (aq) + e Hg (l)
+ -
C) AgCl (s) + e Ag (aq) + Cl (aq) D) Ag+ (aq) + e Ag (s)
Q9. Na+ ion-selective electrode is an example of:
A) glass membrane B) solid-state C) liquid-based membrane D) inert electrode
Q10. A cyanide ion-selective electrode obeys the equation E= constant - 0.059 log [CN-],
where [CN-] ( µM). An unknown solution read -0.23 V. After addition of 1.0 µM CN-
(final concentration) the solution read -0.248 V. The concentration of cyanide in the
sample is ----- µM.
A) 1.00 B) 3.00 C) 2.00 D) 4.00
Q11. Cadmium in drinking water was determined by polarography. If the measured
current was 5.0 mA for the sample and 10 mA after addition of 50 µM Cd2+ (final
concentration). The concentration of Cd2+ in the original sample is ---- µM.
A) 100 B) 50 C) 75 D) 25
Q12. Lead ( E ½ = - 0.43 V) is determined by polarography. A possible error in measured
current could be due:
A) oxidation of mercury B) reduction of H+ C) reduction of un-removed
dissolved oxygen D) all of these.
Q13-18. Consider the following half reactions:
Fe3+ + e Fe2+ E0= 0.77 V, Sn4+ + 2e Sn2+ E0= 0.19 V
Ce4+ + e Ce3+ E0= 1.65 V
Q13. Calculate the charge required to reduce 0.10 mol of Fe3+ to Fe2+? (F= 96490 C/mol
e)
A) 1.93 x 103 C B) 9.649 x 102 C C) 1.93 x 104 C D) 9.649 x 103 C
Q14. Calculate the average current passing in Sn4+ solution, if it was reduced to Sn2+ at a
rate of 3.0 mmol/h? (F= 96490 C/mol e)
A) 0.228 A B) 0.114 A C) 0.161 A D) 0.322 A
Q15. Calculate the equilibrium constant for reaction of Fe3+ with Sn2+ ?
A) 4.58 x 1019 B) 2.22 x 10-20 C) 7.9 x 1013 D) 1.26 x 10-14
Q 16-18: A 25 mL of 0.05 M Sn2+ solution was titrated with 0.05 M Ce4+. Calculate E :
Q16. After addition of 15 mL Ce4+:
A) 0.179 V B) 0.279 V C) 0.19 V D) 0.29 V
Q17. At the equivalent point:
A) 0.777 V B) 0.677 V C) 0.97 V D) 0.92 V
Q18. After addition of 75 mL Ce4+:
A) 1.65 V B) 1.75 V C) 1.73 V D) 1.63 V
You might also like
- AP Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQsDocument5 pagesAP Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQsMohammed AbdelhakeemNo ratings yet
- LT Iit Che DPT - 15 - 21.02.2024Document3 pagesLT Iit Che DPT - 15 - 21.02.2024Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Electro Chemistry AssaignmentDocument11 pagesElectro Chemistry AssaignmentGadde Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CHE102FF03PDocument5 pagesCHE102FF03PDhrumilParikhNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Worksheet SolutionsDocument11 pagesElectrochemistry Worksheet SolutionsAnivia12100% (1)
- Chemistry 12 Term 1 (2023 24)Document8 pagesChemistry 12 Term 1 (2023 24)lardemuydiNo ratings yet
- 1 ElectrochemistryDocument18 pages1 ElectrochemistryPriyaranjanNo ratings yet
- MadeEjee Chemistry YouTube Channel Electrochemistry QuestionsDocument7 pagesMadeEjee Chemistry YouTube Channel Electrochemistry QuestionsDheeraj YadavNo ratings yet
- Wa0063.Document3 pagesWa0063.BucksUpNo ratings yet
- RedoEqui 3 2 12Document3 pagesRedoEqui 3 2 12Huzeyfa Hassan LatheefNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Practice ProblemsDocument16 pagesCH 11 Practice ProblemsAnivia12100% (1)
- MCQ - Test 3 With - KeyDocument6 pagesMCQ - Test 3 With - KeyShubham Baxla (CSEAIML23310662409:30)No ratings yet
- SRI CHAITANYA IIT ACADEMY CHEMISTRY DOCUMENTDocument19 pagesSRI CHAITANYA IIT ACADEMY CHEMISTRY DOCUMENTggk20130% (2)
- Electro Chemistry AssaignmentDocument9 pagesElectro Chemistry AssaignmentGadde Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 102-211-Final-Zero-versionDocument12 pagesCHEM 102-211-Final-Zero-versionfrak ksaNo ratings yet
- STD 12 - Chemistry - AssignmentDocument2 pagesSTD 12 - Chemistry - AssignmentHetalben PatelNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Chem 135 Blue - AnswersDocument10 pagesExam 2 Chem 135 Blue - AnswersSerena GaskellNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering - Redox Reactions & ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesChemical Engineering - Redox Reactions & ElectrochemistryAndreaForteRuizNo ratings yet
- Soal (1) (Repaired)Document9 pagesSoal (1) (Repaired)Inda AlwanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry MCQ SendDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry MCQ SendRajendra ChikkamathNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Echem 2014Document1 pageTopical Test Echem 2014irnihafizan6812No ratings yet
- KooferDocument9 pagesKooferslilani_1No ratings yet
- Chemistry 2015Document15 pagesChemistry 2015Muhammad ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Olympiad Questions ElectrochemDocument3 pagesOlympiad Questions ElectrochemdivikjainvmcNo ratings yet
- U-I-Water technology-MCQDocument15 pagesU-I-Water technology-MCQAdharshNo ratings yet
- AP Electrochemistry Problem Set 2021Document7 pagesAP Electrochemistry Problem Set 2021Vineeth SendilrajNo ratings yet
- 01 ExerciseDocument29 pages01 ExerciseAkashGauravNo ratings yet
- 218 FinalDocument17 pages218 FinalmhaymourNo ratings yet
- 2 QP ElectrochemistryDocument6 pages2 QP ElectrochemistrysachinNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: 0 8 0 79 0 34 2 37 Ag / Ag - HG / HG - Cu / Cu - MG / MGDocument11 pagesElectrochemistry: 0 8 0 79 0 34 2 37 Ag / Ag - HG / HG - Cu / Cu - MG / MGAnikin Skywalker100% (1)
- 01 - CHREV131E - Exam 1 - Chemistry For Engineers - 25Document3 pages01 - CHREV131E - Exam 1 - Chemistry For Engineers - 25John Frix AlejanoNo ratings yet
- Redox QuizDocument5 pagesRedox QuizSherey FathimathNo ratings yet
- 1412finalsample KeyDocument18 pages1412finalsample KeyErnesto Tarroza Yap Jr.No ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Document9 pagesWorksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Dagim YenenehNo ratings yet
- 12TH Grade Electrochemistry Worksheet-1Document3 pages12TH Grade Electrochemistry Worksheet-1Amen RaipurNo ratings yet
- Exam t2 2011.12 Chemistry f6 p1Document10 pagesExam t2 2011.12 Chemistry f6 p1asjawolverineNo ratings yet
- Useful Information on Gas Laws, Equilibria, and ThermochemistryDocument11 pagesUseful Information on Gas Laws, Equilibria, and ThermochemistryAhmadAlabadiNo ratings yet
- 02 ElectrochemistryDocument6 pages02 ElectrochemistryGeorgette RepunteNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesElectrochemistryGokul NathNo ratings yet
- 3 - Tut CoulometryDocument2 pages3 - Tut CoulometryAyandaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY Practice QuestionsChhabi YadavNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Questions Answers KeyDocument1 pageElectrolysis Questions Answers KeyAman9692No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry PDFDocument20 pagesElectrochemistry PDFHarsh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDocument16 pagesThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- AP Chapter 17 - ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesAP Chapter 17 - Electrochemistrytcarr1224No ratings yet
- A. Multiple Choice and Short Answer Section. Circle The Letter Corresponding To The BestDocument6 pagesA. Multiple Choice and Short Answer Section. Circle The Letter Corresponding To The BestArvin DalisayNo ratings yet
- USCH31Document17 pagesUSCH31Arsene LupinNo ratings yet
- Unofficial Acs Practice Test 01 ADocument11 pagesUnofficial Acs Practice Test 01 AMaggie Zhang100% (1)
- Electrochemistry Module PDFDocument31 pagesElectrochemistry Module PDFNavdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Worksheet 2: Done in FigDocument8 pagesElectrochemistry Worksheet 2: Done in Figrezwanur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Ch2 MCQ PDFDocument6 pagesCh2 MCQ PDFPratibha BhondeNo ratings yet
- Ch05 Ch08 SuppDocument8 pagesCh05 Ch08 SuppHà Thị Thanh TịnhNo ratings yet
- UNSCO 2014 ExamDocument8 pagesUNSCO 2014 ExamwakuserNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument16 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentramanji1021No ratings yet
- Reduction-Oxidation Reactions and ElectrochemistryDocument14 pagesReduction-Oxidation Reactions and Electrochemistrykaushi123No ratings yet
- Mains-Narayana Question Paper For Specific TopicsDocument11 pagesMains-Narayana Question Paper For Specific Topics10C-sai sachin adithya .Mk-TNo ratings yet
- Class-Xii (Chemistry) Sumit Sir SirDocument2 pagesClass-Xii (Chemistry) Sumit Sir Sirmanyag1605No ratings yet
- Directions: This Examination Contains A Total of 80 Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pagesDirections: This Examination Contains A Total of 80 Multiple ChoiceLemi NegesoNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Convective Mass Transfer 3Document11 pagesConvective Mass Transfer 3talaNo ratings yet
- Convective Mass TransferDocument3 pagesConvective Mass TransfertalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Binary DistillationDocument127 pagesChapter 2 Binary DistillationtalaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-6-Honey Bee Biology Queen With VoiceDocument7 pagesLecture-6-Honey Bee Biology Queen With VoicetalaNo ratings yet
- Extraction ExperimenDocument20 pagesExtraction ExperimentalaNo ratings yet
- HAZOP ExampleDocument4 pagesHAZOP Examplereguieg hichemNo ratings yet
- Plane Wave Reflection Coefficient From Near Field MeasurementsDocument7 pagesPlane Wave Reflection Coefficient From Near Field MeasurementsraulreyesvillagranaNo ratings yet
- A Framework and Methodology For Evaluating E-Commerce Web SitesDocument15 pagesA Framework and Methodology For Evaluating E-Commerce Web SitesVic KyNo ratings yet
- TRA1 MessageDocument5 pagesTRA1 MessageguestNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between The Academic Performance of Woking and NonDocument8 pagesThe Difference Between The Academic Performance of Woking and NonMr.nutshell CoronelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Piezoelectric CeramicsDocument33 pagesChapter 4-Piezoelectric Ceramicssantsex111No ratings yet
- Topographic Map of VenusDocument1 pageTopographic Map of VenusHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Absolute Value ProblemsDocument8 pagesSimplifying Absolute Value ProblemslmlNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Activity 1Document1 pagePractical Research 2 Activity 1Pepito Manloloko100% (1)
- Pricing Determination Procedure PDFDocument62 pagesPricing Determination Procedure PDFTaslimNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics: Question and Answers (Question Bank)Document12 pagesDigital Electronics: Question and Answers (Question Bank)api-297153951100% (1)
- OLTC FailureDocument18 pagesOLTC FailurevtpsNo ratings yet
- Mandatory Reading 00 3438581Document26 pagesMandatory Reading 00 3438581AgalievNo ratings yet
- Distrib: Probability Distribution AnalysisDocument17 pagesDistrib: Probability Distribution AnalysisLiz castillo castilloNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy ReviewsDocument13 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy ReviewsMohammadreza MalekMohamadiNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument41 pagesLecture NotesAkeem Emmanuel Uy Feria100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE Physics Block4 ElectricityDocument8 pagesCambridge IGCSE Physics Block4 ElectricityRattee SirirojtanadolNo ratings yet
- Ethernet gateway data sheet with PoEDocument3 pagesEthernet gateway data sheet with PoEAlexander Lopez VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- FFHDocument763 pagesFFHnilesh2215No ratings yet
- DS - Module: Team EmertxeDocument113 pagesDS - Module: Team EmertxevijaykumarsinganaNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation of Pulley & Belt DriveDocument8 pagesDesign Calculation of Pulley & Belt Drivesiva107198887% (31)
- Juju ElectricalDocument20 pagesJuju ElectricalAnkit AkashNo ratings yet
- Online Shopping Survey ResultsDocument5 pagesOnline Shopping Survey ResultsAlyssa Nikki VersozaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Algorithms For Swarm Intelligence PDFDocument14 pagesOverview of Algorithms For Swarm Intelligence PDFmenguemengueNo ratings yet
- Beckman Coulter HematologyDocument249 pagesBeckman Coulter HematologyIbrahim Ahmad100% (3)
- Touch screen wheelchair controlDocument3 pagesTouch screen wheelchair controlKhatriZabirNo ratings yet
- AC800F F2K Connect B1 6.2 CONFIGURATIONDocument43 pagesAC800F F2K Connect B1 6.2 CONFIGURATIONassessorNo ratings yet
- Peter-Linz-Automata BUET Download PDFDocument2 pagesPeter-Linz-Automata BUET Download PDFmalang0% (2)
- Bagi Yang Masih Awam Memakai Google Sheet, File Ini Bisa Didownload Dengan Klik File Download MS. ExcelDocument67 pagesBagi Yang Masih Awam Memakai Google Sheet, File Ini Bisa Didownload Dengan Klik File Download MS. Excelwisnu pranata adhiNo ratings yet
- General Purpose & Power Relays GuideDocument20 pagesGeneral Purpose & Power Relays GuideMahesh KumbharNo ratings yet